Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
gauthammcu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Untitled document
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesUntitled Document
Uploaded by
gauthammcuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
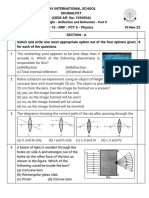
Section A
1.(d) diffraction bands become narrower and crowded together
2.(a) plane
3.(d) photoelectric effect
4.(a) λι=λ₂
5.(d) invisible
6.(c) by using white light instead of monochromatic light
7.(d) fringe width remains the same
8.d) only central fringe is white and all other fringes are coloured
9.(c) be four times
10.(d) 800 mm
11.(c) Real and large
12.(a) Total internal reflection
13.(c) The Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
14.a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the
Assertion
15.(d) Both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
16.(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the
Assertion.
Section D
29.i)(a) 5 cm, 35 cm
ii) (b) 10 cm
iii) (d) large focal length
iv) (d) astronomical telescope.
30.i) (a) -26.7cm
ii) (b) diverging lens
iii) (b) single convex lens
iv) (d) between F and optical centre
Section E
31.i)Define a wavefront. How is it different from a ray?
II) Using Huygens’s construction of secondary wavelets draw a diagram showing the passage of
a plane wavefront from a denser to a rarer medium. Using it verify Snell’s law.
32.(a) In Young’s double slit experiment, describe briefly how bright and dark fringes are
obtained on the screen kept in front of a double slit. Hence obtain the expression for the fringe
width.
(b) The ratio of the intensities at minima to the maxima in the Young’s double slit experiment is
9: 25. Find the ratio of the widths of the two slits.
a) Refer question no. 23
b.
33.i)Draw a ray diagram for the formation of image of a point object by a thin double
convex lens having radii of curvature R1 and R2. Hence derive lens maker’s formula.
ii) A converging lens has a focal length of 10 cm in air. It is made of a material of
refractive index 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, find its new
focal length.
You might also like
- Class Xii - CH-9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks WiseDocument37 pagesClass Xii - CH-9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks Wisesamaran270s100% (1)
- Ch9-10 CBSE 2023Document4 pagesCh9-10 CBSE 2023tebor93898No ratings yet
- 12th Physics EM - 2nd Revision Test 2022 Model Question Paper - A Series - English Medium PDF DownloadDocument4 pages12th Physics EM - 2nd Revision Test 2022 Model Question Paper - A Series - English Medium PDF Downloadsubashini udayakumarNo ratings yet
- JEE - Physics - Wave OpticsDocument23 pagesJEE - Physics - Wave OpticsSanjana KumariNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document22 pagesCH 10terasaini77No ratings yet
- Solution Science Class 10 - ScienceDocument3 pagesSolution Science Class 10 - ScienceSTUDENTS DREAM BOX - CBSENo ratings yet
- Physics vst-1Document2 pagesPhysics vst-1Hemanta JenaNo ratings yet
- 0ptics by MeDocument11 pages0ptics by MesagarNo ratings yet
- Wp-Content Uploads 2010 01 Question-Bank-IVDocument3 pagesWp-Content Uploads 2010 01 Question-Bank-IVmohit44yadav88No ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument5 pagesWave Opticsphysicist sharmaNo ratings yet
- P510/2 Physics JULY 2012 Paper2Document8 pagesP510/2 Physics JULY 2012 Paper2Mutsyaba Victor JuniorNo ratings yet
- Worksheet_LIGHT_(REFRACTION)_C-XDocument2 pagesWorksheet_LIGHT_(REFRACTION)_C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics PracticeDocument3 pagesWave Optics PracticeSurekaNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Ray OpticsDocument19 pagesPhysics XII Ray OpticsKartik YadavNo ratings yet
- Competancy Based Quesions - Ray OpticsDocument8 pagesCompetancy Based Quesions - Ray OpticsmapuclouddigitalworldNo ratings yet
- g10 ScienceDocument21 pagesg10 ScienceMOHAMMADMUNAWARSAIFNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 M5 2023-24Document3 pagesPhysics Class 12 M5 2023-24Sonu6 SiddNo ratings yet
- 50Q - Ray OpticsDocument10 pages50Q - Ray Opticskabir singhNo ratings yet
- UACE KCB MOCK Phy2 PDFDocument8 pagesUACE KCB MOCK Phy2 PDFTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- Phys12sqp - 2Document3 pagesPhys12sqp - 2ShreeNo ratings yet
