Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 PP
Uploaded by
BlancCanvasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 PP
Uploaded by
BlancCanvasCopyright:
Available Formats
1) Good morning.
a) Our topic for discussion today is about environmental, health, and safety effects of power plants.
2) Our report is divided into five parts starting with coal-fired power plants, followed by nuclear,
geothermal, hydro and lastly wind power plants.
3) So, all of us already know or have prior knowledge about what a power plant is.
a) It is basically a facility that converts energy into electricity.
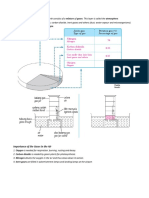
4) Now, let’s start with coal-fired power plants and its E,H, & S Effects
5) Coal-fired Power Plants undergo a lot of process before maka generate ug electricity from coal
a) When we say coal, is a fossil fuel composed mostly of carbon and hydrocarbons and marelease
rana iyang energy through combustion.
b) Let’s watch this video on how it works.
6) Now, let’s go back to our main topic starting with its environmental effects
a) So, from the video alone we can pin point the causes of environmental impacts of coal power
plant which are mainly coal mining, burning of the coal, and the need of a lot of water to feed to
the boiler.
b) Unsa man diay naa ana, nganong bad man sya for the environment.
c) Climate change is coal’s most serious, long-term, global impact.
1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): The combustion of coal releases large amounts of
carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas contributing to global warming
and climate change.
Methane (CH4): Coal mining and processing can release methane,
another potent greenhouse gas.
2. Air Pollution:
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Burning coal produces sulfur dioxide, which
contributes to acid rain and can harm respiratory health.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Coal combustion releases nitrogen oxides, which
can contribute to smog formation and respiratory issues.
Particulate Matter: The burning of coal generates fine particles that can
be harmful when inhaled, leading to respiratory and cardiovascular
problems.
3. Water Use and Pollution:
Water Consumption: Coal-fired power plants require large amounts of
water for cooling. This can impact local water sources and ecosystems.
Water Pollution: Disposal of coal ash, a byproduct of combustion, can
contaminate water with heavy metals and other pollutants.
4. Land Use and Habitat Destruction:
Mining Impact: Coal mining can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion,
and the alteration of landscapes. It may also lead to the displacement of
local communities and wildlife.
5. Waste Generation:
Coal Ash: Coal combustion produces ash containing various pollutants,
including heavy metals like mercury, lead, and arsenic. Proper disposal of
coal ash is crucial to prevent water and soil contamination.
6. Respiratory and Cardiovascular Issues:
Particulate Matter (PM): Fine particles released during the combustion of
coal can penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to respiratory problems
such as asthma, bronchitis, and aggravated chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD). PM is also associated with cardiovascular issues.
7. Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Exposure:
Respiratory Problems: SO2 emissions from coal combustion can irritate
the respiratory system, exacerbate asthma, and lead to the development of
respiratory diseases.
8. Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Exposure:
Respiratory Issues: NOx can contribute to the formation of ground-level
ozone and fine particulate matter, both of which are harmful to respiratory
health.
9. Mercury Exposure:
Neurological Effects: Mercury emissions from coal combustion can
contaminate water bodies, leading to the bioaccumulation of mercury in
fish. Consuming contaminated fish can result in mercury exposure, which is
particularly harmful to the developing nervous systems of fetuses and
young children.
10. Climate Change-Related Health Effects:
Heat-Related Illnesses: The contribution of coal combustion to climate
change can result in more extreme weather events, leading to increased
heat-related illnesses and deaths.
