Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BID202 - Interior Construction-II
BID202 - Interior Construction-II
Uploaded by
chhayainstituteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BID202 - Interior Construction-II
BID202 - Interior Construction-II
Uploaded by
chhayainstituteCopyright:
Available Formats
BID 202: Interior Construction-II
Contents
Practical 1: Staircase - Types & Materials ............................................................................................... 2
Practical 2: Floors-Types & Materials ................................................................................................... 16
Practical 3: False Ceiling –Types- suspended ceilings with concealed lighting arrays & ducting, various
materials - metals, POP, etc. ................................................................................................................. 36
Practical 4: Specialty partition & paneling, Insulating material, Thermal Material, Acoustical, Other
Insulating Materials. ............................................................................................................................. 46
Practical 5: Study of Chairs with costing ............................................................................................... 56
Practical 6: Study of Bed (single & double) with costing. ..................................................................... 67
Practical 7: Study of Sofa with costing .................................................................................................. 75
Practical 8: Study of Space Dividers with costing ................................................................................. 80
Practical 9: Study of Built-in-furniture - Wardrobe with costing. ......................................................... 84
Practical 10: Study of Dining table with costing ................................................................................... 91
Practical 11: Study of Wall Units with costing ...................................................................................... 95
Practical 12: Study of Curtain types with costing ............................................................................... 100
Practical 13: Study of Counters of Bars with costing .......................................................................... 106
Practical 14: Study of Bank Executive Tables with costing. ................................................................ 112
Practical 15: Study of Conference Tables with costing ....................................................................... 119
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 1
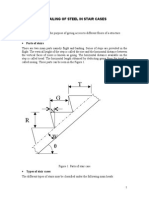
Practical 1: Staircase - Types & Materials
Structure
1.0 Introduction
1.1 Objectives of the Practical
1.2 List of Instruments required
1.3 Procedure
1.4 Points to Remember
1.5 Exercise
1.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
1.0 Introduction
Staircase is a means of ascent and descent provided between floors.
Main terms used in staircase are as follows:
1. Run – run is the total length measured horizontally. This is from the start of the
first step to the mid-landing. Refer figure (1.27).
2. Riser – the vertical measurement measured on the step is called riser. Refer figure
(1.17).
3. Tread – the upper part of the step is called tread. Refer figure (1.17).
4. Step – a pair of riser and tread is called a step.
5. Going – the distance measured horizontally between two faces of consecutive
risers is called going. Refer figure (1.18).
6. Nosing – the projected part of the tread beyond the face of the riser is called
nosing. Refer figure (1.18).
7. Scotia– additional support provided between the riser and tread is called
Scotia.Refer figure (1.18).
8. Flight – it is a continuous series of steps between the landings.Refer figure (1.1).
9. Walking line – an approximate line of movement of the users on a staircase while
ascending or descending is called as walking line; this line is about 450mm from
the centre of the handrail of the staircase.
10. Bull nose step – this step is generally provided at the starting point of the
staircase. Its end forms a circular shape in the plan - Refer figure(1.21.)
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 2
11. Dancing step – the steps are not in a right angle to the run of the staircase and
have a gentle angle, Refer figure(1.24.)
12. Winder– this is a triangular shaped step provide at the turning of the staircase.
The winders radiate from a single point to change the direction of the flight. Refer
figure (1.8).
13. String – the side member placed inclined to support the free ends of the steps is
known as string. Refer figure (1.26).
14. Newel post– this is a main post provided at the end of flight to support the strings
and the handrails. Refer figure (1.20).
15. Baluster–these are vertical members provided between the string and the handrail.
Refer figure (1.19).
16. Landing – the horizontal platform provided between two flights is called a landing.
17. Handrail– this is a rail running parallel to the string line for giving the support to
the users. Refer figure (1.19).
18. Soffit – the bottom surface of the staircase is called soffit; this is generally covered
for aesthetic purposes. Refer figure (1.15).
19. Pitch – the inclined angle of the staircase with the floor is called the pitch. Refer
figure (1.27).
The Stairs are classified as follows:
1. Single flight or Straight stairs –the stair with single flight is called straight stairs
or single flight stair. Refer figure ( 1.1, 1.2)
Fig 1.1: Straight stairs
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 3
Fig 1.2: View of straight stairs
2. Quarter turn stair– this is generally provided in the corner space; this stair turns at
a right angle. Refer figure ( 1.3, 1.4)
Fig 1.3: Quarter - turn
Fig1.4: View of quarter-turn stairs
3. Bifurcated stairs - Quarter turn stairs that branch into two flights at the mid
landing are known as bifurcated stairs. Refer figure ( 1.5, 1.6)
Fig1.5: Bifurcated stairs
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 4
Fig1.6: View of bifurcated stairs
4. Half-turn stairs – this stair turns at two right angles. There are two types of half
turn stairs - dog-legged stairs or open newel stairs Refer figure (1.7). In dog legged
type of stairs, the flights run in opposite directions without any space in between
them and the junction is generally provided with mid landing or winders. In open
newel type of stairs, there is an opening or a well between the flights in the plan,
refer figure (1.8, 1.9).
Fig1.7: Dog-legged Stair Fig1.8: Open Newel Stair
Fig1.9: View of dog-legged Stair
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 5
5. Three-quarter turnstairs –this stair turns through three right angles and forms an
open well between them.Refer figure ( 1.10)
Fig1.10: Three-quarter – turn stair
6. Spiral stairs – in this type of stairs, all the steps radiate from the centre; all the
winders are used to give a spiral form to it. Refer figure ( 1.11, 1.12, 1.13)
Fig1.11: Elevation Fig1.12: Spiral stairs
Fig1.13: Plan
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 6
Stairs can be constructed by using the following materials –
1. Stone. Refer figure ( 1.14, to 1.17)
2. Wood. Refer figure ( 1.18 to 1.23)
3. Brick. Refer figure ( 1.24)
4. Metal. Refer figure ( 1.25)
5. RCC. Refer figure ( 1.26 to 1.29)
Fig1.14: Rectangular stone Fig1.15: Spandrel stone step
Fig 1.16: Detail of marble stair
Fig1.17: Tread and Riser in stone step
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 7
Wooden Stair–
Fig 1.18: Wooden Stair detail at Riser and tread
Fig 1.19: Typical Baluster and Hand Rail
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 8
Fig 1.20: Newel Post
Fig 1.21: Bull Fig1.22: Splayed Fig1.23: Round-ended
Fig 1.24: Dancing step
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 9
Fig 1.25: Brick stair
Fig 1.26: Metal Stair
R.C. C. Staircase –
Fig 1.27: Typical R.C. C. Staircase- Section
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 10
Fig 1.28: Typical R.C. C. Staircase - Plan
Fig 1.29: Detail of stair-case.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 11
Fig 1.30: Details of hand rail
To Design a stair the number of the risers and the treads can be calculated based on the
following formula-
• The number of risers required = total height of the floor ÷ height of the riser
• Number of the treads = number of risers – 1
1.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to –
1. Identify the types of staircase and make appropriate use of staircase in interiors.
2. To design a staircase in various materials.
1.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
1.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board. Refer figure (1.30)
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 12
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure
(1.30).
Fig 1.30: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required number of equal parts by using construction
lines. Please note that at this stage students are expected to understand the proper
division of the plate without showing any construction lines of division; the open space
between the drawings should separate them from each other. Refer figure (1.31)
Fig 1.31: Drawing plate
• Draft types of stairs in the first half and draw the stairs in different material in the other
blocks or design the presentation as per your wish by keeping in mind the important
elements to be presented; if required make two or more plates.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 13
1.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles where it is necessary.
5. Main terms used in a staircase are as follows:
Run – run is the total length measured horizontally from the start of the first
step to the mid-landing.
Riser – the vertical measurement measured on the step.
Tread – the upper part of the step is called tread.
Step – a pair of riser and tread is called a step.
Going – horizontal distance between two faces of consecutive risers.
Nosing –projected part of the tread beyond the face of the riser.
Scotia – additional support provided between the riser and tread.
Flight – it is a continuous series of steps between the landings.
Walking line – this is an approximate line of users on a staircase.
Bull nose step – this step is generally provided at the starting point of the
staircase.
Dancing step – the steps are not in a right angle to the run of the staircase.
Winder – this a triangular shaped step provided for turning the staircase.
String – the side member placed inclined to support the free ends of the steps.
Newel post – this is a main post provided at the end of the flight.
Baluster – these are vertical members provided between the string and the
handrail.
Landing - the horizontal platform provided for rest between two flights.
Handrail – this is a rail running parallel to the string line for giving support.
Soffit – the bottom surface of the staircase is called a soffit.
Pitch – the angle of the staircase with the floor.
6. Stairs can be constructed by using the following materials –
i. Stone
ii. Wood
iii. Brick
iv. Metals
v. RCC
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 14
1.5 Exercise
• Document various types of stair designs (photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of types and design of stairs for better
understanding.
1.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 15
Practical 2: Floors-Types & Materials
Structure
2.0 Introduction
2.1 Objectives of the Practical
2.2 List of Instruments required
2.3 Procedure
2.4 Points to Remember
2.5 Exercise
2.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
2.0 Introduction
The flooring and its finishes are very important in interiors as it is the base for all the
activities carried out in any space. Hence the flooring should be proposed by keeping in mind
various aspects:
1. The flooring should be durable and be able to withstand all day to day activities.
2. It should be water proof.
3. It should be easy to maintain.
4. It should be antiskid.
5. It should be selected on the basis of the use of space; for example - timber is ideal for
dancing floor.
6. Aesthetically pleasing, etc.
o Study the different floor finishes given below:
o Concrete flooring – it is a very basic form of flooring; only concrete is used
for laying this flooring. It is low-cost, very durable and commonly used for
parking deck, warehouses, industries, etc. Refer figure (2.1 to 2.3).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 16
Fig 2.1: Concrete flooring
Fig 2.2: Grid for Concrete flooring
Fig 2.3: Detail of Concrete floor
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 17
Concrete floor is laid by making a grid of appropriate size depending upon the size of
the floor to be laid. It also depends on the amount of the mix made for one time
pouring; the grid line spaces are filled with tar for finishing. Refer figure (2.4).
Fig 2.4: Tinted exposed concrete in various patterns
o Stone – Granite, Marble, Slate, Sandstone, etc are most popular stones used
for floor finish.Refer figure (2.5 to 2.9).
\\\
Fig 2.5: Various colored and textured Granite
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 18
Fig 2.6: Sand Stone
Fig 2.7: Lime Stone
Fig 2.8: Marble
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 19
Fig 2.9: Marble flooring Pattern
Typical Flooring Design – Refer figure (2.10, 2.11).
Fig 2.10: Marble tile flooring Pattern
Fig 2.11: Marble tile flooring Pattern
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 20
Methods of Installation of marble flooring-Refer figure (2.12).
1. Mortar bed
Fig 2.12: Detail at mortar bed
2. Mortar bed (Thin Set Mortar)Refer figure (2.13).
Fig 2.13:Detail
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 21
3. Mortar bed (Thin Set Mortar)Refer figure (2.14).
Fig 2.14: Detail
o Bricks and Brick Pavers – these are mainly used for external areas; for
pathways, in landscaping, etc. fixed with and without grouted joints. The
pavers have very interesting shapes and we can make very good design
patterns by various combinations; available in various textures and colors.
Refer figure (2.15 to 2.18).
Fig 2.15: Brick flooring with Grouted Joints
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 22
Fig 2.16: Brick flooring without Grouted Joints
Fig 2.17: Paver pattern
Fig 2.18: Detail for brick / paver
o Ceramic tiles - Ceramic is fine grade earthenware with good translucency and a hard
glaze. The earliest ceramics were pottery objects that were made from clay only or
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 23
clay mixed with other materials and then hardened in fire. Later on, the ceramics were
glazed and fired to create a smooth and colored surface. Nowadays, Ceramics include
not only domestic and art objects but also industrial and building products. In the last
century, new ceramic materials have been developed for use in advanced ceramic
engineering, for e.g. in semiconductors.
o Ceramic
Floor tiles are very popular as they are available in various colors and designs and
have a glossy and matt finish; ideal for interior work. Refer figure (2.19 to 2. 22).
Fig 2.19: Ceramic tile flooring
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 24
Fig 2.20: Design by using two different colors in ceramic tiles
Fig 2.21: Base for fixing the ceramic tile
Fig 2.22: Decorative ceramic tile
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 25
o Terrazzo flooring – it is installed in a mortar in a thickness of about ½" to
¾" suitable for concrete base and very durable. This is casted on site and the
floor is joint less. This provides us with the facility of designing a pattern of
our choice for the flooring. Refer figure (2.23 to 2.27).
Fig 2.23: Terrazzo flooring detail
Fig 2.24: Terrazzo Granite Marble Chips with Colored cement
Fig 2.25: Brass Divider Stripes
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 26
Fig 2.26: Detail of terrazzo flooring
Fig 2.27: Terrazzo detail at Corner of base and wall
o Wooden flooring – this type of flooring is made by using wooden strips and
hence it is also called as wooden strip flooring. This flooring gives very good
insulation. Generally ¾" x 2 ¼"cross sectional size is used; the strips interlock
with each other by tongue and groove joint at the edges. Refer figure .Refer
figure (2.28 to 2.30).
Fig 2.28: Wooden strip flooring (pre-finished or finished in-place)
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 27
Fig 2.29: Blind Nailed strip flooring
Fig 2.30: Detail of fixing TW Flooring Battens
o Resilient Flooring – it is basically a vinyl composition; very thin 1/8″ available in
rolls or tile forms in a wide range of colors and patterns. Low in cost and moderately
durable; can be fixed by adhesives and very quick to fix. It can be laid on almost any
existing floor surface. Refer figure (2.31).
Fig 2.31: Vinyl flooring
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 28
o Carpets– Carpets are available in natural as well as artificial fibers. The fibres are
woven with a strong base. With various design styles mainly used for indoors, carpets
can be fixed by gluing or by just laying on any existing floor surface. Refer figure
(2.32 , 2.3.3 ).
Fig 2.32: Carpets
Fig 2.33: Carpet with three colors
Floor Construction for Sound Insulation –Refer figure (2.34)
Fig 2.34: Detail of Floor Sound Insulation
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 29
In this unit, we will work on the construction and design of the flooring – the fixing
interlocking, laying of the flooring, etc.
2.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical, you will be able to –
Do the planning of a flooring layout.
Suggest the design in the flooring layout.
Finalize the best suited alternative in the space.
2.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
2.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (2.35).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 30
Fig 2.35: Title block
• List the rooms in the flat
Living room & Dining area
Kitchen
Bed room
Bathroom
• Draft the Measurement plan of the Flat. Indicate the doors and windows. Refer figure
(2.36, 2.37).
Fig 2.36: Plan
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 31
Fig 2.37:Furniture layout
• Draw the grid of the flooring tiles in the room as per the size of the floor tiles keeping
in mind the furniture placement i.e. the design created by the tiling should not get cut
by the furniture. Refer figure (2.38).
Fig 2.38: Flooring layout
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 32
• Now the grid pattern is ready and this is the simplest form of laying the flooring. But,
if you want to make it better we shall have to work further on it.
To start with, first refer the furniture layout and mark the flooring area which will be
under the fixed furniture and counters. This area will not be visible to us once all the
furniture is placed as per the furniture layout. That means, this area can be given the
flooring which is economical and with minimum number of joints.
Now the balance area which is visible to us needs optimum attention while designing
the flooring layout.
Remember, the complete area of the room is not always visible; so making some
design in axial symmetry for the flooring is not a very good design idea for a room
occupied with large furniture. The entire floor of the living and bed rooms is not
visible at any time from any position, but this can be done in case of smaller areas like
bathrooms, passage, balconies, etc. Refer figure (2.39).
Fig 2.39: Complete the legend
Note: the legend given for flooring layout will have following details –
• Make of floor
• Material
• Color
• Size
• Quantity.Refer figure (2.40).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 33
Fig 2.40: Complete the drawing
2.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
5. In the layout, start fixing the tile from the center of the room.
6. Suggest the designs, if any, in the layout for the area visible clearly.
7. Borders and complete design in the flooring are more appropriate in smaller areas like
passages, bathrooms or open areas (areas not occupied by furniture).
8. Use same color for the skirting on the wall.
9. Use Cuddapah or any other economical stone under the covered areas such as kitchen
counters, etc. to cut down on the cost as these areas are not directly visible.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 34
2.5 Exercise
• Draw five alternatives for the flooring layout by using various materials.
• Do market survey and collect various types of flooring materials
• Do three case studies of flooring patterns executed for a residential site.
2.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 35
Practical 3: False Ceiling –Types- suspended ceilings with concealed
lighting arrays & ducting, various materials - metals, POP, etc.
Structure
3.0 Introduction
3.1 Objectives of the Practical
3.2 List of Instruments required
3.3 Procedure
3.4 Points to Remember
3.5 Exercise
3.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
3.0 Introduction
Ceilings are major open surface areas in any room. Hence, proper care should be taken while
designing them. Reflected false ceiling layout, as the name suggests, is a layout showing the
design & planning of the false ceiling. This is the only surface that has maximum visibility
and so one can design the entire room’s ceiling as one unit.
The false ceiling is provided in the interiors for various purposes -
1. To hide the projection of beams and sunken slabs.
2. To accommodate the ducts, electrical wiring conduits, light fixtures, etc.
3. For aesthetics.
4. To attain harmony in design.
5. To reduce cubic content of the room, for lowering the load on AC.
6. For heat insulation in case of top floor.
7. For acoustical treatment, etc.
While designing the false ceiling, the reference of the furniture layout and flooring layout can
be used as basic elements. To make it interesting, various levels can be created or if the
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 36
existing ceiling is uneven, a leveled ceiling can be created by design. Other than aesthetics,
false ceiling has a number of added advantages –
a. To hide the uneven projections of beams, sunk slab, etc.
b. To conceal the A/C ducts, wiring, electrical fittings, etc.
c. To reduce down the cubic contents of the room so as to reduce the load on the
A/C.
d. Acts as an insulator for top floors.
Now let us understand how to design a false ceiling. As we know, it is the planning and
designing of the ceiling. First and foremost, draw the layout of the room and by taking the
reference of the furniture try to create patterns or levels by using moldings or by giving
different levels in the ceiling. Remember that the ceiling also accommodates light fixtures,
fans and accessories like chandeliers that are suspended from the main ceiling. The pattern
created in the ceiling can be made more interesting if it is supported by the appropriate
arrangement of the light fixtures, fans and other ceiling suspended items.
For example, if the false ceiling pattern is square, the four corners of it can have the light
fixtures and the center of the square pattern can have the fan. As the false ceiling reduces the
height of the room, preferably white color or any pastel tints of colors can be used. This also
helps in reflecting the lights and gives more light in the area below it. The false ceiling can be
classified on the basis of the finishing material used for it -
1. Plaster of Paris - POP false ceiling
2. Teakwood false ceiling
3. Aluminum false ceiling
4. Glass false ceiling
5. Paper false ceiling
6. Fabric false ceiling
7. Plastic false ceiling, etc.
According to the function of the room, the appropriate finishing material can be suggested.
For example, POP false ceiling is the most popular material for residential spaces whereas in
industrial buildings, metal or plastic false ceilings are appropriate.
Now, we shall study a few of them in detail.
1. Plaster of Paris - POP False ceilings (Plaster of Paris) Hung Suspension System
Material used –Finishing material - POP and Paint, etc.
Frame - GI Channel or metal
Fixing – Steel screws
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 37
This type of ceiling is very popular as it is the most economical. It is very convenient to
repair as the old POP can set with new POP and give a fresh look. One more very important
quality is that it can be molded and set very fast. Also, it can be molded in any desired form.
Let’s study the following example of a POP false ceiling.
We will first understand how to draft the Reflected false ceiling layout. Draft the
Measurement plan of the flat but do not indicate the doors & windows. Refer figure (3.1 to
3.8).
Fig 3.1: Plan
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 38
Fig 3.2: Reflected false ceiling layout showing cutouts for light fixtures
Fig 3.3: Section showing the drop levels of false ceiling
Fig 3.4: Detail at “X”Fig 3.5: Detail at “Y”
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 39
Fig 3.6: Detail of cornice
Fig 3.7: Detail at Wall
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 40
Fig 3.8: Detail at light fixture
2. Teakwood false ceiling
Material used – Finishing material is TW Boards and screws, etc.
Frame - GI Channel or metal
Fixing – Steel screws
This type of ceiling provides high thermal insulation from roof. As timber is used for
finishing, it gives a rich look to the interior.
Let’s study the following example of teakwood false ceiling. Refer figure (3.9).
Fig 3.9: Typical Detail of TW ceiling
3. Aluminum False ceiling
Material used – Finishing material is Aluminum cladded tiles / Acoustical tiles and
screws, etc. Refer figure (3.10).
Frame - GI Channel or metal
Fixing – Steel screws
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 41
If the Aluminum cladded perforated tiles are used, it helps in acoustics. It is ideal for
large public spaces, office, etc. As aluminum is used for finishing, it gives a neat look
to the interior, reflects the light and makes the interior brighter.
Let’s study the following example of aluminum false ceiling.
Fig 3.10: Typical Detail of Aluminum ceiling
4. Partly Glass False ceiling
Material used – Finishing material is Glass with POP/Aluminum cladded tiles /
Acoustical tiles and screws, PVC lining, etc. Refer figure (3.11).
Frame- GI Channel or metal
Fixing – Steel screws
This combination is useful for canceling the light fixture and also rendering with color
light. It is ideal for residential spaces, conference rooms, etc.
Let’s study the following example of partly glass false ceiling.
Fig 3.11: Typical Detail of Partly glass ceiling
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 42
3.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to – Propose the design and constructional
details for providing and fixing the false ceilings.
3.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
3.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (3.12).
Fig 3.12: Title block
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 43
• Divide the drafting area into four parts for drawing plan, two sections and details
proposed by using construction lines.
Note: the specification given for ceiling layout will have following details –
• Make of false ceiling tiles
• Material
• Color
• Size
• Quantity
• Fixing method
Fig 3.13:False ceiling layout
• Draft each type of the drawing in the planned space or design the presentation as per
your wish by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented. Refer figure
(3.13).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 44
3.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
3.5 Exercise
• Document various types of false ceiling designs (photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of false ceilingfor better understanding.
3.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 45
Practical 4: Specialty partition & paneling, Insulating material,
Thermal Material, Acoustical, Other Insulating Materials.
Structure
4.0 Introduction
4.1 Objectives of the Practical
4.2 List of Instruments required
4.3 Procedure
4.4 Points to Remember
4.5 Exercise
4.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
4.0 Introduction
Partitions are one of the main building components used to divide the space for various
activities in an interior. The brick walls are the most common partitions used in a building;
similarly other materials like timber, ply, glass, etc. are used for making partitions. In some
cases, composite partitions are also used.
1. Partition wall – Using Brick - The partition thickness is generally as that of the brick
size (approx. 100 mm).This is the simplest of all; only bricks with cement mortar are used
to make the partition. It is incombustible with one hour fire-rating. These partitions are
solid and have a good resistance to damage. Acoustically also, very good as the
transmission loss is 45 decibels. It has very low maintenance, is aesthetically rich but has
poor light reflection. Refer figure (4.1).
View of the brick partition Elevations
Fig 4.1: Partition wall
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 46
The same brick work can be made more stable by plastering itwith cement and the cement
wall surface can be further painted for the desired look; generally15mmthk., this plaster is
preferred for the internal walls. In this case, the brick work partition thickness is more than
that of the brick partition without the plaster. Due to the plaster, the partition becomes more
durable and by adding the paint finish to it; it helps in light reflection to make the interior
brighter. It also increases the fire resistance capacity of the partition. Various types of
textures can be given to these partitions for aesthetics. Refer figure (4.2).
Fig 4.2: Partition wall with plaster
2. Partition walls – Concrete Hollow blocks - The partition thickness (approx. 100
mm)or may change as per the size used for partition. It has one hour incombustible
fire rating. It is solid and is shock resistant. It is also good for acoustic properties i.e.
40 decibels. As the cement hollow blocks are more accurate in size and shape, they
give a very good finished look if constructed properly and add to the aesthetics of an
interior. Refer figure (4.3).
View of the brick partition Elevations
Fig 4.3: Hollow Block Partition wall
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 47
Like regular clay bricks, these cement hollow blocks can be similarly plastered for more
durability and better finish. Refer figure (4.4). These blocks insulate the interior as the
partition has a hollow space; this space provides more insulation to the interiors from the
extreme weather outside. One more advantage is that it is comparatively light in weight.
Fig 4.4: Hollow block Partition wall with plaster
3. Partition wall – a. Plywood finish partition & b. Thermal, acoustical partition
a. Plywood finish partition–This is a lightweight partition composed of 50× 100
TW members fixed 400 mm apart and provided with 4mm or 6mm plywood from
both the sides and finished with two coats of paint. Refer figure (4.5). This takes
less time for construction than that of the traditional brick partition, but is less
durable. Acoustically good, around 39 decibels. It gives good light reflection.
Fig 4.5: Plywood Finish Partition
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 48
Study the typical frame work for the studs and ply partition. Refer figure (4.6).
Fig 4.6: Typical frame work for the studs and ply partition
b. Thermal, Acoustical partition – this is a special type of partition composed of 50× 100
TW studs covered by a double layer of gypsum boards on each side. Refer figure (4.7, 4.8).
A 40mm thick fibrous insulation Blanket is added between the studs for thermal and
acoustical insulation.
Fig 4.7:Thermal Partition
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 49
Fig 4.8:Acoustical Partition
PANELING
Paneling is a type of wall covering done by using various finishes. Generally wall paneling is
done to achieve the following –
1. To give a proper leveled surface.
2. To provide and fix various materials on the wall by cladding them.
3. To insulate the interior.
4. To achieve good acoustics in interior.
5. For aesthetics, etc.
Study the details given of paneling made by TW Frame, ply and gypsum board. Refer figure
(4.9 to 4.14).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 50
Fig 4.9: PLAN
Fig 4.10: ELEVATION
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 51
Fig 4.11: Detail @ X
Fig 4.12: Detail @ Y
Fig 4.13: Detail @ Skirting
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 52
Fig 4.14: Sectional Detail of Acoustical Wall paneling
4.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical, you will be able to make working drawings for Partitions and
Paneling and able to suggest the appropriate partition in an interior based on the function of
the space.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 53
4.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
4.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (4.15).
Fig 4.15: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(4.16).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 54
Fig 4.16: Title block
• Design the presentation as per your wish by keeping in mind the important elements to
be presented.
• Make two different plates for Partition and Paneling.
4.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
4.5 Exercise
• Document various types of partition designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of partition façade for better understanding.
4.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 55
Practical 5: Study of Chairs with costing
Structure
5.0 Introduction
5.1 Objectives of the Practical
5.2 List of Instruments required
5.3 Procedure
5.4 Points to Remember
5.5 Exercise
5.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
5.0 Introduction
Study the chair given below -Refer figure (5.1 to 5.5).
Fig 5.1: Plan of the chair
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 56
Fig 5.2: Sectional Plan.
Fig 5.3: Part section and front elevation of chair
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 57
Fig 5.4: Detail at front leg
Fig 5.5: Detail at arm rest
5.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to – Propose the design and constructional
details for upholstered chairs.
5.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 58
5.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (5.6).
Fig 5.6: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(5.7).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 59
Fig 5.7: Title block with specification and estimate.
• Draft the details of the chair in the blocks or design the presentation as per your wish
by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the chair.
Estimate: - We have studied the types of estimates. You can make use of any of the methods
to give an estimate of the chair.
To work out the proper estimate, three main factors need to be considered -
1. Material
2. Labour
3. Finishing
1. Material - the material used for making the furniture shares the major of the expenses. Like
in this case, TW is the main material. The material has one more component i.e. hardware.
While calculating the material we will start with the structural frame work first. The chair
skeleton comprises of a seat, a back and four legs with arm rests.
2. Labour – the labour for the furniture will mainly depend on the time it requires to make the
furniture. If the furniture has more intricate design, it will take more time as also labor will
be more for the same. Also, if the design of the furniture requires more of skill, this will
also increase the cost of the skilled labour.
This indicates that the time taken and the design have a direct impact on the labour
estimate.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 60
3. Finishing – this factor mainly depends on the material cost and the skill level required as
well and the time required for finishing of the same. To make it simpler, let’s put these
factors in tabular forms.
Estimate Chart -
Sr. Basic Size / Rate** Hardware Finishing Labour Estimate
No. Materials / Specification / Fastener materials **
Components/
Items
01 Leather 1 Metre Same
Seat One no.
450 X 550 X 12 --
mm Thk.
Back rest One no.
450 X 500 X 12 --
mm Thk.
Front legs 37 X 37 X 500 Rubber
Clear
mm solution /
hand
Screws,
Two nos. polish
nails, etc.
Back legs 37 X 37 X 1.2 Clear
mm hand
Two nos. polish
Hand rest 55 X30 X 500 Clear
mm hand
Two nos. polish
Foam rubber 450 X 550 Leather
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 61
** Students are advised to check the market rate and complete the Estimate for the
chair.
Also, study the details of the second chair given below -Refer figure (5.8 to 5.14).
Fig 5.8: Plan of the chair.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 62
Fig 5.9: Side Elevation of the Chair
Fig 5.10: Front Elevation of the Chair
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 63
Fig 5.11: Sectional Front Elevation of the Chair
Fig 5.12: Sectional Side Elevation of the Chair
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 64
Fig 5.13: Detail at arm rest.
Fig 5.14: Detail at back rest
5.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
5.5 Exercise
• Document various types of upholstered chair designs (PhotographS).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 65
• Do your own research and make sketches of chairsfor better understanding.
5.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 66
Practical 6: Study of Bed (single & double) with costing.
Structure
6.0 Introduction
6.1 Objectives of the Practical
6.2 List of Instruments required
6.3 Procedure
6.4 Points to Remember
6.5 Exercise
6.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
6.0 Introduction
Types of bed are according to their sizes; the smallest standard size starts from 660 X 990
mm called Bassinet. Then we have Infant crib size 760 X 1320 mm, Junior crib 838 X 1447
mm, Youth bed 914 X 1930 mm, Twin bed 990 X 2032 mm, Twin extra-long 990 X 2133
mm, Double / Full bed 1371 X 1905 – 2133 mm, Queen 1524 X 2032, Queen extra-long
1524 X 2133 mm, King 1930 X 2032 mm and California king 1930 X 2133 mm. Refer figure
(6.1).
Fig 6.1: Plan of the bed
The height of thebed can be as low as 300 mm to 450 mm; the height of bed may be up to
750 mm in case of hospital beds or sometimes higher and adjustable as per the use. But for
residential use, the bed can preferably have a height of 450mm.
The width for a single bed is 1.00 m and length 1.80 m.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 67
Study the single bed given below Refer figure (6.1 to 6.6).
Fig 6.2: Plan of the bed
Fig 6.3: Side elevation of the bed
Fig 6.4: Section showing the detail construction of bed in block board
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 68
Fig 6.5: Detail at “A”
Fig 6.6: Detail at “B”
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 69
Study the double bed given below. Refer figure (6.7, 6.8).
Fig 6.7: Plan of the bed
Fig 6.8: Side elevation of the bed
Note: Students are advised to suggest the different materials and finishes in their drawings.
The example is given just for understanding. Please give blown up details wherever required.
Refer figure (6.9 to 6.12).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 70
Study the following bed and its estimate.
Fig 6.9: Front elevation of the bed
Fig 6.10: Plan of the bed
Fig 6.11: Side elevation of the bed
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 71
Fig 6.12: Detail dimensions at front face of bed
BED [SIZE 5′ 6″ x 6′ 6″]
Amount
Materials Quantity
in rupees
18 mm Ply 7′ x 4′ 3 Nos. 5355
18mm Ply 7′ x 3′ 3 Nos. 7140
18mm Ply 6′ x 4′ 1 No. 2040
15mm Ply 7′ x 3′ 4Nos. 7140
2′ X 1′ Wood 55 RFT 1925
Laminate Main 2 Sheets 3600
Laminate White 12 Sheets 5400
Nail - 17 No. 500 grams 260
Nail -19 No. 250grams 160
Nail -14 No. 500 grams 340
Adhesive 3Kg 320
Masking Tape 8Nos. 280
Labour Rs. 7,600
Total Amount Rs. 41,560
6.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical, you will be able to make the working drawing for beds.
6.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 72
6.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (6.13).
Fig 6.13: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(6.14).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 73
Fig 6.14: Title block with Specification and Estimate
• Draft the details of bed in the blocks or design the presentation as per your wish by
keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification give the estimate of the bed.
6.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
6.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the bed you have designed. Follow the method given in this unit.
• Document various types of bed designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of beds for better understanding.
6.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 74
Practical 7: Study of Sofa with costing
Structure
7.0 Introduction
7.1 Objectives of the Practical
7.2 List of Instruments required
7.3 Procedure
7.4 Points to Remember
7.5 Exercise
7.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
7.0 Introduction
Study the details given of a sofa. Refer figure (7.1 to 7.4).
Fig 7.1: View of Sofa
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 75
Fig 7.2: Plan of sofa
Fig 7.3: Side elevation of sofa
Fig 7.4: Sectional side elevation of sofa
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 76
Study the example given below and give the estimate for the same.Refer figure (7.5 to 7.7).
Fig 7.5: Front elevation of sofa
Fig 7.6: Side elevation of sofa
Fig 7.7: Front &Side elevation of Three- seater Sofa
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 77
7.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to – design and give the estimate for a sofa
seating.
7.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
7.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (7.8).
Fig 7.8: Title block
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 78
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(7.9).
Fig 7.9: Title block with Specification and Estimate
• Draft the details of sofa in the blocks or design the presentation as per your wish by
keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the sofa.
7.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
7.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the sofa. Follow the method given in unit no 6.
• Document various types of sofa designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of sofa for better understanding.
7.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 79
Practical 8: Study of Space Dividers with costing
Structure
8.0 Introduction
8.1 Objectives of the Practical
8.2 List of Instruments required
8.3 Procedure
8.4 Points to Remember
8.5 Exercise
8.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
8.0 Introduction
Study the space dividers shown below; the space divider can be full as a partition or it can
half in height, about a meter in height.
The function of both types remains the same i.e. to divide the room space for various
activities.Refer figure (8.1 to 8.3).
Fig 8.1: Elevation showing frame with finish
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 80
Fig 8.2: Plan of Space divider
Fig 8.3: Detail at skirting level
8.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to design and give the estimate for a space
divider.
8.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
8.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 81
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (8.4).
Fig 8.4: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(8.5).
Fig 8.5: Title block with Specification and Estimate
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 82
• Draft the details of the space divider in the blocks or design the presentation as per
your wish by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the space
divider.
8.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
8.5 Exercise
• Give estimate for the space divider. Follow the method given in unit no 6.
• Document various types of space divider designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of space dividers for better understanding.
8.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 83
Practical 9: Study of Built-in-furniture - Wardrobe with costing.
Structure
9.0 Introduction
9.1 Objectives of the Practical
9.2 List of Instruments required
9.3 Procedure
9.4 Points to Remember
9.5 Exercise
9.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
9.0 Introduction
Study the wardrobe shown below; two illustrations are given – there is slight difference in the
dimensions and the design. Students are advised to make at least three options in design for
understanding of a wardrobe in detail.Refer figure (9.1 to 9.6).
Illustration No. 1 – Study the detail given for the wardrobe
Fig 9.1: Section Plan
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 84
Fig 9.2: Front Elevation Fig 9.3: Section
Fig 9.4: Detail at A Fig 9.5: Detail at B
Fig 9.6: Detail at C
IllustrationNo. 2 – Study the estimate given for the wardrobe Refer figure (9.7 to 9.9).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 85
Fig 9.7: Front Elevation
Fig 9.8: Sectional Plan
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 86
Fig 9.9: Section
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 87
The Estimate has mainly two factors i.e. Materials and labour.
WARDROBE
Amount in
Materials Quantity
Rupees
18 mm ply 7′ x 4′ 4 Nos. 9520
18mm Ply 7′ x 3′ 2 Nos. 3570
15 mm ply 7′ x 4′ 1No. 2380
15mm Ply 7′ x 3′ 1 No. 1785
6 mm ply 7′ x 4′ 2Nos. 1960
6mm Ply 6′ x 3′ 2 Nos. 1260
Laminate Main 3 Sheets 5400
Laminate White 12 Sheets 6600
Adhesive 10Kg 3250
Handle 6 Nos. 850
14 No. Nail 1 Kg 450
11/4 X17 500 grams 260
17 X 1 500grams 180
Masking Tape 16 Nos. 720
Labour charge Rs. 18,000
Total Amount Rs. 56,185/-
9.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to – design the working drawing for wardrobe
and work out the estimate.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 88
9.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
9.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference.
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (9.10).
Fig 9.10: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(9.11).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 89
Fig 9.11: Title block with Specification and Estimate
• Draft the details of wardrobe in the blocks or design the presentation as per your wish
by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the wardrobe.
9.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
9.5 Exercise
• Workout the estimate for the wardrobe which you have designed.
• Document various types of wardrobe designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of wardrobe for better understanding.
9.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 90
Practical 10: Study of Dining table with costing
Structure
10.0 Introduction
10.1 Objectives of the Practical
10.2 List of Instruments required
10.3 Procedure
10.4 Points to Remember
10.5 Exercise
10.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
10.0 Introduction
Study the dining table given below. Refer figure (10.1 to 10.4).
Fig 10.1:Front elevation
Fig 10.2:Side elevation
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 91
Fig 10.3Plan
Fig 10.4:Details
DINING TABLE [SIZE 2′6″ x 5′ 0″]
Materials Quantity Amount in Rupees
18 mm ply 6′ x 3′ 2 Nos. 2700
18mm Ply 6′ x 2′ 1 Nos. 600
1 ¼ x 1 Wood 16RFT 320
2 X 1Wood 24RFT 840
12 mm Glass 12.5 Sq. ft. 5625
Laminate 1 Sheet 1800
Adhesive 1Kg 325
14 No 250grams 80
1 ¼ X 17 200grams 60
Masking Tape 2 No 60
Labour charge Rs. 4,600
Total Amount 17,710
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 92
10.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to prepare the working drawing for dining table
and work out the estimate.
10.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
10.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (10.5).
Fig 10.5: Title block
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 93
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(10.6).
Fig 10.6: Title block with Specification and Estimate.
• Draft the details of the dining table in the blocks or design the presentation as per your
wish by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the dining table.
10.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
10.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the dining table you have designed. Follow the method given in
the unit.
• Document various types of dining table designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of dining tables for better understanding.
10.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 94
Practical 11: Study of Wall Units with costing
Structure
11.0 Introduction
11.1 Objectives of the Practical
11.2 List of Instruments required
11.3 Procedure
11.4 Points to Remember
11.5 Exercise
11.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
11.0 Introduction
Study the typical wall unit given below. Refer figure (11.1 to 11.3).
Fig 11.1: Front elevation showing detail of Wall Unit
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 95
Fig 11.2: Section
Fig 11.3: Plan
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 96
T V UNIT
Materials Quantity Amount in Rupees
18 mm ply 7′ x 4′ 1 No 2380
18mm Ply 7′ x 3′ 2 No 3570
8 mm ply 7′ x 3′ 1No 800
8mm Ply 6′ x 3′ 1 No 820
Laminate Main 2 Sheet 3600
Laminate White 6 Sheet 2700
Adhesive 3Kg 975
Handle 6 No 850
Nails 14 No. 1 Kg 450
11/4 x17 500grams 260
17 x 1 500 grams 180
Masking Tape 8 No 320
Labour charge Rs. 10,825
Total Amount Rs. 27,730
11.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to design the working drawing for wall unit and
work out the estimate.
11.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 97
11.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (11.4).
Fig 11.4: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(11.5).
Fig 11.5: Title block with specification and estimate
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 98
• Draft the details of wall unit in the blocks or design the presentation as per your wish
by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the wall unit.
11.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
11.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the wall unit that you have designed. Follow the method given in
the unit.
• Document various types of wall unit designs (Photographs).
• Do your own research and make sketches of wall units for better understanding.
11.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 99
Practical 12: Study of Curtain types with costing
Structure
12.0 Introduction
12.1 Objectives of the Practical
12.2 List of Instruments required
12.3 Procedure
12.4 Points to Remember
12.5 Exercise
12.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
12.0 Introduction
Study the various curtains and their fixing by using curtain rods or other curtain fixing aids.
Refer figure (12.1 to 12.17).
Fig 12.1: Café curtains Fig12.2: Ruffled Tieback curtains
Fig 12.3: Fringed segment with Café curtains Fig 12.4:Fabric wrapped pole draped
valance
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 100
Fig 12.5: Café curtains with gathered valance Fig 12.6:Tieback damask drapery
with balled Fringe
Fig 12.7: Staggered tieback with plain edge asymmetric panels
Fig 12.8: Flush mount closed top Fig 12.9: Inside mount bracket
Fig 12.10: Finialson window
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 101
Fig 12.11: Finials
Fig 12.12: Finials
Fig 12.13: PVC pipe with elbows
Fig 12.14: Extra wide telescopic rod
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 102
Fig 12.15: One way telescopic fitting
Fig 12.16: Width of curtain and overlapping on sides
Fig 12.17: Height of curtain half and full height
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 103
12.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to provide and fix various curtain types with
costing.
12.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
12.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (12.18).
Fig 12.18: Title block
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 104
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(12.19).
Fig 12.19: Title block with specification and estimate
• Draft the details of curtain in the blocks or design the presentation as per your wish by
keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the curtain.
12.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
12.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the curtain. Follow the method given in unit no 11.
• Document various types of curtain designs by photographs.
• Do your own research and make sketches of curtains for better understanding.
12.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 105
Practical 13: Study of Counters of Bars with costing
Structure
13.0 Introduction
13.1 Objectives of the Practical
13.2 List of Instruments required
13.3 Procedure
13.4 Points to Remember
13.5 Exercise
13.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
13.0 Introduction
Study the bar counter given below -Refer figure (13.1, 13.2).
Fig 13.1: Plan of bar counter
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 106
Fig 13.2: Section of bar counter @ X-X
Study one more design for a bar counter given below.Refer figure (13.1 to 13.6).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 107
Fig 13.3: Front elevation
Fig 13.4: Side elevation
Fig 13.5: Plan of bar counter
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 108
Fig 13.6: Section of bar counter
13.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to design and give the estimate for the bar
counter.
13.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
13.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 109
• Make the standard title block.Refer figure (13.17).
Fig 13.7: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(13.18).
Fig 13.8: Title block with specification and estimate
• Draft the details of bar counter in the blocks or design the presentation as per your
wish by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 110
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the bar counter.
13.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
13.5 Exercise
• Give estimate for the bar counter. Follow the method given in unit no 11.
• Document various types of bar counter designs by photographs.
• Do your own research and make sketches of bar counters for better understanding.
13.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 111
Practical 14: Study of Bank Executive Tables with costing.
Structure
14.0 Introduction
14.1 Objectives of the Practical
14.2 List of Instruments required
14.3 Procedure
14.4 Points to Remember
14.5 Exercise
14.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
14.0 Introduction
Study the bank executive table given below - Refer figure (14.1 to 14.5).
Fig 14.1: Plan of the table
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 112
Fig 14.2: Rear elevation
Fig 14.3: Front and side elevations
Fig 14.5: Detail of table molding
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 113
Study the second example for a more decorative design. Refer figure (14.6 to 14.9).
Fig 14.6: Front elevation
Fig 14.7: Rear elevation
Fig 14.8: Side elevation of visitor’s seating
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 114
Fig 14.9: Plan of the table with seating arrangement
EXECUTIVE TABLE
Materials Quantity Amount in
Rupees
18 mm ply 7′ x 3′ 2 Nos. 3570
18mm Ply 8′ x 3′ 4 Nos. 7200
Glass 21 RFT 7350
Laminate 2 Sheets 7600
Adhesive 3Kg 1150
Nails - 17 No. 500 grams 260
19 No. 250 grams 160
14 No. 500 grams 340
S.S Stud 4 Nos. 1200
Masking Tape 6 Nos. 240
Labour charge Rs. 8,800.00
Total Amount Rs. 37,870.00
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 115
SIDE TABLE
Materials Quantity Amount in
Rupees
18 mm ply 8′ x 4′ 1 No. 2720
18mm Ply 6′ x 3′ 2 Nos. 3060
8mm Ply 6′ x 3′ 1 No. 630
Main Laminate 1 Sheet 1800
White Laminate 4 Sheet 1800
Adhesive 2Kg 640
Nails - 17 No. 200 grams 360
19 No. 250 grams 160
14 No. 500 grams 340
Masking tape 6 Nos. 240
Lock 2 Nos. 300
Labour charge Rs. 3,500.00
Total Amount Rs. 15,550.00
14.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to design the bank executive table and work out
the estimate.
14.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 116
14.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (14.10).
Fig 14.10: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(14.11).
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 117
Fig 14.11: Title block with specification and estimate
• Draft the details of bank executive table in the blocks or design the presentation as per
your wish by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the bank
executive table.
14.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles wherever necessary.
14.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the bank executive table that you have designed. Follow the
method given in this unit.
• Document various types of bank executive table designs by photographs.
• Do your own research and make sketches of bank executive tables for a better
understanding.
14.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 118
Practical 15: Study of Conference Tables with costing
Structure
15.0 Introduction
15.1 Objectives of the Practical
15.2 List of Instruments required
15.3 Procedure
15.4 Points to Remember
15.5 Exercise
15.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
15.0 Introduction
Study the Conference table given below -Refer figure (15.1 to 15.6).
Fig 15.1: Plan of Conference Table
Fig 15.2: Enlarged plan of Conference Table
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 119
Fig 15.3: Front elevation
Fig 15.4: Side elevation
Fig 15.5: Detail of table molding
Fig 15.6: Detail of leg
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 120
CONFERENCE TABLE
Materials Quantity Amount in Rupees
18 mm ply 8′ x 4′ 2 Nos. 4800
18mm ply 8′ x 3′ 4 Nos. 7200
2 ½ x 11/8x 6 22.5 1680
2 x 2 ½ S P TW 52RFT 2460
Lipping 84 RFT 1680
Laminate 3 Sheets 4500
Adhesive 3Kg 1150
Nails -14 No. 0. 350 kg 120
1X17 0.200 kg 80
19 No. 0.200 kg 45
Masking Tape 4 Nos. 120
Labour charge Rs. 10,000.00
Total Amount Rs. 33,835.00
15.1 Objectives of the Practical
After studying this practical you will be able to design Conferences tablesand work out the
estimate.
15.2 List of Instruments Required
(1) Drawing board, (2) Drawing paper, (3) Cello tape, (4) T-square, (5) Set-square set,
(6) Pencils, (7) Erasers, (8) Scale, (9) Rough cotton cloth.
15.3 Procedure
Record all Sketches and notes in journal for your reference
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 121
First and foremost, with the help of a rough cotton cloth clean the drawing board, the T-
square and all the other drawing instruments. Place the drawing board on the table with the
working edge of the drawing board on your left-hand side.
• Place the drawing paper on the drawing board at about equal distances from the top, the
bottom, the left and the right edges of the drawing board.
• Now stretch the paper gently to make it perfectly flat on the board. By applying light
pressure to the paper on the board, fix the paper on the board by using the cello tape (in
angles)on the four corners of the paper. There should be no air entrapped while fixing the
paper to the board.
• Make the standard title block. Refer figure (15.7).
Fig 15.7: Title block
• Divide the drafting area into required parts by using construction lines. Refer figure
(15.8).
Fig 15.8: Title block with specification and estimate
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 122
• Draft the details of conference table in the blocks or design the presentation as per your
wish by keeping in mind the important elements to be presented.
• In the area given for estimation and specification, give the estimate of the conference
table.
15.4 Points to Remember
1. Use proper instruments for drafting.
2. Use appropriate scale for drafting.
3. Do not erase construction lines.
4. Give specification and titles where is necessary.
15.5 Exercise
• Give the estimate for the conference table. Follow the method given in unit no 5.
• Document various types of conference table designs by photographs.
• Do your own research and make sketches of conference table for better understanding.
15.6 Professor’s Remark and Sign
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 123
Reference material
Sr.
No. Author Title Publisher & Address
Joseph De Chaira
JulliusPanero Time Saver Standard for
Interior Design & Space
1 Martin Zelnik Planning Mcgraw Hill, New York
2 John Pile Interior Design Harry N. Adry Publishers
3 Ahmed Kasu Interior Design TWAIN Pub. Bombay
JulliusPanero Whitney Library
Human Dimensions and
4 Martin Zelnik Interior Spaces New York
Beginning of Interior
5 PhillisSleen Allen Environment New York
Basic Design of
6 ShirishBapat Anthropometry Bela books Publishers
Living Area (Interior
7 ShirishBapat Space) Bela books Publishers
Francis D K
8 Ching Interior Design Illustrated Van Norstrund, New Delhi
Design Fundamental in 1st
9 V. S. Parmar architecture Somaiya Pub. Pvt. Ltd.
BID 202: Interior Construction-II Page 124
You might also like
- Wickes Kitchen Self Fit Customer Care GuideDocument52 pagesWickes Kitchen Self Fit Customer Care Guidegregmcn90% (21)
- Aircraft Design of WWII: A SketchbookFrom EverandAircraft Design of WWII: A SketchbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Brief Guide to the History of Architectural StylesFrom EverandBrief Guide to the History of Architectural StylesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Plastering: Presented byDocument18 pagesPlastering: Presented byVighnesh MalagiNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Staircase According To Eurocode2Document11 pagesStructural Design of Staircase According To Eurocode2prakash100% (1)
- Chalk Dust and Tahong Shells Used To Make ChalkDocument4 pagesChalk Dust and Tahong Shells Used To Make Chalk_piad100% (3)
- World Trade ParkDocument33 pagesWorld Trade ParkDevendra Sharma67% (3)
- 4.CE 315 - Chapter 2B - Stairs 3CE-2Document39 pages4.CE 315 - Chapter 2B - Stairs 3CE-2Mt KulisNo ratings yet
- Introduction of StaircaseDocument9 pagesIntroduction of StaircaseRuzengulalebih ZEta's-ListikNo ratings yet
- Escaleras - HassounDocument28 pagesEscaleras - HassounAndres FelipeNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 Stairs, Floors and RoofsDocument40 pagesLec 7 Stairs, Floors and RoofsTanvir ShovonNo ratings yet
- BS 6100-1-3-4Document12 pagesBS 6100-1-3-4Leed ENNo ratings yet
- Stair CaseDocument9 pagesStair CaseMohamed NkNo ratings yet
- Unit Preparation Anb:-Interpretation of Plans: StructureDocument13 pagesUnit Preparation Anb:-Interpretation of Plans: StructureramonlinebooksNo ratings yet
- Ducting PresentationDocument50 pagesDucting Presentationapi-3022311770% (1)
- 7 Stair DesignDocument16 pages7 Stair Designkriengsak ruangdechNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete ColumnDocument29 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete ColumnDuyên Trịnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Types of StairsDocument12 pagesTypes of Stairsfaris danial100% (1)
- Stairs BMC 140824050212 Phpapp02Document74 pagesStairs BMC 140824050212 Phpapp02Harshi Garg100% (2)
- What Is Stairs ?Document38 pagesWhat Is Stairs ?rajeshNo ratings yet
- Stair Notes 2018.PDF-1Document14 pagesStair Notes 2018.PDF-1RahulSinghRajputNo ratings yet
- CE 2100 Details of Construction IDocument65 pagesCE 2100 Details of Construction IMARUFNo ratings yet
- StairsDocument74 pagesStairsArchana AcchuNo ratings yet
- Design of Staircase 1197052627390217 2Document22 pagesDesign of Staircase 1197052627390217 2Prashant Narvankar100% (1)
- 14 - StairsDocument42 pages14 - StairsHumza ShahidNo ratings yet
- Building Construction - Stair DesignDocument16 pagesBuilding Construction - Stair DesignRobert LaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Staircase Types, Analysis and DesignDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Staircase Types, Analysis and Designzeru32611720% (1)
- StairsDocument41 pagesStairsDeepthideepu100% (2)
- Unit8 PDFDocument14 pagesUnit8 PDFVictor OmotoriogunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2yonatanNo ratings yet
- StairsDocument49 pagesStairsHanaaAl-GhanimNo ratings yet
- 4 StairsDocument41 pages4 StairsMian Afzaal 72No ratings yet
- StairsDocument41 pagesStairsSaqlainNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Stair, Lifts and EscalatorsDocument6 pagesChapter-5 Stair, Lifts and EscalatorsPratik GhimireNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: StaircasesDocument19 pagesCivil Engineering: StaircasesGurraacha AbbayyaaNo ratings yet
- Kharagpur - Staircase Design PDFDocument38 pagesKharagpur - Staircase Design PDFjmusopole50% (2)
- StaircaseDocument9 pagesStaircaseNNo ratings yet
- SSB05 Detailed Design of TrussesDocument131 pagesSSB05 Detailed Design of TrussesElton MaroNo ratings yet
- Staircases: Download Civil Engineering EbookDocument38 pagesStaircases: Download Civil Engineering EbookYudirwan Tanjung100% (1)
- Design of StairsDocument14 pagesDesign of StairsRegieBacharoNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument13 pagesEngineering DrawingVIVEK V SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Stairs PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Stairs PDFCrunch BotNo ratings yet
- StairsDocument22 pagesStairsPtpgStucNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Stair CaseDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Stair Casemria03908No ratings yet
- Stair CaseDocument14 pagesStair CaseSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Q 01 TCBC 201 strairsINFORMATION SHEET 05Document4 pagesQ 01 TCBC 201 strairsINFORMATION SHEET 05Francis OmaraNo ratings yet
- StairDocument7 pagesStairZafar AlamNo ratings yet
- StaircaseDocument14 pagesStaircaserameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- ARC 252.2 Building Construction I B. Arch II / II Chapter Eight: Stair and Its GeometryDocument10 pagesARC 252.2 Building Construction I B. Arch II / II Chapter Eight: Stair and Its GeometryAsanka RanathungaNo ratings yet
- Tiếng Anh Trong Xây Dựng: Bài GiảngDocument50 pagesTiếng Anh Trong Xây Dựng: Bài GiảngTrọng NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Triangular Methods To Transfer Surface Shapes To A DevelopmentDocument15 pagesTriangular Methods To Transfer Surface Shapes To A DevelopmentIrish Gallego100% (1)
- Stairs and Its GeometryDocument10 pagesStairs and Its GeometryBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 13a - Diseño de EscalerasDocument49 pages13a - Diseño de EscalerasKaren Esther Acuña VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Design Example of Six Storey BuildingDocument51 pagesDesign Example of Six Storey BuildingRajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Architectural Symbols. Line Conventions, and Material ConventionsDocument19 pagesArchitectural Symbols. Line Conventions, and Material ConventionscrazybuttfulNo ratings yet
- Stairs: To Afford The Means of Ascent and Descent Between Various Floors of The BuildingDocument26 pagesStairs: To Afford The Means of Ascent and Descent Between Various Floors of The BuildingAnn GertrudeNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Detailing and Construc PDFDocument40 pagesStructural Design Detailing and Construc PDFIbnuyusoff77No ratings yet
- Practical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemFrom EverandPractical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemNo ratings yet
- Residential Interior Design: A Guide To Planning SpacesFrom EverandResidential Interior Design: A Guide To Planning SpacesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Stair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareFrom EverandStair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareNo ratings yet
- Robert Maillart's Bridges: The Art of EngineeringFrom EverandRobert Maillart's Bridges: The Art of EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- English Pedagogical Module 6: CareersDocument24 pagesEnglish Pedagogical Module 6: CareersFanny Vera100% (1)
- BOQ For Dehshar High SchoolDocument6 pagesBOQ For Dehshar High SchoolFaisal CoolNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Estimate Sheet: OccupantsDocument23 pagesCooling Load Estimate Sheet: Occupantsvin ssNo ratings yet
- Is 2185-1 (2005) - Concrete Masonry Units, Part 1 - Hollow and Solid Concrete BlocksDocument14 pagesIs 2185-1 (2005) - Concrete Masonry Units, Part 1 - Hollow and Solid Concrete Blocksprashant gargNo ratings yet
- Report On Laboratory and Site Visit 2Document9 pagesReport On Laboratory and Site Visit 2Vijay JamadarNo ratings yet
- Vetotouch Effects - Decorative Coating Brochure 2017 Website - en - 52Document4 pagesVetotouch Effects - Decorative Coating Brochure 2017 Website - en - 52SHAIK ASIMUDDINNo ratings yet
- Sample Schedule of WorksDocument23 pagesSample Schedule of WorksOliver Bray100% (1)
- QS Mode of Measurement SheetDocument5 pagesQS Mode of Measurement SheetPrashant100% (1)
- Hull Building BoardDocument19 pagesHull Building BoardAlexander Florin100% (1)
- MoC ReviewerDocument37 pagesMoC ReviewerRonaldNo ratings yet
- Toyota Gujrat Motors Civil Works BoqDocument3 pagesToyota Gujrat Motors Civil Works BoqJahanzeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Application of Gypsum Sheathing: Standard Specification ForDocument3 pagesApplication of Gypsum Sheathing: Standard Specification ForAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Tile Adhesives, Tile Grouts and Plastering SkimDocument30 pagesTile Adhesives, Tile Grouts and Plastering SkimNykha Alenton100% (1)
- Gypsum ProductsDocument23 pagesGypsum ProductsRiya KvNo ratings yet
- Community Centre AnjiDocument21 pagesCommunity Centre AnjiPankaj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Quantities of Interior Civil Work at First FloorDocument6 pagesAbstract of Quantities of Interior Civil Work at First FloorSantanu ShresthaNo ratings yet
- MS - Kaveri IDEMI PDFDocument16 pagesMS - Kaveri IDEMI PDFAnjum AttarNo ratings yet
- Is 13849 PDFDocument517 pagesIs 13849 PDFsauravNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 (CEMENT) Cementing Material - Chapter ThreeDocument117 pagesCHAPTER 6 (CEMENT) Cementing Material - Chapter ThreeMitiku AregieNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Nitobond PVA: Multipurpose PVA Adhesive, Sealer and Cement AdmixtureDocument4 pagesFosroc Nitobond PVA: Multipurpose PVA Adhesive, Sealer and Cement AdmixtureVincent JavateNo ratings yet
- Estimating & Costing - C4 PDFDocument35 pagesEstimating & Costing - C4 PDFkumarNo ratings yet
- 233a2 Pil CC Systems BrochureDocument32 pages233a2 Pil CC Systems BrochurebhusanNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument8 pagesDental MaterialsSamantha Khyle Corpuz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dowel Pin - Snap Fit Technique: A Novel Split Cast TechniqueDocument4 pagesDowel Pin - Snap Fit Technique: A Novel Split Cast TechniqueIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Upper FloorsDocument41 pagesUpper FloorsTeoh Zhi Tong60% (5)
- Project Cost 18 Feb 2015Document137 pagesProject Cost 18 Feb 2015SarinNo ratings yet