Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sexual Reproduction
Uploaded by
Sherilyn Apostol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesSexual reproduction requires genetic material from both male and female gametes or sex cells. The male gametes are contained in pollen which must be transferred to the female pistil for fertilization to occur. This results in seeds being produced that contain a mix of genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic diversity in offspring. Flowering plants use a process called pollination for sexual reproduction, where pollen from the stamen must reach the stigma of the pistil for reproduction.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSexual reproduction requires genetic material from both male and female gametes or sex cells. The male gametes are contained in pollen which must be transferred to the female pistil for fertilization to occur. This results in seeds being produced that contain a mix of genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic diversity in offspring. Flowering plants use a process called pollination for sexual reproduction, where pollen from the stamen must reach the stigma of the pistil for reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesSexual Reproduction
Uploaded by
Sherilyn ApostolSexual reproduction requires genetic material from both male and female gametes or sex cells. The male gametes are contained in pollen which must be transferred to the female pistil for fertilization to occur. This results in seeds being produced that contain a mix of genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic diversity in offspring. Flowering plants use a process called pollination for sexual reproduction, where pollen from the stamen must reach the stigma of the pistil for reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
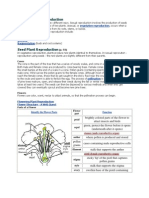
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction requires genetic material (DNADNA) from two parents. The
parent plants have male and female sex cells, called gametes. The genetic material
from the male and female gametes combines to produce offspring. We call this
process fertilization. The product of sexual reproduction are seeds.
Seeds produced through fertilization contain genetic material from both parents. As
a result, the offspring are not genetically identical to either of the parent plants.
This genetic diversity can help them survive if the environment changes.
Flowering plants reproduce sexually through a process called pollination.
Flowers contain male sex organs called stamens and female sex organs
called pistils. The anther is the part of the stamen that contains pollen. Pollen
contains the male gametes. Pollen must be moved to a part of the pistil called
the stigma for reproduction to take place.
Parts of a flower (Let’s Talk Science using an image by Clker-Free-Vector-Images via
Pixabay).Image - Text Version
The outermost parts of the flower are green structures called sepals. They protect
the flower before it opens. Inside the sepals are the petals. These are usually
colourful. Petals on flowers are actually modified leaves. Within the petals are
the stamens. Each stamen contains a filament topped by pollen-producing cells.
The innermost part of the flower is the carpel. The carpel contains the ovary. This
is where the eggs, or ovules, are located. The pollen from another flower must
enter the ovary and fertilize an ovule in order for a seed to start developing.
You might also like
- The Perpetuation of LifeDocument11 pagesThe Perpetuation of LifeClaire E Joe86% (14)
- Plant Breeding As A HobbyDocument20 pagesPlant Breeding As A HobbyJirobuchon100% (1)
- Sexual Vs Asexual Reproduction in Plants and Animals 1Document14 pagesSexual Vs Asexual Reproduction in Plants and Animals 1api-264004169No ratings yet
- Integrated Science Assignment: Name of Students: Jeheil Albert Tyreice John Jerome KingDocument10 pagesIntegrated Science Assignment: Name of Students: Jeheil Albert Tyreice John Jerome KingDa bertNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument3 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsmallorca albertNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Document8 pagesEarth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Section 3 Lesson 1Document74 pagesIGCSE Biology Section 3 Lesson 1Arta riaNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant ReproductionDocument6 pagesTypes of Plant ReproductionNaNa Liyana Elias INo ratings yet
- 10 BiologyDocument4 pages10 BiologyTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument1 pageSexual Reproduction of PlantsSheryn E. PallocNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument10 pagesREPRODUCTIONRuth ViernesNo ratings yet
- A. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionDocument5 pagesA. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionJoy MagbutongNo ratings yet
- Reproduciton in Crops Plant 2023Document68 pagesReproduciton in Crops Plant 2023lemma4aNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringblistedxNo ratings yet
- The Perpetuation of LifeDocument11 pagesThe Perpetuation of LifeJianna ClementeNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesDocument76 pagesFlowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesRaja InaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notesalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants and HumansDocument15 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants and HumansAndre GreenNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- Biology For Kids - Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesBiology For Kids - Flowering PlantsUche AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual Reproductionshashwatdwivedi9000No ratings yet
