Professional Documents
Culture Documents
States of Matter Solids Liquids and Gases
Uploaded by
Matipa DembureOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
States of Matter Solids Liquids and Gases
Uploaded by
Matipa DembureCopyright:
Available Formats
THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF
MATTER
All matter is made up of particles.
The particles are too small to be seen by
the naked eye.
The particles are always moving
The particles are arranged differently in
solids, liquids and gases.
Definition of matter: matter is anything
that has mass and occupies space. This
means all matter has mass and volume.
The kinetic theory of matter
The kinetic theory helps to explain the way in which
matter behaves. The evidence is consistent with the
idea that all matter is made up of tiny particles.
The main points of the theory are:
l All matter is made up of tiny, moving particles,
invisible to the naked eye. Different substances
have different types of particles (atoms, molecules
or ions) which have different sizes.
l The particles move all the time. The higher the
temperature, the faster they move on average, ie the higher
the kinetic energy the particles possess.
l Heavier particles move more slowly than lighter
ones at a given temperature.
The kinetic theory can be used as a scientific model
to explain how the arrangement of particles relates to
the properties of the three states of matter.
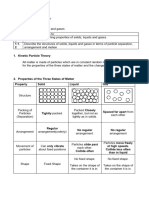
The three states of matter
Matter exists in three different states: solid, liquid and gas.
Ref page 85 focus on combined Science.
The following diagrams show the arrangement of particles in
solids, liquids and gases.
Identify the states P, Q and R.
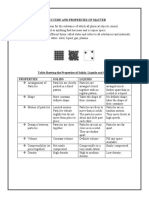
The table below summarises the properties of matter in each of the three states.
Properties State of matter
Solid Liquid Gas
Arrangement of Particles are arranged The particles arranged The particles are
particles in a regular pattern. in a random manner. arranged in a random
manner.
Separation of particles Particles are tightly The particles are still The particles are far
packed. There are no touching, but they are apart, with very large
spaces between the not as closely packed spaces between them.
particles. as in the solid state. The particles do not
touch at all.
Forces of attraction Very strong forces Strong forces , but Very weak forces of
between the particles weaker than in solids attraction.
and stronger than in
gases.
Movement Vibrate on spot, they The particles flow in The particles move
vibrate in their fixed and out of each other; randomly( in all
positions. the particles slide past directions) at high
each other. speed
Shape Fixed shape Take the shape of the Have no fixed shape
container, have no
fixed shape.
Volume Fixed volume Fixed volume Have no fixed volume;
Take the volume of
the container/ they fill
all the available space.
compressibility Cannot be compressed Can be slightly Can be easily
compressed compressed.
Question: Explain why solids cannot be compressed while gases can be easily compressed.
Evidence of particulate nature of matter – diffusion, dilution, Brownian movement, effect of
temperature
Expansion and Contraction
- Thermal expansion and contraction
- Applications in solids and liquids
Compressibility – of gases, atmospheric pressure
Solubility – heat, particle size, stirring
Question: a. Describe the changes of state.
b. of these changes of state, which ones need to absorb energy and which ones release
energy to the surroundings when they happen? Classify them into endothermic and exothermic
processes.
You might also like
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Kinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Document1 pageKinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Clint ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- 04 - Jack - QA LINAC PDFDocument30 pages04 - Jack - QA LINAC PDFamirNo ratings yet
- You Have The Mark of The Beast Not Forwarding This To Nine People So Saith The Lord Your GodDocument70 pagesYou Have The Mark of The Beast Not Forwarding This To Nine People So Saith The Lord Your GodGo Og100% (1)
- AAAC Stranded CondDocument13 pagesAAAC Stranded Condgvsbabu63No ratings yet
- Particle Nature of MatterDocument45 pagesParticle Nature of MatterDina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument39 pagesKinetic Particle Theoryh8alfred100% (1)
- Chemisty Notes O-LevelDocument97 pagesChemisty Notes O-LevelMunashe BinhaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration ProblemDocument12 pagesAcceleration ProblemEllaAdayaMendiolaNo ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument36 pagesThree States of MatterFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument1 pageMATTERL NarineNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids and Gases PropertiesDocument3 pagesSolids, Liquids and Gases PropertiesMohamed AmrNo ratings yet
- TP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument2 pagesTP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterThabang Sbo PhokontsiNo ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Mass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)Document2 pagesMass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)hajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gas (Solid, Liquid) - Project YakapDocument16 pagesProperties of Gas (Solid, Liquid) - Project YakapGeraldine Angel MirandaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry: The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesIGCSE Chemistry: The Particulate Nature of MatterVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- Matters in Our SurroundingDocument48 pagesMatters in Our SurroundingXm PiratesNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsRudra aminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheorymartynchekycNo ratings yet
- Notes The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument5 pagesNotes The Particulate Nature of MatterMihika ShethNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionDocument27 pagesThermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionSaad BBNo ratings yet
- Year 9 - States of Matter: Single Award Science (Chemistry)Document2 pagesYear 9 - States of Matter: Single Award Science (Chemistry)Christiana Van DortNo ratings yet
- Ram Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Document5 pagesRam Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Ram Gelo HawayNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Solid, Liquid, Gas ? Asked by (Student), On 18/10/10 AnswersDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Solid, Liquid, Gas ? Asked by (Student), On 18/10/10 AnswersRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Boom Notes For Sec2Document7 pagesBoom Notes For Sec2Varsha Balasubramanian (Bowenss)No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Particulate Nature of MatterDocument71 pagesChap 1 Particulate Nature of MatterAqua StarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesAanvi TripathiNo ratings yet
