0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views6 pagesGeometry Basics for Students
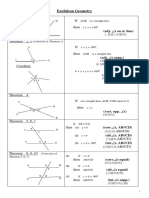
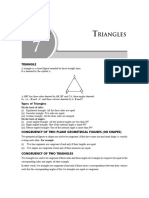
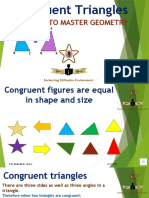
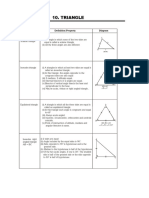
This document provides a summary of key facts and concepts related to geometry and congruent triangles. It includes 12 facts about basic geometry, such as the sum of angles on a line and at a point. It then discusses congruent triangles, noting they have the same shape and size, and corresponding angles and sides are equal. Three conditions for determining if triangles are congruent are presented: side-side-side (SSS), side-angle-side (SAS), and angle-side-angle (ASA). An example problem demonstrates using corresponding parts of congruent triangles to solve for missing angle measures. In summary, the document reviews basic geometry rules and defines congruent triangles, their corresponding parts, and how to determine if triangles
Uploaded by
kennethdevera01Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views6 pagesGeometry Basics for Students
This document provides a summary of key facts and concepts related to geometry and congruent triangles. It includes 12 facts about basic geometry, such as the sum of angles on a line and at a point. It then discusses congruent triangles, noting they have the same shape and size, and corresponding angles and sides are equal. Three conditions for determining if triangles are congruent are presented: side-side-side (SSS), side-angle-side (SAS), and angle-side-angle (ASA). An example problem demonstrates using corresponding parts of congruent triangles to solve for missing angle measures. In summary, the document reviews basic geometry rules and defines congruent triangles, their corresponding parts, and how to determine if triangles
Uploaded by
kennethdevera01Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd