Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9th Grade Biology Fall Final Exam Review Flashcards Quizlet
Uploaded by
yksarahh4kCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9th Grade Biology Fall Final Exam Review Flashcards Quizlet
Uploaded by
yksarahh4kCopyright:
Available Formats
9thTry
Grade Biology
the fastest F…! flashcards
way to create
Study
Free trial
Study sets, textbooks, questions
9th Grade Biology Fall Final
Exam Review
159 studiers today 4.8 (19 reviews)
Tap the card to flip
What is biology?
Study of life
Tap the card to flip
1 / 203
In-class activity
Classic Live
Checkpoint
!
Self-study activity
Flashcards
Learn
Test
Match
Q-Chat
Created by
sa26727
9th grade biology fall final exam review
Coach Rabe
WHS
Share
Students also viewed
Answer the following questions-Final exa…
55 terms
naturists Preview
Terms in this set (203) Original
What is biology?
Study of life
What is a stimulus and describe how an
organism could respond to an internal
stimulus.
A stimulus is anything that causes an
organism to respond. An organism
could respond to an internal stimulus by
ongoing internal processes. EX: empty
stomach causes the organism feel he
need to eat for energy
Hypothesis=
an explanation to a question, an
educated guess
Quantitative information=
results in numerical data that can be put
into a table or graph
What are the characteristics of living
things?
Have an orderly structure, produce
offspring, grow and develop, and adjust
to changes in the environment
List the steps of the scientific method.
Observation-make a hypothesis-
collecting data- publishing the results-
forming a theory- developing a new
hypothesis- and revising the theory
What is a species?
A group of organisms that can
interbreed and produce fertile offspring
in nature
Name the components of the SI system
of measurement.
Gram, meter, Celsius, liter
Growth=
increase in the amount of living material
and the formation of new structures
Independent Variable=
condition of the experiment that is
tested
Dependent Variable=
the condition that results from changes
in the independent variable
Mixture=
a combination of substances in which
the individual components retain their
own properties
Covalent bond=
sharing of electrons between atoms
What are the 4 elements that make up
96% of the human body?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and
Nitrogen
Atoms=
smallest particle of an element that has
the characteristics of that element
Explain why water is a polar molecule.
Water is a molecule with an unequal
distribution of charge, the Oxygen side
is (-) and the hydrogen side is (+) due to
the sharing of electrons in the covalent
bond
What occurs in the process of diffusion?
Movement of particles from an area of
high concentration to an area of low
concentration
Describe the basic components of:
proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and
nucleic acids
Proteins = amino acids
Carbohydrates = C, H, O -> sugars
(saccharides)
Lipids = fats, oils, waxes made of C, and
H
Nucleic Acid = nucleotides
What is an enzyme?
A protein that changes the rate of
chemical reactions
Development=
all of the changes that take place during
the life cycle of an organism
Theory=
explanation of natural phenomenon that
is supported by a large body of
scientific evidence
Ion=
an atom that has gained or lost an
electron giving it a charge ( + or - )
Qualitative information=
observational data that is a description
of observations
Ionic bond =
attraction of opposite charges between
ions (ion= atom that gained or lost an
electron)
Solution=
a mixture in which one or more
substances are dissolved in another
substance
What is the function of the cell
membrane?
it allows materials to enter the cell
regardless of the environment.it
maintains homeostasis by removing
waste and excess materials.it has
selective permeability (allows some
materials in while keeping others out)
How do phospholipids interact with
water to help from the cell membrane?
-the phospholipid bilayer (make up the
cell membrane and it has polar heads
and nonpolar tails) water is polar
molecule and is found inside and
outside the cell (but is repelled by the
nonpolar tails), the water is attracted to
the polar heads and repelled by the
non polar tails
Explain 4 roles proteins play in the cell
membrane.
Cell surface markers (Identifies the cell).
Transport proteins move substances
across the cell membrane. Receptor
protein (Recognizes and binds to
substance outside of cell). Enzymes
(helps speed up chemical reactions)
Draw and label a phospholipid
molecule.
Polar head and non polar tail
prokaryotic:
have NO membrane bound organelles
they are unicellular and lack a nucleus
(bacteria cells)
eukaryotic:
have membrane bound organelles and
a nucleus (plant and animal cells)
Plant cells:
chlorophyll, cell walls, larger vacuoles,
chloroplasts, plastids
Animals cells:
Dont have chlorophyll, cell walls, larger
vacuoles, chloroplasts, plastids
What are the 3 main ideas of the cell
theory?
