Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inverse Function
Uploaded by
Meilisa MeilisaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inverse Function
Uploaded by
Meilisa MeilisaCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
6 Inverse of a Function
Essential Question How can you sketch the graph of the inverse of
a function?
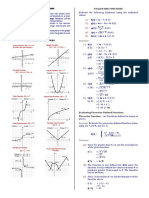
Graphing Functions and Their Inverses
Work with a partner. Each pair of functions are inverses of each other. Use a
graphing calculator to graph f and g in the same viewing window. What do you notice
about the graphs?
CONSTRUCTING
VIABLE a. f(x) = 4x + 3 b. f(x) = x3 + 1
ARGUMENTS x−3 3—
g(x) = — g(x) = √x − 1
4
To be proficient in math,
you need to reason — —
c. f (x) = √ x − 3 d. f (x) = −√ x + 2
inductively and make a
plausible argument. g(x) = x2 + 3, x ≥ 0 g(x) = (2 − x)2, x ≤ 2
Sketching Graphs of Inverse Functions
Work with a partner. Use the graph of f to sketch the graph of g, the inverse function
of f, on the same set of coordinate axes. Explain your reasoning.
a. y b. y y=x
8 8
4 y=x 4
y = f(x)
−8 −4 4 8 x −8 −4 4 8 x
−4
y = f(x)
−8 −8
c. y d. y
8 8
y = f(x) 4 4
y=x y = f(x) y=x
−8 −4 4 8 x −8 −4 4 8 x
−4 −4
−8 −8
Communicate Your Answer
3. How can you sketch the graph of the inverse of a function?
4. In Exploration 1, what do you notice about the relationship between the equations
of f and g? Use your answer to find g, the inverse function of
f(x) = 2x − 3.
Use a graph to check your answer.
Section 4.6 Inverse of a Function 231
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 231 1/30/15 3:36 PM
4.6 Lesson What You Will Learn
Explore inverses of functions.
Find and verify inverses of nonlinear functions.
Core Vocabul
Vocabulary
larry Solve real-life problems using inverse functions.
inverse functions, p. 233
Previous Exploring Inverses of Functions
input You have used given inputs to find corresponding outputs of y = f (x) for various types
output of functions. You have also used given outputs to find corresponding inputs. Now you
inverse operations will solve equations of the form y = f (x) for x to obtain a general formula for finding
reflection the input given a specific output of a function f.
line of reflection
Writing a Formula for the Input of a Function
Let f(x) = 2x + 3.
a. Solve y = f(x) for x.
b. Find the input when the output is −7.
SOLUTION
a. y = 2x + 3 Set y equal to f(x).
y − 3 = 2x Subtract 3 from each side.
y−3
—=x Divide each side by 2.
2
b. Find the input when y = −7.
−7 − 3
x=— Substitute −7 for y.
Check 2
f(−5) = 2(−5) + 3 −10
=— Subtract.
2
= −10 + 3
= −7 ✓ = −5 Divide.
So, the input is −5 when the output is −7.
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
Solve y = f(x) for x. Then find the input(s) when the output is 2.
1. f(x) = x − 2 2. f(x) = 2x2 3. f(x) = −x3 + 3
In Example 1, notice the steps involved after substituting for x in y = 2x + 3 and after
y−3
substituting for y in x = —.
2
y−3
y = 2x + 3 x=—
2
Step 1 Multiply by 2. Step 1 Subtract 3.
Step 2 Add 3. Step 2 Divide by 2.
inverse operations
in the reverse order
232 Chapter 4 Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 232 1/30/15 3:36 PM
Notice that these steps undo each other. Functions that undo each other are called
inverse functions. In Example 1, you can use the equation solved for x to write the
UNDERSTANDING inverse of f by switching the roles of x and y.
