Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rockwell Hardness Material Testing
Uploaded by
BHOOMIKA RAJCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rockwell Hardness Material Testing
Uploaded by
BHOOMIKA RAJCopyright:
Available Formats
FngincenR
BMSInstitue of Technology &Mgmt. Denartment of Mechanical
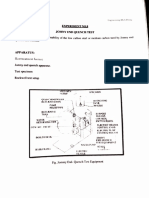
Rockwell hardness Tester
Specificutions
MODEL RASN
Major Load 60,100,1 5OKgf
Minor Load
10Kg
Max. Test Height 222mm
Depth of Throat : 130mm
with main screw proVided
P o the apparatus: Closed circuit consists of cast iron body.
ne homent of table. Weights are placed under hydraulic dash-noint with a lever in contact,
and to the
time controller is
provided at the end of lever, which transmits the pressure on plunger
Work piece. Main screw is çovered by a telescopic cover ta-pretect-it from dust and damages wnmie
handling. Load selector is provided for selection of load for different materials and ditterent
indentors. Indentors cover for protecting the indentor while handling.
Pivot vee
Main Screw
Load Hanger
Dial Gauge
Load Selector Gear
tachment
Indentor
Indentor Holder
Load
Lock
Testing Table
Main Screw
cover(Telescopic cover)
Handle for movernent of
table up and down
Carn fitted
loading lever
Plunger Plunger ball with spring
Spring
Dash pot
th Level adjusting legs
Fig.: Rockwell Hardness Testing Machine
BMS Institute of
Technology &Mgmt Denatment of Mechanical Engineering,
Procedure:
I: belore conducting the experiment clean the work surface.
worktable and make sure the
machine is in unload condition.
Depehding on the material to be tested. select the indentor and load with reterence to the
standard chart.
3. Fix the
indentor and set the load by using load selector.
ene testing material on the worktable and rotate the handle of the main screw
in
clockwise so that table moves in
upward direction.
OKotate the handle until the small needle in the scale
the load by rotating the load lever
indicator reaches the set point. Appy
from unload to load position.
0. Wait until the big needle in the
scale comes to comnplete rest position, release the load by
rotating the load lever from load position to
unload position.
I. The number where the big needle rests after
releasing the load is the hardness number or
that material.
S. Remove the material by rotating the handle of the main
screw in anticlock wise direction.
9. Hardness numbers of
different materials are found by using same procedure.
Rockwell hardness standards tests, testing
machines, calibration
STHE 13-20, Sandad Test Mathods for Racknel Hardnes and Rockoel Supehicia Hrdnes t letalik
aterids.
Machires, 199-09-J1
reence locis, 1990-01
hardened
iron.
case malleable 100 .Aluminium,
steel!. etc. metals. than
hardened iron, deep pearlitic bearing iron haraness
malleable titanium, alloys. hardermalleable
scale. metals. cupronickel etc materials Rockwell
case iron, and and steel irons,
hardened materials
shallow alloys, malleable Rockwellsteel, aloys, sheet
B metals HRH
and aluminum hardened magnesium soft and malleable pearliticbearing irons
soft direct
the thin copper-nickel-zinc other
steel, pearlitic
on very
thin steels, 100 case and
and shallow
case and malleable the
alloys, alloys,and alloys,metals other
carbides, soft irons,than medium aluminum Hardness
Scales steel steel
include
harder copper and
alloys, cast and irons, aluminiumhardened sheet
magnesium
Typical
use Cement ed hard iron, Annealed hardened copper, plastics method
Copper Steel,materialssteel Cast
Malleable
and soft
Thin
steel thin beryllium tÉme
uses (100
kgf) (150 kgf) (100
kgf) (100
kgf) (150
kgf) steels, case and alloys,
case
metals, hardness
N (60
588.4kgf) 980.7
N 1471
N 980.7
N 980.7
N 588.4
N (60
kgi) 1471
N Rockwellthin medium testing
and Total
Preliminary
force irons, aluminium bearing
carbides,
soft Rockwell
copperbronze,
symbol 98.07kgf)
(10 98.07 N (10 N (10
kgf) 98.07 kgf) 98.07
N (10 N (10
kgf) 98.07kgf) alloys,cast and rapid
N N (10
kgf) Spheroconical
N (10
98.07kgf) 98.07 Typical
Applicationof HRM....}....
