Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Here Is A Photo of A Table With Some Objects Which Are Glasses
Uploaded by
lucas bOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Here Is A Photo of A Table With Some Objects Which Are Glasses
Uploaded by
lucas bCopyright:
Available Formats
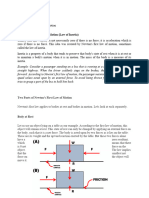
Here is a photo of a table with some objects which are glasses, a computer
mouse and a pen. They are applying a force on the table because of
gravity and their own weight. Newton´s 3rd law states that for every
action (force) in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction. If object A
exerts a force on object B, object B also exerts an equal and opposite force
on object A. That what happens here. The table exerts an equal net force
(a net force is a combination of all the forces acting on an object) of all the
objects to push them up. The forces are obviously equal because if not,
the table will push up the objects too much to the air or the objects will
fall. This force of the table occurs because the weight of the book causes
the table to deform slightly so that it pushes back on the book like a coiled
spring. This doesn´t happen with every object, it depends on its weight.
The objects on the image can be supported by the table, but if they weigh
a lot then this law of action and reaction can´t happen.
The third law of Newton talks about a more fundamental, the
conservation of the momentum. The latter remains true even in cases
where Newton's statement does not do, for example fields of force as well
as material bodies a quantity of motion, and when the quantity of is
defined correctly, also in quantum mechanics. Mathematically, if a body A
exerts a force F on body B, then B simultaneously exerts a force −F→ on A,
or in vector equation form,
F⃗ AB= −F⃗ BA
You might also like
- Newton's Three Law of MotionDocument3 pagesNewton's Three Law of MotionArlyn Pong Pling PioNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Motion : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandThe Laws of Motion : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 4 NotesYuxin LiuNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of Motion and Free FallDocument25 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motion and Free FallScribd-957616100% (2)
- Forces on a Girl AnalyzedDocument50 pagesForces on a Girl AnalyzedemailymNo ratings yet
- 05 PH Newtons LawsDocument22 pages05 PH Newtons Lawsapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Dynamics: CausesDocument20 pagesDynamics: CausesperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Basic Physics SE-Force Difficulty LevelDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Basic Physics SE-Force Difficulty LeveltsoniffNo ratings yet
- A Deductive Proof of Newton's Third LawDocument4 pagesA Deductive Proof of Newton's Third LawMoaz EldegwyNo ratings yet
- Notes in Newton's Law of MotionDocument5 pagesNotes in Newton's Law of MotionAngelica RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 101 - Phys101lDocument4 pagesExperiment 101 - Phys101lthomas melgarNo ratings yet
- NEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsDocument20 pagesNEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion1Document6 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion1darlei byerotNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)Document14 pagesLecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)verboseNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument27 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedNisanur BaştorNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws SummaryDocument1 pageNewton's Laws Summary『IntTouchz』No ratings yet
- Experiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisDocument5 pagesExperiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisJerome LangitNo ratings yet
- 05 Newtons LawsDocument16 pages05 Newtons LawsLuisNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion ExplainedDocument7 pagesForces and Motion ExplainedMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- L1 Newton'sLawsDocument61 pagesL1 Newton'sLawsArafat AnikNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionNasr UllahNo ratings yet
- 0301 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument4 pages0301 Newton's Laws of MotionimfizicsNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument6 pagesNewtonJosh “MrSmart”No ratings yet
- Newton'S Three Laws of Motion: by Aybak Basuony Dont Hate On Me This Presentation Was Done On My PhoneDocument6 pagesNewton'S Three Laws of Motion: by Aybak Basuony Dont Hate On Me This Presentation Was Done On My PhoneAybak BasuonyNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument11 pagesNewton's Third Law of MotionScribd-95761650% (2)
- Physical Science Unit 9Document2 pagesPhysical Science Unit 9Bluematwo TwoNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Mass M and Weight WTDocument4 pagesThe Difference Between Mass M and Weight WTMuhannad AbdulRaoufNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion: 1. When The Speed of Objects Approaches (1% or More) The Speed of Light inDocument12 pagesForce and Motion: 1. When The Speed of Objects Approaches (1% or More) The Speed of Light inOğulcan KüçükNo ratings yet
- Discussion 5:: Answer 1Document2 pagesDiscussion 5:: Answer 1john cenaNo ratings yet
- Newton 120 AnswersDocument6 pagesNewton 120 AnswersNovenalista Domitilla FlavianaNo ratings yet
- Newton's 3 Laws of MotionDocument6 pagesNewton's 3 Laws of MotionRyan L. NodaloNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJoseph Bernard Cantre DalusongNo ratings yet
- Group 4's Report on Newton's Laws of MotionDocument26 pagesGroup 4's Report on Newton's Laws of MotionSheralyne Daz PequinaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesPhysics: Newton's Laws of MotionClydeNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Easy As Apple Pie!Document44 pagesNewton's Laws: Easy As Apple Pie!RITUPARNA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Document19 pagesNewtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Aimee Gallego AngoluanNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Physics Multiple Assignment: - S. YogavarshaDocument16 pagesPhysics Multiple Assignment: - S. YogavarshaMithu VarshaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Proportional: Clarification NeededDocument1 pagePhysical Science Proportional: Clarification NeededbabakotoNo ratings yet
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document23 pagesGroup 5Gavin avNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesLaws of MotionJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- The Law of Motion Explained: Force, Inertia and EquilibriumDocument30 pagesThe Law of Motion Explained: Force, Inertia and EquilibriumNurulWardhani11No ratings yet
- Free-Body Diagrams PDFDocument33 pagesFree-Body Diagrams PDFRITUPARNA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Physics Research Project On Newton's Laws of Motion (3rd Law Specifically)Document9 pagesPhysics Research Project On Newton's Laws of Motion (3rd Law Specifically)Ranjitha RaviproluNo ratings yet
- Ltop Physics - 2qDocument1 pageLtop Physics - 2qAbigail MadambaNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesAssignment in Physical ScienceEda Angela OabNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyIrene QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Assignment of PhysicsDocument23 pagesAssignment of PhysicsZeeshan Jutt0% (1)
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet
- f5 Physics Newtons LawsDocument3 pagesf5 Physics Newtons LawsDesmond simpsonNo ratings yet
- CP Physics Ms. MorrisonDocument11 pagesCP Physics Ms. MorrisonDwight StephensonNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics 1 - Newtons LawsDocument7 pagesAp Physics 1 - Newtons Lawsapi-293989776No ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument27 pagesNewton's Third Law of MotionJayhia Malaga JarlegaNo ratings yet
- ANSWER-KEYDocument11 pagesANSWER-KEYPETER SALIVIONo ratings yet
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNo ratings yet
- Newton's FindingsDocument6 pagesNewton's Findingspspvgk murthyNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law Explains His Second LawDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law Explains His Second Lawdva222No ratings yet