Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Tissue
Uploaded by
Reanne Meregildo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views26 pagesOriginal Title
ANIMAL-TISSUE (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views26 pagesAnimal Tissue
Uploaded by
Reanne MeregildoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
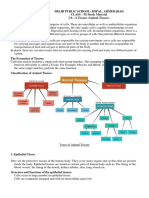
- A group of cells similar in structure,
function, and origin is called tissues.
- In animals, the structure of a tissue
depends on its function.
- An animal body is made of four
different types of tissues.
- They have been classified based on the
type of cell, function, and location in
the body.
The four basic types of Animal
Tissue
Epithelial tissue
• is a type of tissue made up of tightly
packed cells
• commonly seen outside the body as
coverings or as linings of organs and
cavities
• Examples of epithelial tissue include the
skin, the lining of the mouth and nose, and
the lining of the digestive system.
FUNCTIONS OF EPITHELIAL TISSUE:
• Provides a barrier between the external environment and
the organ it covers.
• Specialized to function in secretion and absorption.
• Protects organisms from microorganisms, injury, and fluid
loss.
• Excretes waste products such as sweat from the skin.
How they look
How many layers
Cells that make up epithelial tissues can
have a distinct arrangement:
• Simple Squamous Epithelium
> plate-like cells; for exchange of material through
diffusion
• Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
> The tissue is made of cube-shaped cells, it is
for secretion.
CELLS LOCATION FUNCTION
• Simple Columnar Epithelium
>brick-shaped cell; for secretion and
active absorption
CELLS LOCATION FUNCTION
• Stratified Squamous Epithelium
> multilayered and regenerates quickly; for
protection
CELLS LOCATION FUNCTION
• Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
> found mainly in glands, which specialize in
selective absorption and secretion by the
gland into blood or lymph vessels.
CELLS LOCATION FUNCTION
• Pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium
> single layer cells; may just look stacked
because of varying height; for lining of
respiratory tract; usually lined with cilia.
CELLS LOCATION FUNCTION
Connective tissues
• are made up of fibrous cells
• Blood and bone are examples of specialized
connective tissues.
• The cells of the connective tissue are separate by
non- living material called extracellular matrix.
• These tissues help hold other tissues together like
during the formation of organs and have the ability
to stretch and contract positively.
FUNCTIONS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE:
• Help to hold other tissues together like
during the formation of organs and have
the ability to stretch and contract positively
• Maintaining mineral homeostasis
• connect and support the different tissues,
organs, and parts of the body.
Blood
is made up of plasma (ie.,
liquid extracellular
matrix) that contains
water, salts, and
dissolved proteins;
erythrocytes that carry
oxygen (RBC), leukocytes
for defense (WBC), and
platelets for blood
clotting.
It is the only fluid
connective tissue.
Connective tissue proper (CTP)
- is made up of loose connective
tissue that is made up of
collagenous fibers found in
tendons and ligaments (holds
bones together and keeps
them in place).
- Adipose tissues are examples
of loose connective tissues
that store fats which functions
to insulate the body and store
energy.
Cartilage
- is characterized by collagenous
fibers embedded in chondroitin
sulfate.
- Chondrocytes are the cells that
secrete collagen and chondroitin
sulfate.
- Cartilage functions as cushion
between bones.
- They are present at the tips of
external ears, bronchi, vertebral
column, etc.
Bone
- is a mineralized connective
tissue made by bone-forming
cells called osteoblasts which
deposit collagen.
- It is a hard-connective tissue
which forms the framework
of the body.
- The matrix of collagen is
combined with calcium,
magnesium, and phosphate
ions to make the bone hard.
Muscle tissues
• are tissues composed of long cells called
muscle fibers that allow the body to move
voluntary or involuntary.
• Movement of muscles is a response to
signals coming from nerve cells.
FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLE TISSUE:
• Muscle contractions are responsible for
virtually all the movements of the body, both
inside and out.
• The contraction helps the organs carry out their
functions. For example, when smooth muscle in
the stomach contracts, it squeezes the food
inside the stomach, which helps break the food
into smaller pieces.
- These muscles can be categorized into
the following:
- Skeletal -striated in appearance;
voluntary movements; enable humans
to move and perform daily activities.
