Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Assignment 2
Uploaded by
Rakshitha JayashankarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math Assignment 2
Uploaded by
Rakshitha JayashankarCopyright:
Available Formats
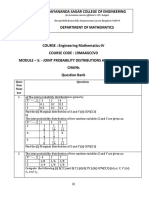
VIVEKANANDA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE-560074
MATHEMATICS FOR COMPUTER SCIENCE (BCS301), ASSIGNMENT-2
MODULE II, JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS & MARKOV CHAINS
0 1 0
1. S.T P = [ 1 01 1] is a regular stochastic matrix. Also find unique fixed probability vector.
0
0
2 2
2 1
0 3 3
1 1
2. Prove that the Markov chain whose t .p .m is P = 0 is irreducible.
2 2
1 1
[ 0]
2 2
3. Three boys A,B,C are throwing a ball to each other. A always throws ball to B and B always throws ball
to C. But C is just as likely to throws the ball to B and A. If C was the first person to throw the ball, find
the probabilities that 1.A has the ball, 2. B has the ball 3. C has the ball, for the fourth throw
4. Define stochastic matrix, Markov chains.
5. A man’s smoking habits are as follows. If he smokes filter cigarette’s one week, he switches to non-
filter cigarette’s the next week with probability 0.2 , on the other hand, if he smokes non filter
cigarette’s one week there is probability of 0.7 that he will smoke non filter cigarette’s the next week
as well. In a long run how often does he smoke filter cigarettes?
0 1 0
1 1 1
6. Find the unique fixed probability vector of the regular stochastic matrix A =[6 2 3]
2 1
0 3 3
1
¾ 4
7. Find the unique fixed probability vector of the regular stochastic matrix A= [ 1 1]
2 2
8. Define absorbing state, transient state, recurrent state
9. The joint distribution of two random variables X and Y is as follows.
X\Y -2 -1 4 5
1 0.1 0.2 0 0.3
2 0.2 0.1 0.1 0
Compute the following a) E(X) and E(Y) b) E(XY) c) X and Y d) COV(X,Y) e) (X,Y)
10. The joint probability distribution table for two variables X and Y is as follows.
X\Y -4 2 7
1 1/8 1/4 1/8
5 1/4 1/8 1/8
Find a) E( X,Y) b) SD.s of X,Y
c) Covariance of X and Y d ) Correlation of X and Y
11. Suppose X and Y are independent random variables with the following respective
distribution, find the joint distribution of X and Y. Also verify that COV(X,Y) =0
xi 1 2
y -2 5 8
f(xi) 0.7 0.3
g(y) 0.3 0.5 0.2
12. The joint probability distribution table for two variables X and Y is as follows.
X\Y 3 4 5
2 1/6 1/6 1/6
5 1/12 1/12 1/12
7 1/12 1/12 1/12
Find a) E( X,Y) b) SD.s of X,Y c) Covariance of X and Y d ) Correlation of X and Y
13. A coin is tossed 3 times. Let X denotes 0 or 1 according as a tail or head occurs on the first toss. Let Y
denotes the total number of tails which occur. Determine the marginal distribution of X and Y
14. Every year, a man trades his car for a new car. If he has a Maruti, he trades it for an ambassador. If
he has an ambassador, he trades it for a Santro. However if has a Santro, he is just as likely to trade it
for a new Santro as to trade it for a Maruti or an ambassador. In 2000, he bought his first car which was
a Santro. Find the probability that in 2002 he had i) Santro ii) Maruti.
15. A salesman’s territory consists of 3 cities A, B, C. He never sells in the same city for 2 consecutive
days. If he sells in city A then the next day he sells in the city B. However if he sells in either B or C then
the next day he is twice as likely to sell in the city A as in the other city. In long run how often does he
sell in each of the cities.
