Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lcms Saliva Sample Report
Uploaded by
DaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lcms Saliva Sample Report
Uploaded by
DaniCopyright:
Available Formats
TEST REPORT
8605 SW Creekside Place
Beaverton, OR 97008
Phone: 503-466-2445 Fax: 503-466-1636
# D2019 11 25 001 S Samples Received Samples Collected
Ordering Provider: 11/25/2019 Saliva - 11/21/19 07:20
Getuwell
Report Date
11/26/2019
Patient Name: LCMS Saliva PCOS
Patient Phone Number:
Gender Last Menses Height Waist
Female Unspecified 5 ft 5 in 40 in
DOB Menses Status Weight BMI
11/6/1994 (25 yrs) Pre-Menopausal - Irregular 195 lb 32.4
TEST NAME RESULTS | 11/21/19 RANGE
Salivary Steroids & Other Analytes (LC-MS/MS)
Estradiol 3.2 H 1.0-2.9 pg/mL Premeno-luteal
Estriol 1 <3.0 pg/mL Premenopausal Luteal
Estrone 10.4 H 3.2-7.9 pg/mL Premeno-luteal
Ethinyl Estradiol <0.4 <0.4 pg/mL
Pregnenolone Sulfate 10 1-23 pg/mL
Progesterone 60 L 66-196 pg/mL Premeno-luteal
Ratio: Pg/E2 (Saliva
LCMS) 19 L 23-196
Allopregnanolone <15.0 <15 pg/mL
17OH-Progesterone 45 H 6-28 pg/mL
Androstenedione 110 H 36-93 pg/mL
Testosterone 40 H 7-22 pg/mL
DHT 30 H <25 pg/mL
DHEA 113 77-287 pg/mL
DHEAS 6.9 0.8-8.0 ng/mL
7-keto DHEA 100 41-130 pg/mL
11-Deoxycortisol 52 H 12-48 pg/mL
Cortisol 6.7 H 2.5-6.2 ng/mL Morning
Cortisone 20 10.0-23.3 ng/mL Morning
CLIA Lic # 38D0960950
11/26/2019 11:05:57 AM
The above results and comments are for informational
purposes only and are not to be construed as medical
David T. Zava, Ph.D.
Laboratory Director
Alison McAllister, ND.
(Ordering Provider unless
1 of 6
advice. Please consult your healthcare practitioner for otherwise specified on page 1)
diagnosis and treatment.
© 1998-2019 ZRT Laboratory, LLC. All rights reserved.
LCMS Saliva PCOS
TEST REPORT | Results continued # D2019 11 25 001 S
TEST NAME RESULTS | 11/21/19 RANGE
Salivary Steroids & Other Analytes (LC-MS/MS)
Corticosterone 60 11-66 pg/mL
Aldosterone 65 H 16-63 pg/mL
Melatonin 17 3-22 pg/mL
Anastrozole <5 <5 pg/mL
Finasteride 265 >5 pg/mL Finasteride
Letrozole <5 <5 pg/mL
<dl = Less than the detectable limit of the lab. N/A = Not applicable; 1 or more values used in this calculation is less than the detectable limit. H = High. L = Low.
Therapies
2.5 mg oral Finasteride (Proscar, Propecia) (Pharmaceutical)
CLIA Lic # 38D0960950
11/26/2019 11:05:57 AM
The above results and comments are for informational
purposes only and are not to be construed as medical
David T. Zava, Ph.D.
Laboratory Director
Alison McAllister, ND.
(Ordering Provider unless
2 of 6
advice. Please consult your healthcare practitioner for otherwise specified on page 1)
diagnosis and treatment.
© 1998-2019 ZRT Laboratory, LLC. All rights reserved.
