Professional Documents
Culture Documents
D and F Test
Uploaded by
krishnakumarsingh966210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThis document contains 17 questions related to transition metals, coordination compounds, and biomolecules. Some of the key topics covered include:
1) The reasons why d-block elements are called transition elements and why some transition metal ions exhibit different oxidation states.
2) The steps involved in preparing potassium chromate and potassium permanganate from their respective ore sources.
3) Lanthanoid contraction and its consequences on the properties of lanthanide elements.
4) Characteristics and applications of transition metals including their high atomization enthalpies and role as catalysts.
5) Properties of coordination complexes including their hybridization states, shapes, and magnetic behaviors.
6) Monomers
Original Description:
Original Title
d and f test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 17 questions related to transition metals, coordination compounds, and biomolecules. Some of the key topics covered include:
1) The reasons why d-block elements are called transition elements and why some transition metal ions exhibit different oxidation states.
2) The steps involved in preparing potassium chromate and potassium permanganate from their respective ore sources.
3) Lanthanoid contraction and its consequences on the properties of lanthanide elements.
4) Characteristics and applications of transition metals including their high atomization enthalpies and role as catalysts.
5) Properties of coordination complexes including their hybridization states, shapes, and magnetic behaviors.
6) Monomers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageD and F Test
Uploaded by
krishnakumarsingh96621This document contains 17 questions related to transition metals, coordination compounds, and biomolecules. Some of the key topics covered include:
1) The reasons why d-block elements are called transition elements and why some transition metal ions exhibit different oxidation states.
2) The steps involved in preparing potassium chromate and potassium permanganate from their respective ore sources.
3) Lanthanoid contraction and its consequences on the properties of lanthanide elements.
4) Characteristics and applications of transition metals including their high atomization enthalpies and role as catalysts.
5) Properties of coordination complexes including their hybridization states, shapes, and magnetic behaviors.
6) Monomers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
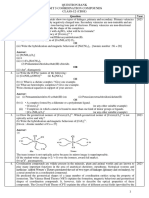
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA NO-1 DHANBAD
(D and f block + coordination + biomolecules)
Class-XII F.M.-35
1. Why d block elements are called transition elements? 1
2. Why is Cr2+ reducing and Mn3+ oxidising when both have d4configuration ? 1
3. Write steps involved in the preparation of 2
(i) K2Cr2O7 from chromite ore and
(ii) KMnO4 from pyrolusite ore.
4. What is meant by the term lanthanoid contraction? What are its consequences 3
5. Assign reasons for the following: 5
(i) The enthalpies of atomisation of transition elements are high.
(ii) The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
(iii) Transition metals are form alloys.
(iv) TheE0value for the Mn 3+ / Mn 2+ couple is much more positive than that of
Cr3+/Cr 2+.
(v) Scandium (Z =21) does not exhibit variable oxidation states and yet it is regarded as
a transition element.
6. What are chelating liagand and ambident ligand? 1
7. Write the IUPAC name of [CO (NH3 )4 Br2] 2 [ZnCl4 ]. 1
8. Which vitamin is a complex compound of cobalt ? 1
9. Write the state of hybridization, the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following 3
complexes: a. [Fe(CN6)]4–, b. [Ni(CN)4]2–, c. [Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2]–
(At nos.: Cr = 24, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
10. Why is [NiCl4]2– paramagnetic but [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic? 1
11. Name the products of hydrolysis of sucrose. Why is sucrose not a reducing sugar? 2
12. (a) Draw a diagram to show splitting of d orbitals in octahedral complexes 2
(b) what is Crystal field stablising energy(CFSE)
13. What happens when glucose is reacted with (i) HI (ii) Br2 water (iii) HNO3 3
14. Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes ‘pernicious anaemia’ 1
15. Differentiate between (i) amilose and amilopectin 3
(ii) Globular and fibrous proteins (iii) RNA and DNA
16. Explain what is meant by 3
(i)a glycosidic linkage (ii) Invert sugar (iii) Denatured protein
17. Write monomers of (i) Lactose (ii) maltose 2
You might also like
- 8.d and F-Block Elements KCET PYQsDocument2 pages8.d and F-Block Elements KCET PYQsPunith kumarNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Practice Exam 1Document10 pagesCHM 101 Practice Exam 1Mark PrestwichNo ratings yet
- American Welding SocietyDocument2 pagesAmerican Welding SocietykurniawanNo ratings yet
- A List of Reports On German and Japanese Technology Prepared by American InvestigatorsDocument61 pagesA List of Reports On German and Japanese Technology Prepared by American Investigatorseliahmeyer50% (2)
- DPSGZB XIIth Chemistry MCQ's Subjective Questions ExportDocument4 pagesDPSGZB XIIth Chemistry MCQ's Subjective Questions ExportMj Chemistry FacultyNo ratings yet
- D & f-BLOCK ELEMENTS MARKSWISE QUESTIONSDocument9 pagesD & f-BLOCK ELEMENTS MARKSWISE QUESTIONSSachin GuptaNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Chapter Coordination Wise QP 2022-23Document8 pages12th Class Chapter Coordination Wise QP 2022-23Gunjan BisenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Paper Coordination CompoundDocument14 pagesChemistry Sample Paper Coordination Compoundbachpankapyar071No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Exemplar Chapter 8Document11 pages12 Chemistry Exemplar Chapter 8Fayezee techieNo ratings yet
- Class XII: CHEMISTRY (Theory)Document24 pagesClass XII: CHEMISTRY (Theory)Study EasyNo ratings yet
- D and F Block and Coordination Compounds - Previous YearDocument5 pagesD and F Block and Coordination Compounds - Previous Yearsibi johnNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chem-4. D and F Block ElementsDocument4 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chem-4. D and F Block Elementsnr249488No ratings yet
- Apc - Pi 18Document2 pagesApc - Pi 18Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- D Block TestDocument3 pagesD Block TestDivij JainNo ratings yet
- d-BLOCK and f-BLOCKDocument20 pagesd-BLOCK and f-BLOCKHiranmoyNo ratings yet
- Unit Test - 4 Class-Xii Sub.-Chemistry Time:01:30 Hrs Mm:40Document2 pagesUnit Test - 4 Class-Xii Sub.-Chemistry Time:01:30 Hrs Mm:40Nihar Ranjan NikuNo ratings yet
- D-Block Elements WorkbookDocument42 pagesD-Block Elements WorkbookStudy BuddyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Kit (Chemistry-200 L) -Vol. 2 - 看图王 PDFDocument60 pagesTutorial Kit (Chemistry-200 L) -Vol. 2 - 看图王 PDFAijin JiangNo ratings yet
- D and F-Block ElementsDocument21 pagesD and F-Block ElementsGavin GroverNo ratings yet
- Ajai Kumar Coordination Chemistry-1Document18 pagesAjai Kumar Coordination Chemistry-1Sudipyo NaskarNo ratings yet
- Test Paper On Chapter 8 The D and F Block Elements Class 12 ChemistryDocument2 pagesTest Paper On Chapter 8 The D and F Block Elements Class 12 ChemistryjacksucksatlifeNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-8. D and F Block ElementsDocument3 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-8. D and F Block ElementsererrerNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Past PapersDocument4 pagesD and F Block Past PapersYash RajputNo ratings yet
- D-And F-Block ElementsDocument5 pagesD-And F-Block ElementsArchanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- GSQ/M-20 Chemistry Paper XVIII (CH-304) Inorganic ChemistryDocument3 pagesGSQ/M-20 Chemistry Paper XVIII (CH-304) Inorganic ChemistryDuryodhanNo ratings yet
- Question 811531Document2 pagesQuestion 811531aryantinu123No ratings yet
- Mock Board 1Document5 pagesMock Board 1Arjun PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Question Bank English Medium 216216Document46 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Question Bank English Medium 216216MUKESH KUMAR RNo ratings yet
- D - and F-Block Elements - Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesD - and F-Block Elements - Questions and AnswersVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- 2-Excellent Chemistry Assignment D-And F-Block ElementsDocument5 pages2-Excellent Chemistry Assignment D-And F-Block ElementsSachin B SNo ratings yet
- Review Question On Coordination Compounds 2022Document6 pagesReview Question On Coordination Compounds 2022Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- Transition Element-Past Years QuestionsDocument3 pagesTransition Element-Past Years QuestionshidayahyusofNo ratings yet
- Subjective Assessment - I 2021-22 Class XII Chemistry Time: 2 Hrs. M.M. 50Document3 pagesSubjective Assessment - I 2021-22 Class XII Chemistry Time: 2 Hrs. M.M. 50vedNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Element TestDocument2 pagesD and F Block Element TestasNo ratings yet
- Cbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-XiiDocument7 pagesCbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-XiiANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKMahrishiShukla100% (1)
- Leep 509Document13 pagesLeep 509AlloooNo ratings yet
- Topic Practice 3: Very Short Answer Type Questions - 1 MarkDocument7 pagesTopic Practice 3: Very Short Answer Type Questions - 1 MarkDebasis GhosalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Kolkata Region 2 Pre Board Examination - 2014-15Document5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Kolkata Region 2 Pre Board Examination - 2014-15NareshNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Coordination SolutionDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Coordination Solutionsuryansh.yt9641No ratings yet
- Arihant Coordination CompoundDocument3 pagesArihant Coordination CompoundUpasana NathNo ratings yet
- D & F DPPDocument9 pagesD & F DPPDarxter DarxNo ratings yet
- SCH 300 Comparative Study of S-And P-Block Elements CAT-2Document2 pagesSCH 300 Comparative Study of S-And P-Block Elements CAT-2keybateNo ratings yet
- 8.the D-And F-Block ElementsDocument15 pages8.the D-And F-Block ElementsDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Final RevisionDocument3 pagesCoordination Compounds Final RevisionROWA new year CelebrationNo ratings yet
- D-&f-Block ElementsDocument23 pagesD-&f-Block ElementsDimpy Girl143No ratings yet
- Co Ordination CompoundsExerciseDocument4 pagesCo Ordination CompoundsExercisepinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry - Practice Sheet-5 - Only QuestionDocument3 pagesInorganic Chemistry - Practice Sheet-5 - Only Questionprakharsingh0606No ratings yet
