Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Doc1 - Sports Science Questions Past Paper Style
Uploaded by
direnbudhani03Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Doc1 - Sports Science Questions Past Paper Style
Uploaded by
direnbudhani03Copyright:
Available Formats
Seh science correction -
Mcq –
1) B
2) A
3) C
4) A
5) A
6) B
7) Explain how cardiac output is maintained during prolonged exercise?
Ans) cardiovascular drift- during high intensity exercises stoke volume decreases since
you lose liquid in sweating and your heart rate increase. stroke volume and cardiac
volume increase, arise in blood temp. rehydrate with electrolyte drinks.
8) Describe the mechanics of ventilation during high intensity interval training.
Ans) (the mechanics of breathing is how you breath) for inhalation the diaphragm
contacts and the intercostal muscle relaxes and the external intercostal muscle
contracts and the rib size increases.
9) Explain the process of gaseous exchange in the alveoli.
Ans) goes against the alveoli membrane since movement is from high to low oxygen is
higher cardon dioxide pressure is higher partial pressure in blood.
10) Outline chemical control of ventilation during exercises?
Ans) chemo receptors detect a decrease in ph. or an increase in co2. Blood acidity
levels are detected by the chemo receptors.
11) Outline nervous control of ventilation during exercise?
Ans ) the brain stem receives message from nerve cells and sends back
12) Comment on the variability of diastolic blood pressure during dynamic and static
exercise?
Ans) diastolic blood pressure during dynamic exercises would remain the same and
during the static exercise it would increase, the average diastolic blood pressure for an
average adult is 80.
13) outline the functions of two components of blood
Wbc help in immune function and protect from diseases. Platelets help assist in blood
clotting to prevent bleeding when there’s an injury
13) 14) Describe the cardiovascular adaptions resulting from enduring training?
Ans) llower resting heart rate from training, lower exercise heart rate when working at
intensity
15 ) explain why a fitness trainer can expect maximal oxygen consumption to vary for
a family of males and females, children and adult.
Ans 15)
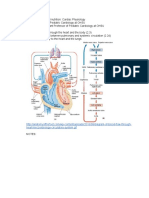
The pulmonary circulation travels deoxygenated blood to the lungs where it then gets
You might also like
- Minimalist Introduction To Anesthesiology Rev 1.5Document12 pagesMinimalist Introduction To Anesthesiology Rev 1.5Syafiqah HaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsHayley Welsh100% (1)
- SMCH 30Document15 pagesSMCH 30Cita BudiartiNo ratings yet
- Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition Ellis Test BankDocument11 pagesEkg Plain and Simple 4th Edition Ellis Test Bankbrandicarrilloretfdampgw100% (10)
- Lectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsDocument4 pagesLectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsAndrew SagalovNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument6 pagesExercise PhysiologyMunazzah IjazNo ratings yet
- RPT CardioDocument2 pagesRPT CardioBrad PamnaniNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cardiovascular System: An Introduction To Chapters 9 - 24 and Chapter 36 Guyton and Hall, 12 EditionDocument10 pagesOverview of Cardiovascular System: An Introduction To Chapters 9 - 24 and Chapter 36 Guyton and Hall, 12 EditionbahahahahNo ratings yet
- Scientific Article For Use With Question 7 - A Red Card For The HeartDocument13 pagesScientific Article For Use With Question 7 - A Red Card For The HeartAmar MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Lecture 5 (Part I-II) September 28, 2005 October 5, 2005 EXS 558 Dr. MoranDocument44 pagesCardiovascular System: Lecture 5 (Part I-II) September 28, 2005 October 5, 2005 EXS 558 Dr. MoraneliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesActivity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary 3 2010 With AnswersDocument14 pagesCardiopulmonary 3 2010 With AnswersWenzy Cruz100% (2)
- Cardiopulmonary SystemDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary SystemFirna AlishaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cardiac Output FINALDocument9 pages1 - Cardiac Output FINALNiruja Sri100% (1)
- University of California, Davis College of Biological Sciences Exercise Biology Major in NPBDocument1 pageUniversity of California, Davis College of Biological Sciences Exercise Biology Major in NPBaung1987No ratings yet
- BEPAA-Organ Systems A and P - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (H.S. 10-12)Document27 pagesBEPAA-Organ Systems A and P - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (H.S. 10-12)Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Buceo ApneaDocument8 pagesBuceo ApneasurftraderNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Response To Exercise in Athletes The "Supernormal Heart No Ovlidar 2017Document21 pagesAcute and Chronic Response To Exercise in Athletes The "Supernormal Heart No Ovlidar 2017Cristian YanezNo ratings yet