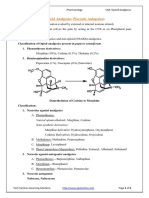
Saliva Steroid Cascade
O
O O
O
O O HO
S S
O O HO O
HO O
Pregnenolone Sulfate DHEA-S 7-Keto DHEA
ST SU ST SU
11β-HSD1
O O OH
O
OH
HO HO HO HO HO
CYPSCC 17, 20-Lyase TYPE 1
Cholesterol Pregnenolone 17-OH Pregnenolone DHEA Androstenediol
3β-HSD
O O
OH
O
17α-OH
O 17β-HSD
OH
HO
H 5α-R O O O O
3α-HSD 17, 20-Lyase TYPE 1
Allopregnanolone Progesterone 17-OH Progesterone Androstenedione Testosterone
TYPE 2
21-OH
AR AR 5α-R FIN
ANZ, LTZ
OH
OH OH
O
O OH
O
OH
O
O O HO HO H
TYPE 1
11-Deoxycorticosterone 11-Deoxycortisol Estrone Estradiol DHT
TYPE 2
11β-OH CYP3A4
17β-HSD
OH HO
O O OH
HO HO
OH
OH
O O HO
Corticosterone Cortisol Estriol
KEY
AS 11β-HSD1 17β-HSD2 AR - Aromatase
AS - Aldosterone Synthase
OH
O OH
O O ST - Sulfotransferase
HO O OH SU - Sulfatase
Analytes in bold are reported by ZRT
O O
Aldosterone Cortisone
Steroid Synthesis Inhibitors Synthetic Contraceptive Estrogen Melatonin
N N
HN O
N O
OH
NH
O
N N
N
N N
N N O N
HO H
N H H
Anastrozole Letrozole Finasteride
Ethinyl Estradiol Mel
ANZ LTZ FIN
LCMS Saliva PCOS
TEST REPORT | Patient Reported Symptoms # D2019 11 25 001 S
Disclaimer: Symptom Categories below show percent of symptoms self-reported by the patient compared to total available symptoms for each category. For
detailed information on category breakdowns, go to www.zrtlab.com/patient-symptoms.
SYMPTOM CATEGORIES RESULTS | 11/21/19
Estrogen / Progesterone Deficiency 25%
Estrogen Dominance / Progesterone Deficiency 47%
Low Androgens (DHEA/Testosterone) 28%
High Androgens (DHEA/Testosterone) 69%
Low Cortisol 30%
High Cortisol 40%
Hypometabolism 23%
Metabolic Syndrome 76%
SYMPTOM CHECKLIST MILD MODERATE SEVERE
Aches and Pains
Acne
ADD/ADHD
Addictive Behaviors
Allergies
Anxious
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Bleeding Changes
Blood Pressure High
Blood Pressure Low
Blood Sugar Low
Body Temperature Cold
Bone Loss
Breast Cancer
Breasts - Fibrocystic
Breasts - Tender
Chemical Sensitivity
Cholesterol High
Constipation
Depressed
Developmental Delays
Eating Disorders
Fatigue - Evening
Fatigue - Morning
Fibromyalgia
Foggy Thinking
Goiter
Hair - Dry or Brittle
Hair - Increased Facial or Body
Hair - Scalp Loss
Headaches
Hearing Loss
Heart Palpitations
Hoarseness
Hot Flashes
Incontinence
Infertility
Irritable
Libido Decreased
Mania
CLIA Lic # 38D0960950
11/26/2019 11:05:57 AM
The above results and comments are for informational
purposes only and are not to be construed as medical
David T. Zava, Ph.D.
Laboratory Director
Alison McAllister, ND.
(Ordering Provider unless
4 of 6
advice. Please consult your healthcare practitioner for otherwise specified on page 1)
diagnosis and treatment.
© 1998-2019 ZRT Laboratory, LLC. All rights reserved.
