Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connective Tissue Questions
Uploaded by
iamroshdinho0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views20 pagesConnective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in the human body. It performs several important functions including binding and supporting structures, storing fat, transporting substances, protecting against disease, and repairing tissue damage. The main cell types present in connective tissue are fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells. Connective tissue consists of ground substance, fibers, and cells. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix, including collagen fibers. Common types of connective tissue include areolar tissue, adipose tissue, blood, cartilage, bone, and dense irregular connective tissue.
Original Description:
Original Title
connective tissue questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConnective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in the human body. It performs several important functions including binding and supporting structures, storing fat, transporting substances, protecting against disease, and repairing tissue damage. The main cell types present in connective tissue are fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells. Connective tissue consists of ground substance, fibers, and cells. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix, including collagen fibers. Common types of connective tissue include areolar tissue, adipose tissue, blood, cartilage, bone, and dense irregular connective tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views20 pagesConnective Tissue Questions
Uploaded by
iamroshdinhoConnective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in the human body. It performs several important functions including binding and supporting structures, storing fat, transporting substances, protecting against disease, and repairing tissue damage. The main cell types present in connective tissue are fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells. Connective tissue consists of ground substance, fibers, and cells. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix, including collagen fibers. Common types of connective tissue include areolar tissue, adipose tissue, blood, cartilage, bone, and dense irregular connective tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
T OR F
1. Loose Connective Tissue: Made of collagen or other elastic fibers;
holds organs in place; found under the skin
2. Fibrous Connective Tissue: Non-elastic collagen-forming; a tendon
connects bone to muscles
3. Adipose: Stores fat tissue; pads, stores, and insulates energy
4. Cartilage: A flexible skeletal muscle that is found at the end of bones
5. Bone: Strong mineral that provides the framework for the body
6. Blood: Different from other connective tissues; transports and
immunity
7. The major function of connective tissue include Binding and
supporting
8. Connective tissues bind structures together, form a framework and
support for organs and the body as a whole, store fat, transport
substances, protect against disease, and help repair tissue damage.
9. Most connective tissues have a good blood supply but some do not.
10. Three of the most common are the fibroblast, macrophage, and
mast cell.
11. Connective tissue has three main components: Ground substance,
Fibers, Cells.
12. All connective tissue cell types derive from Mesenchyme.
13. Mesenchyme derives from embryonic mesoderm, except head
mesenchyme, which derives from the neural crest (mesectoderm).
14. Mesenchyme is a type of connective tissue
15. Areolar Tissue is a common form of loose connective tissue.
16. areolar tissue is found in both the dermis and subcutaneous layers
of the skin
17. Areolar tissue is also found in or around mucous membranes, and
around blood
vessels, nerves, and the organs of the body.
18. Connective tissue is the most abundant and diverse tissue type in
the human body.
19. Adipose tissue is a type of connective tissue that stores energy in
the form of fat.
20. Blood is considered a type of connective tissue.
21. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is avascular and lacks
nerve fibers.
22. Tendons and ligaments are examples of dense irregular connective
tissue.
23. Collagen is the most abundant protein in connective tissue and
provides strength and support.
24. Bone is a specialized form of connective tissue with a solid matrix
composed of calcium salts.
25. Areolar tissue is a loose connective tissue that serves as a universal
packing material between other tissues.
26. Fibroblasts are the main cells responsible for producing the
extracellular matrix in connective tissue.
27. Mast cells are involved in the immune response and are commonly
found in connective tissue.
28. Reticular fibers are composed of the protein elastin and provide
flexibility to connective tissue.
29. Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear and provides support
with flexibility.
30. Dense regular connective tissue forms tendons and ligaments and
is characterized by parallel collagen fibers.
31. Loose connective tissue contains more cells and fewer fibers
compared to dense connective tissue.
32. The ground substance in connective tissue is composed of cells and
protein fibers.
33. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread type of cartilage in the
body and is found in the nose and trachea.
34. Adipocytes are cells found in adipose tissue responsible for storing
and releasing fat.
35. Macrophages are immune cells that play a role in phagocytosis and
are present in connective tissue.
36. The extracellular matrix in bone tissue contains hydroxyapatite
crystals, providing hardness and rigidity.
37. Fibrous capsules surrounding organs, such as the kidney, are made
up of dense irregular connective tissue.
38. Mesenchyme is an embryonic connective tissue that gives rise to
all other connective tissues.
