Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics MCQs For Class 12 CH 11 Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
Uploaded by
Akshith Reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views7 pagesH
Original Title
Physics MCQs for Class 12 Ch 11 Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentH
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views7 pagesPhysics MCQs For Class 12 CH 11 Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
Uploaded by
Akshith ReddyH
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Physics MCQs for Class 12 with Q.4.
In which of the following,
Answers Chapter 11 Dual Nature emission of electrons does not
of Matter and Radiation take place?
Q.1. Cathode ray consists of (a) Thermionic emission
(a) photons (b) X-rays emission
(b) electrons (c) Photoelectric emission
(c) protons (d) Secondary emission
(d) α-particles
AnswerAnswer: (b)
AnswerAnswer: (b) Cathode ray Q.5. Photoelectric emission
consists of electrons occurs only when the incident
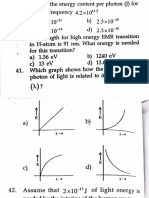
Q.2. A discharge takes place light has more than a certain
between the two electrodes on minimum
applying the electric field to the (a) power
gas in the discharge tube. The (b) wavelength
cause of this fluorescence was (c) intensity
attributed to (d) frequency
(a) the radiations which appeared
to be coming from the anode AnswerAnswer: (d)
(b) the radiation which appeared Q.6. Which of the following when
to be coming from the cathode falls on a metal will emit
(c) the protons coming from the photoelectrons ?
cathode (a) UV radiations
(d) the protons coming from the (b) Infrared radiation
anode (c ) Radio waves
(d) Microwaves
AnswerAnswer: (b) The
fluorescence was caused due to AnswerAnswer: (a) Emission of
the radiations appeared to be electron from a substance under
coming from the cathode called the action of light is photoelectric
cathode rays. effect. Light must be at a
Q.3. The presently accepted value sufficiently high frequency. It
of charge/mass (e/m) is may be visible light, U.V, X-rays.
(a) 1.66 x 10–19 c/kg So U.V. cause electron emission.
(b) 9.1 x 1011 c/kg Q.7. Particle like behavior of light
(c) 1.76 x 1011 c/kg arises from the fact that each
(d) 9.1 x 1019 c/kg quanta of light has definite …X…
and a fixed value of …Y.. just like
AnswerAnswer: (c) a particle, Here, X and Y refer to
(a) frequency, energy required to take out electron from
(b) shape, volume the metal surface
(c) energy, frequency
(d) energy, momentum
(c) the minimum amount of
AnswerAnswer: (d) Einstein energy required to take out the
arrived at the important result that electron from the metal surface
the light quantum can also be (d) None of these
associated with momentum hv/c AnswerAnswer: (c) A certain
A definite value of energy as well minimum amount of energy is
as momentum is a strong sign that required to pull the electron out
the light quantum can be from the surface of the metal. This
associated with a particle. This minimum energy required by an
particle was later named photon. electron to escape from the metal
Q.8. The wave nature of light was surface is called the work function
established by (i) Maxwell’s of the metal.
equations (ii) Fraunhoffer’s lines Q.10. The work function of a
(iii) Hertz experiment (iv) metal is independent of
Einstein’s theory (i) nature of the surface of the
(a) (i) and (ii) only metal
(b) (ii) and (iv) only (ii) dimensions of the metal
(c) (i) and (iii) only (iii) properties of the metal
(d) (iii) and (iv) only (iv) abundance of the metal
(a) (i) only
AnswerAnswer: (c) The (b) (i) and (iii)
Maxwell’s equations of (c) (ii) and (iii)
electromagnetism and Hertz (d) (ii) and (iv)
experiment on the generation and
detection of electromagnetic AnswerAnswer: (d) The work
waves in 1887, strongly function of a metal depends upon
established the wave nature of the properties of the metal and the
light. nature of its surface.
Q.9. The work-function of a metal Q.11. The theory of quantisation
is of electric charge was given by
(a) the minimum current required (a) William Crookes
to take out electron from the metal (b) J. J. Thomson
surface (c) R.A. Millikan
(b) the maximum frequency (d) Wilhelm Hallwachs
AnswerAnswer: (c) R.A. (c) electrons and protons
Millikan’s famous oil-drop (d) only electrons
experiment led him to propose the
theory of quantisation of electric AnswerAnswer: (d) All
charge. photosensitive substances emit
Q.12. In photoelectric effect, electrons when illuminated by
electrons are ejected from metals, light.
if the incident light has a certain Q.15. The photoelectric current
minimum does not depend upon the
(a) wavelength (i) frequency of incident light
(b) frequency (ii) work function of the metal
(c) amplitude (iii) stopping potential
(d) angle of incidence (iv) intensity of incident light
(a) (i) and (iv) only
AnswerAnswer: (b) The minimum (b) (ii) and (iii) only
frequency above which the (c) (iii) only
electrons are ejected from the (d) (ii) only
metal surface, is called the
threshold frequency for that metal. AnswerAnswer: (c) Beyond the
No electrons are emitted if the threshold frequency the
frequency of the incident light is photoelectric current increases
less than the threshold frequency. with increase in intensity.