LCMS Saliva PCOS
TEST REPORT | Patient Reported Symptoms continued # D2019 11 25 001 S
SYMPTOM CHECKLIST MILD MODERATE SEVERE
Memory Lapse
Mood Swings
Muscle Size Decreased
Nails Breaking or Brittle
Nervous
Night Sweats
Numbness - Feet or Hands
OCD
Panic Attacks
PreMenstrual Dysphoric Disorder BLANK
Pulse Rate Slow
Rapid Aging
Rapid Heartbeat
Skin Thinning
Sleep Disturbed
Stamina Decreased
Stress
Sugar Cravings
Sweating Decreased
Swelling or Puffy Eyes/Face
Tearful
Triglycerides Elevated
Urinary Urge Increased
Uterine Fibroids
Vaginal Dryness
Water Retention
Weight Gain - Hips
Weight Gain - Waist
Lab Comments
Estradiol (E2) and estrone (E1) are higher than reference ranges for a premenopausal woman assuming that the saliva sample was collected
during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle (note: patient indicates irregular menstrual cycles). Symptoms are consistent with chronic high
estrogens (estrogen dominance), which is usually associated low progesterone (Pg) relative to estradiol (i.e. low Pg/E2 ratio). For optimal effects
of estradiol its level should be within mid-luteal ranges (about 1.5-3 pg/ml) and well balanced with progesterone, optimally with a Pg/E2 ratio of
about 100-500. Consider means to lower the high estradiol with diet (more fiber, colored vegetables, less red meat, fewer empty carbohydrates),
exercise, stress reduction, and natural progesterone. Progesterone helps regulate estradiol by increasing the levels and activity of enzymes that
convert it to less active estrone and then to inert estrone sulfate. Progesterone at high physiological concentrations seen during the luteal phase
of the menstrual cycle (10-30 mg), or used as progesterone therapy also down-regulate cellular estrogen receptors in target tissues such as the
breasts and uterus, preventing estradiol from stimulating further cell hypertrophy and proliferation that occur during mid follicular phase/
ovulation, and in women approaching menopause with excessive estradiol synthesis and luteal insufficiency (low progesterone).
Progesterone (Pg) is lower than luteal range and is not well balanced with estradiol (low Pg/E2). Low Pg is consistent with symptoms of
estrogen dominance. The downstream Pg metabolite allopregnanolone (AlloP) is very low (less than detectable range). AlloP is a potent
neuroactive steroid in the brain that amplifies the anxiolytic (calming) actions of GABA on the GABAergic neurons, which helps balance the
anxiogenic (stimulating) actions of excessive levels of estrogens. Allopregnanolone is created from progesterone through the actions of 5-alpha
reductase (5aR) and 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3aHSD), which convert Pg to 5-hydroxyprogesterone (5OHPg) and then to AlloP.
This individual reports use of Finasteride, a potent synthetic inhibitor of 5aR that blocks conversion of T to DHT, and Pg to 5OHP, a precursor to
AlloP. Very low AlloP is likely the result of Finasteride therapy to suppress symptoms of androgen excess, as self-reported. While Finasteride has
been shown to be effective for treating hair loss and hirsutism caused by high testosterone/DHT, it can cause adverse side effects such as
anxiety and depression, symptoms commonly associated with low AlloP.
Testosterone (T), is higher than reference range for a premenopausal woman. Precursors for testosterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17OHP)
and androstenedione (Adione) are also higher than range. However, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the downstream metabolite of T and
responsible for many of the final actions of androgens at the cellular level, is lower than detectable range, indicating low 5 alpha reductase (5aR)
activity. This individual indicates recent use of Finasteride, a 5aR inhibitor often used by women with PCOS and symptoms of androgen excess
such as scalp hair loss, acne, and excessive facial/body hair. By inhibiting 5aR this often results in accumulation of hormones upstream of the
inhibitor, which would include T, Adione, and 17OHP. High levels of these hormones in combination with high estrogens, low progesterone,
CLIA Lic # 38D0960950
11/26/2019 11:05:57 AM
The above results and comments are for informational
purposes only and are not to be construed as medical
David T. Zava, Ph.D.
Laboratory Director
Alison McAllister, ND.
(Ordering Provider unless
5 of 6
advice. Please consult your healthcare practitioner for otherwise specified on page 1)
diagnosis and treatment.
© 1998-2019 ZRT Laboratory, LLC. All rights reserved.