MATHEMATICAL f(x) = 2x + 3 original function
x−3
g(x) = — inverse function
TERMS 2
The term inverse functions Because inverse functions interchange the input and output values of the original
does not refer to a new function, the domain and range are also interchanged.
type of function. Rather, Original function: f(x) = 2x + 3 y
it describes any pair of f
functions that are inverses. x −2 −1 0 1 2 6
y −1 1 3 5 7 4
y=x
x−3
Inverse function: g(x) = — g
2
−4 4 6 x
x −1 1 3 5 7
y −2 −1 0 1 2
−4
The graph of an inverse function is a reflection of the graph of the original function.
The line of reflection is y = x. To find the inverse of a function algebraically, switch
the roles of x and y, and then solve for y.
Finding the Inverse of a Linear Function
Find the inverse of f (x) = 3x − 1.
SOLUTION
Method 1 Use inverse operations in the reverse order.
f(x) = 3x − 1 Multiply the input x by 3 and then subtract 1.
To find the inverse, apply inverse operations in the reverse order.
x+1
g(x) = — Add 1 to the input x and then divide by 3.
Check 3
6 x+1 1 1
The inverse of f is g(x) = —, or g(x) = —x + —.
f 3 3 3
g
−9 9
Method 2 Set y equal to f(x). Switch the roles of x and y and solve for y.
y = 3x − 1 Set y equal to f(x).
−6 x = 3y − 1 Switch x and y.
The graph of g appears to be a x + 1 = 3y Add 1 to each side.
reflection of the graph of f in the
x+1
line y = x. ✓ —=y
3
Divide each side by 3.
x+1 1 1
The inverse of f is g(x) = —, or g(x) = — x + —.
3 3 3
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
Find the inverse of the function. Then graph the function and its inverse.
1
4. f(x) = 2x 5. f(x) = −x + 1 6. f(x) = —3 x − 2
Section 4.6 Inverse of a Function 233
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 233 1/30/15 3:36 PM
Inverses of Nonlinear Functions
In the previous examples, the inverses of the linear functions were also functions.
However, inverses are not always functions. The graphs of f(x) = x2 and f(x) = x3 are
shown along with their reflections in the line y = x. Notice that the inverse of f(x) = x3
is a function, but the inverse of f (x) = x2 is not a function.
y y
4 4
g(x) = 3 x
2 2
f(x) = x2
−4 −2 2 4 x −4 −2 2 4 x
−2 f(x) = x3
x = y2
−4 −4
When the domain of f (x) = x2 is restricted to only nonnegative real numbers, the
inverse of f is a function.
Finding the Inverse of a Quadratic Function
Find the inverse of f(x) = x2, x ≥ 0. Then graph the function and its inverse.
SOLUTION
f(x) = x2 Write the original function.
y = x2 Set y equal to f(x).
x = y2 Switch x and y.
—
f(x) = x2,
±√ x = y Take square root of each side. x≥0
STUDY TIP y
6
If the domain of f were The domain of f is restricted to nonnegative
restricted to x ≤ 0, then values of x. So, the range of the inverse must 4 g(x) = x
the inverse would be also be restricted to nonnegative values.
—
g(x) = −√x . —
2
So, the inverse of f is g(x) = √ x .
2 4 6x
You can use the graph of a function f to determine whether the inverse of f is a function
by applying the horizontal line test.
Core Concept
Horizontal Line Test
The inverse of a function f is also a function if and only if no horizontal line
intersects the graph of f more than once.
Inverse is a function Inverse is not a function
y f y f
x x
234 Chapter 4 Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 234 1/30/15 3:36 PM
Finding the Inverse of a Cubic Function
Consider the function f (x) = 2x3 + 1. Determine whether the inverse of f is a function.
Then find the inverse.
SOLUTION
Graph the function f. Notice that no horizontal line
f(x) = 2x3 + 1
intersects the graph more than once. So, the inverse
y
of f is a function. Find the inverse. 4
y = 2x3 + 1 Set y equal to f(x).
Check 2
x= 2y3 +1 Switch x and y.
5
f x − 1 = 2y3 Subtract 1 from each side. −2 2 x
g x−1
— = y3 Divide each side by 2.
−5 7 2
√x −2 1 = y
—
3
— Take cube root of each side.