Q.13. Which of the following Q.16. The stopping potential is
metals is not sensitive to visible directly related to
light? (a) the work function of the metal
(a) Caesium (b) intensity of incident radiation
(b) Sodium (c) the saturation current for the
(c) Rubidium given frequency
(d) Cadmium (d) the kinetic energy gained by
the photoelectrons
AnswerAnswer: (d) Cadmium is
sensitive to ultraviolet light while AnswerAnswer: (d)
the rest are sensitive even to Q.17. The wave theory of light
visible light. does not explain
Q.14. A photosensitive substance (a) polarisation
emits _____when illuminated by (b) diffraction
light. (c) photocurrent
(a) only protons (d) interference
(b) only neutrons
AnswerAnswer: (c) Photocurrent AnswerAnswer: (c) The
can be explained with particle diffraction of electrons show
nature of light. wave nature of electrons.
Q.18. Photoelectric effect can be Q.21. Photons are deflected by
explained by (a) electric field only
(a) wave theory of light (b) magnetic field only
(b) Bohr’s theory (c) electromagnetic field
(c) quantum theory of light (d) None of these
(d) corpuscular theory of light
AnswerAnswer: (d) Photons are
AnswerAnswer: (d) Photocurrent not deflected by electric and
can be explained with particle magnetic fields as they are
nature of light. electrically neutral.
Q.19. In Einstein’s picture of Q.22. Electrically, photons are
Photoelectric emission, the (a) positively charged
photoelectric emission does not (b) negatively charged
take place by (c) neutral
(a) continuous emission of energy (d) strongly charged, may be
from radiation positive or negative
(b) continuous absorption of
energy from radiation AnswerAnswer: (c) Photons are
(c) discrete absorption of energy quantum of light which are
from radiation electrically neutral.
(d) discrete emission of energy Q.23. In a photon-particle
from radiation collision, the quantity that does
not remain conserved is
AnswerAnswer: (b) The (a) total energy
photoelectric emission takes place (b) total momentum
by discrete absorption of energy (c) number of photons
from radiation. (d) None of these
Q.20. The particle nature of light
is not confirmed by AnswerAnswer: (c) In a photon –
(a) photoelectric effect particle collision, the number of
(b) scattering of X-rays by photons may not be conserved.
electrons The photon may be absorbed or a
(c) diffraction of electrons new photon may be created.
(d) compton effect Q.24. Of the following properties,
the photon does not possess
(a) rest mass
(b) momentum (a) is zero for all
(c) energy (b) is same for all
(d) frequency (c) lies between zero and infinity
(d) lies between zero and a finite
AnswerAnswer: (a) Photon has no maximum
rest mass.
Q.25. It is essential to consider AnswerAnswer: (d)
light as a stream of photons to Q.29. Photoelectric effect shows
explain (a) wave like behaviour of light
(a) diffraction of light (b) paritcle like behaviour of light
(b) refraction of light (c) both wavelike and paticle like
(c) photoelectric effect behaviour
(d) reflection of light (d) neither wave like nor particle
like behaviour of light
AnswerAnswer: (c) Photoelectric
effect can be explained by AnswerAnswer: (b) Photoelectric
quantum nature of light i.e. light effect is accounted by particle like
as a stream of photons. bahaviour of light (i.e. by
Q,26. Photoelectric effect was quantum theory of light)
discovered by Q.30. A photoelectric cell
(a) Hertz converts
(b) Hallwachs (a) light energy into heat energy
(c) Lenard (b) light energy to sound energy
(d) Millikan (c) light energy into electric
energy
AnswerAnswer: (a) Hertz (d) electric energy into light
discovered first the photoelectric energy
effect in 1887.
Q.27. The momentum of a photon AnswerAnswer: (c) Photoelectric
of wavelength λ is cell converts light energy into
(a) hλ electric energy.