LCMS Saliva PCOS
TEST REPORT | Comments continued # D2019 11 25 001 S
irregular menstrual cycles, and symptoms of androgen excess (e.g. loss of scalp hair, increased facial/body hair, and/or acne) strongly suggest
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), a condition found to occur in approximately 8-10% of premenopausal women. PCOS is closely
associated with excessive weight gain, poor diet consisting of excessive carbohydrate consumption, and insulin resistance. Various natural and
synthetic inhibitors are used to lower the androgenic burden by inhibiting T synthesis (synthetic progestins, LH antagonists) or DHT synthesis by
inhibition of 5aR (Finasteride, Saw Palmetto, natural progesterone). While all are effective for reducing DHT, if inhibition is excessive it could
lead to very low levels of DHT’s downstream metabolite 3a5a-androstanediol (Adiol), a neuroactive steroid with beneficial actions on the
gabaergic and dopaminergic receptors in the brain. Low Adiol may exacerbate symptoms associated with low dopamine, which include food
craving, low stamina, lack of focus, moodiness, forgetfulness, fatigue, apathy, and feelings of depression and sadness. If these adverse
symptoms have become more problematic with use of Finasteride consider reducing dosage or consider other more natural means to block
excessive formation of DHT (e.g. natural progesterone, treatment for insulin resistance if problematic).
The adrenal androgen precursors DHEA, DHEA-sulfate (DHEA-S), and 7-keto DHEA are within reference ranges for a premenopausal female.
DHEA and 7-Keto DHEA are present in saliva in approximately equal amounts. Supplementation with DHEA raises levels of DHEA and
downstream metabolites such as androstenedione, testosterone, and estrogens estrone and estradiol. In contrast, 7-keto DHEA, while it has
beneficial anabolic effects and amplifies the actions of thyroid hormones, does not metabolize to downstream androgens or estrogens, like
DHEA. Supplementation with 7-keto DHEA raises only its levels in saliva, resulting in a very high 7-keto DHEA/DHEA ratio. Supplementation
with DHEA results in a very high DHEA/7-keto DHEA ratio and is useful for identifying individuals that may knowingly or unknowingly be using
supplements that contain DHEA.
Cortisol is slightly elevated and its upstream precursors 11-deoxycortisol and 17-OH progesterone are also within the upper quadrant and higher
than the reference ranges, respectively. Higher levels of these adrenal cortisol precursors and cortisol, in combination with high androgens are a
hallmark of PCOS. Elevated cortisol is associated with insulin resistance, high insulin and hyperglycemia, and the etiology of PCOS. Stress
reduction, removal of inflammatory foods, and natural progesterone can help counter the negative effects of chronic high cortisol. High cortisol
likely contributes to self-reported sleep disturbances.
Aldosterone and its precursor corticosterone are higher than reference ranges, consistent with self-reported high blood pressure. Aldosterone is
produced in the outer most zone of the adrenal gland. It regulates the body’s levels of sodium and potassium through its actions on the kidney to
increase sodium reabsorption and increase potassium excretion. High aldosterone (hyperaldosteronism) occurs frequently in women with PCOS
and insulin resistance. High aldosterone is correlated directly with higher C-reactive protein, thickening of the intima-media of the carotid artery,
lower HDL-cholesterol, and lower serum potassium, all of which increase lifetime risk for cardiovascular disease. Natural therapies to treat
insulin resistance (weight control, diet, exercise, stress reduction, etc.), or synthetic drugs (e.g. Spironolactone, calcium channel blockers) to
treat the more immediate deleterious effects of high aldosterone and low potassium should be discussed with a health care practitioner.
Melatonin in the first morning saliva sample is within expected reference range. This test only measures the first morning saliva, which if
collected on awakening should be within reference range, as is not meant to evaluate melatonin at night before bed. However, if early nighttime
melatonin is low this may aggravate being able to fall asleep. Melatonin is an antioxidant and supplementation may help with better sleep
patterns and help lower cortisol, which at high levels contributes to insulin resistance.
