Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TEEG Wk6
Uploaded by
James SarabiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TEEG Wk6
Uploaded by
James SarabiaCopyright:
Available Formats
COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
TEACHING ENGLISH IN THE ELEMENTARY GRADES (LANGUAGE ARTS)
WEEK 6
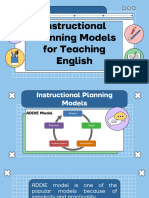
Learning Content Instructional Planning Models for Teaching English
Learning Objectives Identify various instructional planning models used in
teaching English
Compare instructional planning models identified
Adapt a model in designing one’s own instructional plan.
Reference Reyes, R. II. (2021). A Course Module for Teaching English in the
Elementary Grades (Language Arts). Quezon City: Rex Book Store,
Inc.
Instructional planning models help define the elements and activities that would guide
the development of instruction. The following models are just some of the models that could
provide the major components in instructional planning.
ADDIE MODEL
Analysis
Evaluation Design
Implementation Development
The ADDIE model is one of the popular models because of its simplicity and practicality.
The model is traditionally used not just in classrooms, but also in training programs and
analyzing existing curricula. Each of the steps in the model provides an outcome that will be
used in the next. The model is composed of the following elements:
Analysis
Analysis step is where the instructional goals and objectives are established. The
learning environment is also determined, and the learners’ existing skills and knowledge are
identified. The teacher analyzes the context of the learning environment in order to identify
these factors. Some of questions that need to be answered in this phase are:
Who are the learners and what are their characteristics?
What learning outcomes are expected?
What are the constraints that exist? What materials are available?
How much time is available?
1|Page MARY GRACE D. CADAYDAY, LPT
COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
Design
The design phase deals with creating an outline of the instruction. This is where the
learning objectives, learning content, strategies to be used, activities, materials, assessment,
and other media needed are put in place. The design phase is logical and sequential. It should
consider how the lesson will be delivered to the learners.
Development
The development phase is where activities, materials, media, and other content
necessary to deliver the instruction based on the design phase are put together. Here, the
teacher needs to take into consideration the methods of delivery determined by the design
phase.
Implementation
During the implementation phase, the instruction is given to the learners and the teacher
should take some time to observe how the learners react to the instruction provided to them.
Furthermore, the teacher would also need to ensure that all equipment and materials necessary
to deliver the lesson are all complete and working like computers, storage devices, internet
connection, or the number of copies of materials.
Evaluation
In the evaluation phase, the teacher looks into the learners’ score results and the notes
that were taken during the implementation phase. The teacher can then analyze these results
and make appropriate adjustments in the next sessions. Some questions that could be
answered in this phase are:
Were the learning objectives attained?
Which parts of the plans worked well? Which ones did not?
What could be done differently in the next lesson or session?
Kemp Design Model
The Kemp Design Model (also known as the Morrison, Ross, and Kemp Model) follows a
circular structure, and its elements should be taken as independent elements. One advantage of
this model is that teachers and instructional designers are given the flexibility to begin the
design process from any of the elements rather than work in a linear fashion as would other
models.
The Kemp Model has nine elements:
Instructional Problems – determine the specific goals and identify the instructional issues that
could arise.
Learner Characteristics – identify the traits and characteristics of learners that should be taken
into consideration in the planning process
Task Analysis – Make course content clear, and analyze the proposed task components in
relation to the goals and purpose of the course
Instructional Objectives – define the instructional objectives and the desired learning outcomes
Content Sequencing – ensure the instructional content are structured sequentially and logically
Instructional Strategies – design the instructional strategies in such a way that individual
learners would be able to learn the content and attain the learning outcomes
Designing the Message – plan the instructional message and the appropriate mode of delivery
Instructional Delivery – develop the necessary instruments in order to effectively achieve the
instructional goals and objectives, taking into consideration the materials available to the
teacher
2|Page MARY GRACE D. CADAYDAY, LPT
COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
Evaluation Instruments – design and development of the appropriate formative and summative
assessments to determine whether the instructional goals and objectives were attained
Instructional
Problems
Evaluation Learner
Instruments Characteristics
Instructional
Task Analysis
Delivery
Designing the Instructional
Message Objectives
Instructional Content
Strategies Sequencing
ARCS Model
The ARCS model is developed by John Keller in the 1980s. The model’s unique feature
is that it focuses more on the motivation of the learners, ensuring that they are kept engaged
during instruction. Rather than focusing on steps to take in the development of the instructional
plan, the model provides components ARCS has four components:
Attention – This refers to the interests of the learners. This is a critical part of the model as it is
the initial hook of the learners’ attention.
Relevance – This component refers to the usefulness of the learning content so that the
learners could create a connection between it and the real world.
Confidence – This component develops the expectation of success and progress among the
learners, and at the same time gives the learners the opportunity to control their learning
processes. This is important as the learners will have a rough estimation of their probability of
success in the conduct of instruction.