39. Areolar tissue contains a large number of elastic fibers, providing
elasticity to the tissue.
40. Fibrocartilage is found in intervertebral discs and provides both
support and flexibility.
41. Dense irregular connective tissue forms the dermis of the skin and
is resistant to stretching in multiple directions.
42. The extracellular matrix of cartilage is rich in blood vessels,
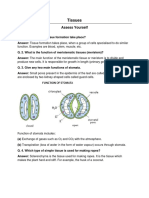
ensuring rapid nutrient delivery to chondrocytes.
43. White blood cells are not typically found in connective tissue.
44. Ligaments connect bone to bone, while tendons connect muscle to
bone.
45. Edema, or swelling, may occur when there is an accumulation of
fluid in areolar tissue.
46. Osteocytes are mature bone cells embedded in the lacunae of the
bone matrix.
47. Collagen fibers in connective tissue provide tensile strength and
resistance to stretching.
48. Elastic fibers are composed of the protein elastin and can recoil to
their original shape after stretching.
49. Chondrocytes are the primary cell type in bone tissue responsible
for mineralization.
50. The extracellular matrix in blood is known as plasma, and it
contains cells, platelets, and dissolved proteins.
51. Fibroblasts in connective tissue produce collagen fibers and ground
substance.
52. The matrix of blood is more fluid compared to the solid matrix of
bone tissue.
53. Tendons attach muscles to bones, allowing for movement and joint
stabilization.
54. Cartilage is well-vascularized, ensuring rapid healing in case of
injury.
55. Mast cells release histamine and other chemicals in response to
injury or inflammation.
56. The stroma of organs, such as the liver, is composed of dense
regular connective tissue.
57. Reticular connective tissue forms the framework of organs like the
spleen and lymph nodes.
58. Loose connective tissue serves as a reservoir for water and salts in
the body.
59. Areolar tissue contains a high density of adipocytes, contributing
to its role in energy storage.
60. The extracellular matrix in connective tissue is primarily composed
of water.
61. Elastic cartilage is found in joints and provides cushioning and
shock absorption.
62. Dense regular connective tissue is commonly found in the walls of
large arteries.
63. Macrophages in connective tissue are involved in the removal of
cellular debris and pathogens.
64. Chondroitin sulfate is a key component of the extracellular matrix
in bone tissue.
65. Adipose tissue functions as insulation to conserve body heat.
66. The extracellular matrix of blood is composed of collagen fibers.
67. Connective tissue is not involved in the transmission of mechanical
forces between muscles and bones.
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER
68. What is the most abundant tissue type in the human body?
a. Epithelial tissue
b. Connective tissue
c. Muscle tissue
d. Nervous tissue
69. Which of the following is not a function of connective tissue?
a. Support
b. Protection
c. Contraction
d. Transportation
70. What is the primary function of adipose tissue?
a. Storage of energy
b. Conduction of nerve impulses
c. Oxygen transport
d. Hormone secretion
71. Which of the following is considered a fluid connective tissue?
a. Bone
b. Cartilage
c. Blood
d. Adipose tissue
72. Which cell type is responsible for producing the extracellular
matrix in connective tissue?
a. Adipocytes b. Fibroblasts c. Chondrocytes d. Osteocytes
73. Collagen, a fibrous protein, provides which of the following to
connective tissue?
a. Elasticity
b. Rigidity
c. Tensile strength
d. Contraction
74. What type of connective tissue forms the framework of organs
such as the spleen and lymph nodes?
a. Reticular connective tissue
b. Dense regular connective tissue
c. Areolar tissue
d. Elastic connective tissue
75. Which type of cartilage is found in the intervertebral discs?
a. Hyaline cartilage
b. Elastic cartilage
c. Fibrocartilage
d. Compact cartilage
76. Tendons connect muscles to:
a. Nerves
b. Bones
c. Blood vessels
d. Organs
77. Which connective tissue type is characterized by a solid matrix
composed of calcium salts?