CLIA Lic # 38D0960950
11/26/2019 11:05:57 AM
The above results and comments are for informational
purposes only and are not to be construed as medical
David T. Zava, Ph.D.
Laboratory Director
Alison McAllister, ND.
(Ordering Provider unless
6 of 6
advice. Please consult your healthcare practitioner for otherwise specified on page 1)
diagnosis and treatment.
© 1998-2019 ZRT Laboratory, LLC. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Toxicology Report For Rapper Lil PeepDocument5 pagesToxicology Report For Rapper Lil PeepKOLD News 13100% (6)
- Cycle Guide-SteroidsDocument105 pagesCycle Guide-SteroidsPhidellio Marius82% (17)
- Patient Name Mr. B K Jha Uhid Lab No Sample Date Receiving Date 29/12/2021 12:19PMDocument7 pagesPatient Name Mr. B K Jha Uhid Lab No Sample Date Receiving Date 29/12/2021 12:19PMron fratomNo ratings yet
- S60 - VCC Ayurveda & Medic: Patientreportscsuperpanel - General - Panel - Analyte - SC (Version: 6)Document12 pagesS60 - VCC Ayurveda & Medic: Patientreportscsuperpanel - General - Panel - Analyte - SC (Version: 6)Shubhit PrasadNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Controlled DrugsDocument1 pageSchedule of Controlled DrugsKaye AbordoNo ratings yet
- Test Reports PDFDocument8 pagesTest Reports PDFabhishek5810No ratings yet
- S51 - Aarogya Patho Lab Vim - 512 Sailashree Vihar, Chandrasekharpur, Bhubaneswar - 751024Document10 pagesS51 - Aarogya Patho Lab Vim - 512 Sailashree Vihar, Chandrasekharpur, Bhubaneswar - 751024Ashis Kumar MuduliNo ratings yet
- L37 - Mr. Ashish Narang - FPSC Paramount Tulip Shop No.9, Paramount Tulip, Delhi Road, SAHARANPUR, UP. C-8629994444, 8629990007Document13 pagesL37 - Mr. Ashish Narang - FPSC Paramount Tulip Shop No.9, Paramount Tulip, Delhi Road, SAHARANPUR, UP. C-8629994444, 8629990007vishal pundirNo ratings yet
- A26 - Walk in Paschim Vihar Ii: NoteDocument2 pagesA26 - Walk in Paschim Vihar Ii: NoteLakshay MahajanNo ratings yet
- Zy24r1ayjqzfi0yjuvi0mayl PDFDocument2 pagesZy24r1ayjqzfi0yjuvi0mayl PDFAnonymous 3OYSY7r100% (1)
- L37 - FPSC Saharanpur 4 G-36, Parshvnath Plaza, Court Road, SAHARANPUR-247001, Cont. - 9319141888Document13 pagesL37 - FPSC Saharanpur 4 G-36, Parshvnath Plaza, Court Road, SAHARANPUR-247001, Cont. - 9319141888Saurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- SL Report-287060681Document7 pagesSL Report-287060681SubhaNo ratings yet
- Serum ChemistryDocument1 pageSerum Chemistrysystemop651No ratings yet
- Muneca Izquierdo 2023 11 01 1529Document1 pageMuneca Izquierdo 2023 11 01 1529ucivetperuNo ratings yet
- 5ded66d6-1410-4590-ac97-cba8de91f7d2Document6 pages5ded66d6-1410-4590-ac97-cba8de91f7d2sahatwarccNo ratings yet
- L16 - Bhopal Lab Ii Home Visit Plot No.05, Mandakini Housing Society, Near Apurti Shopping Mall, Kolar Main RD BhopalDocument8 pagesL16 - Bhopal Lab Ii Home Visit Plot No.05, Mandakini Housing Society, Near Apurti Shopping Mall, Kolar Main RD BhopalMaxxPain Gaming & MusicNo ratings yet
- PdfText - 2024-03-15T191650.936Document1 pagePdfText - 2024-03-15T191650.936jayanthmahesh0403No ratings yet
- L89 - Muzaffar Nagar Cc3 Shop No. 11, Near Dr. Dharampal Singh Sadar Bazar Muzaffarnagar 251001Document4 pagesL89 - Muzaffar Nagar Cc3 Shop No. 11, Near Dr. Dharampal Singh Sadar Bazar Muzaffarnagar 251001shivang ranaNo ratings yet
