Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Liezel PadillaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Liezel PadillaCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamics
1st Law: Energy conserved, its form can be converted.
2nd Law: Energy can flow equilibrate.
3rd Law: “Driving force” for equilibration uniquely defined.
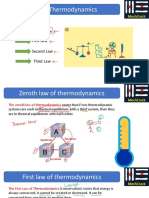
4th Law: Zeroth Law.
Zeroth Law should be named before the 3 Laws.
ABC should be equal with each other.
Applied
• Thermometer – as the temperature increases, the mercury
expands and increases in the tube
• 1st Law of Thermodynamics:
- Heat is a form of energy, and as what other forms of energy is subject to, it follows law of
conservation of energy.
Example:
Coal is a type of rock, but for scientists, coal is a form of energy when undergoes combustion
that creates electricity.
This Law applies in the Nuclear Powerplant.
• 2nd Law of Thermodynamics:
- Clasius Statement
It is impossible for any system in such way that the sole result would be the end.
- Kevin Planck Statement
It is impossible to devise a heat engine that takes heat from the hot reservoir ( Q H ) and
converts all the energy into useful external work without losing heat to the cold
reservoir ( Q C ).
- Entrophy Statement
High to Low
Perfect is Impossible
• 3rd Law of Thermodynamics:
- The entrophy of any crystalline substance at absolute zero will be equal to zero.
ABSOLUTE ZERO (1 KELVIN)
Sci-Vlog ( Form of Lecture)
1. Heat - energy that is transferred from one body to another as the result of a difference in
temperature.
2. Use of Heat - heat is used to cook food such as boiling water and frying eggs. When a lot of
heat is added, even metal will melt. In a car factory, heat is used to melt metal so that it can be
shaped to build cars.
3. Law of Heat - law of heat exchange states that the heat lost by a hot object is equal to the
heat gained by a cold object.
4. Everyday use of Heat - heat is used to generate electricity at a thermal power plant for our
daily lives.
You might also like
- 2.0 Basic Concepts On ThermodynamicsDocument17 pages2.0 Basic Concepts On ThermodynamicsLeo JohnNo ratings yet
- Presentation of ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesPresentation of Thermodynamicss18228230959No ratings yet
- 2020 ME1 Introduction Lecture 1 Draft June 25 LECTURE1Document16 pages2020 ME1 Introduction Lecture 1 Draft June 25 LECTURE1Natasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- Law of ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesLaw of ThermodynamicsOmar Faruk100% (1)
- Online WK 2 Session 1 - Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageOnline WK 2 Session 1 - Laws of Thermodynamicsgenx radzNo ratings yet
- Chap 8 ThermochemistryDocument58 pagesChap 8 ThermochemistryNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer-1Document22 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer-1Alhaj MassoudNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The RelationshipsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The Relationshipslarison09No ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageLaws of ThermodynamicsJane Marie GarciaNo ratings yet
- Section-7 Thermodynamic LawsDocument9 pagesSection-7 Thermodynamic LawsTaiga CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument6 pagesHeat and TemperatureJavontay StewartNo ratings yet
- 0 Thermal Physics 2009Document9 pages0 Thermal Physics 2009api-27085921No ratings yet
- Basic-Thermodynamics 1Document4 pagesBasic-Thermodynamics 1Kawie AñeroNo ratings yet
- Mret 101Document226 pagesMret 101Mohammad Hasibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Heat Work Temperature EnergyDocument2 pagesThermodynamics: Heat Work Temperature EnergyRima SadekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 ThermochemistryDocument24 pagesChapter 3.1 ThermochemistryHarry PablicoNo ratings yet
- The Four Laws of Thermodynamics-The Fundamental Principles ofDocument5 pagesThe Four Laws of Thermodynamics-The Fundamental Principles ofEnigma YTNo ratings yet
- Nature of Heat & Temperature 2022Document22 pagesNature of Heat & Temperature 2022Gabriella SteeleNo ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics PDFDocument325 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics PDFNaMatazuNo ratings yet