−3
√x −2 1 .
—
So, the inverse of f is g(x) = 3
—
Finding the Inverse of a Radical Function
—
Consider the function f (x) = 2√ x − 3 . Determine whether the inverse of f is a
function. Then find the inverse.
SOLUTION
Graph the function f. Notice that no horizontal line y
8
intersects the graph more than once. So, the inverse
of f is a function. Find the inverse.
6 f(x) = 2 x − 3
—
y = 2√ x − 3 Set y equal to f(x).
4
—
x = 2√ y − 3 Switch x and y.
— 2 2
x2 = ( 2√ y − 3 ) Square each side.
Check
x2 = 4(y − 3) Simplify. 2 4 6 8 x
9
g x2 = 4y − 12 Distributive Property
f x2 + 12 = 4y Add 12 to each side.
1
—4 x2 +3=y Divide each side by 4.
−1 14
−1 Because the range of f is y ≥ 0, the domain of the inverse must be restricted to x ≥ 0.
So, the inverse of f is g(x) = —14 x2 + 3, where x ≥ 0.
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
Find the inverse of the function. Then graph the function and its inverse.
—
7. f(x) = −x2, x ≤ 0 8. f(x) = −x3 + 4 9. f(x) = √ x + 2
Section 4.6 Inverse of a Function 235
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 235 1/30/15 3:36 PM
Let f and g be inverse functions. If f (a) = b, then g(b) = a. So, in general,
f (g(x)) = x and g( f (x)) = x.
REASONING
ABSTRACTLY Verifying Functions Are Inverses
Inverse functions undo x+1
Verify that f (x) = 3x − 1 and g(x) = — are inverse functions.
each other. So, when you 3
evaluate a function for a SOLUTION
specific input, and then
evaluate its inverse using Step 1 Show that f (g(x)) = x. Step 2 Show that g( f (x)) = x.
the output, you obtain the
x+1 g( f(x)) = g(3x − 1)
original input.
( )
f (g(x)) = f —
3
3x − 1 + 1
x+1 =—
= 3(
3 )
— −1 3
3x
=—
=x+1−1 3
=x ✓ =x ✓
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
Determine whether the functions are inverse functions.
3—
10. f(x) = x + 5, g(x) = x − 5 11. f(x) = 8x3, g(x) = √ 2x
Solving Real-Life Problems
In many real-life problems, formulas contain meaningful variables, such as the radius r
in the formula for the surface area S of a sphere, S = 4πr2. In this situation, switching
the variables to find the inverse would create confusion by switching the meanings of S
and r. So, when finding the inverse, solve for r without switching the variables.
Solving a Multi-Step Problem
Find the inverse of the function that represents the surface area of a sphere, S = 4πr2.
Then find the radius of a sphere that has a surface area of 100π square feet.
SOLUTION
Step 1 Find the inverse of the function. Step 2 Evaluate the inverse when
S = 100π.
S = 4πr2
√
—
S 100π
— = r2 r= —
4π 4π
√4Sπ = r
—
The radius r must be positive, so —
— = √25 = 5
disregard the negative square root.
The radius of the sphere is 5 feet.
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
12. The distance d (in meters) that a dropped object falls in t seconds on Earth is
represented by d = 4.9t 2. Find the inverse of the function. How long does it take
an object to fall 50 meters?
236 Chapter 4 Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 236 1/30/15 3:36 PM
4.6 Exercises Dynamic Solutions available at BigIdeasMath.com
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
1. VOCABULARY In your own words, state the definition of inverse functions.
2. WRITING Explain how to determine whether the inverse of a function is also a function.
3. COMPLETE THE SENTENCE Functions f and g are inverses of each other provided that f(g(x)) = ____ and
g( f(x)) = ____.
4. DIFFERENT WORDS, SAME QUESTION Which is different? Find “both” answers.
Let f(x) = 5x − 2. Solve y = f(x) for x and then Write an equation that represents a reflection of
switch the roles of x and y. the graph of f(x) = 5x − 2 in the x-axis.