- Final Report Patient Progress Report: Steroid Hormone Tests (Saliva)Document2 pagesFinal Report Patient Progress Report: Steroid Hormone Tests (Saliva)Kaveh EshkoftiNo ratings yet
- S53 - Syed Kashif Ghani-Fpsc Zakir Nagar: Patientreportscsuperpanel - General - Panel - Analyte - SC (Version: 6)Document11 pagesS53 - Syed Kashif Ghani-Fpsc Zakir Nagar: Patientreportscsuperpanel - General - Panel - Analyte - SC (Version: 6)Khalid Mohammad Khalid TanwiriNo ratings yet
- LFT LalpathDocument2 pagesLFT Lalpathmoyic39272No ratings yet
- Surendra KumarDocument2 pagesSurendra KumarUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- Cczzst5oiztfamqh0e0xjjeaDocument2 pagesCczzst5oiztfamqh0e0xjjeaUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- FBCReport Aspx2Document2 pagesFBCReport Aspx2RahulNo ratings yet
- A03 - Mr. Pratap Narayan Jaiswal - (Jaiswal Pathology) Jaiswal Pathology CC, Rajapal Chauraha, Kachehari Road, Pratapgarh, Uttar PradesDocument10 pagesA03 - Mr. Pratap Narayan Jaiswal - (Jaiswal Pathology) Jaiswal Pathology CC, Rajapal Chauraha, Kachehari Road, Pratapgarh, Uttar PradesShubham KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Tata Memorial Hospital: Units InvestigationDocument2 pagesTata Memorial Hospital: Units InvestigationSATISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 08, 2022Document11 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 08, 2022artemis 0516No ratings yet
- This Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesDocument2 pagesThis Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesAyazNo ratings yet
- Form HSL Pemeriksaan TernewDocument3 pagesForm HSL Pemeriksaan Ternewvika eenNo ratings yet
- Allreports 1Document2 pagesAllreports 1Girish LunaviyaNo ratings yet
- ZRT Neurotransmisores Reporte Muestra 0422Document19 pagesZRT Neurotransmisores Reporte Muestra 0422Job MonobeNo ratings yet
- Patient Name Mr. Umesh Jain Uhid Lab No Sample Date Receiving Date 03/04/2021 11:40AMDocument1 pagePatient Name Mr. Umesh Jain Uhid Lab No Sample Date Receiving Date 03/04/2021 11:40AMAkshay ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- 9443243103::::: Blood: Dhanvantri Nagar, Pondicherry - 605006, IndiaDocument1 page9443243103::::: Blood: Dhanvantri Nagar, Pondicherry - 605006, IndiaSurbhi JainNo ratings yet
- LIVER PROFILE LFT Test Report Format Example Sample Template Drlogy Lab ReportDocument1 pageLIVER PROFILE LFT Test Report Format Example Sample Template Drlogy Lab ReportM ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Hasil Toxoplasma YantiDocument155 pagesHasil Toxoplasma YantiSyafri YentiNo ratings yet
- Labreport V SMSH 24 5782051 PDFDocument2 pagesLabreport V SMSH 24 5782051 PDF32vivaanNo ratings yet
- Mrs. V.DHANALAXMIDocument2 pagesMrs. V.DHANALAXMIAnonymous lSZ9JVNo ratings yet
- Baba ReportDocument11 pagesBaba ReportRajarshi BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Gulapa, Hanah Gracia Besar 2371011421Document3 pagesGulapa, Hanah Gracia Besar 2371011421Hanah GulapaNo ratings yet
- Dr. HalimDocument2 pagesDr. HalimmembermemNo ratings yet
- 66 Year Female 25423511041: Patient NameDocument1 page66 Year Female 25423511041: Patient NameTarek SalemNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument14 pagesReportWaseem FarooqNo ratings yet
- Patient Data Profile Form-1Document9 pagesPatient Data Profile Form-1souvicknag99No ratings yet