- Biophysics LectureDocument38 pagesBiophysics Lectureinfofact849No ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics by Hilary. D. BrewsterDocument325 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics by Hilary. D. BrewsterPitagoras MoraisNo ratings yet
- ENSC 14A - Chapter 1Document40 pagesENSC 14A - Chapter 1deusleanNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsmaruder.sllayerNo ratings yet
- MEFC0303-Report 01Document13 pagesMEFC0303-Report 01Jermain Liam EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics SRI RANJANIDocument14 pagesThermodynamics SRI RANJANIKiranshreeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesLesson 2 - ThermodynamicsElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Thermo HistoryDocument15 pagesThermo HistorySiegfred LaborteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Thermal Energy: What's Hot and What's NotDocument27 pagesChapter 12: Thermal Energy: What's Hot and What's Notkarina2227No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesThermodynamicspaopaoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoDreathfulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ThermochemistryDocument36 pagesChapter 7 ThermochemistryMuhammad IzuanNo ratings yet
- The Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesThe Laws of ThermodynamicsAhad AmerNo ratings yet
- Classical Thermodynamics of Phase Equilibria: Only With Systems of One ComponentDocument52 pagesClassical Thermodynamics of Phase Equilibria: Only With Systems of One ComponentthchouNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDocument46 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsMatthew ShieldsNo ratings yet
- Week3 Renewable Energy SourcesDocument20 pagesWeek3 Renewable Energy SourcesgeorgiadisgNo ratings yet
- Law's of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesLaw's of ThermodynamicsRoselyn BenavidezNo ratings yet
- Basicsofthermodynamics 151006214440 Lva1 App6891Document30 pagesBasicsofthermodynamics 151006214440 Lva1 App6891Shahdura Hammad ThauriNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic PrimcipleDocument35 pagesThermodynamic PrimcipleMahima tiwariNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesThermodynamicsfayaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- JJ207 Thermodynamic Topic 2 First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesJJ207 Thermodynamic Topic 2 First Law of ThermodynamicsAh Tiang50% (2)
- Laws of Thermodynamics: Dr. Kamla Rawat Jamia HamdardDocument9 pagesLaws of Thermodynamics: Dr. Kamla Rawat Jamia HamdardLauvNo ratings yet
- Introduction Thermal FluidDocument17 pagesIntroduction Thermal FluidshingkeongNo ratings yet
- თერმოდინამიკა 1Document34 pagesთერმოდინამიკა 1მარიამ ალავიძეNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Introduction To The Three Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamics: Introduction To The Three Laws of ThermodynamicsSangam Choudhary100% (1)
- BASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Lecture Notes 2 Part 1Document4 pagesBASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Lecture Notes 2 Part 1Joanna SalandananNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument15 pagesHeat and Mass Transferverify nameNo ratings yet
- PP1UNIT2Document63 pagesPP1UNIT2Kiran AnemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry StudyguideDocument4 pagesChemistry StudyguideCHRIST IAN JAN PALGANNo ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesLaws of ThermodynamicsSwadhin SahuNo ratings yet
- 3 Laws Governing Thermodynamics 2Document28 pages3 Laws Governing Thermodynamics 2erioNo ratings yet
- The Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument49 pagesThe Laws of ThermodynamicsAtal Khan PushtoonNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument36 pagesThermochemistryJayadevi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy TransferDocument2 pagesThermal Energy Transferfatimahehe31323No ratings yet
- The Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument49 pagesThe Laws of ThermodynamicsArif IsmantoNo ratings yet
- Second Law of EntrophyDocument22 pagesSecond Law of EntrophyMia Betia BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Law of ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesLaw of ThermodynamicsEmmanuel Kenneth Contreras PotoyNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: A Dynamical Systems ApproachFrom EverandThermodynamics: A Dynamical Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)