Soft
force Cemented hard steel iron,.Annealed Phosphor
Copper the and
scale Spheroconical (/%s)
mm Spheroconical
Ball,(/:s") 1.588(/6")
mm Ball, mm
Steel, Thin .Cast of readou
Ball, mm) 1.588
3.175
Indenter bal, diameter) diamond1.588
a(if Ball, diamond diamond ( HRL..... HRS
.......
. Advantages
....
Rockwell type
... Zinc,HRK...
lead ........
HKP
HRV.
numbe
HRA.HRB. HRC HRDHRE HRF HRG HRR.
symbol HRG
Scale HRA HRB HRC HRD HRE HRF
Hardness
number
Engineering
Hardness steel?
Mechanical scale
of
properties tester?
test?
testing? hardiness
ofDenartment Brinnel's
in
Load mechanical example.
Kgf strength? hardness
annealing?
normalising toughness.over Rockwell
with
Indentor the formed? and test
indentationw.r.t
in normalizing? formed? number Rockwell
anneal1ng.
heated/cooled
and tempering
on tests?hardness and in
tempering used
indentor: treatment annealing is hardness
indentor: it hardnesshardness
Material is between of scales
advantages
Mgmt. the ithow how
tested of purpose
of indenter
and
diamond purpose of different
& heat of is between and diagram of
effects between
significance
Teçhnology the specimen
objective is martensite,
What
quenching
of term austenite uses difference
Diameter
of VIVA
QUESTIONS the are
What
the the TTT the the the
Differentiate
Angle SI. No the Difference an
Heat
Treatment
the the are
of 2 3 4 State
Define is are is is
are
is Explain is are are
Institute Observation: Conclusion: How What What What What What Hardness
What What What What What
1. 2.
BMS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 8. 9.
10. 11, 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17, 18.
7.
You might also like
- Captiva 2013 Systema Electric 3.0Document13 pagesCaptiva 2013 Systema Electric 3.0carlos martinez50% (2)
- Rockwell Hardness TestDocument7 pagesRockwell Hardness TestMostafizur Rahman Sobuj100% (1)
- Bored Socket in BasaltDocument8 pagesBored Socket in BasaltGULF PILING LLCNo ratings yet
- Wall Mounted Jib CraneDocument5 pagesWall Mounted Jib CraneRameez Ali FaridiNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Hardness Test Determines Steel Specimen HardnessDocument5 pagesRockwell Hardness Test Determines Steel Specimen HardnessArpan DalaiNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab Project EmatDocument6 pagesOpen Ended Lab Project EmatAnas SattiNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR OF ENGINEERING MATERIALS LAB Report 1Document11 pagesMECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR OF ENGINEERING MATERIALS LAB Report 1nadeem ranaNo ratings yet
- som 1Document3 pagessom 1mjayrajsharma19No ratings yet
- Load CellDocument6 pagesLoad CellnikitaNo ratings yet
- Load Cells: Leann Armbrust Travis WyattDocument14 pagesLoad Cells: Leann Armbrust Travis Wyattthulinh12a1No ratings yet
- Steel Hardness Tester Model 415CDocument2 pagesSteel Hardness Tester Model 415CRAJIV GandhiNo ratings yet
- Rockwell EditDocument5 pagesRockwell Editf20220676No ratings yet
- Rockwell Hardness Test ExplainedDocument5 pagesRockwell Hardness Test ExplainedShivansh PathakNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Hardness Test: Name: Mohit Soni Roll No: 142 Batch: S2 Reflection ReportDocument5 pagesRockwell Hardness Test: Name: Mohit Soni Roll No: 142 Batch: S2 Reflection ReportMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Load CellsDocument12 pagesLoad CellsHakije LakherNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Hardness Test Results for MetalsDocument19 pagesRockwell Hardness Test Results for MetalsMai Huong Bui ThiNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology Lahore: Mirza Haider Ali BaigDocument5 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology Lahore: Mirza Haider Ali BaigMirza TouheedNo ratings yet
- Correlation of Hardness Values To Tensile Strength: Semih Genculu, P.EDocument9 pagesCorrelation of Hardness Values To Tensile Strength: Semih Genculu, P.ERakesh DasNo ratings yet
- Transfer Cars Trolleys: 0.5 - 200 TonsDocument4 pagesTransfer Cars Trolleys: 0.5 - 200 Tonsram_babu_59No ratings yet
- By Richard L. Stowe and Donnie L. AinsworthDocument32 pagesBy Richard L. Stowe and Donnie L. AinsworthKimi NcNo ratings yet
- Portable Hardness Test: Application Range - Primary IndustriesDocument6 pagesPortable Hardness Test: Application Range - Primary IndustriesAbdallah El-ashriNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument15 pagesHardness TestAnand KvNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument5 pagesTensile Testjung biNo ratings yet
- SVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School Technology Management and Engineering Strength of Materials LabDocument4 pagesSVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School Technology Management and Engineering Strength of Materials LabBender GamingNo ratings yet
- Reflection Report On Rockwell Hardness Tes 2Document3 pagesReflection Report On Rockwell Hardness Tes 2Prashant PawarNo ratings yet
- Practical Considerations For Successful Hardness TestingDocument3 pagesPractical Considerations For Successful Hardness Testingsy wangNo ratings yet
- TWA Assembly BrochureDocument2 pagesTWA Assembly BrochureNaqib FuadNo ratings yet
- Emm Unit 5Document32 pagesEmm Unit 5dharma212000No ratings yet
- The Performance and Service Life of Wire Ropes Under Deep Koepe and Drum Winders Conditions - Laboratory SimulationDocument9 pagesThe Performance and Service Life of Wire Ropes Under Deep Koepe and Drum Winders Conditions - Laboratory SimulationRicardo Ignacio Moreno MendezNo ratings yet
- Hardness Testing Lab ReportDocument8 pagesHardness Testing Lab Reportnit528No ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab Project Emat PDFDocument7 pagesOpen Ended Lab Project Emat PDFAnas SattiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.9 Jomny End QuenchDocument3 pagesExperiment No.9 Jomny End QuenchZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Hardness TheoryDocument4 pagesHardness Theorykostas.sierros937491% (11)
- Rockwell hardness test explainedDocument9 pagesRockwell hardness test explainedMahrukh JavedNo ratings yet
- Hardeness TestDocument6 pagesHardeness TestDilshan MiurangaNo ratings yet
- Hardness Lab Results and Analysis of Five MaterialsDocument4 pagesHardness Lab Results and Analysis of Five MaterialsJan YsNo ratings yet
- Crawler Crane PDFDocument191 pagesCrawler Crane PDFmajdi jerbiNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test ResultsDocument7 pagesHardness Test ResultsAmyHuiNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 2Document2 pagesExperiment - 2Pradyot DeoliaNo ratings yet
- Load Cells Erwin KohlerDocument12 pagesLoad Cells Erwin Kohlerfriend_ammyNo ratings yet
- KULI Electric Chain HoistsDocument4 pagesKULI Electric Chain HoistsMostafa EidNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab ManualDocument57 pagesMos Lab ManualsuswagatNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Iman PML-6Document5 pagesFicha Tecnica Iman PML-6Ruben TapiaNo ratings yet
- Vibrating Wire Load Cells: Model SeriesDocument2 pagesVibrating Wire Load Cells: Model Seriesacls5005No ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportDulshan uddeepanaNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain Testing and Hardness Evaluation MethodsDocument9 pagesStress Strain Testing and Hardness Evaluation MethodskNo ratings yet
- Load Cell Fundamentals Strain Gauge TransducersDocument14 pagesLoad Cell Fundamentals Strain Gauge TransducersKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Joining Methods and ERW Spot Welding ProcessDocument92 pagesJoining Methods and ERW Spot Welding ProcessHimanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Mounting Adjusting Pump UnitDocument2 pagesMounting Adjusting Pump UnitRalf JonesNo ratings yet
- HardnessDocument21 pagesHardnessJerry Man UtdNo ratings yet
- MM 8th Lab ReportDocument8 pagesMM 8th Lab ReportIbrahim AfridiNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Hardness Test.... 1Document2 pagesRockwell Hardness Test.... 1rafai167% (3)
- How To Evaluate and Install A Load CellDocument3 pagesHow To Evaluate and Install A Load CellMurad ShahNo ratings yet
- Asphalt 6 ColorDocument25 pagesAsphalt 6 Colorkumar814.dkNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials Lab ManualDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials Lab ManualHarood Nishat100% (1)
- Search: Marine EnginDocument4 pagesSearch: Marine EnginHim SatiNo ratings yet