- NPSLE With Normal PCTDocument67 pagesNPSLE With Normal PCTIswanto Korompot MonoarfaNo ratings yet
- Value: 04/11/2018 3314 MR. Akshay Duggal 25 Yrs. M 04/11/2018Document2 pagesValue: 04/11/2018 3314 MR. Akshay Duggal 25 Yrs. M 04/11/2018AKshay DuggalNo ratings yet
- S27 - Lpl-Srinagar 140-A, Kak Sarai, Karan Nagar, SRINAGAR-190010, J&K SrinagarDocument6 pagesS27 - Lpl-Srinagar 140-A, Kak Sarai, Karan Nagar, SRINAGAR-190010, J&K Srinagarishfaq shafiqNo ratings yet
- LFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test NameDocument4 pagesLFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test Namemetepraju0210No ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism (Iem) Summary Report: Sr. No. Test Methodology Result Test TypeDocument2 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism (Iem) Summary Report: Sr. No. Test Methodology Result Test TypeMallikharjunaRao medaNo ratings yet
- Samuel BloodworkDocument3 pagesSamuel BloodworkPaez R MarcoNo ratings yet
- Renal Profile Letterhead With SignDocument1 pageRenal Profile Letterhead With Signsantanu2020barikNo ratings yet
- S60 - Morvinandan Diagnostic Centre LLP: Patientreportscsuperpanel - Urine - Examination - SC (Version: 6)Document10 pagesS60 - Morvinandan Diagnostic Centre LLP: Patientreportscsuperpanel - Urine - Examination - SC (Version: 6)Sarah ZiaNo ratings yet
- S28 - Mr. Kanthala Narender Reddy (Vedic Diagnostics) H.NO.-1-98/13/1, MADHAPUR, Hyderabad-500081, Telanagana ShaikpetDocument9 pagesS28 - Mr. Kanthala Narender Reddy (Vedic Diagnostics) H.NO.-1-98/13/1, MADHAPUR, Hyderabad-500081, Telanagana ShaikpetSiva rajNo ratings yet
- N8 R 9 W3 Pupeyo RF RTWB 42 BRDocument2 pagesN8 R 9 W3 Pupeyo RF RTWB 42 BRPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- 5ykgogrgmtd3pwbpedotjsidDocument10 pages5ykgogrgmtd3pwbpedotjsidKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Battana...Document7 pagesBattana...Ujjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Nilai LabDocument94 pagesLampiran Nilai LabediNo ratings yet
- U5ybmhbn41kp4qk2olovs5wfDocument14 pagesU5ybmhbn41kp4qk2olovs5wfSagar VashisthNo ratings yet
- Date 24/dec/2022 08:32AM 03/dec/22 09:33AM 26/nov/22 09:05AM Unit Bio Ref IntervalDocument11 pagesDate 24/dec/2022 08:32AM 03/dec/22 09:33AM 26/nov/22 09:05AM Unit Bio Ref IntervalAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Nama: Alamat: Umur: Diagnosa:: CatatanDocument1 pageNama: Alamat: Umur: Diagnosa:: CatatanPU Trii ChandraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - I: TEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)Document1 pageChemistry - I: TEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)aaaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument15 pagesBiochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Conventional Units Result Si Units Test Result: Patient Id Ecd14100001810 Chargeslip No Ecdlab190125396Document2 pagesConventional Units Result Si Units Test Result: Patient Id Ecd14100001810 Chargeslip No Ecdlab190125396Tintin Maras YariNo ratings yet
- Birth Control Made Simple 2010Document5 pagesBirth Control Made Simple 2010Richard WahlNo ratings yet
- Opiods MorphineDocument4 pagesOpiods MorphinevysakhmohanannairNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Laporan Psikotropika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFDocument8 pagesRekapitulasi Laporan Psikotropika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFLucia Shinta RatnaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Sedative Hypnotic DrugsDocument21 pagesSedative Hypnotic DrugstamaNo ratings yet
- Biorad Lyphocheck Immunoassay Plus Control: Revision 1 (Ref) 370, 40390 Level 1 - 3 2022-12-31Document1 pageBiorad Lyphocheck Immunoassay Plus Control: Revision 1 (Ref) 370, 40390 Level 1 - 3 2022-12-31MaherNo ratings yet
- Injectable MethandienoneDocument2 pagesInjectable MethandienoneovizdikNo ratings yet
- Marquis Mecke Mandelin Simon Lieberman N Froehde Folin: SubstanceDocument5 pagesMarquis Mecke Mandelin Simon Lieberman N Froehde Folin: Substancebob oblawNo ratings yet
- Androgenic Supplementation in Men - Effects of Age Herbal ExtractDocument154 pagesAndrogenic Supplementation in Men - Effects of Age Herbal ExtractMaria PopaNo ratings yet
- Lista de Sustancias 2020 DistribuidorDocument15 pagesLista de Sustancias 2020 DistribuidorRafael ValdezNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Januari 2022Document13 pagesRekapitulasi Januari 2022fajriazaidabdazizNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High AlertDocument3 pagesDaftar Obat High AlertLupus BoyssNo ratings yet
- FDM ATR Drugs Chemical Name IndexDocument8 pagesFDM ATR Drugs Chemical Name Indexamin138irNo ratings yet
- Androstenedione: Charles E. Yesalis, MPH, SCD, Pennsylvania State UniversityDocument5 pagesAndrostenedione: Charles E. Yesalis, MPH, SCD, Pennsylvania State UniversityJohn DNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Aub PatientDocument1 pagePathophysiology Aub PatientArvin John ManuelNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl: DilutiiDocument3 pagesFentanyl: DilutiiTabitha KimNo ratings yet
- Nolvadex Tablets and Nolvadex Dosage Zxdse PDFDocument2 pagesNolvadex Tablets and Nolvadex Dosage Zxdse PDFfrostbaby8No ratings yet
- Tabla 2023-1Document31 pagesTabla 2023-1Pedro NavajaNo ratings yet
- ANXIOLITICEDocument21 pagesANXIOLITICEFratila IulianaNo ratings yet
- Miller's Drug Delivery SystemsDocument1 pageMiller's Drug Delivery SystemsNandor KissNo ratings yet
- Max 360mg/d Codein Max 12 Tabs/d Max 4g/d Max 1.2 G 2.4g/d Max 120mg/dDocument3 pagesMax 360mg/d Codein Max 12 Tabs/d Max 4g/d Max 1.2 G 2.4g/d Max 120mg/dSamantha LuiNo ratings yet
- Androgen & Antiandrogen: Dr. Wening Sari, DR., M.KesDocument24 pagesAndrogen & Antiandrogen: Dr. Wening Sari, DR., M.KesNarti RajakNo ratings yet
- 400 3 NarcoticsDocument27 pages400 3 Narcoticsfirdaus92No ratings yet
- Opioid Analgesics - Narcotic Anlagesics - 0Document6 pagesOpioid Analgesics - Narcotic Anlagesics - 0Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The History of SteriodsDocument26 pagesThe History of SteriodsAriw AmpatNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Laporan Psikotropika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFDocument10 pagesRekapitulasi Laporan Psikotropika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFSandi kongNo ratings yet
- Notice: Schedules of Controlled Substances Production Quotas: Schedules I and II— 2006 AggregateDocument4 pagesNotice: Schedules of Controlled Substances Production Quotas: Schedules I and II— 2006 AggregateJustia.comNo ratings yet
- FWA Prepayment Review Records Request: InstructionsDocument7 pagesFWA Prepayment Review Records Request: Instructionsabdulla.mho23No ratings yet