Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cerebrum Occipital Lobe Anatomy & Function Atf
Uploaded by
siti.220010019Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cerebrum Occipital Lobe Anatomy & Function Atf
Uploaded by
siti.220010019Copyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 8/16/2021
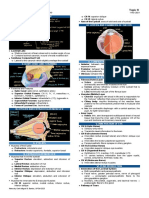
7. OCCIPITAL LOBE
Neurology | Cerebrum: Occipital Lobe Anatomy & Function Medical Editor: Camilla E. Fiorucci
Perceives objects on the
OUTLINE ipsilateral side.
I) STRUCTURE
II) FUNCTION
III) SUMMARY
III) REFERENCES
o Once the information has reached the Primary Visual
cortex, we are aware that we are looking at object,
but we still can’t recognize it.
STRUCTURE
o Example:
(A) BOUNDARIES Visual stimuli is basketball
Parieto-occipital sulcus: separates occipital lobe from
parietal lobe
Pre-occipital notch: by tracing an imaginary line
between the Pre-occipital notch and the lateral sulcus it’s
possible to separate the occipital lobe from the temporal
lobe
II) FUNCTION
Two different cortices are found in the occipital lobe: (B) VISUAL ASSOCIATION CORTEX
Primary Visual cortex
o Most posterior one
Visual Association cortex
(A) PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX
Involved in analyzing, recognizing, memorizing and
understanding a visual stimulus.
The Visual Association Cortex receives the image from
the Primary Visual cortex and elaborates its
characteristics:
Involved in conscious awareness of visual stimuli o Shape
Visual pathway: o Color
o Size
o Movement
Then, compares it to past memories → allows us to
recognize the object
o We can recognize that the object is a basketball
(1) Clinical significance
A lesion in the Visual Association cortex causes Visual
Agnosia
The patient is able to see the object, since the visual
pathway up to the Primary visual cortex is intact, but can’t
recognize it.
o Example: the patient will see the basketball, and will
be able to say that there’s something in front of them,
Figure 1: Visual pathway but won’t be able to tell that it’s a basketball.
o Visual stimulus
III) SUMMARY
• The retina is subdivided in 2 portions:
The occipital lobe is located in the most posterior portion
o Temporal retina: lateral, does not of the cerebral cortex, between the Parieto-occipital
decussate at the optic chiasm.
sulcus and pre-occipital notch
Perceives objects on the
It contains:
contralateral side. o Primary Visual cortex (V1):
o Nasal retina: medial, decussate at the Responsible for conscious awareness of visual
optic chiasm.
stimuli
OCCIPITAL LOBE ANATOMY & FUNCTION NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #7 1 of 2
End point of the visual pathway
o Visual Association cortex:
Responsible for understanding and recognizing a
visual stimulus
Compares the stimulus to past memories
If damaged → Visual Agnosia
IV) REFERENCES
1. Le T, Bhushan V, Sochat M, Chavda Y, Zureick A. First Aid
for the USMLE Step 1 2018. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical;
2017
2. Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Anatomy & Physiology. Hoboken, NJ:
Pearson; 2020.
3. Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical Physiology.; 2017.
4. Urry LA, Cain ML, Wasserman SA, Minorsky PV, Orr RB,
Campbell NA. Campbell Biology. New York, NY: Pearson; 2020.
5. Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL,
Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. New York
etc.: McGraw-Hill Education; 2018.
6. Felten DL, O'Banion MK, Maida ME. Netter's Atlas of
Neuroscience. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Health
Sciences; 2015
7. Hall, John E. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical
Physiology. 13th ed., W B Saunders, 2015.