You might also like
- Cosmology in (2 + 1) -Dimensions, Cyclic Models, and Deformations of M2,1. (AM-121), Volume 121From EverandCosmology in (2 + 1) -Dimensions, Cyclic Models, and Deformations of M2,1. (AM-121), Volume 121No ratings yet
- 2 Mathematics Important Ten Marks Question Bank PDFDocument16 pages2 Mathematics Important Ten Marks Question Bank PDFSaralashunNo ratings yet
- IV-Sem-IT-Module-5-Joint Probability Distribution and Markov Chain-QBDocument6 pagesIV-Sem-IT-Module-5-Joint Probability Distribution and Markov Chain-QBAmogh RNo ratings yet
- P&S Unit-4 and 5Document3 pagesP&S Unit-4 and 5zzzzzNo ratings yet
- MTH3251 Financial Mathematics Exercise Book 15Document18 pagesMTH3251 Financial Mathematics Exercise Book 15DfcNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS - I(B) IMPORTANT QUESTIONSDocument15 pagesMATHEMATICS - I(B) IMPORTANT QUESTIONSMoscowNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2017-18 - ECE2005 - TH - TT304 - VL2017185001360 - Reference Material IV - CatI - A2 - Slot - KeyDocument3 pagesWINSEM2017-18 - ECE2005 - TH - TT304 - VL2017185001360 - Reference Material IV - CatI - A2 - Slot - KeyCh PranushaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 1Document5 pagesProblem Sheet 1Divyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Neki zadaci za veobuDocument1 pageNeki zadaci za veobumarerema94No ratings yet
- BCS301Document4 pagesBCS301sagarblazaNo ratings yet
- BIVARIATE DISTRIBUTION HOMEWORKDocument4 pagesBIVARIATE DISTRIBUTION HOMEWORKNigar QurbanovaNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Similarity Transformations 15Document15 pages1.8 Similarity Transformations 15Mae RohNo ratings yet
- 442HW Ii StatDocument2 pages442HW Ii StataliNo ratings yet
- Introductory Econometrics Question BankDocument2 pagesIntroductory Econometrics Question BankNandini BhatlaNo ratings yet
- 86 MarksDocument5 pages86 Marksdevsaini2024No ratings yet
- Vibration of A Free Free Beam Under TensDocument10 pagesVibration of A Free Free Beam Under Tensjean.vasco94No ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Term 2 Sample Paper Test 09 2021 22Document2 pagesMaths Class Xii Term 2 Sample Paper Test 09 2021 22sarav dhanuNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Problem SheetDocument4 pagesKinematics Problem SheetAnkit PandaNo ratings yet
- 8c1c6cff 108工程機率ch3作業Document3 pages8c1c6cff 108工程機率ch3作業孔令洋No ratings yet
- Ques Pre-Pspm KMPPDocument4 pagesQues Pre-Pspm KMPPewine0529No ratings yet
- cat-1-bmc-catDocument2 pagescat-1-bmc-catprittycarol8No ratings yet
- Stat332 PDFDocument3 pagesStat332 PDFBless TettehNo ratings yet
- BSC 3 Sem Statistics (Statistical Methods) Summer 2018Document3 pagesBSC 3 Sem Statistics (Statistical Methods) Summer 2018Sanjana ParateNo ratings yet
- Difference-Type Estimators For Estimation of Mean in The Presence of Measurement ErrorDocument21 pagesDifference-Type Estimators For Estimation of Mean in The Presence of Measurement ErrorScience DirectNo ratings yet
- MT271 Tutorial Sheet 4Document3 pagesMT271 Tutorial Sheet 4Albert TembaNo ratings yet
- Random Variable 2Document25 pagesRandom Variable 2KuldeepPaudelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8BDocument10 pagesTutorial 8BaNo ratings yet
- Test1213 2qDocument3 pagesTest1213 2qmeettoavi059No ratings yet
- 211803382459engineering Maths-I (2020-21) - FinalDocument1 page211803382459engineering Maths-I (2020-21) - FinalSubhasish ShitNo ratings yet
- SR Maths - IIB Important QsDocument23 pagesSR Maths - IIB Important QsKeerthana100% (1)
- SimpleLinearRegression PDFDocument86 pagesSimpleLinearRegression PDFkappi4uNo ratings yet