Satisfaction – As there is a direct correlation between motivation and satisfaction, the learners
should have a sense of success and fulfillment after achieving their learning goals and
objectives during the learning process.
KELLER’S ARCS MODEL OF MOTIVATION
3|Page MARY GRACE D. CADAYDAY, LPT
COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
Attention Relevance
ARCS
Satisfaction Confidence
TEACHING ENGLISH IN THE ELEMENTARY GRADES (LANGUAGE ARTS)
WEEK 6
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
Name: Lindyl Love Dinorog Score: 30
Year Level: BEED 3
Directions: What elements of an instructional planning model do you think are the most
important? Create a diagram of your own instructional planning model below. Explain the
elements that you included in your model.
In my model, I included all of the essential elements of instructional planning, including needs
assessment, design, development, implementation, evaluation, and revision. The needs assessment is crucial
for determining the purpose and objectives of the instruction, while the design and development phases
focus on creating a comprehensive and engaging instructional experience. The implementation phase
involves delivering the instruction to the target audience, while the evaluation and revision phases are used
to continuously improve the instruction.
4|Page MARY GRACE D. CADAYDAY, LPT
COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
5|Page MARY GRACE D. CADAYDAY, LPT
You might also like
- Leadership Skills: High School Manual: Violence Prevention ProgramFrom EverandLeadership Skills: High School Manual: Violence Prevention ProgramNo ratings yet
- MC Eng 1 - 095932Document7 pagesMC Eng 1 - 095932Joederick Sinforoso OlimpoNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONAL PLANNING MODELS ReportingDocument27 pagesINSTRUCTIONAL PLANNING MODELS ReportingleaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Instructional Planning ModelsDocument8 pagesComparing Instructional Planning ModelsAllyssa Jean MausaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning Models Explained in 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesInstructional Planning Models Explained in 40 CharactersMequen AlburoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning Models for Teaching EnglishDocument9 pagesInstructional Planning Models for Teaching EnglishSophie MantoNo ratings yet
- Jerrold Kemp: Instructional Design ModelDocument37 pagesJerrold Kemp: Instructional Design Modelivan_ROY31087624No ratings yet
- Educ 229 For FinalsDocument19 pagesEduc 229 For FinalsMary Grace Ygot ParachaNo ratings yet
- Instructional-Planning-Models-for-Teaching-EnglishDocument3 pagesInstructional-Planning-Models-for-Teaching-EnglishPhil Collen D. CaloNo ratings yet
- PCK 2 MidtermDocument5 pagesPCK 2 MidtermKristina GlaseNo ratings yet
- Phases of Curriculum DevelopmentDocument14 pagesPhases of Curriculum DevelopmentnerrizakyutNo ratings yet
- Dme 302 - Design, Development, and Evaluation of Mathematics MaterialsDocument37 pagesDme 302 - Design, Development, and Evaluation of Mathematics MaterialsJinky ValdezNo ratings yet
- Ma. Elena Oblino Abainza: Principles in Material Design (NUNAN, 1988) Design, Development and Dissemination of MaterialsDocument22 pagesMa. Elena Oblino Abainza: Principles in Material Design (NUNAN, 1988) Design, Development and Dissemination of Materialsshimeath delrosarioNo ratings yet
- Answer, Module 4,5,6Document14 pagesAnswer, Module 4,5,6Janz Jacob FloresNo ratings yet
- IsedpatDocument10 pagesIsedpatmjmarirporrasNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Educ 129Document64 pagesModule 3 Educ 129Rose Ann Madenancil100% (1)
- Engineering Course Design NBA March 2020Document10 pagesEngineering Course Design NBA March 2020Chandra Shekar MedarNo ratings yet
- Teacher and School Curriculum Module 2Document6 pagesTeacher and School Curriculum Module 2Vanjo MuñozNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesLecture in Lesson PlanningAngela GamayonNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning ModelsDocument15 pagesInstructional Planning ModelsNorjianah WaliNo ratings yet
- Midterm Week 4 Lesson Addie ModelDocument6 pagesMidterm Week 4 Lesson Addie ModelCecelien Salgado AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lecture Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesLecture Lesson PlanningAnne Bautista100% (1)
- Seminars On Problems Met During Practice Teaching: Learning Module inDocument16 pagesSeminars On Problems Met During Practice Teaching: Learning Module inAlexa Marie CondeNo ratings yet
- Integrating Differentiated Instruction & Understanding by Design: Connecting Content and Kids, 1st EditionDocument10 pagesIntegrating Differentiated Instruction & Understanding by Design: Connecting Content and Kids, 1st EditionLogan KelleyNo ratings yet