Write an equation that represents a reflection of
the graph of f(x) = 5x − 2 in the line y = x. Find the inverse of f (x) = 5x − 2.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 5–12, solve y = f(x) for x. Then find the 22. REASONING Determine whether each pair of
input(s) when the output is −3. (See Example 1.) functions f and g are inverses. Explain your reasoning.
5. f(x) = 3x + 5 6. f(x) = −7x − 2 a.
x −2 −1 0 1 2
1
7. f(x) = —2 x − 3
2
8. f(x) = −—3 x + 1 f(x) −2 1 4 7 10
9. f(x) = 3x3 10. f(x) = 2x 4 − 5
x −2 1 4 7 10
11. f(x) = (x − 2)2 − 7 g(x) −2 −1 0 1 2
12. f(x) = (x − 5)3 − 1 b.
x 2 3 4 5 6
In Exercises 13–20, find the inverse of the function. Then f(x) 8 6 4 2 0
graph the function and its inverse. (See Example 2.)
13. f(x) = 6x 14. f(x) = −3x x 2 3 4 5 6
15. f(x) = −2x + 5 16. f(x) = 6x − 3 g(x) −8 −6 −4 −2 0
1 1
17. f(x) = −—2 x + 4 18. f(x) = —3 x − 1 c.
x −4 −2 0 2 4
2 1 4 1
19. f(x) = —3 x − —3 20. f(x) = −—5 x + —5 f(x) 2 10 18 26 34
21. COMPARING METHODS Find the inverse of the
function f(x) = −3x + 4 by switching the roles of x x −4 −2 0 2 4
and y and solving for y. Then find the inverse of the
1 1 1 1 1
function f by using inverse operations in the reverse g(x) —2 —
10
—
18
—
26
—
34
order. Which method do you prefer? Explain.
Section 4.6 Inverse of a Function 237
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 237 1/30/15 3:36 PM
In Exercises 23–28, find the inverse of the function. Then 3—
39. f(x) = 2√ x − 5 40. f(x) = 2x2 − 5
graph the function and its inverse. (See Example 3.)
23. f(x) = 4x2, x ≤ 0 24. f(x) = 9x2, x ≤ 0 41. f(x) = x4 + 2 42. f(x) = 2x3 − 5
√2x 3+ 4
—
3—
25. f(x) = (x − 3)3 26. f(x) = (x + 4)3 43. f(x) = 3√ x + 1 44. f(x) = − 3 —
27. f(x) = 2x4, x ≥ 0 28. f(x) = −x6, x ≥ 0
f(x) = −3√
—
1 4x − 7
45. f(x) = — x5 46. —
ERROR ANALYSIS In Exercises 29 and 30, describe and 2 3
correct the error in finding the inverse of the function.
47. WRITING EQUATIONS What is the inverse of the
✗
29. function whose graph is shown?
f(x) = −x + 3
3
y = −x + 3 A g(x) = —2 x − 6
○ y
−x = y + 3 3
B g(x) = —2 x + 6
○ 2 4 6 x
−x − 3 = y
−2
2
C g(x) = —3 x − 6
○
✗
30.
f(x) = —17 x 2, x ≥ 0 2
D g(x) = —3 x + 12
○
y = —17 x 2
x = —17 y 2 48. WRITING EQUATIONS What is the inverse of
1
f(x) = −— 3
64 x ?
7x = y 2
— 3—
± √7x = y A g(x) = −4x3
○ B g(x) = 4√
○ x
3— 3—
C g(x) = −4√
○ x D g(x) = √−4x
○
USING TOOLS In Exercises 31–34, use the graph to In Exercises 49–52, determine whether the functions are
determine whether the inverse of f is a function. Explain inverse functions. (See Example 6.)
your reasoning.
x
31. 10 32. 10
49. f(x) = 2x − 9, g(x) = — + 9
2
f x−3
f 50. f(x) = —, g(x) = 4x + 3
4
−5
√x +5 9 , g(x) = 5x − 9
8 —
51. f(x) = 5
— 5
−5 5
−1 −8
x+4
f(x) = 7x − 4, g(x) = (
7 )
3/2
52. 3/2 —
33. 6 34. 6
f f 53. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS The maximum hull
−5 5 −5 5 speed v (in knots) of a boat with a displacement hull
—
can be approximated by v = 1.34√ℓ, whereℓ is the
waterline length (in feet) of the boat. Find the inverse
function. What waterline length is needed to achieve a
−10 −8
maximum speed of 7.5 knots? (See Example 7.)
