Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Test - Edited
Uploaded by
Kloe-Rose LemmonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Test - Edited
Uploaded by
Kloe-Rose LemmonCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Trigonometry test
Student name:
1 Find, correct to four decimal places:
a sin 71 ° b cos 54 ° c tan112 ° 13 '
d sin 13 ° 48 '
2 Find the acute angle θ , correct to the nearest minute, given that:
a sin θ=0.75 b cos θ=0.45 c tanθ=1.17
d tanθ=−2.12
3 Find, correct to two decimal places, the side marked x in each triangle below.
a b
c d
4 Find, correct to the nearest minute, the angle θ in each triangle below.
a b
© Cambridge University Press 2019 1
c d
5 Use the special triangles to find the exact values of:
a sin 60 b tan 45 c cos 45
d sec 60 e cosec 45 f cot 30
6 A vertical pole stands on level ground. From a point on the ground 7 metres from its
base, the angle of elevation of the top of the pole is 29 °. Find the height of the pole,
correct to the nearest centimetre.
7 At what angle, correct to the nearest degree, is a 5 metre ladder inclined to the
ground if its foot is 2.75 metres out from the wall?
8 A motorist drove 60 km from town A to town B on a bearing of 054° T, and then
drove 85 km from town B to town C on a bearing of 144° T
a Explain why ∠ ABC=90 °
b How far apart are the towns A and C, correct to the nearest kilometre?
c Find ∠ BAC , and hence find the bearing of town C from town A, correct to the
nearest degree.
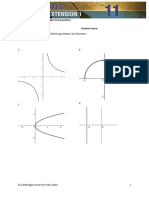
9 Sketch each graph for 0 ° ≤ x ≤360 ° ,
a y=cos x b y=sin x c y=tan x
10 Write each trigonometric ratio as the ratio of its related acute angle, with the
correct sign attached.
a sin 135 ° b cos 300 ° c tan225 °
d cos 240 °
11 Find the exact value of:
a cos 150 ° b sin 300 ° c tan240 °
d cos 240 °
12 Use the graphs of the trigonometric functions to find these values, if they exist
a sin 180 ° b tan270 ° c cos 0°
d sin 270 °
© Cambridge University Press 2019 2
13 Use Pythagoras’ theorem to find whichever of x, y or r is unknown. Then write down
the values of sin θ , cos θ and tanθ
a b
13
14 a If tan α = and α is acute, find the values of sin α and cos α .
9
b If sin β=
√7 and β is acute, find the values of cos β and tan β .
3
−43
c If tanθ= and 270 ° <θ<360 ° , find the values of sin θ and cos θ .
13
d If sin A=
√ 7 and 90 ° < A<180 ° , find the values of cos A and tan A .
6
15 Simplify:
1 1 sin θ
a b c
sec θ cot θ tan θ
d 1−cos2 θ e 2
cose c θ−cot θ
2
f 2
tan θ−sec θ
2
16 Prove the following trigonometric identities.
a sin θ cosec θ=1 b cot θ tanθ=1
sin θ
c ¿ cos θ d 2
3 sin θ−2=1−3 cos θ
2
tan θ
cot θ sec θ cos θ+sin θ 2 2 cosec θ tan θ 2
e + = f sin θ cot θ− =−sin θ
sin θ tan θ 2
sin θ sec θ
17 Solve each trigonometric equation for 0 ° ≤ x ≤360 ° .
© Cambridge University Press 2019 3
1 1
a sin x= b cos x= c tan x=1
2 √2
1 2
d sin x=0 e tan x= f sec x=
2 √3
g √ 3 sin x−1=0 h 2 cos x−√ 3=0 i 2
tan x=1
cos (x−60 °)= √
1 3
j sin 2 x= k l cos x=−√ 3 sin x
2 2
18 Solve each equation for 0 ° ≤ x ≤360 ° by reducing it to a quadratic equation in u. Give
your solution correct to the nearest minute where necessary.
a cos θ−2 cos2 θ=0 b 2
2 sin θ +3 sin θ=– 1
c 3 tan 2 θ−7 tan θ=– 4
19 Use the sine rule or the cosine rule in each triangle to find x , correct to one decimal
place.
a b
c d
20 Calculate the area of each triangle, correct to the nearest cm2.
a b
© Cambridge University Press 2019 4
21 Use the sine rule or cosine rule in each triangle to findθ , correct to the nearest
minute.
a b
c d
22 A triangle has sides 8 cm, 9 cm and 11 cm. Use the cosine rule to find one of its
angles and hence find the area of the triangle, correct to the nearest cm 2.