- Brown Aesthetic and Beauty Fashion Business Thesis Defense Presentation PDFDocument31 pagesBrown Aesthetic and Beauty Fashion Business Thesis Defense Presentation PDFMaria Carmela CalinogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 DepEd Guidelines On Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesLesson 1 DepEd Guidelines On Instructional PlanningJeanmae Omalyao MakilingNo ratings yet
- SS-19-Module-3Document18 pagesSS-19-Module-3Rosell May SumogatNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Curriculum Planning, Design, and OrganizationDocument36 pagesUnit Ii Curriculum Planning, Design, and OrganizationEloisa GabrielNo ratings yet
- Planning Teaching & Learning: Curriculum Design and DevelopmentDocument24 pagesPlanning Teaching & Learning: Curriculum Design and DevelopmentAneeka FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document111 pagesModule 1Judy Nel PlesingNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design Models and Methods Chapter SummaryDocument5 pagesInstructional Design Models and Methods Chapter SummaryWarren JaraboNo ratings yet
- Benlac Module 7 1Document11 pagesBenlac Module 7 1Jomar LopezNo ratings yet
- Materials Development ModelsDocument11 pagesMaterials Development ModelsAlfeo OriginalNo ratings yet
- Instructionalmodules 150309100609 Conversion Gate01Document13 pagesInstructionalmodules 150309100609 Conversion Gate01gerlyn tabucalNo ratings yet
- Ed05 Module 3 Lesson 1 PDFDocument14 pagesEd05 Module 3 Lesson 1 PDFMark Stephen RavelasNo ratings yet
- Bab 03. Addie ModelDocument4 pagesBab 03. Addie ModelChai Siaw YenNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 PDFDocument13 pagesUnit 14 PDFJaysonGayumaNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan IsDocument6 pagesA Lesson Plan IsJames Revin Gulay IINo ratings yet
- Edu 7 Module 2Document8 pagesEdu 7 Module 2Monalisa AbanielNo ratings yet
- Remedial Instructions in English (Prelim) - Course PackDocument11 pagesRemedial Instructions in English (Prelim) - Course PackCindy BuhianNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanningDocument48 pagesLesson PlanningTeacherMhurzNo ratings yet
- Instructional Materials Development ProcessDocument9 pagesInstructional Materials Development ProcessAnn Rachel CuadraNo ratings yet
- ADDIE Model Report Word FileDocument3 pagesADDIE Model Report Word Fileconz12No ratings yet
- Instructional Planning Models For Teaching English - 20240318 - 195626 - 0000Document11 pagesInstructional Planning Models For Teaching English - 20240318 - 195626 - 0000Cas, JayfersonNo ratings yet
- Week 4-5 - Materials Development ModelsDocument11 pagesWeek 4-5 - Materials Development ModelsAlfeo OriginalNo ratings yet
- K to 12 Daily Lesson PlanningDocument28 pagesK to 12 Daily Lesson PlanningJhamie Lah50% (2)
- Policy Guideliness DLL Making Deped OrderDocument37 pagesPolicy Guideliness DLL Making Deped OrderANDELYNNo ratings yet
- What, Why and How To Evaluate A CurriculumDocument32 pagesWhat, Why and How To Evaluate A CurriculumJeremias De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Social Science Learning ModuleDocument80 pagesSocial Science Learning ModuleSAMUEL REYESNo ratings yet
- Curriculum and Materials Design Presentation by JOYCE AGUILODocument13 pagesCurriculum and Materials Design Presentation by JOYCE AGUILOKenneth GSalakNo ratings yet
- Assessing Learning OutcomesDocument36 pagesAssessing Learning OutcomesAllison Yambao CastroNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Yee Bee Choo IpgkthoDocument57 pagesLecturer: Yee Bee Choo IpgkthoHarith Fahmie Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design in Online Course Development - Mary Roween C. RodriguezDocument15 pagesInstructional Design in Online Course Development - Mary Roween C. RodriguezRoden RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Interrelationship of Curriculum ComponentsDocument2 pagesInterrelationship of Curriculum ComponentsRuby Corazon EdizaNo ratings yet
- Method - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Document90 pagesMethod - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Dr. Tapan Kr. Dutta100% (1)
- Dick and Carey Learning Design Model ExplainedDocument17 pagesDick and Carey Learning Design Model ExplainedArinasikahNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development4Document12 pagesCurriculum Development4Teacher SallyNo ratings yet
- Curriculum EvaluationDocument57 pagesCurriculum Evaluationmm coffeeNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Entrepreneurship in Elt - 10%: AddieDocument7 pagesTask 3 Entrepreneurship in Elt - 10%: AddieVesto JalmavNo ratings yet