- Cardiac – striated with intercalated disk
for synchronized heart contraction;
involuntary; performs coordinated
contractions that allow your heart to
pump blood through your circulatory
system.
- Smooth – not striated muscle with
tampered ends; involuntary; it serves a
variety of functions.
Nervous tissues
• are composed of nerve cells called neurons and
glial cells that function as support cells.
• These neurons sense stimuli and transmit electrical
signals throughout the animal body.
• Neurons connect to other neurons to send signals.
• The dendrite is the part of the neuron that receives
impulses from other neurons while the axon is the
part where the impulse is transmitted to other
neurons.
FUNCTIONS OF NERVOUS TISSUE:
• Responsible for the carrying of electrical
and chemical signals from the brain and
central nervous system to the periphery,
and vice versa
• Transmit nerve impulses around the body
• These tissues are composed of nerve cells called
neurons and glial cells that function as support cells.
• These neurons sense stimuli and transmit electrical
signals throughout the animal body.
• Neurons connect to other neurons to send signals.
• The dendrite is the part of the neuron that receives
impulses from other neurons while the axon is the
part where the impulse is transmitted to other
neurons.
Typical structure of neurons
You might also like
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Tructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and CellmodificationDocument53 pagesTructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cellmodificationako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Cell ModificationDocument1 pageCell ModificationReginald Bien Gaganao PelayoNo ratings yet
- Cells-and-Tissues 1Document33 pagesCells-and-Tissues 1Susan Batan BandongNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument29 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue GKDocument6 pagesAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9Document38 pagesTissues Class 9vaidika.soni12009No ratings yet
- Structure of Animal Tissue g12 BIODocument53 pagesStructure of Animal Tissue g12 BIOSimon A. Peter JohnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Unit-1 PDFDocument27 pagesAnatomy Unit-1 PDFdharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument47 pagesAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2 Cell Specialisation in Multicellular OrganismsDocument18 pages2.2.2 Cell Specialisation in Multicellular Organismsche sal100% (1)
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioalulodizeeNo ratings yet
- 6 Bio200 Chapter 11Document38 pages6 Bio200 Chapter 11api-153638948No ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument45 pagesAnimal TissueAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- 9 A NewDocument62 pages9 A NewPrejith KNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of AnimalsDocument27 pagesCell and Tissue of AnimalsUtami100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- Grade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Document55 pagesGrade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Purvi Prakash KNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- DR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesDocument49 pagesDR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesAnnie Khan100% (1)
- Cell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemDocument22 pagesCell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDDocument82 pagesAnimal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Types and Cell ModificationDocument47 pagesTissue Types and Cell ModificationBheya Samantha MontieroNo ratings yet
- 6 Histologi 1 - Jaringan DasarDocument25 pages6 Histologi 1 - Jaringan DasarAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- Animal Tissue PPT by KanishkaDocument20 pagesAnimal Tissue PPT by KanishkaKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1Document45 pagesAnimal Tissues 1sirajNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument27 pagesTissueemilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument60 pagesTissuesANDREI JESHA GINEZNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of AnimalsDocument41 pagesParts and Functions of AnimalsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant TissueDocument48 pagesAnimal and Plant TissuePortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- HP I P2 Tissues and MembranesDocument38 pagesHP I P2 Tissues and MembranesNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- Different Body Tissues: By: Group 4Document25 pagesDifferent Body Tissues: By: Group 4Aisha Mae Cañete JawadNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- 45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pages45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Gen Biology 1Document9 pagesGen Biology 1Alghester PiangcoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Tissues 4Document65 pagesTissues 4marianisie448100% (3)
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Ipshita Kundu (BGKV, Salt Lake)Document9 pagesAnimal Tissues: Ipshita Kundu (BGKV, Salt Lake)Reeddhi KunduNo ratings yet
- Prelims Topic 1 - Review of Human BodyDocument18 pagesPrelims Topic 1 - Review of Human BodypanizalesmariajoseNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Image) Description and LocationDocument10 pagesTissues (Image) Description and LocationJOHNNY YNo ratings yet
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- Cell Modifications and TissuesDocument4 pagesCell Modifications and TissuesElla PascuaNo ratings yet
- Tissues NTBDocument39 pagesTissues NTBAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocument39 pagesC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues: Rochelle M. Delos Santos Ii-A1 Bs-BiologyDocument54 pagesConnective Tissues: Rochelle M. Delos Santos Ii-A1 Bs-BiologyJordan Ramos100% (1)
- CH 3 Classification of ElementsDocument24 pagesCH 3 Classification of Elementssachin aggarwal100% (1)
- Biology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowDocument35 pagesBiology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- PPT - TissuesDocument55 pagesPPT - TissuesTarun Bisen100% (1)
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Learning Task 2 Social ExperimentDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - Learning Task 2 Social ExperimentReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- M2l1a1 BDocument1 pageM2l1a1 BReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- M2L1A1Document1 pageM2L1A1Reanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument25 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q1 Las 1Document4 pagesGB1 Q1 Las 1Reanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument22 pagesCell TheoryReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- The Future of Information TechnologyDocument4 pagesThe Future of Information TechnologyReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 2Document36 pagesf1 Chapter 2mexfloziaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesSanjay AdakNo ratings yet
- 1 Homeostasis and Temp Regulation HWDocument11 pages1 Homeostasis and Temp Regulation HWMichelle ClancyNo ratings yet
- Karan ProjectDocument12 pagesKaran ProjectAnshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataDocument34 pagesExercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Department of Agril. Entomology College of Agriculture, DapoliDocument69 pagesDepartment of Agril. Entomology College of Agriculture, DapoliVaibhav DafaleNo ratings yet
- Musculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Document22 pagesMusculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Anonymous vwR8xcIxNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System MCQsDocument4 pagesSkeletal System MCQsTahir Aziz100% (3)
- Digestion HandoutDocument4 pagesDigestion HandoutStephanie ZammitNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of PrawnDocument16 pagesDigestive System of Prawnyayeg raja100% (1)
- Histology of The Cardiovascular System#Document36 pagesHistology of The Cardiovascular System#DonaldNo ratings yet
- Gray's Anatomy OnlineDocument2 pagesGray's Anatomy OnlineMatthew AxeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 WorksheetDocument5 pagesLesson 1 WorksheetJhunner BuanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy Reviewer Nervous SystemCristinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology For NursesDocument39 pagesAnatomy and Physiology For NursesUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapman's Reflexes and Viscero-Somatic Refexes - William H. Devine, DO - Presentation 94 Slides PDFDocument94 pagesChapman's Reflexes and Viscero-Somatic Refexes - William H. Devine, DO - Presentation 94 Slides PDFYuldash100% (1)
- Science (Reproductive System) Grade 6Document4 pagesScience (Reproductive System) Grade 6Nurwulan Yuni HapsariNo ratings yet
- Bio100 - Le3 ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio100 - Le3 ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- Week 13-14 Part 1Document3 pagesWeek 13-14 Part 1Loren Joy S. SulayaoNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge About Human BodyDocument6 pagesGeneral Knowledge About Human Bodyجنید سلیم چوہدری100% (4)
- CPP 202 Lecture Note OnlineDocument6 pagesCPP 202 Lecture Note OnlineJeremiah OlarewajuNo ratings yet
- Goethe On BirdsDocument7 pagesGoethe On BirdsTorsten SchwankeNo ratings yet
- Listening and Speaking 2 Q: Skills For Success Unit 2 Student Book Answer KeyDocument5 pagesListening and Speaking 2 Q: Skills For Success Unit 2 Student Book Answer KeyNhật LinhNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization in AnimalsDocument4 pagesLevels of Organization in AnimalsSudesh RathodNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument30 pagesAnimal KingdomRupa MitraNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science Week3 Digestive SystemDocument55 pagesQ2 Science Week3 Digestive Systemuni dearestNo ratings yet
- 2023 QPDocument27 pages2023 QPNiketa TennakoonNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 1 and 2) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsDocument13 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 1 and 2) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsJeffrey Yumang100% (1)
- Evolution (Lamarck and Lamarckism)Document20 pagesEvolution (Lamarck and Lamarckism)saria jabeenNo ratings yet
- Biology Definition, History, Concepts, Branches, & Facts BritannicaDocument1 pageBiology Definition, History, Concepts, Branches, & Facts BritannicaDiamant MusicNo ratings yet