In Exercises 35–46, determine whether the inverse
of f is a function. Then find the inverse.
(See Examples 4 and 5.)
35. f(x) = x3 − 1 36. f(x) = −x3 + 3 Waterline length
— —
37. f(x) = √ x + 4 38. f(x) = √ x − 6
238 Chapter 4 Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 238 1/30/15 3:36 PM
54. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS Elastic bands 59. REASONING You and a friend are playing a number-
can be used for exercising to provide a range of guessing game. You ask your friend to think of a
resistance. The resistance R (in pounds) of a band positive number, square the number, multiply the
can be modeled by R = —38 L − 5, where L is the total result by 2, and then add 3. Your friend’s final answer
length (in inches) of the stretched band. Find the is 53. What was the original number chosen? Justify
inverse function. What length of the stretched band your answer.
provides 19 pounds of resistance?
60. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that
unstretched every quadratic function whose domain is restricted
to nonnegative values has an inverse function. Is your
friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
61. PROBLEM SOLVING When calibrating a spring scale,
you need to know how far the spring stretches for
stretched various weights. Hooke’s Law states that the length a
spring stretches is proportional
to the weight attached spring with
to it. A model for one unweighted weight
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS In Exercises 55–58, match scale isℓ = 0.5w + 3, spring attached
the graph of the function with the graph of its inverse. whereℓ is the total
length (in inches) of the
55. 56. 3
stretched spring and w
y y 0.5w
is the weight (in pounds)
2 2 of the object.
a. Find the inverse
−4 −2 2 4x −4 2 4x
function. Describe
−2 −2 what it represents. Not drawn to scale
b. You place a melon on the scale, and the spring
57. 58. stretches to a total length of 5.5 inches. Determine
y y the weight of the melon.
2 c. Verify that the functionℓ = 0.5w + 3 and the
inverse model in part (a) are inverse functions.
−4 −2 2 4x −4 −2 2 4x
−2 −2 62. THOUGHT PROVOKING Do functions of the form
y = x m/n, where m and n are positive integers, have
inverse functions? Justify your answer with examples.
A. B.
y y 63. PROBLEM SOLVING At the start of a dog sled race
2 2
in Anchorage, Alaska, the temperature was 5°C. By
the end of the race, the
temperature was −10°C.
−4 −2 4x −2 2 4x
The formula for converting
−2 −2 temperatures from degrees
Fahrenheit F to degrees
Celsius C is C = —59 (F − 32).
C. D.
y y a. Find the inverse function.
Describe what it represents.
2 2
x b. Find the Fahrenheit temperatures at the start and
−4 −2 2 −4 −2 2 4x end of the race.
−2 c. Use a graphing calculator to graph the original
function and its inverse. Find the temperature that
is the same on both temperature scales.
Section 4.6 Inverse of a Function 239
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 239 1/30/15 3:36 PM
64. PROBLEM SOLVING The surface area A (in square 69. DRAWING CONCLUSIONS Determine whether the
meters) of a person with a mass of 60 kilograms can statement is true or false. Explain your reasoning.
be approximated by A = 0.2195h 0.3964, where h is the
a. If f(x) = x n and n is a positive even integer, then
height (in centimeters) of the person.
the inverse of f is a function.
a. Find the inverse function. Then estimate the height
b. If f(x) = x n and n is a positive odd integer, then
of a 60-kilogram person who has a body surface
the inverse of f is a function.
area of 1.6 square meters.