a. Areolar tissue
b. Bone tissue
c. Blood
d. Elastic tissue
78. Mast cells in connective tissue release:
a. Collagen
b. Histamine
c. Adiponectin
d. Myosin
79. Where is elastic cartilage commonly found in the human body?
a. Nose
b. Knee joint
c. Intervertebral discs
d. Trachea
80. Which of the following is an embryonic connective tissue?
a. Areolar tissue
b. Mesenchyme
c. Dense regular connective tissue
d. Reticular tissue
81. The ground substance in connective tissue is primarily composed
of:
a. Collagen fibers
b. Elastic fibers
c. Cells
d. Proteoglycans
82. What is the main function of dense irregular connective tissue?
a. Provides strength and support
b. Allows for stretching in multiple directions
c. Stores energy
d. Acts as a universal packing material
83. Osteocytes are the mature cells found in:
a. Blood
b. Bone tissue
c. Cartilage
d. Adipose tissue
84. The extracellular matrix of cartilage is avascular, meaning it lacks:
a. Nerves
b. Blood vessels
c. Collagen fibers
d. Elastic fibers
85. Where is areolar tissue commonly found in the body?
a. Skin
b. Tendons
c. Bone
d. Muscles
86. Fibroblasts are cells responsible for producing:
a. Collagen fibers b. Elastic fibers c. Reticular fibers d. All of the above
87. Cartilage is more flexible than bone due to the presence of:
a. Collagen fibers
b. Elastic fibers
c. Calcium salts
d. Osteocytes
88. Which type of connective tissue forms the dermis of the skin and is
resistant to stretching in multiple directions?
a. Dense regular connective tissue b. Dense irregular connective tissue
c. Elastic connective tissue d. Reticular connective tissue
89. The matrix of blood is known as:
a. Plasma
b. Serum
c. Lymph
d. Hemolymph
90. What is the main function of adipocytes in adipose tissue?
a. Produce collagen fibers
b. Store and release fat
c. Produce blood cells
d. Transmit nerve impulses
91. Where are macrophages commonly found in connective tissue?
a. Skin b. Blood vessels c. Cartilage d. Bone
92. Which of the following is a characteristic of elastic connective
tissue?
a. High tensile strength
b. Resistance to stretching
c. Recoil to original shape
d. Dense mineralization
93. Chondrocytes are the primary cells found in:
a. Bone tissue
b. Blood
c. Cartilage
d. Areolar tissue
94. Ligaments connect:
a. Bone to muscle
b. Muscle to muscle
c. Bone to bone
d. Tendon to tendon
95. Edema, or swelling, may occur when there is an accumulation of
fluid in which connective tissue?
a. Adipose tissue
b. Areolar tissue
c. Reticular tissue
d. Elastic tissue
96. The extracellular matrix of blood contains a network of:
a. Collagen fibers
b. Elastic fibers
c. Reticular fibers
d. Proteoglycans
97. Which type of cartilage is found in the external ear and provides
support with flexibility?
a. Hyaline cartilage
b. Fibrocartilage
c. Elastic cartilage
d. Dense cartilage
98. What is the primary function of reticular connective tissue?
a. Provides tensile strength
b. Forms the framework of organs
c. Stores energy
d. Connects bones to muscles
99. Where is fibrous capsules, such as those surrounding organs like
the kidney, composed of dense irregular connective tissue?
a. Visceral peritoneum
b. Parietal peritoneum
c. Parietal pleura
d. Visceral pleura
100. Mesenchyme is an embryonic connective tissue that gives rise to:
a. Bone tissue
b. Blood
c. All other connective tissues
d. Cartilage
101. Which type of connective tissue serves as a reservoir for water and
salts in the body?
a. Adipose tissue
b. Areolar tissue
c. Reticular tissue
d. Elastic tissue
102. Which of the following is NOT a function of areolar tissue?
a. Support and binding of organs
b. Defense against pathogens
c. Energy storage
d. Elasticity
103. The extracellular matrix in connective tissue is composed of:
a. Cells only
b. Fibers only
c. Cells and ground substance
d. Ground substance only
104. The stroma of organs, such as the liver, is commonly composed of
which type of connective tissue?