23 a Find the side a in ∆ ABC , where ∠ C=60 ° , b=24 cm and the area is 30 cm2.
b Find the size of ∠ B in ∆ ABC , where a=9 cm, c=8 cm and the area is 18 cm2.
24 A helicopter H is hovering above a straight, horizontal
road AB of length 750 m. The angles of elevation of H
from A and B are 56o and 38o respectively. The point C
lies on the road directly below H.
© Cambridge University Press 2019 5
750 sin 56°
a Use the sine rule to show that HB= .
sin 86 °
b Hence find the height CH of the helicopter above to road, correct to the nearest
metre.
25 A man is setting in a boat at P, where the angle of
elevation of the top T of a vertical cliff BT is 13 ° . He
then rows 50 metres directly towards the cliff to Q,
where the angle of elevation of T is 27o.
50 sin 13
a Show that TQ= using the sine rule
sin 14
b Hence find the height h of the cliff, correct to the nearest tenth of a metre.
26 A ship sailed 120 nautical miles from port P to port Q on a
bearing of 040oT. It then sailed 250 nautical miles from
port Q to port R on a bearing of 140oT.
a Explain why ∠ PQR=80 ° .
b Find the distance between ports R and P, correct to the
nearest nautical mile.
c Find the bearing of port R from port P, correct to the nearest degree.
27 From two points P and Q on horizontal ground, the angles
of elevation of the top T of a monument that is 8m high are
15 ° and 12 ° respectively. It is known that∠ PBQ=70 °,
where B is the base of the monument.
a Show that PB=8 tan 75° , and find a similar expression
for QB.
b Hence determine the distance between P and Q, correct
to the nearest metre.
28 The diagram below shows an open wooden crate in the shape of a rectangular
prism. The base is 1.7 metres by 1.1 metres, and the height is 0.8 metres.
a Find, correct to the nearest millimetre the length of the base diagonal BD.
© Cambridge University Press 2019 6
b Find, correct to the nearest millimetre the length of the longest metal rod BS that
will fit in the box.
c Find, correct to the nearest minute angle that the rod BS makes with the base.
© Cambridge University Press 2019 7
29 The points P, Q and B lie in a horizontal plane. From P, which is due west of B, the
angle of elevation of the top of a tower AB of height h metres is 36o. From Q, which
is on a bearing of 196o from the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower
is 27o. The distance PQ is 250 metres.
a Explain why ∠ PBQ=74 ° .
b Show that h2 =¿
2
250
2 2
cot 36° + cot 27 ° −2 cot27 ° cot 36 ° cos 74 °
c Hence find the height of the tower, correct to the
nearest metre.
30 In each diagram, find CD correct to the nearest centimetre.
a b
© Cambridge University Press 2019 8
31 Two towers AB and PQ stand on level ground. Tower AB is 23 metres taller than
tower PQ. From A, the angles of depression of P and Q are 24 ° and 71° respectively
a Use ∆ AKP to show that KP=BQ=23 tan66 ° .
b Use ∆ ABQ to show AB=23 tan66 ° tan71 °.
c Hence find the height of the shorter tower, correct to the
nearest metre.
d Solve the problem again by finding AP using ∆ AKP and
then using the sine rule in ∆ APQ .
32 Two trees T1 and T2 on one bank of a river are 78 metres apart. A sign S on the
opposite bank is between the trees and the angles ST1T2 and ST2T1
are 40 ° 45 ' and 51 ° 34 ' respectively.
a Find ST1 in exact form.
b Hence find the width of the river, correct to the nearest metre.
33 In the diagram to the right, ∠ ACD=β , ∠ BCD=α , AB=h and
BD=x .
h cos β
a Show that BC= .
sin(α + β )
h sin α cos β
b Hence show that x= .
sin (α + β)
34 A ship sails 73 nautical mules from P to Q on a bearing of 033 ° T .
It then sails 91 nautical miles due east from Q to R.
a Explain why ∠ PQR=123 °.
© Cambridge University Press 2019 9
b How far apart are P and R, correct to the nearest nautical mile?
35 The points P, Q and B lie in a horizontal plane. From P, which is
due west of B. The angle of elevation of the top of a tower AB of
height h metres is 37 ° . From Q, which is on a bearing of 213 ° from
the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 41 ° .
The distance PQ is 225 metres.
a Explain why ∠ PBQ=57 ° .
2
2 225
b Show that h = 2 2 .
cot 37 ° +cot 41 °−2 cot 41 ° cot 37 ° cos 57 °
c Hence find the height of the tower, correct to the nearest metre.
36 A triangular pyramid ABCD has base BCD and perpendicular height AD.
a Find BD and CD in terms of h.
b Use the cosine rule to show that 2 h2=3 x 2−√ 3 xh
h
c Let u= . Write the result of the previous part as a
x
quadratic equation in u, and hence show that:
h 3 √ 3−√ 3
= .
x 4
© Cambridge University Press 2019 10
Answers
1 a 0.9455
b 0.5878
c -2.4484
d 0.2385
2 a 48o35’
b 63o15’
c 49o29’
d -64o45’
3 a 15.05
b 8.82
c 12.31
d 5.08
4 a 37o59’
b 61o21’
c 51o1’
d 49o4’
5 a
√3
2
b 1
1
c
√2
d 2
e √2
f √3
6 3.88 metres
7 56.63 metres
8 a Using alternate angles we can see that the first part of∠ ABC is 54 ° . The
other part of the angle equates to 36 ° as the angle of a straight line adds
up to 180 ° . Summing the two angles∠ ABC=54 ° +36 °=90 °.
© Cambridge University Press 2019 11
b 104 km
c 55o
9 a
10 a sin 45 °
b cos 60°
c tan 45°
© Cambridge University Press 2019 12
d -cos 60°
−√ 3
11 a
2
−√ 3
b
2
c √3
−1
d
2
12 a 0
b Does not exist
c 1
d −1
3 4 3
13 a sin θ= , cos θ= and tanθ=
5 5 4
b sin θ=
7
, cos θ=
√6 and tanθ= 7
√ 55 √55 √6
13 9
14 a sin α = , cos α=
5 √10 5 √ 10
b cos β=
√2,
3
tan β =
√ 7
2
−43 13
c sin θ= , cos θ=
√ 2018 √2018
d cos A=
−√ 29
6
, tan A=
√ 7
29
15 a cos θ
b tanθ
c cos θ
2
d sin θ
e 1
f -1
17 a 30° , 150°
b 45° , 315°
© Cambridge University Press 2019 13
c 45° , 225°
d 0° , 360°
e 26o34’, 206o34’
f 30° , 330°
g 35° 16’, 144° 44 '
h 30° , 330°
i 45° , 135° , 225° , 315°
j 15° , 75° , 195° , 255°
k 30° , 90°
l 150° , 330°
18 a 60° , 90° , 270° , 300°
b 210° , 270° , 330°
c 45° , 53° 8 ’, 225° , 233° 8’
19 a 13.5
b 4.5
c 15.1
d 7.5
20 a 48 cm2
b 58 cm2
21 a 38° 37’
b 63° 45’
c 33° 58’
d 118° 10’
22 35 cm2
23 a 2.89 cm
b 30°
24 b 384 m
25 b 21.1 m
© Cambridge University Press 2019 14
26 a Using alternate angles we can see that the first part of∠ PQR is 40 ° . The
other part of the angle also equates to 40° as the angle of a straight line
adds up to 180 ° . Summing the two angles∠ PQR=40 ° + 40°=80 °.
b 258 nm
c 113
27 b 47 m
28 a 2.025 m
b 2.177 m
c 21° 33’
29 c 121 m
30 a 11.20 m
b 20 cm
c 5.92 m
31 c 127m
'
78sin 51 ° 34
32 a ST1¿ '
sin 80 ° 41
b 40 m
34 b 144
35 189 m
h h
36 a BD= , CD=
tan 45 ° tan 30 °
© Cambridge University Press 2019 15
You might also like
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- C3 Trigonometry D - QuestionsDocument2 pagesC3 Trigonometry D - QuestionsBenny NguyenNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- 5.trigonometry at A Glance 1Document1 page5.trigonometry at A Glance 1vamshiNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument3 pagesTrigonometryTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- l-22_introduction_to_trigonometryDocument3 pagesl-22_introduction_to_trigonometrysoorya_taNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Introduction To Trigonometry Study NotesDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Introduction To Trigonometry Study Notesramniwaschak08No ratings yet
- E3Qtri XDocument12 pagesE3Qtri XRevelationNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument7 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesPartha MajumderNo ratings yet
- C3 Trigonometry C - QuestionsDocument1 pageC3 Trigonometry C - Questionsarbaaz mohammedNo ratings yet
- Lessson 9 TrigonometryDocument11 pagesLessson 9 Trigonometryjamesmorara3No ratings yet
- Eew ps4Document6 pagesEew ps4stfirstfir stlastlaNo ratings yet
- ( + 2 Ab+b ( 2ab+b: A+b) A A B) ADocument5 pages( + 2 Ab+b ( 2ab+b: A+b) A A B) AsiewthiangNo ratings yet
- Review Math UT TrigonometryDocument1 pageReview Math UT TrigonometryTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument76 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- PrimingDocument3 pagesPrimingLoranel EspirituNo ratings yet
- MTP 4 Trigonometry ExercisesDocument1 pageMTP 4 Trigonometry ExercisesExercitusNo ratings yet
- Trigo ReviewDocument4 pagesTrigo ReviewDaniel VargasNo ratings yet
- A2 Maths QuestionsDocument2 pagesA2 Maths QuestionsIshwarya SivakumarNo ratings yet
- قوانين المثلثاتDocument4 pagesقوانين المثلثاتmmqNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRY QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesTRIGONOMETRY QUESTIONSRaghav MadanNo ratings yet
- Precal ExamDocument5 pagesPrecal ExamKisha PunsalanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Trigonometric Functions: SectionDocument27 pages2.2 - Trigonometric Functions: SectionMario Alberto Nuño CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PDFDocument16 pagesFormula Sheet PDFmaliathNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Trigonometry in Triangles September 2023Document75 pagesGR 11 Trigonometry in Triangles September 2023zmiqbal786No ratings yet
- Trigonometry 21 35Document7 pagesTrigonometry 21 35vishnusubs8989No ratings yet
- C3 Trigonometry E - QuestionsDocument1 pageC3 Trigonometry E - QuestionsBenny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerDocument4 pagesPre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerJovy OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerDocument4 pagesPre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerJovy OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Precalculus: Trigonometric PracticeDocument6 pagesPrecalculus: Trigonometric PracticeMixhelle AmankwahNo ratings yet
- 2-Revision of Introduction To Mathematics and Calculus I-1445HDocument23 pages2-Revision of Introduction To Mathematics and Calculus I-1445HnazifnanifNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsJulie Ailene AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Buổi 6, Chap 5Document6 pagesBài Tập Buổi 6, Chap 5Hà PhươngNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry at A GlanceDocument5 pagesTrigonometry at A Glancelakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Maths HY RevisionDocument5 pagesMaths HY RevisionQwertyNo ratings yet
- Trig Identities & ProofsDocument7 pagesTrig Identities & Proofsfreda licudNo ratings yet
- Theory - ExerciseDocument63 pagesTheory - ExerciseRonan HenriquesNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering ReviewDocument3 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering ReviewRosette de AsisNo ratings yet
- T4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstDocument3 pagesT4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstjuanesz98No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument6 pagesTrigonometrylee_yi_5No ratings yet
- VCE Unit 2 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceDocument17 pagesVCE Unit 2 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceMikiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities Worksheet SolvedDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Identities Worksheet SolvedYuri SamozvanovNo ratings yet
- 04a. Secant, Cosecant and CotangentDocument2 pages04a. Secant, Cosecant and CotangentKarman DharniNo ratings yet
- Trigo SolutionsDocument47 pagesTrigo SolutionsPrincess Morales100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Review-5Document4 pagesChapter 4 Review-5stealthysky0129No ratings yet
- Mensuration R: Pure MathematicsDocument8 pagesMensuration R: Pure Mathematicsquang hưngNo ratings yet
- Module 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFDocument3 pagesModule 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFNiwled UyNo ratings yet
- Army Public School, Noida Class: XI Assignment Trigonometric FunctionsDocument1 pageArmy Public School, Noida Class: XI Assignment Trigonometric FunctionsPrachiNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: King'S Glory Educational CentreDocument24 pagesAdditional Mathematics: King'S Glory Educational Centreapi-19650882No ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Solution (Ns-104 Electrodynamics Andoptics)Document8 pagesAssignment-3 Solution (Ns-104 Electrodynamics Andoptics)PrajjwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics N3 Trigonomentry Tutorial Notes PDFDocument15 pagesMathematics N3 Trigonomentry Tutorial Notes PDFKatlego MofommeNo ratings yet
- 594IA-07trigonometric functions(37-40)Document2 pages594IA-07trigonometric functions(37-40)wejaloj197No ratings yet
- 05 Ext 3Document3 pages05 Ext 3api-3706821No ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument7 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesMarjun PachecoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lecture Notes - Part2 PDFDocument18 pagesTrigonometry Lecture Notes - Part2 PDFDezzalyn D. Gabriel100% (1)
- SPM Unit 1 & 2 Mixed Review 5Document11 pagesSPM Unit 1 & 2 Mixed Review 5lyu chloeNo ratings yet
- MF19 formulas and tablesDocument16 pagesMF19 formulas and tablesSheryl CoronelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TestDocument16 pagesChapter 4 TestKloe-Rose LemmonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 TestDocument7 pagesChapter 13 TestKloe-Rose LemmonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TestDocument21 pagesChapter 3 TestKloe-Rose LemmonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 TestDocument5 pagesChapter 2 TestKloe-Rose LemmonNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Maths-2 Notes Semester-1Document28 pagesGrade-9 Maths-2 Notes Semester-1Anita ShindeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument18 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesMarcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- Motp Senior Geometry Problem Set 4Document5 pagesMotp Senior Geometry Problem Set 4K. M. Junayed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Final Step-C BookletDocument208 pagesFinal Step-C BookletAkshun Mishra100% (1)
- Trig Formula SheetDocument1 pageTrig Formula SheetNeil BreenNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Revision Worksheet Subject: Mathematics Topic: Congruency of TrianglesDocument4 pagesClass Ix Revision Worksheet Subject: Mathematics Topic: Congruency of TrianglesMr TacoNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 11 HOTS Important Question 22Document8 pagesMaths Class 11 HOTS Important Question 22srinidhiNo ratings yet
- S2 - TrigonometryDocument79 pagesS2 - TrigonometryDylan OtteyNo ratings yet
- Name: Geometry Date: The Isosceles Triangle Theorems Find The Value of X. 1) 2)Document3 pagesName: Geometry Date: The Isosceles Triangle Theorems Find The Value of X. 1) 2)Kerwin SoriaoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Jeemain - GuruDocument9 pagesTrigonometry Jeemain - Gururohan rajNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Mathematics For Calculus International Metric Edition 7th Edition Stewart Solutions ManualDocument37 pagesPrecalculus Mathematics For Calculus International Metric Edition 7th Edition Stewart Solutions Manualrollingdistoma9zcylv100% (19)
- Chapter 10 CirclesDocument19 pagesChapter 10 CirclesDileep Kumar RajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - SimilarityDocument37 pagesChapter 11 - SimilarityauroraNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Trigonometry - EasyDocument41 pagesGeometry and Trigonometry - EasyDiệu Anh HoàngNo ratings yet
- 11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument6 pages11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesQwert RNo ratings yet
- Let Math Major Reviewer-1-77Document77 pagesLet Math Major Reviewer-1-77Alberth Rodillas AbayNo ratings yet
- CH.5 Understanding Elementary Shapes-VI - MATHDocument8 pagesCH.5 Understanding Elementary Shapes-VI - MATHRoshni VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII 3DTrigSineCosineDocument28 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII 3DTrigSineCosinesreelakshmi100% (1)
- MCQ - Trignometry - 2 (Ans)Document23 pagesMCQ - Trignometry - 2 (Ans)Sobithaa SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 6: Problems Involving Right TrianglesDocument21 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 6: Problems Involving Right TrianglesLaviNo ratings yet
- Guj CETMaths 2010Document6 pagesGuj CETMaths 2010Kirtiman SinhaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument26 pages3 - Trigonometric FunctionsZamanoden D. UndaNo ratings yet
- State If The Triangles in Each Pair Are Similar. If So, State How You Know They Are Similar and Complete The Similarity StatementDocument4 pagesState If The Triangles in Each Pair Are Similar. If So, State How You Know They Are Similar and Complete The Similarity StatementRalph GodinezNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Word Problems WorksheetDocument20 pagesQuadratic Equation Word Problems WorksheetQamar JamilNo ratings yet
- 031 SR SM Modul Matematik JPN Sabah-83-102Document20 pages031 SR SM Modul Matematik JPN Sabah-83-102DARANISAI A/P RAVI MoeNo ratings yet
- Transversal Study GuideDocument8 pagesTransversal Study Guideapi-376958280100% (1)
- Triangles - MananDocument10 pagesTriangles - Mananapi-196653447No ratings yet
- Review Module 3 Trigonometry Part 1Document1 pageReview Module 3 Trigonometry Part 1KrishaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry PropertiesDocument18 pagesTrigonometry PropertiesDeepanshu AgarwalNo ratings yet