You might also like
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Technology List and Perspectives For Transition Finance in AsiaDocument132 pagesTechnology List and Perspectives For Transition Finance in AsiaEconomic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia100% (1)
- Harmful Effects of Coal and PetroleumDocument1 pageHarmful Effects of Coal and PetroleumAj CarilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Pollution) Part 1Document53 pagesUnit 2 (Pollution) Part 1kumar.abhinav1015No ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- Chemistry AirDocument2 pagesChemistry AirREAL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument74 pagesAir PollutionSaneet AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry NotesDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry NotesApoorva S. MallickNo ratings yet
- Determination of Toxic Content From Coal Based Power PlantDocument31 pagesDetermination of Toxic Content From Coal Based Power PlantaneezaNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution FinalDocument23 pagesAir Pollution Finalnamansehgal3006No ratings yet
- Air PollutantsDocument1 pageAir PollutantsGelend 555 gelendNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument530 pagesAir PollutionHarshwardhan UndeNo ratings yet
- SAU1306Document93 pagesSAU1306JugarNo ratings yet
- CARBON COMPOUNDS: Pollution Aspects: Received Date: Jan. 2020 Revised: April 2020 Accepted: June 2020Document9 pagesCARBON COMPOUNDS: Pollution Aspects: Received Date: Jan. 2020 Revised: April 2020 Accepted: June 2020Vaibhav SiddharthNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsDocument16 pagesICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Environment and PollutionDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Environment and PollutionFaniaayu RahmaNo ratings yet
- Group Work Assignment (Pollution Control)Document9 pagesGroup Work Assignment (Pollution Control)Amizero DivineNo ratings yet
- Dept of Chemistry 18CHE12/22 Sai Vidya Institute of TechnologyDocument22 pagesDept of Chemistry 18CHE12/22 Sai Vidya Institute of TechnologyshreyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1Soudip patiNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument11 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document38 pagesPresentation 4Hubab AhmadNo ratings yet
- SIS Final NotesDocument23 pagesSIS Final NotesRabiya shaukatNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document10 pagesActivity 2Lester Alfred OlasimanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science & Disaster ManagementDocument131 pagesEnvironmental Science & Disaster ManagementJyothis T SNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry Class-XiDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry Class-XiSatyaSaraswatNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentphanhaibangNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument11 pagesGlobal Warmingghataksampa816No ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Ch14: Environmental Chemistry TOP ConceptsDocument9 pagesClass XI Chemistry Ch14: Environmental Chemistry TOP ConceptsGurmeetNo ratings yet
- Coal ProductionDocument5 pagesCoal ProductionhannahNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Environmental PollutionDocument17 pagesMeaning of Environmental PollutionSrividya SNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Introduction PollutionDocument9 pagesUnit - I Introduction PollutionNaveen AshraeNo ratings yet
- CLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionDocument12 pagesCLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionHirakjyoti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Gaseous Waste To Environment and HealthDocument13 pagesEffects of Gaseous Waste To Environment and HealthTeererai KaguraNo ratings yet
- Lesson-27 5Document42 pagesLesson-27 5ANKUR CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- MuhojaDocument6 pagesMuhojaSire MkubwaNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument12 pagesAir PollutionAman Ahmed MokamiNo ratings yet
- Renewabl e Energy CH 1 PowerPointDocument139 pagesRenewabl e Energy CH 1 PowerPointJacob Todd HewellNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument3 pagesGreenhouse EffectElwin Ooi100% (1)
- M4-Environmental Pollution-1Document23 pagesM4-Environmental Pollution-1SHRAVAN JEEVAL B ANo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: Dr. Hemanta MedhiDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Science: Dr. Hemanta MedhiItmej NNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument40 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryharryNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Chemistryrajesh.pandey9870606No ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry - Shobhit Nirwan PDFDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry - Shobhit Nirwan PDFVarun MadaanNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Envs Project Reg No 1151211031520 Roll No 203115110012Document38 pagesSem 2 Envs Project Reg No 1151211031520 Roll No 203115110012Sudip SahaNo ratings yet