- Dicky CareyDocument5 pagesDicky CareyAna MurilloNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship-2Document13 pagesTechnopreneurship-2James SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Techno SolutionDocument18 pagesTechno SolutionJames SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm ExamJames SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Special and Inclusive Education 1 SEMESTER S.Y. 2021-2022Document1 pageFoundations of Special and Inclusive Education 1 SEMESTER S.Y. 2021-2022James SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Special and Inclusive Education 1 SEMESTER A.Y. 2021-2022Document1 pageFoundations of Special and Inclusive Education 1 SEMESTER A.Y. 2021-2022James SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Special and Inclusive Education 1 SEMESTER A.Y. 2021-2022Document1 pageFoundations of Special and Inclusive Education 1 SEMESTER A.Y. 2021-2022James SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Answer For Foundation of EducationDocument4 pagesAnswer For Foundation of EducationvnintraNo ratings yet
- 02 - THCS- Tổ Chức Dạy Hoc Tiếng Anh ở TrườngDocument3 pages02 - THCS- Tổ Chức Dạy Hoc Tiếng Anh ở TrườngTrang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Productivity NinjaDocument89 pagesProductivity NinjaLeyah ChristyNo ratings yet
- 3 Lesson Exemplar SHS EAPPDocument4 pages3 Lesson Exemplar SHS EAPPMARIA CHEZLENE MANAIGNo ratings yet
- Inside Out Movie Review and Emotion Through SelfDocument5 pagesInside Out Movie Review and Emotion Through SelfAeeshaNo ratings yet
- Gen 002 - P1Document5 pagesGen 002 - P1Rochelle Las PiñasNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageCebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesSisles HoneyNo ratings yet
- Cooperative LearningDocument4 pagesCooperative LearningCeling MayangNo ratings yet
- No Read No Pass ThesisDocument71 pagesNo Read No Pass ThesisMichael BatallaNo ratings yet
- 9990 Example Candidate Responses Paper 1 (For Examination From 2018)Document30 pages9990 Example Candidate Responses Paper 1 (For Examination From 2018)Mtendere Joseph ThomboziNo ratings yet
- Name: DATE: September 7, 2022 COURSE & YEAR: BSED - IV MathematicsDocument2 pagesName: DATE: September 7, 2022 COURSE & YEAR: BSED - IV Mathematicsrose FrondaNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology in OrthodonticsDocument69 pagesChild Psychology in OrthodonticsShristi ChahalNo ratings yet
- Still Alice ReviewDocument5 pagesStill Alice Reviewsloapz1No ratings yet
- Chapter-15 TFNDocument17 pagesChapter-15 TFNLoraine SandovalNo ratings yet
- Identifying Human Characteristics and QualitiesDocument1 pageIdentifying Human Characteristics and Qualitieskristine_abasNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making in SchoolsDocument59 pagesDecision-Making in SchoolsFrancois L. Detera100% (1)
- INTERDICIPLINARYDocument3 pagesINTERDICIPLINARYEMMANUEL BERNARDINONo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan 2Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan 2Annalyn Aligor100% (1)
- Chapter 5-Leadership and MotivationDocument62 pagesChapter 5-Leadership and MotivationAklilu GirmaNo ratings yet
- Summary SlaDocument36 pagesSummary SlaNatalia OliveraNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Planleslie banglosNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology MidtermDocument2 pagesCognitive Psychology MidtermnmtrobNo ratings yet
- Linking Theory and PracticeDocument2 pagesLinking Theory and Practiceaida ACHOURNo ratings yet
- A Study On Understanding The Effectiveness of Audiovisual Aids in Improving English Vocabulary in ESL Classrooms - 2023 - Sciedu PressDocument7 pagesA Study On Understanding The Effectiveness of Audiovisual Aids in Improving English Vocabulary in ESL Classrooms - 2023 - Sciedu PressHarold TrefforNo ratings yet
- Rooting Gilbert's Multi-Modal Argumentation in Jung, and Its Extension To LawDocument40 pagesRooting Gilbert's Multi-Modal Argumentation in Jung, and Its Extension To LawibeghoucheneNo ratings yet
- Puntambekar 2010 Tools For Scaffolding Students in A Complex Learning Environment What Have We Gained and What Have We MissedDocument13 pagesPuntambekar 2010 Tools For Scaffolding Students in A Complex Learning Environment What Have We Gained and What Have We MissedCristhian AndresNo ratings yet
- REFLECTION PAPER 21st CENTURY LITERATUREDocument1 pageREFLECTION PAPER 21st CENTURY LITERATUREdumapiasbernalyn02No ratings yet
- Teaching Elementary Arts NotesDocument5 pagesTeaching Elementary Arts NotesKyzelle AllapitanNo ratings yet
- Comics Strips, Short Stories and Pupils' Reading ComprehensionDocument6 pagesComics Strips, Short Stories and Pupils' Reading ComprehensionPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Teaching Learning MaterialsDocument3 pagesTeaching Learning MaterialsOzelle PoeNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenFrom EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)