- PHRS ReproductionDocument4 pagesPHRS ReproductionsallyfrankenwarteNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument32 pagesReproductionArpita SinghNo ratings yet
- Reprodcution in PlantsDocument10 pagesReprodcution in Plantsargin.dhtNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument34 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsHannah AraojoNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in VegetablesDocument46 pagesModes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in Vegetablessyamkavitha100% (4)
- How Do Org ReproduceDocument32 pagesHow Do Org ReproducePankaj Kumar100% (1)
- Mode of Reproduction in PlantsDocument3 pagesMode of Reproduction in PlantsBik BokNo ratings yet
- Asexual Sexual ReproductionDocument32 pagesAsexual Sexual ReproductionReymart VillapeñaNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal ReproductionDocument7 pagesPlant Animal ReproductionKyla Renz de LeonNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument4 pagesModes of ReproductionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 Reproduction and FertilizationDocument11 pagesWEEK 5 Reproduction and FertilizationPrince Jariz SalonoyNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproductin NotesDocument7 pagesPlant Reproductin NotesTasneem HamdyNo ratings yet
- Growing Food MaterialDocument4 pagesGrowing Food MaterialWajeea Asif - 76826/Coordinator/HSPRNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFDocument18 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFCatherine Mistiola100% (1)
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsShan PMCNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument12 pagesReproduction in PlantsAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Organismal BiologyDocument3 pagesOrganismal BiologyOtot DaNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocument15 pagesModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- BIOLOGY-PLANT-SEXUAL-REPRODUCTION-SCRIPT Tata's TouchDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY-PLANT-SEXUAL-REPRODUCTION-SCRIPT Tata's TouchRoselyn RicaforteNo ratings yet
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDocument25 pagesPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument40 pagesLecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument2 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsMichael TimsonNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument29 pagesReproductionWapapha Gen-Rev MuzilaNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentDocument22 pagesPlant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentNix TanNo ratings yet
- Flowering PollinationDocument9 pagesFlowering Pollinationo0breaker0oNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument24 pagesLecture 1 - Asexual and Sexual Reproductioneixeroayalos101No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument4 pagesPlant ReproductionAaliyah CatiilNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Specialized Structure of Angiosperms Figure 2. Difference Between Self-Pollination and Cross PollinationDocument2 pagesFigure 1. Specialized Structure of Angiosperms Figure 2. Difference Between Self-Pollination and Cross PollinationKaye Ann CarelNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionExceil Matthew Carpio100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document17 pagesChapter 6sheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- Cbse X Sexual Reproduction in Plants: ScienceDocument12 pagesCbse X Sexual Reproduction in Plants: ScienceDaniel SunnyNo ratings yet
- Handout ReproductionDocument2 pagesHandout ReproductionCandy Concepcion PadizNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 2022Document97 pagesReproduction in Plants 2022Newera WizzzNo ratings yet
- Pollinator Monitoring for Citizen Scientists: A HandbookFrom EverandPollinator Monitoring for Citizen Scientists: A HandbookNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- What Is The Visible Light SpectrumDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Visible Light SpectrumSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- What Is Biblical StewardshipDocument4 pagesWhat Is Biblical StewardshipSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Primary ColorsDocument10 pagesPrimary ColorsSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Sherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- 4 Principles of StewardshipDocument2 pages4 Principles of StewardshipSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Heat EnergyDocument2 pagesHeat EnergySherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument2 pagesInternetSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument2 pagesFlowering PlantsSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Printed MaterialsDocument6 pagesPrinted MaterialsSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument4 pagesModes of ReproductionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- The 5 R's of Waste ManagementDocument3 pagesThe 5 R's of Waste ManagementSherilyn Apostol100% (1)
- Lesson Plan-Math - ComputationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan-Math - ComputationSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- HyperboleDocument2 pagesHyperboleSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Epp56 Q1 W6 JosepulidojrDocument14 pagesEpp56 Q1 W6 JosepulidojrSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet