Professional Documents
Culture Documents
H 2
Uploaded by
nalku1508Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
H 2
Uploaded by
nalku1508Copyright:
Available Formats
Introduction:
As the world grapples with the urgent need to transition to sustainable energy
sources, the aviation industry is exploring innovative solutions to reduce its
environmental impact. One promising avenue is the development of hydrogen-
powered aircraft. This essay delves into the concept of a hydrogen aircraft, exploring
its design, benefits, challenges, and the potential it holds for a greener future in
aviation.
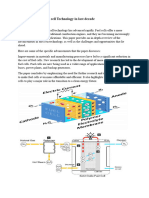
Hydrogen Aircraft Design:
A hydrogen-powered aircraft, often referred to as a "hydrogen plane" or "hydrogen
fuel cell aircraft," relies on hydrogen gas as its primary fuel source. Unlike traditional
aircraft that use fossil fuels, hydrogen aircraft generate electricity through fuel cells,
which combine hydrogen with oxygen to produce electricity, water, and heat. The
generated electricity then powers electric propulsion systems, driving the aircraft's
engines.
The design of a hydrogen aircraft involves the integration of advanced fuel cell
technology, lightweight materials, and efficient aerodynamics. Hydrogen fuel cells
provide a clean and highly efficient energy conversion process, emitting only water
vapor as a byproduct. The aircraft's structure must accommodate the storage and
safe utilization of gaseous hydrogen, which may be stored in high-pressure tanks or
as a cryogenic liquid.
Benefits of Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft:
1. Zero Emissions: One of the primary advantages of hydrogen-powered aircraft
is their potential to produce zero carbon emissions during operation. The only
byproduct of the hydrogen combustion process is water vapor, making these
aircraft environmentally friendly and contributing to efforts to combat climate
change.
2. Increased Efficiency: Hydrogen fuel cells boast higher energy conversion
efficiencies compared to traditional combustion engines. This increased
efficiency can result in longer flight ranges and reduced fuel consumption,
making hydrogen aircraft an attractive option for long-haul flights.
3. Reduced Noise Pollution: Electric propulsion systems powered by hydrogen
fuel cells are inherently quieter than traditional jet engines. This reduction in
noise pollution contributes to a more sustainable and community-friendly
aviation landscape.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite the promising benefits, the development and widespread adoption of
hydrogen-powered aircraft face several challenges:
1. Infrastructure: Establishing a robust infrastructure for hydrogen production,
storage, and distribution is a significant hurdle. The aviation industry would
need to invest in hydrogen refueling stations at airports, mirroring the
challenges faced by electric vehicles in the automotive sector.
2. Storage and Weight: Storing sufficient hydrogen onboard an aircraft while
minimizing weight poses a considerable engineering challenge. Both the
storage containers and the fuel cells must be lightweight and durable, without
compromising safety.
3. Technology Maturity: Hydrogen-powered aircraft are still in the early stages
of development. The technology needs further refinement, rigorous testing,
and certification before it can be widely adopted in commercial aviation.
Conclusion:
The concept of hydrogen-powered aircraft represents a transformative shift in the
aviation industry towards sustainability. While challenges remain, the potential
benefits, including zero emissions, increased efficiency, and reduced noise pollution,
make hydrogen aircraft an exciting prospect for the future. Continued research,
investment, and collaboration between industry stakeholders, governments, and
research institutions will be crucial in overcoming the hurdles and turning the vision
of hydrogen-powered flight into a reality. As the aviation sector seeks to align with
global efforts to address climate change, hydrogen aircraft may emerge as a key
player in shaping the next era of environmentally conscious air travel.