8. Attribution to Figure 1: Miquel Perello Nieto, CC BY-SA 4.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia
Commons
2 of 2 NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #7. occipital lobe
You might also like
- OPHTHA 8.0 Neuro Ophthalmology Fundamentals Dr. AtienzaDocument14 pagesOPHTHA 8.0 Neuro Ophthalmology Fundamentals Dr. AtienzaMaria Gracia YamsonNo ratings yet
- The Special Senses: Vision and HearingDocument34 pagesThe Special Senses: Vision and HearingpuchioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Visual System April 2014Document41 pagesAnatomy Physiology Visual System April 2014levianaNo ratings yet
- VisualDocument3 pagesVisualMelisa HilaireNo ratings yet
- Higher Mental Functions (GEP) 2019c copyDocument30 pagesHigher Mental Functions (GEP) 2019c copykimrmorgan.kNo ratings yet
- Joukal (2017) Anatomy of The Human Visual PathwayDocument16 pagesJoukal (2017) Anatomy of The Human Visual PathwaysektemujibNo ratings yet
- OS 204 Eye and Orbit AnatomyDocument2 pagesOS 204 Eye and Orbit AnatomyCarlo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy of Special Senses: Eyes and EarsDocument13 pagesNeuroanatomy of Special Senses: Eyes and EarsCYNTHIA ARISTANo ratings yet
- Carlson 11e Ch06 wDocument166 pagesCarlson 11e Ch06 wJenelyn Ponce AguiloNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloDocument13 pages3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- 2.biophysics of VisionDocument109 pages2.biophysics of Visionkrueg3rNo ratings yet
- Primary Visual Pathway NeuroscienceDocument27 pagesPrimary Visual Pathway NeuroscienceAngkelova ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Ungerleider & Bell (2011) - Uncovering The Visual Alphabet. Advances in Our Understanding PDFDocument18 pagesUngerleider & Bell (2011) - Uncovering The Visual Alphabet. Advances in Our Understanding PDFJhamil Andre Venero LovatonNo ratings yet
- Orbital Apex Syndrome. A ReviewDocument10 pagesOrbital Apex Syndrome. A ReviewAndrés Faúndez TeránNo ratings yet
- kevt101Document7 pageskevt101RajinderKumarNo ratings yet
- Kevt 101Document7 pagesKevt 101Donald HrangkholNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Anatomy, and Physiology of The Afferent Visual PathwayDocument80 pagesEmbryology, Anatomy, and Physiology of The Afferent Visual PathwayTea Abramia AbramiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueBONGISIPHO HLOPHENo ratings yet
- Aula T2 - Neuropsychology_Sensory_VisualDocument25 pagesAula T2 - Neuropsychology_Sensory_VisualBeatriz SantosNo ratings yet
- p88 99Document12 pagesp88 99Prasanna Venkhatesh VNo ratings yet
- Consciousness As Integrated InformationDocument27 pagesConsciousness As Integrated InformationjackNo ratings yet
- Goals of the Special Senses Lab ActivitiesDocument14 pagesGoals of the Special Senses Lab ActivitiessylNo ratings yet
- Visual SystemDocument37 pagesVisual SystemmalindaNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorder PeadsDocument51 pagesEye Disorder PeadsGrashiaNo ratings yet
- Psychobiology Ch. 6 Vision Lecture NotesDocument23 pagesPsychobiology Ch. 6 Vision Lecture NotesGabriel CardozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Bea SeloterioNo ratings yet
- Visual Perceptual Dysfunctions and Assessment: Made By:gundeep Singh MOT NeurologyDocument74 pagesVisual Perceptual Dysfunctions and Assessment: Made By:gundeep Singh MOT NeurologyPaloma McNo ratings yet
- 02 - Human Eye and Colourful World - X - SSMDocument33 pages02 - Human Eye and Colourful World - X - SSMDøomNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing 1 by 4Document330 pagesDigital Image Processing 1 by 4HVVHGKUHNNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument2 pagesPhysioRaeann Fiona FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Sensorimotor Eye CooperationDocument5 pagesPhysiology of Sensorimotor Eye CooperationAmi MisiciNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNCM 104 Nervous SystemIan Parrocha100% (1)
- Concerning Imagery: Mcgill University, Montreal, CanadaDocument12 pagesConcerning Imagery: Mcgill University, Montreal, CanadaCristina BostanNo ratings yet
- 21 Sent. WORKSHOP IntroductionDocument46 pages21 Sent. WORKSHOP Introductionwarezisgr8No ratings yet
- Resume Visual PathwayDocument3 pagesResume Visual PathwaysindyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Vision: Structure and FunctionDocument74 pagesPhysiology of Vision: Structure and FunctionPrixie AntonioNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Ch13.6 TBDocument6 pagesGr10 Ch13.6 TBnr46jpdxbpNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EyesDocument7 pagesAnatomy of EyesFrancesc Richard WengerNo ratings yet
- Visual System ReportDocument7 pagesVisual System ReportAndre DueñasNo ratings yet
- Author 1: K.Dinakar (2 B.Tech, ECE) Author 2: P.Jagadish Babu (2 B.Tech, ECE)Document8 pagesAuthor 1: K.Dinakar (2 B.Tech, ECE) Author 2: P.Jagadish Babu (2 B.Tech, ECE)Jagadish BabuNo ratings yet
- BMB 413 Neuroscience Online Notes Vol4Document19 pagesBMB 413 Neuroscience Online Notes Vol4Moose KeNo ratings yet
- 0 OphthalmologyDocument12 pages0 OphthalmologyParsaant SinghNo ratings yet
- Visual PathwayDocument1 pageVisual PathwayJohn CoxNo ratings yet
- Sensing and Perceiving 4.2Document18 pagesSensing and Perceiving 4.2Dami TepedeNo ratings yet