- 1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseDocument28 pages1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseJavier Mora BaizNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0735109708005676 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0735109708005676 MainAprilleo ViedroNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drift and Cerebral and Muscle Tissue Oxygenation During Prolonged Cycling at Different Pedalling CadencesDocument12 pagesCardiovascular Drift and Cerebral and Muscle Tissue Oxygenation During Prolonged Cycling at Different Pedalling CadencesBob UeckerleleNo ratings yet
- Heartrate and ExerciseDocument11 pagesHeartrate and ExerciseJay Queue JonnyNo ratings yet
- 5 - Cardiac Output - Ass. Prof. Dalia Abd El-Salam - 2020Document6 pages5 - Cardiac Output - Ass. Prof. Dalia Abd El-Salam - 2020Hossam BaniisNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument220 pagesExercise Physiologypradeep6288100% (1)
- Andrade 2014 Differences in Muscle Strength After ACL Reconstruction Do Not Influence Cardiorespiratory Responses To Isometabolic ExerciseDocument8 pagesAndrade 2014 Differences in Muscle Strength After ACL Reconstruction Do Not Influence Cardiorespiratory Responses To Isometabolic ExerciseJuan PalomoNo ratings yet
- Problematic Questions - Answered by DR - Zsuzsanna MiklósDocument5 pagesProblematic Questions - Answered by DR - Zsuzsanna MiklósDaniel SzeifertNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience 4th Edition Lundy Test BankDocument4 pagesNeuroscience 4th Edition Lundy Test Bankstrangstuprumczi100% (29)
- Cardiac Physiology: Blood Flow, ECG, RegulationDocument5 pagesCardiac Physiology: Blood Flow, ECG, RegulationKANAK KOKARENo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology Adaptations To High-Level Exercise 2012Document5 pagesRespiratory Physiology Adaptations To High-Level Exercise 2012Maria GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modelling in SportDocument32 pagesMathematical Modelling in Sportgerardo davidNo ratings yet
- CBSE CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation Important Questions 2023-24Document15 pagesCBSE CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation Important Questions 2023-24susilmaji92No ratings yet
- Exercises andDocument7 pagesExercises andmustakNo ratings yet
- Jphysiol 2014 272104Document18 pagesJphysiol 2014 272104mustakNo ratings yet
- CV SystemDocument31 pagesCV SystemaletheacolleenpNo ratings yet
- 6 Pack Sept 2013-OEC-Shock-Chapter 10 - NSPDocument23 pages6 Pack Sept 2013-OEC-Shock-Chapter 10 - NSPDonavon GaudetteNo ratings yet
- Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Measures of Sternocleidomastoid Blood Flow During Exercise and HyperpnoeaDocument12 pagesNear-Infrared Spectroscopy Measures of Sternocleidomastoid Blood Flow During Exercise and HyperpnoeaRobsonBorgesNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseAnand VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- NullDocument3 pagesNullapi-26374520No ratings yet
- Cardio 2016Document14 pagesCardio 2016Mhmmd FasyaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition Hillegass Test BankDocument10 pagesEssentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition Hillegass Test Banknancycarrollaocprizwen100% (9)
- Cardiovascular Response To ExerciseDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Response To ExerciseEPMJrNo ratings yet
- Peel 1996 - Cardiopulmonary System and Movement DysfunctionDocument8 pagesPeel 1996 - Cardiopulmonary System and Movement DysfunctionBeto ZamunérNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Quiz: CircleDocument14 pagesPre-Lab Quiz: CircleAcromionangkatan 20No ratings yet
- Cardiac Output HandoutDocument10 pagesCardiac Output Handoutsac50900No ratings yet
- Bio Revision Exercise - Answer KeyDocument11 pagesBio Revision Exercise - Answer Keynmhk89100% (1)
- ©onikienko E. V. Methodical Supply To The Self-Study Option On BiophysicsDocument3 pages©onikienko E. V. Methodical Supply To The Self-Study Option On BiophysicsManda YogeshNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument16 pagesCardiovascularMilena VargasNo ratings yet
- Physiocardiacoutput 171108041156Document20 pagesPhysiocardiacoutput 171108041156Akila AkinsNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Physiology and Determinants of Contractile FunctionDocument29 pagesHeart Failure: Physiology and Determinants of Contractile FunctionQanita Izza KNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis and (1) (1)Document9 pagesData Analysis and (1) (1)khorshid aziziNo ratings yet
- Quiz AnswersDocument102 pagesQuiz Answerssterlingarcher11100% (2)
- Central Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsFrom EverandCentral Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Equine Neck and Back Pathology: Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandEquine Neck and Back Pathology: Diagnosis and TreatmentFrances M. D. HensonNo ratings yet
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Questions and Answers in Small Animal AnesthesiaFrom EverandQuestions and Answers in Small Animal AnesthesiaLesley J. SmithNo ratings yet
- A Sea of Broken Hearts: Patient Rights in a Dangerous, Profit-Driven Health Care SystemFrom EverandA Sea of Broken Hearts: Patient Rights in a Dangerous, Profit-Driven Health Care SystemNo ratings yet