Professional Documents
Culture Documents
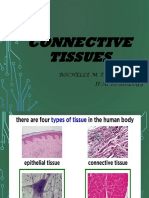
Connective Tissue
Uploaded by
iananicole.b300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Connective tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesConnective Tissue
Uploaded by
iananicole.b30Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
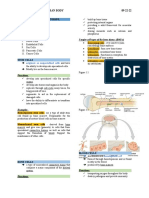
INTRO:
Connective tissue is a diverse group of tissues that provide support, connection,
and insulation for other tissues and organs. It is the most abundant tissue in the body,
and it is found in all organs and tissues except for the avascular tissues, such as the lens
of the eye and the inner ear.
Types of connective tissue:
• Connective tissue proper: This is the most common type of connective tissue,
and it is found throughout the body. It is made up of cells called fibroblasts, which
produce fibers that give the tissue its strength and support. Connective tissue
proper can be loose or dense. Loose connective tissue is found in places where
flexibility is needed, such as the skin and blood vessels. Dense connective tissue
is found in places where strength is needed, such as tendons and ligaments.
• Fluid connective tissue: This type of connective tissue is made up of a liquid
called extracellular matrix, which contains cells called blood cells and lymphatic
cells. Blood is a type of fluid connective tissue that carries oxygen, nutrients, and
waste products throughout the body. Lymph is another type of fluid connective
tissue that helps to remove waste products from the body.
• Supportive connective tissue: This type of connective tissue provides support
and protection to the body. It is made up of two main types: cartilage and bone.
Cartilage is a flexible type of connective tissue that is found in places like the joints
and the ears. Bone is a hard type of connective tissue that is found in the skeleton.
Connective tissue cells:
• Fibroblasts: These are the most common type of cell found in connective tissue.
They produce fibers, such as collagen and elastin, which give the tissue its
strength and support.
• Adipocytes: These are fat cells that store energy. They are found in loose
connective tissue throughout the body.
• Chondrocytes: These are cartilage cells that produce the matrix that makes up
cartilage.
• Osteocytes: These are bone cells that are found within the bony matrix.
• Hematopoietic cells: These are blood cells that are produced in the bone
marrow.
Extracellular matrix (ECM):
The ECM is the non-cellular part of connective tissue. It is made up of fibers and
ground substance. Fibers are made up of proteins, such as collagen and elastin, which
give the tissue its strength and support. Ground substance is a gel-like material that
surrounds the cells and fibers. It contains water, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Functions of connective tissue:
Connective tissue has many important functions, including:
• Support: Connective tissue provides support for the body's organs and tissues.
• Connection: Connective tissue connects the body's organs and tissues together.
• Protection: Connective tissue protects the body's organs and tissues from
damage.
• Transport: Connective tissue helps to transport materials throughout the body,
such as oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
• Energy storage: Connective tissue stores energy in the form of fat.
• Insulation: Connective tissue helps to insulate the body from heat loss.
You might also like
- Ear Canal Granuloma: Presentator: Anggoro Eka Raditya Moderator: Dr. Yayan MitayaniDocument76 pagesEar Canal Granuloma: Presentator: Anggoro Eka Raditya Moderator: Dr. Yayan MitayaniAldy Bima100% (1)
- Topic Types of Connective Tissues in Human BodyDocument13 pagesTopic Types of Connective Tissues in Human Bodysaeed qurashiNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 2Document39 pagesGenbio2 Week 2Noel Vincent AgonoyNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues: Rochelle M. Delos Santos Ii-A1 Bs-BiologyDocument54 pagesConnective Tissues: Rochelle M. Delos Santos Ii-A1 Bs-BiologyJordan Ramos100% (1)
- Animal Tissue GKDocument6 pagesAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Ayham FaisalDocument7 pagesLab Report Ayham Faisalayham omariNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument57 pagesConnective TissueSunil DhatwaliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocument60 pagesHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- Cell SpecializationadpataionDocument67 pagesCell SpecializationadpataionMarc AnthonyNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- HUMAN-ORGAN-SYSTEM, RR11Am (LEC) 2021-NCMC101 (Pelausa, Joel C.)Document19 pagesHUMAN-ORGAN-SYSTEM, RR11Am (LEC) 2021-NCMC101 (Pelausa, Joel C.)Joel PelausaNo ratings yet
- UOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument40 pagesUOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and Membranesnandani ramNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- ?????????? ??????Document6 pages?????????? ??????DEBASISH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 - Revision NotesDocument32 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 7 - Revision Notesshusa harsha100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective TissueLANGWAEMILLNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Notes)Document11 pagesTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Connective Tisssue (General)Document29 pagesConnective Tisssue (General)James ChabuNo ratings yet
- Ingles Medico I: Epithelial TissuesDocument3 pagesIngles Medico I: Epithelial TissuesSamuel RomeroNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument60 pagesTissuesANDREI JESHA GINEZNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueAhmad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveDocument27 pagesConnective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Support and Movement SystemsDocument16 pages1.2. Support and Movement SystemssamiktshyagiriNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesDocument40 pagesCell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Document37 pagesWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- Cell and Tissue of AnimalsDocument27 pagesCell and Tissue of AnimalsUtami100% (1)
- Body Tissues-AnatomyDocument10 pagesBody Tissues-AnatomyJhulianne MarieNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- BSC Connective Tissues PDFDocument54 pagesBSC Connective Tissues PDFPuneeT Raj 470No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument23 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyapi-464344582100% (1)