- 9.13 The Human BrainDocument19 pages9.13 The Human BrainEshitaNo ratings yet
- Ocular dominance columns visual stimulationDocument6 pagesOcular dominance columns visual stimulationAlex MNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument72 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeYerke NurlybekNo ratings yet
- Mchirs Real EstateDocument1 pageMchirs Real EstatechristabelbellzdankyesNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus - Buta KortikalDocument31 pagesLaporan Kasus - Buta KortikalwadejackNo ratings yet
- OCCIPITAL LOBE AND VISUAL REHABILITATIONDocument20 pagesOCCIPITAL LOBE AND VISUAL REHABILITATIONpkm16499No ratings yet
- NeuroDocument174 pagesNeurofhey19100% (3)
- VDR 3 1 DuttonDocument13 pagesVDR 3 1 DuttonAmmad AlikhanNo ratings yet
- Object Recognition: The Ventral Visual Processing StreamDocument7 pagesObject Recognition: The Ventral Visual Processing StreamNeus Sangrós VidalNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument18 pagesSensation and PerceptionCamryn CowardNo ratings yet
- A&P Chapter 9 SensesDocument19 pagesA&P Chapter 9 SensesJeong song parkNo ratings yet
- 1 Online PDFDocument18 pages1 Online PDFFera SherlianaNo ratings yet
- Pattern Recognition by Humans and Machines: Visual PerceptionFrom EverandPattern Recognition by Humans and Machines: Visual PerceptionNo ratings yet
- Imagery: Current Cognitive ApproachesFrom EverandImagery: Current Cognitive ApproachesSydney Joelson SegalNo ratings yet
- The Master and His EmissaryDocument813 pagesThe Master and His EmissaryDimitris Cosmidis100% (70)
- Discovering the Secrets of the Brain Through Mapping Its FunctionsDocument5 pagesDiscovering the Secrets of the Brain Through Mapping Its Functionsivona0mati0No ratings yet
- Primary Progressive Aphasia: A Clinical Approach: Neurological UpdateDocument17 pagesPrimary Progressive Aphasia: A Clinical Approach: Neurological UpdatejerejerejereNo ratings yet
- White MatterDocument19 pagesWhite MatterZoya MoraniNo ratings yet
- Anatomo-Physiologic Basis For Auricular StimulationDocument10 pagesAnatomo-Physiologic Basis For Auricular StimulationMiki ShimizuNo ratings yet
- secfile_4497Document89 pagessecfile_4497timothy.seumanu509No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), An Ischemic Stroke or "BrainDocument30 pagesINTRODUCTION A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), An Ischemic Stroke or "BrainCherie May100% (5)
- CCCNDocument1 pageCCCNsattarin.cNo ratings yet
- Andreasen - Creativity in Art and Science-Are There Two CulturesDocument6 pagesAndreasen - Creativity in Art and Science-Are There Two CulturesKorghulNo ratings yet
- Functional and Neuroanatomical Bases of Developmental Stuttering: Current InsightsDocument17 pagesFunctional and Neuroanatomical Bases of Developmental Stuttering: Current InsightsDai ArhexNo ratings yet
- Left vs Right Brain: Understanding the DifferencesDocument8 pagesLeft vs Right Brain: Understanding the DifferencesPivvkyNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications of Neuroscience-Informed Art TherapyDocument10 pagesPractical Applications of Neuroscience-Informed Art TherapyManu SatoNo ratings yet
- How The Expressive Therapies Continuum Informs Intermodal TransfeDocument37 pagesHow The Expressive Therapies Continuum Informs Intermodal TransfePamela CantillanaNo ratings yet
- AllLectures PDFDocument179 pagesAllLectures PDFthea billonesNo ratings yet
- The Neural Basis of Romantic LoveDocument6 pagesThe Neural Basis of Romantic LoveBooster CNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging - Clinical ApplicationsDocument590 pagesNeuroimaging - Clinical ApplicationsIndera VyasNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Cerebral CortexDocument3 pagesBlood Supply of Cerebral CortexashrafNo ratings yet
- Cia RDP96 00788R001700210016 5Document29 pagesCia RDP96 00788R001700210016 5Juan Manuel MH100% (6)
- Neurological AssessmentDocument13 pagesNeurological AssessmentLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Brain BasedDocument33 pagesBrain BasedDeshpande Shilpa100% (1)
- Shamanism, Phosphenes, and Early Art: An Alternative SynthesisDocument8 pagesShamanism, Phosphenes, and Early Art: An Alternative SynthesisPado BriogNo ratings yet
- Apraxia 2Document25 pagesApraxia 2Vellardo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Rewiev of OCD Theories PDFDocument13 pagesRewiev of OCD Theories PDFDM lamonganNo ratings yet
- The Directive Function of Speech in Development and Dissolution - A. R. LuriaDocument13 pagesThe Directive Function of Speech in Development and Dissolution - A. R. LuriaPamela CNo ratings yet
- Freud's Solution to the Mind/Body Problem ExplainedDocument23 pagesFreud's Solution to the Mind/Body Problem ExplainedHans BogaertNo ratings yet
- Nihms 588714Document31 pagesNihms 588714Diana BastoNo ratings yet
- Dimension in Ges ADocument72 pagesDimension in Ges AEsha Septian Pesilat KbpcNo ratings yet
- The Feeling of What HappensDocument221 pagesThe Feeling of What HappensGabriel Bortolatto88% (8)
- Antonio Damasio S Looking For SpinozaDocument24 pagesAntonio Damasio S Looking For SpinozaBruno XavierNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychoanalysis - The Concious ID Solms PDFDocument16 pagesNeuropsychoanalysis - The Concious ID Solms PDFAndrei PredaNo ratings yet