- Indian Maritime University (A Central University, Government of India)Document2 pagesIndian Maritime University (A Central University, Government of India)trivesh kambojNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Engineering Mathematics-IDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Engineering Mathematics-IkpanchamgamNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Theory of VectorsDocument23 pagesLinear Algebra Theory of VectorsAhmed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- RA - Assignment 1Document1 pageRA - Assignment 1Peng JinNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1 Statistics For Engineers - Mat2001 Module 1 & 2 Submission Date: 20-9-2021Document3 pagesDigital Assignment 1 Statistics For Engineers - Mat2001 Module 1 & 2 Submission Date: 20-9-2021Yogeeswar PydaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3 (17MAT41)Document2 pagesAssignment - 3 (17MAT41)Mayank Saini0% (1)
- Question Bank For Iat-3 CivilDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank For Iat-3 CivilSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Subramanian ManickamNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Civil, Cse, Ece, Eee, Eie, It, Me, Ie & AeDocument3 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Civil, Cse, Ece, Eee, Eie, It, Me, Ie & AerazesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three MultipleDocument15 pagesChapter Three MultipleabdihalimNo ratings yet
- Dssm Imp Questions for End ExaminationsDocument6 pagesDssm Imp Questions for End ExaminationsManu NNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 09 For Term-2 Exam (2021-22)Document2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 09 For Term-2 Exam (2021-22)abcdefghNo ratings yet
- Tifr 2011 PhysicsDocument8 pagesTifr 2011 PhysicsAbhrajit MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 2Document18 pagesModule 2 - 2Jr BagaporoNo ratings yet
- Polya's Orchard Problem Author(s) : Thomas Tracy Allen Source: The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 93, No. 2 (Feb., 1986), Pp. 98-104 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 12/01/2015 20:10Document8 pagesPolya's Orchard Problem Author(s) : Thomas Tracy Allen Source: The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 93, No. 2 (Feb., 1986), Pp. 98-104 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 12/01/2015 20:10RhodesNo ratings yet
- 0 Y, 0 X Otherwise ,) 1 y (X Xe 0) Y, X (F + + + +Document3 pages0 Y, 0 X Otherwise ,) 1 y (X Xe 0) Y, X (F + + + +Raisa RashidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For Random Variables and Stochastic Processes Eem2046 Engineering Mathematics Iv Multimedia UniversityDocument9 pagesTutorial For Random Variables and Stochastic Processes Eem2046 Engineering Mathematics Iv Multimedia UniversityNazmi AzizNo ratings yet
- School of Mathematics, Thapar University, PatialaDocument2 pagesSchool of Mathematics, Thapar University, PatialaAdityaNo ratings yet
- 30 MarksDocument2 pages30 Marksravikumarsharma2412No ratings yet
- B.Tech. (SEM-I) THEORY EXAMINATION 2018-19 MATHEMATICS-IDocument4 pagesB.Tech. (SEM-I) THEORY EXAMINATION 2018-19 MATHEMATICS-IViraj RuhelaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 (Tma 101)Document1 pageAssignment 01 (Tma 101)Aashish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics, Antennas and Propagation NotesDocument85 pagesElectromagnetics, Antennas and Propagation NotesAnum AhmedNo ratings yet
- BEC Question Bank Unit 1Document3 pagesBEC Question Bank Unit 1Alex StackNo ratings yet
- YJCP1Document4 pagesYJCP1Aloysius LamNo ratings yet
- Maths 2017 Prelim Exam Paper 1 Q&ADocument45 pagesMaths 2017 Prelim Exam Paper 1 Q&ALeonard TngNo ratings yet
- Prog-1 Daily Practice Assignment-1 Subject: Physics Chapter: VectorsDocument13 pagesProg-1 Daily Practice Assignment-1 Subject: Physics Chapter: VectorsAkash AbbarapuNo ratings yet
- Mathaeng3 M1-Cu5Document14 pagesMathaeng3 M1-Cu5Gdeity PlaysNo ratings yet
- I. Two Random VariablesDocument24 pagesI. Two Random VariablesTaanzNo ratings yet