- Pollutant: Any Substance That Causes Nuisance or Harmful Effects or Uneasiness To The EcosystemDocument56 pagesPollutant: Any Substance That Causes Nuisance or Harmful Effects or Uneasiness To The EcosystemObotigho Richard IwoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Unit: 1Document13 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Unit: 1Premangshu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Notes On Environmental PollutionDocument8 pagesNotes On Environmental PollutionUvaisNo ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsDocument12 pagesAthmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Topic - Air Pollution Name - Kanchan Vijay Waghade ROLL NO. - BE20S02F010 Branch - Mechanical Engineering YEAR - SECOND YEAR (2020-2021Document21 pagesTopic - Air Pollution Name - Kanchan Vijay Waghade ROLL NO. - BE20S02F010 Branch - Mechanical Engineering YEAR - SECOND YEAR (2020-2021Prachi Rahul PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7rajana ramliNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Persuasive WritingDocument7 pagesAir Pollution Persuasive WritingPamela LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, L-7, Air and AtmosphereDocument5 pagesChemistry, L-7, Air and AtmospheremilliNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument25 pagesAir PollutionDali MondalNo ratings yet
- Đo N Văn Cô Nhung Lesson 20Document2 pagesĐo N Văn Cô Nhung Lesson 20phunglinh792003No ratings yet
- Evs Module 7Document8 pagesEvs Module 7shifa10abhpemsNo ratings yet
- Coal PowGenerationDocument14 pagesCoal PowGenerationBryan CherryNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere GVJDocument8 pagesThe Atmosphere GVJEsai StephenNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle StepsDocument20 pagesThe Carbon Cycle StepsBigLove100% (1)
- Disadvantages of Using Coal To Produce ElectricityDocument20 pagesDisadvantages of Using Coal To Produce Electricitykofi99No ratings yet
- IIT Main Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MasterDocument13 pagesIIT Main Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MasterPalash KurkuteNo ratings yet
- L-17 Sources of Air PollutionDocument6 pagesL-17 Sources of Air PollutionMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Flyash Utilisation 2023Document16 pagesFlyash Utilisation 2023Rajiv kumarNo ratings yet
- Coal Silo Fires and Hot SpotsDocument4 pagesCoal Silo Fires and Hot SpotsbakirNo ratings yet
- Pulverized Coal BurnerDocument8 pagesPulverized Coal BurnerVikk SuriyaNo ratings yet
- Power ResourcesDocument14 pagesPower ResourcesDawoodNo ratings yet
- Amr February 20 PDFDocument112 pagesAmr February 20 PDFfernando quispialayaNo ratings yet
- Flexibility in Conventional Power Plants: Innovation Landscape BriefDocument23 pagesFlexibility in Conventional Power Plants: Innovation Landscape BriefBernard Garcia Orihuela100% (1)
- Electric Vehicles Charging Into The FutureDocument9 pagesElectric Vehicles Charging Into The FutureKen AdamsNo ratings yet
- Tongwaihow Emh211 Thermodynamics Assignment 3Document6 pagesTongwaihow Emh211 Thermodynamics Assignment 3Wai HowNo ratings yet
- Energy - Work - Resources of EnergyDocument23 pagesEnergy - Work - Resources of EnergykhalidNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project Report On NTPC BY Prateek Jain - VIT UniversityDocument117 pagesSummer Training Project Report On NTPC BY Prateek Jain - VIT UniversityPrateek Jain100% (3)
- MVEP 2.0 ENG FINAL (Standard Page)Document44 pagesMVEP 2.0 ENG FINAL (Standard Page)Lâm VũNo ratings yet
- Proposed Design of 600 MW Coal - Fired Power Plant Located at Brgy. Balanga, Lemery, BatangasDocument140 pagesProposed Design of 600 MW Coal - Fired Power Plant Located at Brgy. Balanga, Lemery, BatangasJohn Paul Coñge Ramos100% (1)
- 6.the Solution Approach To Flow Problems Using Tivar 88Document11 pages6.the Solution Approach To Flow Problems Using Tivar 88hadiNo ratings yet
- MAHENDRA SAINI SEMINAR ReportDocument53 pagesMAHENDRA SAINI SEMINAR Reportvideo songNo ratings yet
- A Review and Analysis of Renewable EnergyDocument14 pagesA Review and Analysis of Renewable EnergyHasnain HaiderNo ratings yet
- PowerChina Company Profile 2021Document33 pagesPowerChina Company Profile 2021guntur febri100% (1)
- Wood Pellets Business 11 Feb 2020Document16 pagesWood Pellets Business 11 Feb 2020Aljazari FoundationNo ratings yet
- Eng - 2018 Doosan Ab - 190916Document78 pagesEng - 2018 Doosan Ab - 190916Leck DzNo ratings yet
- Global Coal Plant Tracker Jan 2022Document1,569 pagesGlobal Coal Plant Tracker Jan 2022UmangNo ratings yet
- Study of Equipment Prices in The Power SectorDocument121 pagesStudy of Equipment Prices in The Power Sectoradelafuente2012No ratings yet
- Agora Energiewende - Flexibility in Thermal Power Plants: P P Ramp RateDocument2 pagesAgora Energiewende - Flexibility in Thermal Power Plants: P P Ramp Ratezisis81No ratings yet
- CoalFleet Guideline For Advanced USC Pulverized Coal Power PlantsDocument438 pagesCoalFleet Guideline For Advanced USC Pulverized Coal Power PlantsXuân Huy PhanNo ratings yet
- CQM+ Heat BalanceDocument19 pagesCQM+ Heat BalancesoumitrabanNo ratings yet
- Coal-Fired Power Plant Heat Rate Improvement Options, Part 2 - PowermagDocument11 pagesCoal-Fired Power Plant Heat Rate Improvement Options, Part 2 - PowermagRavi SatyapalNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Performance Characteristics and Energetic Efficiency of Vertical Roller Coal MillDocument17 pagesAn Investigation of Performance Characteristics and Energetic Efficiency of Vertical Roller Coal MillMANOJ KJNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering Problem: According To The Washington Accord Complex Engineering Problems Are Problems ThatDocument1 pageComplex Engineering Problem: According To The Washington Accord Complex Engineering Problems Are Problems ThatAhmad AnsariNo ratings yet
- De Va Dap An HSG 9 Cap Tinh 2021-2022 6a8a61540aDocument11 pagesDe Va Dap An HSG 9 Cap Tinh 2021-2022 6a8a61540acuongNo ratings yet
- Science of The Total Environment: Margarita A. Dmitrienko, Pavel A. StrizhakDocument13 pagesScience of The Total Environment: Margarita A. Dmitrienko, Pavel A. Strizhakoctober monthNo ratings yet
- MN FieldDocument54 pagesMN Fieldarunrajmech09No ratings yet