(b) h/λ Q.31. Light of a particular
(c) λ/h frequency is incident on a metal
(d) h/cλ surface. When the intensity of
incident radiation is increased, the
AnswerAnswer: (b) photoelectric current
Q.28. The photo-electrons emitted (a) decreases
from a metal surface are such that (b) increases
their velocity (c) remains unchanged
(d) sometimes increases and (a) the frequency of the incident
sometimes decreases light
(b) the intensity of the incident
AnswerAnswer: (b) The light
photoelectric current α Intensity (c) the nature of the cathode
of light. (d) All of the above
Q.32. The photoelectric effect is
based on the law of conservation AnswerAnswer: (c) Max. K.E. of
of phtoelectrons emitted is
(a) momentum independent of intensity of
(b) energy incident light.
(c) angular momentum Q.36. Einstein’s photoelectric
(d) mass equation states that
hν = W0 + Ek.
AnswerAnswer: (b) Photoelectric In this equatin, Ek refers to the
effect is based on law of (a) kinetic energy of all the
conservation of energy. emitted electrons
Q.33. The photoelectric effect can (b) mean kinetic energy of the
be understood on the basis of emitted electrons
(a) wave theroy of light only (c) maximum kinetic energy of
(b) electromagnetic theory of light the emitted electrons
only (d) minimum kinetic energy of the
(c) quantum theory of light only emitted electrons
(d) None of these
AnswerAnswer: (c) In the given
AnswerAnswer: (c) relation Ek stands for maximum
Q.34. When light is incident on a K.E. of emitted photoelectrons.
metal surface the maximum Q.37. In the photoeletric effect,
kinetic energy of emitted electrons are emitted
electrons (a) at a rate that is proportional to
(a) vary with intensity of light the amplitude of the incident
(b) vary with frequency of light radiation
(c) vary with speed of light (b) with a maximum velocity
(d) vary irregularly proportional to the frequency of
the incident radiation
(c) at a rate that is independent of
AnswerAnswer: (b)
the emitter
Q.35. The maximum energy of
(d) only if the frequency of the
electrons released in a photocell is
independent of
incident radiations is above a action of an electric field.
certain threshold value (c) electrons come out of a metal
with a constant velocity
AnswerAnswer: (d) (d) which depends on the
Photoelectrons are emitted if the frequency and intensity of
frequency of incident light is incident light wave.
greater than the threshold
frequency. AnswerAnswer: (d) The work
Q.38. The minimum energy function of different metals is
required to eject an electron, from different.
the metal surface is called Q.41. A photoelectric cell is a
(a) atomic energy device which
(b) mechanical energy (a) converts light into electricity
(c) electrical energy (b) converts electricity into light
(d) work function (c) stores light
(d) stores electricity
AnswerAnswer: (d) The minimum
energy required for the emission AnswerAnswer: (a)
of electrons is called work Q.42. Which of the following
function. shows particle nature of light?
Q.39. The work function for (a) Refraction
photoelectric effect (b) Interference
(a) is different for different metals (c) Polarization
(b) is same for all metals (d) Photoelectric effect
(c) depends upon the intensity of
incident light AnswerAnswer: (d)
(d) depends upon the frequency of
incident light
AnswerAnswer: (a) The work
function of different metals is
different.
Q.40. Photoelectric effect is the
phenomenon in which
(a) photons come out of a metal
when it is hit by a beam of
electrons.
(b) photons come out of the
nucleus of an atom under the
You might also like
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument17 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MatterSion GNo ratings yet
- CH 17 Quantum TheoryDocument1 pageCH 17 Quantum TheoryAroon SoojaniNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Nuclei K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsDocument3 pagesAtoms and Nuclei K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsCHIRAG GOWDANo ratings yet
- 11th NEW CHEMISTRY 11-06-2021Document5 pages11th NEW CHEMISTRY 11-06-2021Rishi ParmaniNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics - Exercise - 1Document5 pagesModern Physics - Exercise - 1Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit No 9Document37 pagesUnit No 9naqvilaiba86No ratings yet
- Photo-Electric Effect Exercise Module-6Document15 pagesPhoto-Electric Effect Exercise Module-6Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuantum Theory Questionsdevender singh50% (2)
- Ch11-12 CBSE 2023Document4 pagesCh11-12 CBSE 2023tebor93898No ratings yet
- Jee Main-2023 - Important Replica QS - PhysicsDocument106 pagesJee Main-2023 - Important Replica QS - PhysicsAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dpp. 4 AtomicDocument2 pagesDpp. 4 AtomicChaitanya ShahNo ratings yet
- Physics: Rapid Crash CourseDocument12 pagesPhysics: Rapid Crash CourseHudsun HornetNo ratings yet
- Mod Phy MCQDocument9 pagesMod Phy MCQJoseph M. SalvadorNo ratings yet
- TEST 24 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument4 pagesTEST 24 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matternivasininiva0No ratings yet
- Modern Physics Problem Sheets NewDocument20 pagesModern Physics Problem Sheets NewXyzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5Rana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Atmoic Structure 11thDocument33 pagesAtmoic Structure 11thiitianwasimNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect-1Document2 pagesPhotoelectric Effect-1dddddNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQs For Class 12 CH 12 AtomsDocument8 pagesPhysics MCQs For Class 12 CH 12 AtomsAkshith ReddyNo ratings yet
- FpreboardDocument4 pagesFpreboardDrDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SKN 6 PDFDocument9 pagesSKN 6 PDFKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Top QuestionsDocument8 pagesTop QuestionsgigiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - 1 - (Ass.) - II-final - (E)Document2 pagesAtomic Structure - 1 - (Ass.) - II-final - (E)Amit PratapNo ratings yet
- 11 Dual Nature 2024Document3 pages11 Dual Nature 2024mr.hackr777No ratings yet
- Modern PhyDocument5 pagesModern PhyHira FiazNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023Document8 pagesModern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table QuizDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table QuizGarvit GoyalNo ratings yet
- MODEL QP 2023 With SolutionsDocument23 pagesMODEL QP 2023 With SolutionsAaghash A SNo ratings yet
- 10nov - Physics WorkDocument8 pages10nov - Physics Workpratyushmehta3No ratings yet
- Xenon Chemistry Revision Sheet With AnswersDocument4 pagesXenon Chemistry Revision Sheet With AnswersRachna JainNo ratings yet
- Test For Xii EngkDocument5 pagesTest For Xii EngkKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure MCQS: 1 Year N0tes Chemistry NewDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure MCQS: 1 Year N0tes Chemistry NewHaider Jalal100% (9)
- Sheet of Modern Physics Student Copy With Ans 02-09-2021 1631011715226Document35 pagesSheet of Modern Physics Student Copy With Ans 02-09-2021 1631011715226Mohit KumarNo ratings yet
- X-ray-Exercise 1 - 4Document13 pagesX-ray-Exercise 1 - 4Karlssën DreyarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Science 13Th Edition Shipman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Physical Science 13Th Edition Shipman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFseeressgroined3djz100% (11)
- Final Sam Pap1 +2 Phy 03.03.2021 (1) - MergedDocument13 pagesFinal Sam Pap1 +2 Phy 03.03.2021 (1) - MergedJagdev SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 11 CASE STUDY Dual Nature of Radiation and MATTERDocument29 pagesPhysics XII CH 11 CASE STUDY Dual Nature of Radiation and MATTERNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- DPP-1 To 8 - Modern Physics - JEEDocument54 pagesDPP-1 To 8 - Modern Physics - JEEKeerthana Reddy DomaNo ratings yet
- As Wet-4Document8 pagesAs Wet-4Rsrao JNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Level Practice Test-19: For JEE & NEET AspirantsDocument4 pagesJEE Main Level Practice Test-19: For JEE & NEET AspirantsSunny KumarNo ratings yet
- An Electron in A Target Atom Makes A Transition To The Lowest Energy StateDocument2 pagesAn Electron in A Target Atom Makes A Transition To The Lowest Energy StateSahir HemnaniNo ratings yet
- MCQ'S in Dual Nature of Matter PDFDocument3 pagesMCQ'S in Dual Nature of Matter PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- 101 Test in Physics Chemistry and Mathematics Second ShiftDocument49 pages101 Test in Physics Chemistry and Mathematics Second ShiftAneena GeorgeNo ratings yet
- X-ray-Exercise 1 - 4 Module-6Document13 pagesX-ray-Exercise 1 - 4 Module-6Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Which One of The Following Statement Is NOT True About PhotoelectricDocument11 pagesWhich One of The Following Statement Is NOT True About PhotoelectricVidhi ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Atomic Structure-2Document7 pagesQuestion Bank On Atomic Structure-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Assignment1Document2 pagesDual Nature Assignment1hsofficial910No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Done.p65Document7 pagesAtomic Structure - Done.p65Param shahNo ratings yet
- Abp Quantum Physics Multiple Choice 2009-05-13Document4 pagesAbp Quantum Physics Multiple Choice 2009-05-13ArunmaalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Part-1 Crushing Test Series Cts#4 Chap#5+10 Total Marks 50Document2 pagesChemistry Part-1 Crushing Test Series Cts#4 Chap#5+10 Total Marks 50Zeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- New Modern PhysicsDocument3 pagesNew Modern PhysicsshabbirtechnicalNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument3 pagesAtomic Physicssikatlearning1No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument11 pagesAtomic StructureAli MuratzaNo ratings yet
- 000 - Problems1Document2 pages000 - Problems1Ijaz TalibNo ratings yet
- 11th FIITS-1 CHMDocument3 pages11th FIITS-1 CHMVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- CH 12 MCQ VettingDocument14 pagesCH 12 MCQ VettingSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-04 - Objective Unsolved LevelDocument4 pagesModern Physics-04 - Objective Unsolved LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Qs Based On Photoelectric EffectDocument5 pagesQs Based On Photoelectric EffectsdrgrNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom AssignmentDocument9 pagesStructure of Atom Assignmentaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Chemical Kinetics: The Iodine Clock Reaction: M. Francisco and M. MahusayDocument9 pagesChemical Kinetics: The Iodine Clock Reaction: M. Francisco and M. MahusayJm GarciaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Thermal StressesDocument30 pagesJournal of Thermal Stressesडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection and Other NDE Methods and SymbolsDocument92 pagesVisual Inspection and Other NDE Methods and Symbolstuvu100% (2)
- Mesa (Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis)Document9 pagesMesa (Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis)Francis LinNo ratings yet
- Elements in The History of The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesElements in The History of The Periodic TableIra MahartikaNo ratings yet
- MT Level III Exam Bank AnswersDocument71 pagesMT Level III Exam Bank AnswersEngr Agha Kabir100% (2)
- Api 610 PDFDocument10 pagesApi 610 PDFAlvaro Torres BozzoNo ratings yet
- Cone Tolerance PDFDocument21 pagesCone Tolerance PDFsosu_sorin3904No ratings yet
- ED-I Internal Test 04.08.2021Document2 pagesED-I Internal Test 04.08.2021Sandesh KaradNo ratings yet
- AdiabaticDocument2 pagesAdiabaticapi-225932882No ratings yet
- Rectilinear Kinematics (Continuous Motion)Document12 pagesRectilinear Kinematics (Continuous Motion)Nik RuqiyahNo ratings yet
- Asd VS LRFDDocument107 pagesAsd VS LRFDRicardo Jorge Vieira Pinto67% (3)
- Homwork - 1Document15 pagesHomwork - 1TimoNo ratings yet
- Machine Design IIDocument11 pagesMachine Design IIExequiel MedinaNo ratings yet
- Answers: (Page 3)Document14 pagesAnswers: (Page 3)송준혁No ratings yet
- CEN 512 Pile Capacity Under Axial Load and MomentDocument2 pagesCEN 512 Pile Capacity Under Axial Load and MomentGrace SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Apspdcl - 2012 A.E QPDocument20 pagesApspdcl - 2012 A.E QPVeera ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Mukhlesur Rahman BuiyanDocument60 pagesMukhlesur Rahman BuiyanIshtiyakNo ratings yet
- Multivector Calculus: Journal of Mathematical Analysis AND ApplicationsDocument13 pagesMultivector Calculus: Journal of Mathematical Analysis AND ApplicationsCloue Contad DeriadaNo ratings yet
- Inviscid FlowDocument65 pagesInviscid Flowgerry apriliantoNo ratings yet
- BACAL Integration Unit 1-2Document3 pagesBACAL Integration Unit 1-2theresaperez298No ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document23 pagesExercise 2Tushar RajNo ratings yet
- Rajesh Singh M. Pharm 1 Year: Made byDocument49 pagesRajesh Singh M. Pharm 1 Year: Made byNaman Sharma100% (1)
- Aqa Chem4 QP Jun14Document24 pagesAqa Chem4 QP Jun14mystreet123No ratings yet
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace TableosmanfıratNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Term ProjectDocument7 pagesHeat Conduction Term ProjectRashed KaiserNo ratings yet
- Science Clinic Gr10 Chemistry Questions 2016Document44 pagesScience Clinic Gr10 Chemistry Questions 2016BhekiNo ratings yet
- Ramon Urquijo Kempf NessDocument32 pagesRamon Urquijo Kempf NessWalter Andrés Páez GaviriaNo ratings yet
- BorgWarner DCTWet ClutchesFrictionMtrls GoldDocument45 pagesBorgWarner DCTWet ClutchesFrictionMtrls Goldddeeff715No ratings yet
- CMR MaterialsDocument16 pagesCMR Materialsget2csNo ratings yet