- PoW Tutorial 4Document2 pagesPoW Tutorial 4pratyay gangulyNo ratings yet
- EEE111_Multisim_ManualDocument14 pagesEEE111_Multisim_ManualSHADOW manNo ratings yet
- RD218 Gardan 3110 Ob2226657 NDocument1 pageRD218 Gardan 3110 Ob2226657 Nopen hartigNo ratings yet
- B1 UDO Trace LogDocument14 pagesB1 UDO Trace LogCh M KashifNo ratings yet
- Bartending and Catering: Agenda: Basics of Bartending Bar Tools and EquipmentDocument146 pagesBartending and Catering: Agenda: Basics of Bartending Bar Tools and EquipmentMars Mar100% (1)
- K - LP - Week 24 - Journeys Unit 3 Lesson 14Document8 pagesK - LP - Week 24 - Journeys Unit 3 Lesson 14englishwithmslilyNo ratings yet
- Micro800 4-Channel and 8-Channel Analog Voltage/Current Input and Output ModulesDocument12 pagesMicro800 4-Channel and 8-Channel Analog Voltage/Current Input and Output ModulesSyarifudin WahidNo ratings yet
- Meta Hids by eBPFDocument27 pagesMeta Hids by eBPFninggou.yangNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument18 pagesCollective Bargainingchandni kundel100% (3)
- Audit Chapter 7Document5 pagesAudit Chapter 7Addi Såïñt George100% (2)
- WEG Low Voltage Motor Control Center ccm03 50044030 Brochure English PDFDocument12 pagesWEG Low Voltage Motor Control Center ccm03 50044030 Brochure English PDFRitaban222No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research On Vocabulary and Spelling Skills of A Student Chapters I IIIDocument23 pagesQualitative Research On Vocabulary and Spelling Skills of A Student Chapters I IIIarniza blazoNo ratings yet
- Aling Presing ChichacornDocument2 pagesAling Presing ChichacornMhel Joshua Bautista HermitanioNo ratings yet
- LFJ All OrdersDocument195 pagesLFJ All Orderskate jackNo ratings yet
- ES Model Question Paper With Solution KeyDocument10 pagesES Model Question Paper With Solution Keyvidhya_bineeshNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Nursing Students Knowledge of and Attitudes About Problem Based LearningDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Nursing Students Knowledge of and Attitudes About Problem Based LearningasdasdasdasNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingDocument2 pagesCognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingNik ZazlealizaNo ratings yet
- Australian Institute For Teaching and School Leadership - AITSLDocument5 pagesAustralian Institute For Teaching and School Leadership - AITSLYu LiNo ratings yet
- Williamstown Cannabis Cultivation PlanDocument48 pagesWilliamstown Cannabis Cultivation PlanOltion JaupajNo ratings yet
- The 9 Building Blocks of Business ModelsDocument3 pagesThe 9 Building Blocks of Business ModelsTobeFrankNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Couplant MSDSDocument2 pagesUltrasonic Couplant MSDSAnonymous uhqwokAeU0No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Perfect CompetitionDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Perfect Competition刘文雨杰No ratings yet
- Food, Family, and FriendshipsDocument256 pagesFood, Family, and FriendshipsBianca PradoNo ratings yet
- 01 - Narmada M PhilDocument200 pages01 - Narmada M PhilafaceanNo ratings yet
- VariablesDocument11 pagesVariablesKzy ayanNo ratings yet
- PEOPLE IN MY TOWN - Song Worksheet PAULA 2019Document2 pagesPEOPLE IN MY TOWN - Song Worksheet PAULA 2019PauNo ratings yet
- Omega 1 Akanksha 9069664Document5 pagesOmega 1 Akanksha 9069664Akanksha SarangiNo ratings yet
- SP Manual Addendum For OS 3 - 03Document2 pagesSP Manual Addendum For OS 3 - 03kevmac88No ratings yet
- Ejc-M13 - FN953205Document203 pagesEjc-M13 - FN953205JoséNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Deep Learning Activation Functions When To Use ThemDocument15 pagesFundamentals Deep Learning Activation Functions When To Use ThemfaisalNo ratings yet
- Piano: Grade 2: PiecesDocument4 pagesPiano: Grade 2: PiecesnolozeNo ratings yet