All organisms are composed of one or
more cells. The cells is the basic unit of
structure and organization of all
organisms.All cells come from pre-
existing cells
Describe the plasma membrane and the
function of its 3 parts.
Flexible boundary between the cell and
its environment. It is made up of a
phospholipid bilayer with each
phospholipid having a polar head and a
non-polar tail. Anchored inside the
membrane are proteins which allow
things to enter and leave the cell. Within
the phospholipid bilayer contains
cholesterol which keeps the non-polar
tails from sticking together
If a cell synthesizes large quantities of
proteins which organelles might be
numerous in that cell and why?
Ribosomes: used to make the proteins.
ER: makes the proteins. Golgi Body:
sorts and packages the proteins.
Vacuoles: store the proteins
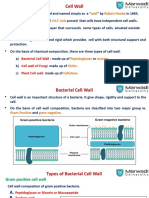
Cell Wall:
rigid structure located outside the
plasma membrane that provides
support and protection (only in plants)
IT IS NOT SELECTIVE
Plasma membrane:
in both plants and animals flexible fluid
boundary, IT IS SELECTIVE!
Robert Hooke:
named cells after the small rooms
monks lived in.
Theodor Schwann:
animals are composed of cells.
Matthias Schleiden:
plants are composed of cells
Considering that a cell's environment is
extremely watery why might lipids be
important to the composition of the
plasma membrane?
Because the lipids are non-polar (tail)
and they help keep water from leaving
the cell while prevent water from
rushing in the cell
See an expert-written answer!
Rough ER:
has ribosomes attached to the ER to
carry out protein synthesis
Smooth ER:
has not ribosomes stores and make
lipids
Compound light microscope:
uses lenses and a light source to
magnify objects up to 1500x
Electron microscope:
uses electron beams to magnify objects
object has to be placed in a vacuum,
and can magnify up to 500,000x
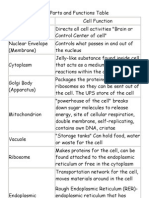
Nucleus:
contains all the directions to make a
protein. (DNA)
Cytoplasm:
clear gelatinous fluid in the cells that is
the site of numerous chemical reactions,
it suspends the organelles.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) -
folded membranes that are the site of
cellular chemical reactions. Proteins and
lipids are manufactured here. It is also a
network of tubules that contributes to
protein distribution.
Golgi Apparatus -
Sorts proteins into packages and sends
them to the appropriate vesicles to be
distributed
Vacuole -
membrane bound sac used for
temporary storage in the cell. Vacuoles
store food enzymes and other materials
the cell may need.
Lysosomes -
organelles that contain digestive
enzymes. digest excess/worn out
organelles food particles, and engulfed
bacteria/virus.
Chloroplasts -
organelles that capture light energy to
convert into chemical energy. are part
of a group of plastids.
Mitochondria -
transform sugar molecules into energy
for the cell. They are found in plant and
animal cells.
Cytoskeleton -
is the support structure of the cell. is
made up of rods called microtubules
and filaments.
Cilia -
Short numerous, and look like hair. They
move in a rowing motion
Flagella -
Long and have a whip-like motion
Microtubules -
are hollow tubes of protein.