You might also like
- Hydrogen Fuel CellDocument6 pagesHydrogen Fuel CellAhmed SamiNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of EDF BLEVE Jet Hybrid EngineDocument6 pagesDesign and Fabrication of EDF BLEVE Jet Hybrid EngineijsretNo ratings yet
- Topic:-: Hydrogen Fuel CellDocument16 pagesTopic:-: Hydrogen Fuel CellRaj NaikNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Ship Propulsion Systems Engineering The Future of Marine TransportationDocument11 pagesAdvancements in Ship Propulsion Systems Engineering The Future of Marine Transportationtechnicalshivam2704No ratings yet
- Recent Progress in The Use of Hydrogen As A Fuel For Internal Combustion EnginesDocument15 pagesRecent Progress in The Use of Hydrogen As A Fuel For Internal Combustion EnginesAnuraag MJNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen-powered aircraft designDocument10 pagesHydrogen-powered aircraft designİsmail KoçNo ratings yet
- HydroDocument3 pagesHydroMoitan PNo ratings yet
- Alternate Fuel For Maritime UseDocument4 pagesAlternate Fuel For Maritime Useprateek prakashNo ratings yet
- Lindberg Anna Research PaperDocument19 pagesLindberg Anna Research PaperAnnaNo ratings yet
- سلبيات وايجابيات انتاج الهيدروجينDocument8 pagesسلبيات وايجابيات انتاج الهيدروجينDamodaNo ratings yet
- Designing and Analysis of Hydrogen Power VehicleDocument11 pagesDesigning and Analysis of Hydrogen Power VehicleAblaqNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen EngineDocument15 pagesHydrogen EngineSAHIL SHAWNo ratings yet
- Baders Assignment 2Document8 pagesBaders Assignment 2Møtshĕgĕtsi GwĕrĕNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of A Hybrid Hydrogen Fuel Cell/Battery Blended-Wing-Body Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-An OverviewDocument23 pagesConceptual Design of A Hybrid Hydrogen Fuel Cell/Battery Blended-Wing-Body Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-An OverviewChicheNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Future RoleDocument6 pagesHydrogen Future RoleUtpal Kumar DuttaNo ratings yet
- Viability Analysis of Underground Miningmachinery Using Green Hydrogen As A FuelDocument10 pagesViability Analysis of Underground Miningmachinery Using Green Hydrogen As A FuelMiguel HerreraNo ratings yet
- Water BikeDocument7 pagesWater BikeBibekananda JujharsinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Rimsha Mukhtiar Energy Engg. Batch 21No ratings yet
- Energies 15 08937 v2Document13 pagesEnergies 15 08937 v2lemme knowNo ratings yet
- The Duel of Sustainable TransportDocument3 pagesThe Duel of Sustainable TransportDa FriendNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen PresentationDocument21 pagesHydrogen PresentationDan ZagoreanuNo ratings yet
- Water Fuel Engine With Power GenerationDocument7 pagesWater Fuel Engine With Power GenerationSantosh Anand100% (1)
- Hydrogen Storage in Porous Silicon - A ReviewDocument12 pagesHydrogen Storage in Porous Silicon - A Reviewgabriela plaiasuNo ratings yet
- The Team Used Xylose - A Simple Plant SugarDocument5 pagesThe Team Used Xylose - A Simple Plant SugarOvaid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment of Hydrogen Production and Consumption in An Isolated TerritoryDocument5 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of Hydrogen Production and Consumption in An Isolated TerritoryGabriel DiazNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen As A Future Source of Commercial FuelDocument1 pageHydrogen As A Future Source of Commercial FuelJohn LetarteNo ratings yet
- Technical Feasibility of Hybrid Propulsion Systems To Reduce ExhaustDocument15 pagesTechnical Feasibility of Hybrid Propulsion Systems To Reduce ExhaustP Venkata SureshNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources in ShippingDocument7 pagesRenewable Energy Sources in ShippingAnonymous e3ceN15No ratings yet