- Cordite Factory Higher Secondary School, Aruvankadu Exam Xii STDDocument3 pagesCordite Factory Higher Secondary School, Aruvankadu Exam Xii STDASWIN SNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Test 5Document7 pagesChemistry - Test 5Ahmed haatimNo ratings yet
- Test - 2 Single Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesTest - 2 Single Choice QuestionsGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I (EM) MQPDocument3 pagesChemistry I (EM) MQPxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Tranisition Elements-03 - Assignments (New)Document13 pagesTranisition Elements-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Elemtents MCQ PRACTICE TEST With SOLUTIONSDocument11 pagesD and F Block Elemtents MCQ PRACTICE TEST With SOLUTIONSRijul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Doc-20231229-Wa0005 231229 012537Document13 pagesDoc-20231229-Wa0005 231229 012537ameentrafiqNo ratings yet
- Objective: Alpha Academy ChemistryDocument1 pageObjective: Alpha Academy Chemistrymuhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- Chem - 2 QP 11-01-22 CamDocument13 pagesChem - 2 QP 11-01-22 CamEZ SHaikhNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Revision 2022Document2 pagesCoordination Compounds Revision 2022Dêêpák Sîñgh Ñîtwál100% (1)
- D and F Block ElementsDocument1 pageD and F Block ElementsSrujana ShettiNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Coordination CompoundsDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper Coordination Compoundsjinop79764No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (LDA) NMDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding (LDA) NMkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Iron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesFrom EverandIron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Metals and Its ApplicationsDocument4 pagesMetals and Its Applicationsmargareth bumatayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GlassDocument8 pagesIntroduction To GlassPd MobiNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection: Multi-Choice Questions Paper 2: World Centre For Materials Joining TechnologyDocument4 pagesWelding Inspection: Multi-Choice Questions Paper 2: World Centre For Materials Joining TechnologyAslanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Equations Worksheet (With Periodic Table)Document2 pagesNuclear Equations Worksheet (With Periodic Table)phydotsiNo ratings yet
- 0620 s09 QP 1Document32 pages0620 s09 QP 1h7h8No ratings yet
- Chang Problems Chapter 2Document10 pagesChang Problems Chapter 2ChaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium WeightDocument30 pagesAluminium WeightEngr.Mmosaad100% (1)
- CHAPTER 7 Exp BiologyDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 7 Exp BiologyAdy Phanterz100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 2 2017 PDFDocument12 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 2 2017 PDFKaran Pratap100% (3)
- Synthesis of Di-Calcium Phosphate Used As Feed Additive For Animals From Phosphate Rock As Potential Cost Effective Raw MaterialDocument11 pagesSynthesis of Di-Calcium Phosphate Used As Feed Additive For Animals From Phosphate Rock As Potential Cost Effective Raw MaterialWafaa NachitNo ratings yet
- ICP-MS Talk ACBDocument31 pagesICP-MS Talk ACBmonday125No ratings yet
- Ncert Redox Reaction SolutionsDocument32 pagesNcert Redox Reaction SolutionsLikhith UsurupatiNo ratings yet
- SMK Puteri Seremban: Chemistry ProjectDocument28 pagesSMK Puteri Seremban: Chemistry ProjectHaemaavadhaanaNo ratings yet
- Kronos Ecochem Ti 5 - 01 - enDocument4 pagesKronos Ecochem Ti 5 - 01 - enDennis LingNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Food Record: Kue Bolu KukusDocument2 pagesAnalysis of The Food Record: Kue Bolu KukusNy NyNo ratings yet
- Class PPT 1Document27 pagesClass PPT 1Ankita SinghNo ratings yet
- All About ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesAll About ElectrochemistryROY JAIVIN A/L SANTHANA DAS MoeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Prefinal PaperDocument4 pagesChemistry Prefinal Paperkuldeep9034.patelNo ratings yet
- ASTM A123 - Zinc Hot Dip Galvanised Coatings On Iron and Steel ProductsDocument4 pagesASTM A123 - Zinc Hot Dip Galvanised Coatings On Iron and Steel ProductsPisut LeelalumlertNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/63Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/63lovely12807No ratings yet
- CH 19 PDFDocument10 pagesCH 19 PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Musha Mudra & SandhiDocument62 pagesMusha Mudra & SandhiDr Debasis Panigrahi100% (3)
- Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in Chlorides EnvironmentsDocument27 pagesStress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in Chlorides EnvironmentsAmbar Shah100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/12Yvonne Poh “Yvonne Poh”No ratings yet
- Specific Heat Calculations WorksheetDocument4 pagesSpecific Heat Calculations WorksheetGhada AbukhadraNo ratings yet
- EJ Handbook.A5Document261 pagesEJ Handbook.A5ElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Element Builder: Samara VandeverDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Element Builder: Samara VandeverSamara VandeverNo ratings yet