b. Verify that function A and the inverse model in
part (a) are inverse functions. 70. HOW DO YOU SEE IT? The graph of the function f
is shown. Name three points that lie on the graph of
USING STRUCTURE In Exercises 65–68, match the the inverse of f. Explain your reasoning.
function with the graph of its inverse. y
4
3—
65. f(x) = √ x − 4
2
3— f
66. f(x) = √ x + 4
−4 −2 4x
—
67. f(x) = √ x + 1 − 3 −2
—
68. f(x) = √ x − 1 + 3
A. y B. y
71. ABSTRACT REASONING Show that the inverse of any
linear function f (x) = mx + b, where m ≠ 0, is also
2 a linear function. Identify the slope and y-intercept of
−8 4x
the graph of the inverse function in terms of m and b.
−4
2 x
72. CRITICAL THINKING Consider the function f(x) = −x.
C. y D. y a. Graph f(x) = −x and explain why it is its own
inverse. Also, verify that f(x) = −x is its own
4
−2 2 x inverse algebraically.
−2 b. Graph other linear functions that are their own
−4 4 8x
inverses. Write equations of the lines you graphed.
−4
c. Use your results from part (b) to write a general
equation describing the family of linear functions
that are their own inverses.
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Reviewing what you learned in previous grades and lessons
Simplify the expression. Write your answer using only positive exponents. (Skills Review Handbook)
4
73. (−3)−3 74. 23 ⋅2 2 75. —3
45
4
76. ( 23 )
—
Describe the x-values for which the function is increasing, decreasing, positive,
and negative. (Section 3.1)
77. y 78. y 79. y
3
4
−2 4x −3 −1 1 3x 4 x
−2 1 3 4 −4
y= x − x
y = 2x2 − 4x −3 3 3
1 25
y = −16 x3 + 16
x
240 Chapter 4 Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
Int_Math3_PE_0406.indd 240 1/30/15 3:36 PM
You might also like
- Alg1 08 Student JournalDocument31 pagesAlg1 08 Student Journalapi-355730898No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AssignmentDocument5 pagesChapter 6 AssignmentPNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics First QuarterDocument3 pagesGeneral Mathematics First QuarterAngelica Manalo PerezNo ratings yet
- Kenyatta Uni Calculus IIDocument129 pagesKenyatta Uni Calculus IIbryan elddie100% (1)
- 9387 Matrices MCQ PDFDocument25 pages9387 Matrices MCQ PDFNikhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Johanna Martinez - Int 3 4.6 ExplorationDocument2 pagesKami Export - Johanna Martinez - Int 3 4.6 ExplorationJohanna MartinezNo ratings yet
- BI Alg2 CH01 Extra PracticeDocument8 pagesBI Alg2 CH01 Extra PracticedeayrackNo ratings yet
- Inverse Functions ExplainedDocument3 pagesInverse Functions ExplainedAranjit DaidNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions: Essential QuestionDocument10 pages2.2 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions: Essential QuestionSaad KhalidNo ratings yet
- Aga A1 1003 ApDocument1 pageAga A1 1003 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- Aga A1 0605 ApDocument1 pageAga A1 0605 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- College Algebra Exam 3 AnswersDocument9 pagesCollege Algebra Exam 3 AnswersPratik PalwaiNo ratings yet
- Inverse and CompositeDocument27 pagesInverse and CompositeBaur TalipNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Transformations of Linear and Absolute Value Functions: Essential QuestionDocument8 pages1.2 Transformations of Linear and Absolute Value Functions: Essential QuestionAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- fl20 Algebra1 Ipe 10Document42 pagesfl20 Algebra1 Ipe 10Sayed MikoNo ratings yet
- Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDocument66 pagesGraphing Polynomial FunctionsThitikorn MetheevuttikornNo ratings yet
- Aga A2 0102 ApDocument1 pageAga A2 0102 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Test Review and SolutionsDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Test Review and SolutionsRCNo ratings yet
- Domain and Range of Inverse Functions PostingDocument21 pagesDomain and Range of Inverse Functions PostingmnemoxeneNo ratings yet
- 12 - Rational Functions 01Document2 pages12 - Rational Functions 01Joshua Dwayne BarnesNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument52 pagesCombinepdfSoby K ThomasNo ratings yet
- Aga A1 0303 ApDocument1 pageAga A1 0303 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- Ch4wbanswers PDFDocument36 pagesCh4wbanswers PDFHanady Ghoneim100% (1)
- Inverse FunctionsDocument20 pagesInverse FunctionsAce CruzNo ratings yet
- MC Ty Linearfns 2009 1Document7 pagesMC Ty Linearfns 2009 1Hannan SabranNo ratings yet
- Laboratory MathsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Mathsshahmeer sultanNo ratings yet
- Bks MaaSL 0402 ws00 XxaannDocument4 pagesBks MaaSL 0402 ws00 Xxaannneraxew739No ratings yet
- Polynomial FunctionsDocument16 pagesPolynomial FunctionsLoremIpsumNo ratings yet
- Edited Las Shs Genmath Cruz1Document7 pagesEdited Las Shs Genmath Cruz1Arboleda Hazel CruzNo ratings yet
- 9781009341837ans_438-481Document44 pages9781009341837ans_438-481aliispowerNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionsDocument34 pagesRational FunctionsJerson HEGINANo ratings yet
- 0661 Polynomial FunctionsDocument11 pages0661 Polynomial Functionsvishalchandola98No ratings yet
- g11 - Algebra of FunctionsDocument2 pagesg11 - Algebra of FunctionsJessie James PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Math 111 Section 3.1 PacketDocument8 pagesMath 111 Section 3.1 PacketLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Graphs of standard functions visualizedDocument12 pagesGraphs of standard functions visualizedghazi membersNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2 Exponential Function of The Form A Greater Than 0.Document3 pagesLesson 4.2 Exponential Function of The Form A Greater Than 0.Midoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manual DownloadDocument190 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manual DownloadEarl Sherrow100% (21)
- General Mathematics: Name: - Score: - Section: - DateDocument4 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Name: - Score: - Section: - DateDE ASIS, JOSHUA Y.No ratings yet
- Operations On FunctionsDocument6 pagesOperations On FunctionsBeta MathematicaNo ratings yet
- E - Quadratic Equations - Worksheet - 4 - Review - AllDocument11 pagesE - Quadratic Equations - Worksheet - 4 - Review - AlletelNo ratings yet
- Inverses of Functions: Section 2.6Document32 pagesInverses of Functions: Section 2.6Ahmed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Aga A1 0504 ApDocument1 pageAga A1 0504 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- MATH 1316 Trigonometry Prerequisite ReviewDocument4 pagesMATH 1316 Trigonometry Prerequisite ReviewAnaNo ratings yet
- 4 Computing Derivatives, Product and Quotient Rules: Math 180 WorksheetsDocument3 pages4 Computing Derivatives, Product and Quotient Rules: Math 180 WorksheetsDeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Function InversesDocument5 pages01 - Function InversesFloribel OleNo ratings yet
- 01 - Function InversesDocument5 pages01 - Function InversesFloribel OleNo ratings yet
- Model exponential and logarithmic functionsDocument5 pagesModel exponential and logarithmic functionsAnoop SreedharNo ratings yet
- Inverse FunctionDocument17 pagesInverse FunctionTANG PEI PEI100% (4)
- TB 2.1 Pgs (47-54)Document8 pagesTB 2.1 Pgs (47-54)Harsh NagoudaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4A - Inverses of FunctionsDocument41 pagesLesson 4A - Inverses of FunctionsNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Graphs: Inflection PointsDocument36 pagesGraphs: Inflection PointsSamarjeet SalujaNo ratings yet
- 02 IP01+Graphing+PiecewiseDocument3 pages02 IP01+Graphing+Piecewisetankumar27No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus inverse functions worksheetDocument2 pagesPre-Calculus inverse functions worksheetHamza YounusNo ratings yet
- Even OddDocument5 pagesEven OddKeizsha LeymaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 PracticeDocument3 pagesTest 1 Practice樊满满No ratings yet
- LIMITSDocument6 pagesLIMITSMia CalimagNo ratings yet
- Cubic Graph Good BreakdownDocument11 pagesCubic Graph Good BreakdownMatthewHarveyNo ratings yet
- Functions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterDocument9 pagesFunctions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterHussein JaberNo ratings yet
- 02 Linear An Quadratic 0001Document1 page02 Linear An Quadratic 0001Arantxa QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- MATHALGIIBU12Quadratic_FunctionsDocument22 pagesMATHALGIIBU12Quadratic_FunctionsMbocaBentoNo ratings yet
- Training Course 6 Quadratic Functions and TransformationsDocument25 pagesTraining Course 6 Quadratic Functions and TransformationsRichardoBrandonNo ratings yet
- Inverse FunctionsDocument12 pagesInverse FunctionsJhowie RoasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Summarycha chaNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Graphing Rational Functions (Full)Document4 pagesGraphing Rational Functions (Full)Denise SorianoNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument11 pages8 PDFJohan TobingNo ratings yet
- Ma 204 IitbDocument21 pagesMa 204 IitbsiddharthballalNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning TreeDocument17 pagesMinimum Spanning TreeGomala MookanNo ratings yet
- 09 Hands-On Activity 1 - Arg: Name: Maryruim C. Canete Bscpe 301Document3 pages09 Hands-On Activity 1 - Arg: Name: Maryruim C. Canete Bscpe 301MingNo ratings yet
- Determinants (CTD) : Evaluating Determinants by Row Reduction (Section 2.2)Document9 pagesDeterminants (CTD) : Evaluating Determinants by Row Reduction (Section 2.2)asahNo ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument10 pagesNumerical DifferentiationAmlan ShomeNo ratings yet
- Vector Matrix Tensor ReviewDocument13 pagesVector Matrix Tensor ReviewmuradbashirNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Linear TransformationsDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Linear TransformationsMathaFuckaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document9 pagesChapter 24Shubham PardeshiNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument13 pagesPresentationnepalamritNo ratings yet
- Continuity Exe SheetDocument31 pagesContinuity Exe SheetSarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- MAT2691 Assignment 02-2022-S2Document12 pagesMAT2691 Assignment 02-2022-S2Carole-ann de BeerNo ratings yet
- LectureWeek6-1 31.03.2023Document86 pagesLectureWeek6-1 31.03.2023SULEYMAN anisNo ratings yet
- MAT377 - Combinatorial Mathematics: Stefan H. M. Van ZwamDocument156 pagesMAT377 - Combinatorial Mathematics: Stefan H. M. Van ZwamPerry01No ratings yet
- Mock Olympiad Solutions - 2014 Winter CampDocument4 pagesMock Olympiad Solutions - 2014 Winter CampAltananyNo ratings yet
- Newton's Divided Difference FormulaDocument6 pagesNewton's Divided Difference FormulamengelhuNo ratings yet
- Test Review KeyDocument4 pagesTest Review Keyapi-262532023No ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations Analytical and Numerical MethodsDocument638 pagesPartial Differential Equations Analytical and Numerical MethodsWilson Moreno100% (2)
- Assignment 1 (MA-102)Document4 pagesAssignment 1 (MA-102)Dhruv SinghalNo ratings yet
- The Gronwall Inequality ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Gronwall Inequality ExplainedMuhammad Abdulloh MNo ratings yet
- Connectivity (Graph Theory) PDFDocument5 pagesConnectivity (Graph Theory) PDFmarsNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory and Its Applications in Power Systems - AreviewDocument4 pagesGraph Theory and Its Applications in Power Systems - AreviewHomeroOjedaNo ratings yet
- Mat 575Document6 pagesMat 575Hf HefneyNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Lecture SldiesDocument16 pagesReal Analysis Lecture Sldiesruchi21july100% (1)
- An Introduction To Petri NetsDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Petri NetsRenato Galois100% (1)