- Hydrogen 02 00005 v2Document25 pagesHydrogen 02 00005 v2Arghya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Hy WireDocument2 pagesHy Wiresyed israr UddinNo ratings yet
- Liquid Hydrogen Powered Commercial AircraftDocument16 pagesLiquid Hydrogen Powered Commercial AircraftLuca Gallo100% (1)
- Hydrogen Fuel CellsDocument2 pagesHydrogen Fuel CellsNavneet KaliaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S266620272200060X MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S266620272200060X MainMaraah IssaNo ratings yet
- Vision of A Hydrogen FutureDocument23 pagesVision of A Hydrogen Futurelaxmi55No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Basics: Hydrogen As An Alternative FuelDocument9 pagesHydrogen Basics: Hydrogen As An Alternative FuelSiddhesh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Aero Soriano 1Document5 pagesAero Soriano 1Margueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication On Hydrogen Engine (Water Fuel) : P.Balashanmugam G.BalasubramanianDocument15 pagesDesign and Fabrication On Hydrogen Engine (Water Fuel) : P.Balashanmugam G.BalasubramanianSubhash S SubbuNo ratings yet
- 7 Technologies To Reduce Fuel Consumption of ShipsDocument6 pages7 Technologies To Reduce Fuel Consumption of ShipsAVINASH ANAND RAONo ratings yet
- Mini Project Final...........Document20 pagesMini Project Final...........Rishika PrasadNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen cars: The advantages and costs of fuel cell technologyDocument7 pagesHydrogen cars: The advantages and costs of fuel cell technologySabri BelaidiNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen CellDocument18 pagesHydrogen CellPratik PatilNo ratings yet
- Future of Energy - Hydrogen Transport Fuelling The Future ArupDocument12 pagesFuture of Energy - Hydrogen Transport Fuelling The Future ArupGNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: Seminar Co-Ordinator Prashant ChauhanDocument23 pagesHydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: Seminar Co-Ordinator Prashant Chauhananubhav srivastavaNo ratings yet
- RER Mod3@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument17 pagesRER Mod3@AzDOCUMENTS - inrahulNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production and Applications a ReviewDocument7 pagesHydrogen Production and Applications a Reviewarwasahmed4No ratings yet
- (Zero-Emission Cars That Run On Hydrogen) : Fuel Cell VehiclesDocument7 pages(Zero-Emission Cars That Run On Hydrogen) : Fuel Cell Vehiclesjeffer094No ratings yet
- Wikipedia On Hydrogen VehicalDocument12 pagesWikipedia On Hydrogen VehicalParihar RaviNo ratings yet
- Mobile Hydrogen Reformers As A Novel Approach To Decarbonise The Transport SectorDocument7 pagesMobile Hydrogen Reformers As A Novel Approach To Decarbonise The Transport SectorDouglas SilvaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen System ValidationDocument4 pagesHydrogen System Validationanita shindeNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen EnergyDocument8 pagesHydrogen Energyeinmal04No ratings yet
- The Potential Role of Hydrogen As A Sustainable Transportation Fuel To Combat Global WarmingDocument11 pagesThe Potential Role of Hydrogen As A Sustainable Transportation Fuel To Combat Global WarmingIshwari HadeNo ratings yet
- Final Report PRK21MS1098Document19 pagesFinal Report PRK21MS1098HARINo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Storage MaterialsDocument36 pagesHydrogen Storage MaterialsSameer AgaleNo ratings yet
- Advancement of Fuel Cell Technology in Last DecadeDocument7 pagesAdvancement of Fuel Cell Technology in Last Decadearmaan.movies123No ratings yet
- Motor HidrogênioDocument12 pagesMotor HidrogênioLuizGustavoVicenteNo ratings yet
- Portable Hydrogen Energy Systems: Fuel Cells and Storage Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandPortable Hydrogen Energy Systems: Fuel Cells and Storage Fundamentals and ApplicationsPaloma Ferreira-AparicioNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Locomotives ReportDocument2 pagesHydrogen Locomotives ReportAdrian DogaruNo ratings yet