a. Dense regular connective tissue
b. Reticular connective tissue
c. Elastic connective tissue
d. Adipose tissue
105. Loose connective tissue contains a high density of:
a. Adipocytes b. Elastic fibers c. Collagen fibers d. Reticular fibers
106. What is the primary function of elastic fibers in connective tissue?
a. Provide tensile strength
b. Allow for stretching and recoil
c. Resist stretching
d. Store energy
107. The extracellular matrix of bone tissue contains crystals of:
a. Calcium phosphate
b. Sodium chloride
c. Potassium sulfate
d. Magnesium carbonate
108. Fibrocartilage is found in:
a. Intervertebral discs
b. External ear
c. Nose
d. Trachea
109. Dense irregular connective tissue is commonly found in the:
a. Epidermis
b. Dermis
c. Hypodermis
d. Subcutaneous tissue
110. Loose connective tissue serves as a reservoir for:
a. Blood
b. Lymph
c. Water and salts
d. Bone marrow
111. Where is fibrocartilage commonly found in the human body?
a. Knee joint
b. External ear
c. Nose
d. Trachea
112. What is the primary function of dense regular connective tissue?
a. Provides strength and support
b. Allows for stretching in multiple directions
c. Stores energy
d. Acts as a universal packing material
113. Macrophages in connective tissue are involved in:
a. Producing collagen fibers
b. Phagocytosis
c. Synthesizing elastin
d. Blood clotting
114. Chondroitin sulfate is a key component of the extracellular matrix
in:
a. Bone tissue
b. Cartilage
c. Blood
d. Adipose tissue
115. Adipose tissue functions as insulation primarily to:
a. Regulate body temperature
b. Provide mechanical support
c. Store energy
d. Facilitate nerve conduction
116. The extracellular matrix of blood is composed of:
a. Collagen fibers
b. Elastic fibers
c. Reticular fibers
d. Plasma
117. Connective tissue is actively involved in the transmission of
mechanical forces between:
a. Nerves and muscles
b. Bones and muscles
c. Ligaments and tendons
d. Cartilage and bone
answers
1. True
2. True
3. True
4. True
5. True
6. True
7. True
8. True
9. True
10. True
11. True
12. True
13. True
14. True
15. True
16. True
17. True
18. True
19. True
20. True
21. True
22. False (Tendons are dense regular connective tissue; ligaments are
dense irregular connective tissue)
23. True
24. True
25. True
26. True
27. True
28. False (Reticular fibers are composed of collagen and glycoproteins)
29. False (Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear)
30. True
31. False (Loose connective tissue contains fewer cells and more fibers
compared to dense connective tissue)
32. True
33. True
34. True
35. True
36. True
37. True
38. True
39. False (Areolar tissue contains a few elastic fibers)
40. True
41. True
42. False (Cartilage is avascular; nutrients reach chondrocytes by
diffusion)
43. False (White blood cells can be found in connective tissue)
44. True
45. True
46. True
47. True
48. True
49. False (Osteoblasts are responsible for mineralization; osteocytes
maintain bone tissue)
50. True
51. True
52. True
53. True
54. False (Cartilage is avascular and heals more slowly than well-
vascularized tissues)
55. True
56. False (The stroma is often composed of loose connective tissue)
57. True
58. True
59. False (Areolar tissue contains a few adipocytes, but it is not the
primary storage tissue)
60. False (The extracellular matrix is primarily composed of fibers and
ground substance)
61. False (Elastic cartilage is found in structures like the external ear)
62. True
63. True
64. True
65. True
66. False (Collagen fibers are a key component of the extracellular matrix
in blood)
67. False (Connective tissue plays a crucial role in the transmission of
mechanical forces between muscles and bones)
68. b. Connective tissue
69. c. Contraction of nerve impulses
70. a. Storage of energy
71. c. Blood
72. b. Fibroblasts
73. c. Tensile strength
74. a. Reticular connective tissue
75. c. Fibrocartilage
76. b. Bones
77. b. Bone tissue
78. b. Histamine
79. a. Nose
80. b. Mesenchyme
81. d. Proteoglycans
82. b. Allows for stretching in multiple directions
83. b. Bone tissue
84. b. Blood vessels
85. a. Skin
86. d. All of the above
87. b. Elastic fibers
88. b. Dense irregular connective tissue
89. a. Plasma
90. b. Store and release fat
91. a. Skin
92. c. Recoil to original shape
93. c. Cartilage
94. c. Bone to bone
95. b. Areolar tissue
96. c. Reticular fibers
97. c. Elastic cartilage
98. b. Forms the framework of organs
99. a. Visceral peritoneum
100. c. All other connective tissues
101. b. Areolar tissue
102. c. Energy storage
103. c. Cells and ground substance
104. b. Reticular connective tissue
105. d. Reticular fibers
106. b. Allow for stretching and recoil
107. a. Calcium phosphate
108. a. Intervertebral discs
109. b. Dermis
110. c. Water and salts
111. a. Knee joint
112. a. Provides strength and support
113. b. Phagocytosis
114. b. Cartilage
115. a. Regulate body temperature
116. d. Plasma
117. b. Bones and muscles
You might also like
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument9 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesfranciscocyrilleNo ratings yet