- Structural Capacities of H-Shaped RC Core Wall Subjected To Lateral Load and Torsion PDFDocument8 pagesStructural Capacities of H-Shaped RC Core Wall Subjected To Lateral Load and Torsion PDFpatricklim1982No ratings yet
- Crane+Cable EngDocument30 pagesCrane+Cable EngHuy Hồ PhướcNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Hardness TestDocument9 pagesMechanical Engineering Hardness TestAhmad AyieNo ratings yet
- Properties of SteelDocument61 pagesProperties of SteelCharizza Montarin CENo ratings yet
- Experiences in The OperationDocument7 pagesExperiences in The OperationUsama Bin SabirNo ratings yet
- Adaboost With Totally Corrective Updates For Fast Face DetectionDocument6 pagesAdaboost With Totally Corrective Updates For Fast Face DetectionNguyen Quoc TrieuNo ratings yet
- Abdul Jabbar (Mechanical Engineer) AGROFEED KSADocument4 pagesAbdul Jabbar (Mechanical Engineer) AGROFEED KSAftimum1No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document31 pagesChapter 5Marvin VinasNo ratings yet
- CatalogDocument12 pagesCatalogjonz afashNo ratings yet
- Jenny Randles - Mind Monsters - Invaders From Inner Space (1990)Document219 pagesJenny Randles - Mind Monsters - Invaders From Inner Space (1990)DirkTheDaring11100% (15)
- Iloc and Loc Uses PDFDocument16 pagesIloc and Loc Uses PDFsaurabhNo ratings yet
- Sleep Hygiene Sleep QualityandDocument8 pagesSleep Hygiene Sleep QualityandVriddhi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- jrc122457 Dts Survey Deliverable Ver. 5.0-3Document46 pagesjrc122457 Dts Survey Deliverable Ver. 5.0-3Boris Van CyrulnikNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureNarayanaNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Electrical Engineering 1994Document10 pagesIAS Mains Electrical Engineering 1994rameshaarya99No ratings yet
- Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)Document6 pagesReliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)Hoang Thanh VanNo ratings yet
- Ac and DC MeasurementsDocument29 pagesAc and DC MeasurementsRudra ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Huawei Technologies Network Router B681Document12 pagesHuawei Technologies Network Router B681Eduardo Vaz RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Ooplabmanual 150412132629 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument146 pagesOoplabmanual 150412132629 Conversion Gate01 PDFyawerjs33% (6)
- Types of FuseDocument10 pagesTypes of FuseRane SiddeshNo ratings yet
- Acdsee Pro 6 End User License AgreementDocument7 pagesAcdsee Pro 6 End User License AgreementJonathon MoranNo ratings yet
- Guia Instalacion ENTECDocument15 pagesGuia Instalacion ENTECHislim SaidNo ratings yet
- Node - Js 8 The Right Way: Extracted FromDocument11 pagesNode - Js 8 The Right Way: Extracted FromRodrigo Románovich FiodorovichNo ratings yet
- 07 FSM PDFDocument25 pages07 FSM PDFnew2trackNo ratings yet
- Well Plan Release NotesDocument28 pagesWell Plan Release Notesahmed_497959294No ratings yet
- Abaqus 6.12: Abaqus Example Problems ManualDocument606 pagesAbaqus 6.12: Abaqus Example Problems ManualThiago GomesNo ratings yet
- 2013 Sunchaser Brochure PDFDocument12 pages2013 Sunchaser Brochure PDFKelly SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Ficha de Seguridad Dispositivo Pruba Doble Recamara 2875 - 2876Document133 pagesFicha de Seguridad Dispositivo Pruba Doble Recamara 2875 - 2876janetth rubianoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Close Relations An Introduction To The Sociology of Families 4th Canadian Edition McdanielDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Close Relations An Introduction To The Sociology of Families 4th Canadian Edition Mcdanieldakpersist.k6pcw4100% (44)
- Ett 531 Motion Visual AnalysisDocument4 pagesEtt 531 Motion Visual Analysisapi-266466498No ratings yet
- Electrical Tools, Eq, Sup and MatDocument14 pagesElectrical Tools, Eq, Sup and MatXylene Lariosa-Labayan100% (2)
- Cesp 105 - Foundation Engineering and Retaining Wall Design Lesson 11. Structural Design of Spread FootingDocument7 pagesCesp 105 - Foundation Engineering and Retaining Wall Design Lesson 11. Structural Design of Spread FootingJadeNo ratings yet
- Automobiles Seat ComfortDocument10 pagesAutomobiles Seat ComfortAnushree DeshingeNo ratings yet