- CC 4: Waves and Optics: I. One MarkquestionsDocument11 pagesCC 4: Waves and Optics: I. One MarkquestionsAk CreationNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave OpticsTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- XII - Revision Sheet - 2 - PhysicsDocument2 pagesXII - Revision Sheet - 2 - PhysicsVipin VNo ratings yet
- DPS - MIS, DOHA- QATAR REVISION ASSIGNMENT 2022-2023 CLASS: X PHYSICSDocument7 pagesDPS - MIS, DOHA- QATAR REVISION ASSIGNMENT 2022-2023 CLASS: X PHYSICSAnabella NavisNo ratings yet
- Xii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsDocument3 pagesXii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsMaster GamingNo ratings yet
- Questions Chapter 9 - ALPDocument3 pagesQuestions Chapter 9 - ALPMujeeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- AIR Objective Test-03 Class 10th Test Paper (06.08.2023) FinalDocument12 pagesAIR Objective Test-03 Class 10th Test Paper (06.08.2023) FinalAli MohammadNo ratings yet
- Optics exam multiple choice and problemsDocument5 pagesOptics exam multiple choice and problemsPakileo LeopakiNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Document12 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- S.5 Phy P2 Eot 1 2003 Revision Past PapersDocument3 pagesS.5 Phy P2 Eot 1 2003 Revision Past Paperskinene richardNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument8 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics MCQDocument8 pagesWave Optics MCQGuru ki physicsNo ratings yet
- VISN1231 Exam Paper 2010Document3 pagesVISN1231 Exam Paper 2010shadowosNo ratings yet
- FREE JEE NEET RAY OPTICS 400 MCQS WITH ANSWERS - KDocument31 pagesFREE JEE NEET RAY OPTICS 400 MCQS WITH ANSWERS - KADITIYANo ratings yet
- Quiz - Phase 6 HE&CW - SoEDocument4 pagesQuiz - Phase 6 HE&CW - SoEnihar.sarkar1975No ratings yet
- Group Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkDocument5 pagesGroup Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkMadhvi ShardaNo ratings yet
- Case Based 10 and 11 CHPDocument19 pagesCase Based 10 and 11 CHPNETRA DAMGUDENo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Entrance Questions HannDocument4 pagesRay Optics Entrance Questions HannPHYSCO BOT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (QB)Document12 pagesWave Optics (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Test MCQDocument2 pagesClass 12 Revision Test MCQkoushikgm2024No ratings yet
- Short Questions on Interference and DiffractionDocument11 pagesShort Questions on Interference and DiffractionNishi SinghalNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsAbhinav Mishra0% (1)
- VITEEE 2011 Previous Year PaperDocument16 pagesVITEEE 2011 Previous Year PaperRaghuvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsMohd SaquibNo ratings yet
- PROJOX ACADEMY/9953118716,9667944902: Physics CTSDocument13 pagesPROJOX ACADEMY/9953118716,9667944902: Physics CTSAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre-Board Exam TestDocument3 pagesPhysics Pre-Board Exam TestGhulam FaridNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 ReviewDocument3 pagesExam 2 Reviewdhruv1117No ratings yet
- CBSE Board Mock Paper 1 XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesCBSE Board Mock Paper 1 XII Physicsrohan sinhaNo ratings yet
- T16 Question Paper For Physics Class 11 91011Document1 pageT16 Question Paper For Physics Class 11 91011Ghulam sabirNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument6 pagesWave OpticsKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 7: Class XII 2023-24 PhysicsDocument6 pagesSample Paper 7: Class XII 2023-24 PhysicsBhaviniNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics MCQDocument5 pagesRay Optics MCQBAAP ka papaNo ratings yet
- Optics-Exam Paper-2009Document3 pagesOptics-Exam Paper-2009shadowosNo ratings yet
- 15-04-2022 - SR Iit Star Batch-Ii& Co SC N120, Co Spark, Nipl Super-60 - Main Model Full Test (MFT-1) QP FinalDocument10 pages15-04-2022 - SR Iit Star Batch-Ii& Co SC N120, Co Spark, Nipl Super-60 - Main Model Full Test (MFT-1) QP FinalRani SaiNo ratings yet
- Q2 OpticDocument4 pagesQ2 OpticsiddhugxeNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Questions on Lenses, Prisms and RefractionDocument2 pagesRay Optics Questions on Lenses, Prisms and RefractionNandanaNo ratings yet
- Get 10% Off Unacademy with Code GGLIVEDocument10 pagesGet 10% Off Unacademy with Code GGLIVESrusti Srujanika100% (1)
- PHYS12SQPDocument3 pagesPHYS12SQPShreeNo ratings yet