- Connectivetissue 3Document26 pagesConnectivetissue 3Tauqeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument91 pagesConnective TissueSamuel ArikodNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- ZOO 112 - Module 1Document26 pagesZOO 112 - Module 1Hakeem LawalNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Biological Hierarchy of OrganismDocument54 pagesBiological Hierarchy of OrganismAndrea BulataoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 BM I Matrix ExtracelDocument48 pages2.1 BM I Matrix ExtracelDanti FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument26 pagesAnimal TissueReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Haroen RasyidDocument41 pagesAnimal Tissue: Haroen Rasyidenkidani100% (1)
- Connective Tissue 4nursing@2024Document67 pagesConnective Tissue 4nursing@2024abdurezakayano724No ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument6 pagesConnective TissuesAmmar ShahidNo ratings yet
- L13-Tissues-20201 2Document22 pagesL13-Tissues-20201 22szrc2wkhtNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Tissue SystemDocument41 pagesTissue Systemrahul royNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy 3 TissuesDocument42 pagesAnaPhy 3 TissuesFeah DaydayNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument32 pagesAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Connective Tissue Yr1Document32 pagesConnective Tissue Yr1aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-277771710No ratings yet
- Epithelium: Source: Wikipedia - Bioligical TissueDocument2 pagesEpithelium: Source: Wikipedia - Bioligical TissueMark PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Biology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowDocument35 pagesBiology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Digestive SystemDocument70 pagesHistology of The Digestive Systemiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY P1 Table SummaryDocument4 pagesPARASITOLOGY P1 Table Summaryiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- R.A. 9165 Sec 4-19 PenaltiesDocument11 pagesR.A. 9165 Sec 4-19 Penaltiesiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Circulatory StudentsDocument45 pagesCirculatory Studentsiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- BooksDocument5 pagesBooksiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Week-3 Q3 HomeostasisDocument28 pagesWeek-3 Q3 HomeostasisLila KystNo ratings yet
- Drug Design Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesDrug Design Questions and AnswersMelavNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Photos - Part 1Document86 pagesHistopathology Photos - Part 1solom islamNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics PDFDocument55 pagesBiomechanics PDFKinjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Notes)Document7 pagesEndocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 9th Edition Lewis Test BankDocument7 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 9th Edition Lewis Test Bankelmerhelenb7446100% (22)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument52 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAjay DNo ratings yet
- Small BowelDocument7 pagesSmall BowelIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Heart-Brain AxisDocument15 pagesHeart-Brain Axiscc vereNo ratings yet
- Otvori Pediatric Surgical Diseases A Radiologic Surgical Case Study ApproachDocument551 pagesOtvori Pediatric Surgical Diseases A Radiologic Surgical Case Study ApproachslatkaNo ratings yet
- Nature 22330Document24 pagesNature 22330Alejandro MarmolejoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System WorksheetDocument7 pagesSkeletal System Worksheet마스러버No ratings yet
- Anatomic Considerations in Dental Implant Surgery: Mitra SadrameliDocument22 pagesAnatomic Considerations in Dental Implant Surgery: Mitra SadrameliSebastián BernalNo ratings yet
- Reading An OCT Image-The BasicsDocument37 pagesReading An OCT Image-The BasicsAlejandro Lalama GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Occupational Analysis and Intervention Plan Emily E. Matthews Touro University of NevadaDocument23 pagesOccupational Analysis and Intervention Plan Emily E. Matthews Touro University of Nevadaapi-238169773No ratings yet
- Physiology, Catecholamines: Stephen Paravati Alan Rosani Steven J. WarringtonDocument2 pagesPhysiology, Catecholamines: Stephen Paravati Alan Rosani Steven J. WarringtonVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Sept19 All Lastday PDFDocument297 pagesSept19 All Lastday PDFAsiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Pathophysiology Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Pathophysiology Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluationjesa_oliveNo ratings yet
- Role of X-Rays in OtolaryngolgoyDocument25 pagesRole of X-Rays in OtolaryngolgoyDr. T. Balasubramanian67% (3)
- Traumatic Brain Injury A Case Report: SCORE:40/50Document10 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury A Case Report: SCORE:40/50Allan CastroNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Apana Vayu in Modern Perspective: August 2018Document8 pagesA Critical Review of Apana Vayu in Modern Perspective: August 2018BrucleeNo ratings yet
- Challenging Neurological Manifestations in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Lcnec A Case Study of Extensive Intracranial and Intradural MetastasesDocument3 pagesChallenging Neurological Manifestations in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Lcnec A Case Study of Extensive Intracranial and Intradural MetastasesHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Cell Types Cell ModificationsDocument4 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Cell Types Cell ModificationswenkamuyNo ratings yet
- Module NCM 107 Pre LimDocument35 pagesModule NCM 107 Pre Limjanina mykaNo ratings yet
- A. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItDocument9 pagesA. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItFrancis100% (1)
- Unit 6 - Topic 6 - Human Physiologyy - (11 HL and SL)Document13 pagesUnit 6 - Topic 6 - Human Physiologyy - (11 HL and SL)John DoeNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Anaesthesia and Pain Management For Burn InjuriesDocument13 pagesChallenges in Anaesthesia and Pain Management For Burn InjuriesArif Setyo WibowoNo ratings yet
- Hyperparathyroidism and HypoparathyroidismDocument44 pagesHyperparathyroidism and Hypoparathyroidismshweta singhNo ratings yet
- WBI05 01 MSC 20180124Document24 pagesWBI05 01 MSC 20180124Asem BarhoushNo ratings yet