You might also like
- Introduction To Bio 101Document132 pagesIntroduction To Bio 101madsdsNo ratings yet
- Biology Review NotesDocument9 pagesBiology Review Notesapi-259727482No ratings yet
- Biology Midterm ReviewDocument19 pagesBiology Midterm ReviewC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- What Makes Animal Cells DifferentDocument14 pagesWhat Makes Animal Cells DifferentGian Carlo Angon100% (1)
- Sciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioDocument56 pagesSciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioRETLAWNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Cell TheoryDocument12 pagesLAS 1 Cell TheoryJeremie CataggatanNo ratings yet
- Bio11 First LE ReviewerDocument9 pagesBio11 First LE ReviewerFREE ARTICLESNo ratings yet
- High School Biology: Comprehensive Content for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Comprehensive Content for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Stem Gbio1 Q1W1Document15 pagesStem Gbio1 Q1W1Sophia Mae MalayNo ratings yet
- Intro Zoology: Study Animal Life & DiversityDocument64 pagesIntro Zoology: Study Animal Life & DiversityKempetsNo ratings yet
- Effective Alternative Secondary Education Biology Module 1Document23 pagesEffective Alternative Secondary Education Biology Module 1Jenny GavinoNo ratings yet
- Stem Gbio1 Q1W1Document10 pagesStem Gbio1 Q1W1Yoi MiyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Life Biological Principles and The Science of ZoologyDocument64 pagesLecture 1. Life Biological Principles and The Science of ZoologyLeopoldo ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Bio Spring Break Answers TypedDocument6 pagesBio Spring Break Answers TypedAJ CootsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BioDocument33 pagesIntroduction To BioLyra Virgilia AbellanaNo ratings yet
- 3 - CellsDocument14 pages3 - Cellswhat is upNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Plant and Animal Cells: California Science Standard 5th Grade - Life SciencesDocument7 pagesLesson 5 Plant and Animal Cells: California Science Standard 5th Grade - Life SciencesLorieNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyDocument8 pagesMid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyAniya HarriottNo ratings yet
- Biology Midterm Study GuideDocument7 pagesBiology Midterm Study Guideapi-313911292No ratings yet
- SOL-Biology-Review-GuideDocument26 pagesSOL-Biology-Review-GuidehtyhongNo ratings yet
- Deeper Life High School Biology NotesDocument78 pagesDeeper Life High School Biology NotesEmmanuel Eyo100% (4)
- Biology GuideDocument14 pagesBiology GuideTania QuintanarNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 LECTURE NOTES - Doc..bakDocument39 pagesBIO 101 LECTURE NOTES - Doc..bakcurbelcurbelNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Intro BiosciDocument57 pagesLec 1 - Intro BiosciKristine VailNo ratings yet
- Bio Long NoteDocument12 pagesBio Long Notejacob guerreroNo ratings yet
- Studyguide AnswerkeyDocument23 pagesStudyguide Answerkeyapi-237676607No ratings yet
- L1. Exploring Life-2024Document39 pagesL1. Exploring Life-2024Cedric HastingsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bio Ni HaydeeDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Bio Ni Haydeesheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- BIO IGCSE NOTES - Copy-1Document9 pagesBIO IGCSE NOTES - Copy-1diegocmakoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Module1Document12 pagesBiochem Module1ShannNo ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument44 pagesAll About CellsRizahNo ratings yet
- Biology: 1rst PartialDocument18 pagesBiology: 1rst PartialValter NúñezNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes.Document263 pagesBiology Notes.Kelvin PhillipNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar Biology Department IntroductionDocument238 pagesUniversity of Gondar Biology Department IntroductionAlemayehu MelkamuuNo ratings yet
- Scope of Biology and Scientific MethodDocument63 pagesScope of Biology and Scientific MethodFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision: Key Terms and ConceptsDocument5 pagesBiology Revision: Key Terms and ConceptsroseNo ratings yet
- Cellular StructureDocument6 pagesCellular StructureVela STEM Naron, Claire KylaNo ratings yet
- Everything you need to know about SPM Biology cell structureDocument15 pagesEverything you need to know about SPM Biology cell structureCahaya Ainie100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science For Grade 7 - Animal and PlantDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science For Grade 7 - Animal and PlantKresha LluismaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 0610iDocument17 pagesBIOLOGY 0610imimoakal24No ratings yet
- Study Guide HomeostasisDocument5 pagesStudy Guide Homeostasisgmanb5100% (1)
- Newly Edited G Biology 10-12Document197 pagesNewly Edited G Biology 10-12Kennedy BwalyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biology Exploring LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Biology Exploring Lifemzunl25476No ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument45 pagesBIOLOGYBenmashour BiaoNo ratings yet