- Zoology Animal TissueDocument54 pagesZoology Animal TissueasuhassNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument34 pagesConnective TissueLizette Joy Cuilan-Camilo100% (1)
- Introduction To The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument39 pagesIntroduction To The Musculoskeletal SystemdesyNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- Introduction To Bio MechanicsDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Bio MechanicsSudeepNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Tissues Test: NameDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Tissues Test: Namestephanieyoung07No ratings yet
- Bones and Cartilage: Developmental and Evolutionary Skeletal BiologyFrom EverandBones and Cartilage: Developmental and Evolutionary Skeletal BiologyNo ratings yet
- Oral Chondroprotective Agents - Part IDocument7 pagesOral Chondroprotective Agents - Part Itaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Animal OrganizationDocument6 pagesAnimal OrganizationAldi RegarNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective TissueLANGWAEMILLNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Module 3 Organization of The Human Body - Tissue (B)Document21 pagesWeek 3 Module 3 Organization of The Human Body - Tissue (B)Kishie Jeyds LaycoNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Connective Tissue - SMDocument52 pages4.1 Connective Tissue - SMManjunathNo ratings yet
- 25 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and ProtectsDocument17 pages25 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and ProtectsJimmy Jamarolin JacaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Connective TissueDocument41 pagesHistology of Connective TissueIbe ClementNo ratings yet
- Eguia Nsc10Document6 pagesEguia Nsc10AJ EguiaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveDocument27 pagesConnective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- المستندDocument7 pagesالمستندمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Topic Types of Connective Tissues in Human BodyDocument13 pagesTopic Types of Connective Tissues in Human Bodysaeed qurashiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument6 pagesConnective Tissueanishpantha530No ratings yet
- CTDocument84 pagesCTNigusu SolomonNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument2 pagesConnective Tissueiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument57 pagesConnective TissueSunil DhatwaliaNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Notes)Document11 pagesTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaNo ratings yet
- Title of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceDocument3 pagesTitle of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceKristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Review QuestionsEmily HessNo ratings yet
- Lab Connective TissueDocument14 pagesLab Connective Tissueشاجوان عباس محمد احمدNo ratings yet
- Connective Tisssue (General)Document29 pagesConnective Tisssue (General)James ChabuNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue ProperDocument15 pagesConnective Tissue ProperFilkal BasnetNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument51 pagesConnective TissueYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Student Packet (ANP)Document7 pagesCh. 4 Student Packet (ANP)Alex ZhangNo ratings yet
- Textus ConnectivusDocument43 pagesTextus ConnectivusShafiraNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesstudDocument53 pagesConnective TissuesstudDanial Sharizul100% (1)
- HPA Lec 3 TissuesDocument46 pagesHPA Lec 3 TissuesPersonal growthNo ratings yet
- Connectivetissue 3Document26 pagesConnectivetissue 3Tauqeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective Tissuesomya mathurNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 3 of 4Document26 pagesTissues Part 3 of 4Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Document6 pagesWork Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Japet Floyd Alipio100% (1)
- Lab Report Ayham FaisalDocument7 pagesLab Report Ayham Faisalayham omariNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument36 pagesConnective TissueSalman NaseebNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument91 pagesConnective TissueSamuel ArikodNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Part 2. CONNECTIVE TISSUES 4Document46 pagesLec 3 Part 2. CONNECTIVE TISSUES 4John Vincent TacalNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#3 MED3Document5 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#3 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- TISSUEDocument15 pagesTISSUEDhananjay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 2Document39 pagesGenbio2 Week 2Noel Vincent AgonoyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument49 pagesConnective TissuePaapa MorrisNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise4 Tissues Hb-1 GalangDocument4 pagesLab Exercise4 Tissues Hb-1 GalangLihza May Alliah GalangNo ratings yet
- Simple Epithelium Stratified EpitheliumDocument2 pagesSimple Epithelium Stratified EpitheliumFlorence Nichole RoganNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphyFlorence Nichole RoganNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument6 pagesConnective TissuecrtgyhujikNo ratings yet
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocument60 pagesHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- ConnecDocument10 pagesConnecT.c. Muhammed YükselNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review TissueDocument4 pagesChapter Review TissueGeorge IvyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Tissues, Cell CyclesDocument90 pagesLecture 5 Tissues, Cell Cyclesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues Notes3 9 CbseDocument2 pagesAnimal Tissues Notes3 9 CbseSrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 BM I Matrix ExtracelDocument48 pages2.1 BM I Matrix ExtracelDanti FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument6 pagesConnective TissuesAmmar ShahidNo ratings yet
- Secret MineralizeDocument2 pagesSecret MineralizeMaricris CosmeNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesConnective Tissue Flashcards - Quizletyamanuel25No ratings yet
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocument16 pagesTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiNo ratings yet
- Nadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueDocument2 pagesNadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueNadiyah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues and Extracellular Matrix 2014-9Document33 pagesConnective Tissues and Extracellular Matrix 2014-9Anonymous J3jLBZa100% (1)
- GenBio1-11 - q1 - Mod2 - Animal Cell Types and Modification - Dumepnas - v2 - FinalDocument31 pagesGenBio1-11 - q1 - Mod2 - Animal Cell Types and Modification - Dumepnas - v2 - FinalJoshua BastianNo ratings yet
- Repair of Full Thickness Articular Cartilage Defects Using IEIK13 Self Assembling Peptide Hydrogel in A Non Human Primate ModelDocument17 pagesRepair of Full Thickness Articular Cartilage Defects Using IEIK13 Self Assembling Peptide Hydrogel in A Non Human Primate Model9147. 5125'321199316No ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Dr. C. C. VisserDocument85 pagesOsteoarthritis: Dr. C. C. VisserAhmad Fathira FitraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Biomechanics: K.S. Halonen, M.E. Mononen, J.S. Jurvelin, J. To ̈yräs, J. Salo, R.K. KorhonenDocument8 pagesJournal of Biomechanics: K.S. Halonen, M.E. Mononen, J.S. Jurvelin, J. To ̈yräs, J. Salo, R.K. KorhonenNikola MijailovićNo ratings yet
- Joints PPT NsDocument89 pagesJoints PPT Ns安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Growth and Development/ Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument41 pagesGrowth and Development/ Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- CARTILAGEDocument19 pagesCARTILAGEMatthew Bryan AdonayNo ratings yet
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Cartilage and BoneDocument31 pagesSpecialized Connective Tissue: Cartilage and Bonelogang48100% (1)
- 8.31 Exercise 4 - TissuesDocument64 pages8.31 Exercise 4 - TissuesMa. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Bone Growth and Factors That Associated With It1234Document7 pagesBone Growth and Factors That Associated With It1234Amanuel TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System Assessment: - OverviewDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletal System Assessment: - OverviewDenise BarayogaNo ratings yet
- OrthopaedicsDocument3 pagesOrthopaedicsnicewanNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1Document9 pagesHuman Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1bmydwoybx482No ratings yet
- Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds For Cartilage and Bone RegenerationDocument8 pagesExtracellular Matrix Scaffolds For Cartilage and Bone Regenerationduverney.gaviriaNo ratings yet
- 6 JointDocument11 pages6 Jointيزن الحارثيNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Biol102 at 31-10-2016Document66 pagesChapter4 Biol102 at 31-10-2016Abdulaziz AHNo ratings yet
- Tissue TransesDocument13 pagesTissue TransesBSMT1A ALMONIA, ERICKA ROSENo ratings yet
- Neet Structural Organisation in Animals TestDocument3 pagesNeet Structural Organisation in Animals TestShrishNo ratings yet
- Bone AnatomyDocument11 pagesBone AnatomyLiam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - 2 - Skeletal SystemDocument31 pagesModule 9 - 2 - Skeletal SystemThea Shaine B. SILARDENo ratings yet
- Canine Osteoarthritis - Understanding The Etiology, Clinical Presentation, and DiagnosisDocument6 pagesCanine Osteoarthritis - Understanding The Etiology, Clinical Presentation, and DiagnosisConstanza RuizNo ratings yet
- Tissue Engineering CWK 1Document16 pagesTissue Engineering CWK 1skc_b37851No ratings yet
- Bone Development and GrowthDocument21 pagesBone Development and GrowthRania ThiniNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu - BaniladDocument5 pagesUniversity of Cebu - BaniladYuuga RikaNo ratings yet