- Alternative FuelDocument4 pagesAlternative FuelJoyNo ratings yet
- Maqo NEMsolarMalaysia SEDA Brochure - Maqo NEM Solar Malaysia SEDA SARE Roof TNB Save ElectricityDocument2 pagesMaqo NEMsolarMalaysia SEDA Brochure - Maqo NEM Solar Malaysia SEDA SARE Roof TNB Save ElectricityMaqo SolarNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Pre AssessmentDocument3 pagesWeek 4 Pre AssessmentHen RyNo ratings yet
- Bluesun 5kw Off Grid Solar SystemDocument1 pageBluesun 5kw Off Grid Solar SystemFernando BerlangaNo ratings yet
- 1.kkrao Green Energy JMR Jan - 2020Document4 pages1.kkrao Green Energy JMR Jan - 2020Prasad NarvaneniNo ratings yet
- Energy Resource Practice-Answers (SISCAC1907548A0)Document2 pagesEnergy Resource Practice-Answers (SISCAC1907548A0)Kynzie BrownNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy in SikkimDocument6 pagesRenewable Energy in SikkimTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- WECA SOLAR For Gurgaon FirstDocument15 pagesWECA SOLAR For Gurgaon FirstvineetbaggaNo ratings yet
- The Greek PV MarketDocument3 pagesThe Greek PV MarketGabriel AvacariteiNo ratings yet
- Solar Hydrogen Production: Splitting Water With UV Is Now at Almost 100% Quantum EfficiencyDocument5 pagesSolar Hydrogen Production: Splitting Water With UV Is Now at Almost 100% Quantum EfficiencyJenny PartozaNo ratings yet
- Puteri - Capacitati - 21 - 01 - 2021 - Ora - 20.xlsx 2Document255 pagesPuteri - Capacitati - 21 - 01 - 2021 - Ora - 20.xlsx 2IvanNo ratings yet
- Upali Daranagama - Solar Energy Devt in Sri LankaDocument24 pagesUpali Daranagama - Solar Energy Devt in Sri LankaADB_SAEN_ProjectsNo ratings yet
- FS RePower EU Actions EN PDFDocument2 pagesFS RePower EU Actions EN PDFjlNo ratings yet
- Project Sales ReportDocument18 pagesProject Sales ReportMudassar MustafaNo ratings yet
- GTU BE Semester VI Exam on Wind and Solar EnergyDocument1 pageGTU BE Semester VI Exam on Wind and Solar Energyfeyayel990No ratings yet
- Kenpark - Financial Analysis of 518.4kWp - 7 Year Rental ModelDocument1 pageKenpark - Financial Analysis of 518.4kWp - 7 Year Rental Modelibti nabilNo ratings yet
- H TEC Datenblatt ME450 EN 23 03Document2 pagesH TEC Datenblatt ME450 EN 23 03Juan Carlos RozoNo ratings yet
- Green EnergyDocument5 pagesGreen EnergyDatz leoNo ratings yet
- Tan Eng Hau - MBIC - Renewable EnergyDocument18 pagesTan Eng Hau - MBIC - Renewable EnergyLeonardo Alexander Renatus PaneNo ratings yet
- Power Resources W.SDocument5 pagesPower Resources W.SRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy by EBCDocument9 pagesRenewable Energy by EBCMd Saidunnabi JohaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy: Environmental Sustainable DesignDocument30 pagesSolar Energy: Environmental Sustainable DesignVaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- NYSERDA 2019 WINNERS RES-Solicitation-Fact-Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesNYSERDA 2019 WINNERS RES-Solicitation-Fact-Sheet PDFMatt BeloNo ratings yet
- Kibawe-Asian Green Energy Solar PV ParkDocument2 pagesKibawe-Asian Green Energy Solar PV ParkcatherineNo ratings yet
- India's Ambitious Renewable Energy TargetsDocument281 pagesIndia's Ambitious Renewable Energy TargetssreenivasNo ratings yet
- Uni of DuhokDocument14 pagesUni of Duhokaa zzNo ratings yet
- Countries With Worst Energy SystemDocument3 pagesCountries With Worst Energy SystemBonnel AlosNo ratings yet
- Working As An Contractor: Solar PanelsDocument2 pagesWorking As An Contractor: Solar PanelsIon PavelNo ratings yet
- If You Want To Save The Environment Imperatives Esl WorksheetDocument2 pagesIf You Want To Save The Environment Imperatives Esl WorksheetIya TemiNo ratings yet
- SamiDocument24 pagesSamiHydra JagguNo ratings yet
- Materi Mbak NadyaDocument4 pagesMateri Mbak NadyaDody GuntamaNo ratings yet