- GED23 (Life Science) PDFDocument25 pagesGED23 (Life Science) PDFtahireslNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesDifferences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCherrina AguilaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Introduction To Biology: by Dr. Navaid SiddiquiDocument114 pagesIntroduction To Biology: by Dr. Navaid SiddiquiSyeda Warisha AmirNo ratings yet
- Intro To Cells 2017Document38 pagesIntro To Cells 2017YHTAK1792No ratings yet
- BIO 110: Intro to BiologyDocument31 pagesBIO 110: Intro to BiologyRag DonovanNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions TableDocument5 pagesCell Parts and Functions TableNyk Khow50% (2)
- Science: How Do We Define Science?: ScientiaDocument9 pagesScience: How Do We Define Science?: ScientiaAlice Del Rosario CabanaNo ratings yet
- General Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Document14 pagesGeneral Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Kerala MekuriyaNo ratings yet
- General Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Document14 pagesGeneral Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Kerala MekuriyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture 1 & 2 Sem I 2011-2012 Introduction To Cell Biology, Cell As The Basic Unit of Life SPINDocument121 pagesCell Biology Lecture 1 & 2 Sem I 2011-2012 Introduction To Cell Biology, Cell As The Basic Unit of Life SPINPrimo Arc100% (1)
- Module in Levels of Biological Organization and Cells: Program StandardDocument26 pagesModule in Levels of Biological Organization and Cells: Program StandardggggangNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Content: - SL and HLDocument71 pagesSyllabus Content: - SL and HLMeryemNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - GenBio 1-Week 1 (23-24)Document41 pagesQuarter 1 - GenBio 1-Week 1 (23-24)Adrienne Skyle SibalaNo ratings yet
- Bio Ist Year McqsDocument244 pagesBio Ist Year Mcqssaraghyuji8No ratings yet
- Animal Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell OrganellesakhileshmoneyNo ratings yet
- Cancers Natural Enemy 06!01!2013Document252 pagesCancers Natural Enemy 06!01!2013straw man100% (3)
- I. Introduction To PathophysiologyDocument23 pagesI. Introduction To PathophysiologyGalina DobrostomatNo ratings yet
- B1 1 Key Concepts in Biology QsDocument22 pagesB1 1 Key Concepts in Biology QsAqeel Abbas NohayNo ratings yet
- LTSC Handbook 2015Document143 pagesLTSC Handbook 2015gwzglNo ratings yet
- Brain-Aging-By Ray PeatDocument2 pagesBrain-Aging-By Ray PeatIURY GABRIEL DUARTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Biology: Exploring LifeDocument35 pagesBiology: Exploring LifesaikhueyNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: Five Kingdom ClassificationDocument10 pagesBiology Project: Five Kingdom ClassificationKINSHUK SINGHNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology quiz questionsDocument13 pagesCell Biology quiz questionskahfiNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasmic inheritance-BIO-231-FKDocument9 pagesCytoplasmic inheritance-BIO-231-FKmalik husnainNo ratings yet
- PBIO211Lec FINALS 1Document26 pagesPBIO211Lec FINALS 1richard respetoNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 2Document6 pagesLab Act 2Bastin ChamNo ratings yet
- Radiobiology 5Document31 pagesRadiobiology 5joaNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity: Unit 10Document29 pagesBiological Diversity: Unit 10rbyq9No ratings yet
- BrockBiologyMicroorganisms 16ed Chp1 2 (57-75)Document19 pagesBrockBiologyMicroorganisms 16ed Chp1 2 (57-75)Bruno RamírezNo ratings yet
- Summary 7ADocument2 pagesSummary 7ATHJNo ratings yet
- Total 1 MarkDocument43 pagesTotal 1 MarkdhNo ratings yet
- No 7 TBT Cell Phone SafetyDocument2 pagesNo 7 TBT Cell Phone Safetypruncu.alianmNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: IGCSE BiologyDocument20 pagesBiological Molecules: IGCSE BiologyRahmat PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That Followapi-242868690100% (1)
- For SchoolDocument1 pageFor Schoolapi-252841138No ratings yet
- Science GK Pack (1 - 8)Document43 pagesScience GK Pack (1 - 8)Ishrat KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Prokaryotic Vs Euksryotic CellDocument26 pagesWeek 2 - Prokaryotic Vs Euksryotic CellKimberly Izza AlientoNo ratings yet
- Blank QuizDocument6 pagesBlank Quizrohan keshriNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Cell Wallpdf 2021 04 14 06 00 56Document33 pagesUnit1 Cell Wallpdf 2021 04 14 06 00 56selestine salemaNo ratings yet
- NTSE STAGE 2 2020-21 Sat Question Paper: FiitjeeDocument22 pagesNTSE STAGE 2 2020-21 Sat Question Paper: FiitjeeKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Listado Libros SpringerDocument479 pagesListado Libros SpringerMichael Cano LombardoNo ratings yet
- f3 Endterm 2 Smartgrade Exams-1Document233 pagesf3 Endterm 2 Smartgrade Exams-1VinnyNo ratings yet
- 2015 ESMO Handbook Translational ResearchDocument147 pages2015 ESMO Handbook Translational ResearchTonette PunjabiNo ratings yet