- NOTES, Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument2 pagesNOTES, Matter in Our Surroundingslogabi3459No ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 2Document19 pagesChemistry Chapter 2Aliana LeeNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document11 pagesiGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Changing StateDocument15 pagesMeeting 2 Changing StateBernadus SuharjoNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Science - All Classes - WB 1st JuneDocument18 pagesYear 7 Science - All Classes - WB 1st JuneTamara Martínez LiriaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter Particle Model PowerpointDocument23 pages1 States of Matter Particle Model Powerpointloupoo80No ratings yet
- Blue and Yellow Textured 2D and 3D Behaviors of Particles in Solid, Liquid, Gas Presentation-2Document18 pagesBlue and Yellow Textured 2D and 3D Behaviors of Particles in Solid, Liquid, Gas Presentation-2Gerald RefilNo ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter (Kinetic Particle Theory)Document56 pages1 States of Matter (Kinetic Particle Theory)YoviNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Theory of MatterDocument11 pagesThe Particulate Theory of MatterLarissaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument3 pagesStates of MatterShivaani TekaleNo ratings yet
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0No ratings yet
- Module 5 - CHANGES IN MATTERDocument17 pagesModule 5 - CHANGES IN MATTERJBM 0531No ratings yet
- Particle Model Explains States of MatterDocument2 pagesParticle Model Explains States of MatterDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- 01.matter Particle Theory States Matter AnswersDocument3 pages01.matter Particle Theory States Matter AnswersJoy Castro GasitNo ratings yet
- Particles in Solids Terminado FullDocument15 pagesParticles in Solids Terminado Fulljhunior carlos eduardo gamboa herreraNo ratings yet
- TP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1Document2 pagesTP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- C1 Chapter 1Document1 pageC1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesExercise 1 - Matter and Its PropertiespututuPLNo ratings yet
- Section 6.0 MatterDocument46 pagesSection 6.0 MatterKennedy MudawarimaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument26 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsULTRA BOSSNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Form 4 VersionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Form 4 VersionNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- Particle Model ExplainedDocument4 pagesParticle Model ExplainedKris_14No ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument15 pagesIntermolecular ForcesKrizthel RockwellNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument36 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterCherry GonzalezNo ratings yet
- States of Matter SummaryDocument1 pageStates of Matter SummarySAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids: 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument10 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids: 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterRusselle Therese DaitolNo ratings yet
- 5.-T-Loop Position and Anchorage ControlDocument7 pages5.-T-Loop Position and Anchorage ControlVerónica Patricia Anicama ChávezNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Practice Problems 7Document24 pagesMechanics Practice Problems 7Nguyễn Trần Minh TríNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Combustion Chamber Design to Reduce NOx EmissionsDocument19 pagesOptimizing Combustion Chamber Design to Reduce NOx EmissionsYummy BeatsNo ratings yet
- 2D Product Sheet 5 PExprt PDFDocument4 pages2D Product Sheet 5 PExprt PDFrafialanNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu General Ash7asc-W - 9710k1222Document16 pagesFujitsu General Ash7asc-W - 9710k1222Liuda Scutaru Zarisneac100% (2)
- Fracture and FatigueDocument21 pagesFracture and FatigueLeandro MarchiNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chemistry BasicsDocument6 pagesSolid State Chemistry BasicsAravindan B BabuNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 ALLDocument35 pagesLecture1 ALLadeelyjNo ratings yet
- Test Results Report Rhino Wood RepairDocument10 pagesTest Results Report Rhino Wood Repairmidzi24No ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuit: Induction Machine Class Instructor: DR - Fahad AlhuwaishelDocument25 pagesMagnetic Circuit: Induction Machine Class Instructor: DR - Fahad AlhuwaishelAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mitchell 1985Document19 pagesMitchell 1985Monal RajNo ratings yet
- Nomextechnicalguide PDFDocument40 pagesNomextechnicalguide PDFFran Rodriguez MariscalNo ratings yet
- TcpTunnel CAD en ReferenceManualDocument52 pagesTcpTunnel CAD en ReferenceManualRaul MejiaNo ratings yet
- Itute 2008 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesItute 2008 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 SolutionsnochnochNo ratings yet
- D 422 - 63 R98 - Rdqymi02m1i5oa - PDFDocument8 pagesD 422 - 63 R98 - Rdqymi02m1i5oa - PDFEnmanuel Cruz0% (1)
- NuclearDocument4 pagesNuclearIbrahim JavedNo ratings yet
- Price Schedule for OSP Backbone Java SectionDocument2 pagesPrice Schedule for OSP Backbone Java Sectionadeng100% (1)
- Geotechnical Design of Shallow Foundations ChapterDocument24 pagesGeotechnical Design of Shallow Foundations ChapterkKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electronics and Microprocessor-201-300-Rohit NegiDocument16 pagesBasics of Electronics and Microprocessor-201-300-Rohit NegiRohit NegiNo ratings yet
- Method of Lighting CalculationsDocument3 pagesMethod of Lighting CalculationsSpencer Josh RegedorNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Nanoparticles From Plant ExtractsDocument10 pagesSynthesis of Nanoparticles From Plant ExtractssitinisasyakirinaNo ratings yet
- Acivity No. 8 GeotechDocument6 pagesAcivity No. 8 Geotechphilip lazaroNo ratings yet
- Ac AssignmentDocument3 pagesAc AssignmentAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintenance: A160-Om-C-May15Document66 pagesOperation & Maintenance: A160-Om-C-May15Gustavo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring Methods, Failure Identification and Analysis For Induction MachinesDocument8 pagesCondition Monitoring Methods, Failure Identification and Analysis For Induction MachinesRamya DeviNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Powder Based Binder Jetting 3d PrinterDocument9 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Powder Based Binder Jetting 3d PrinterMukundhan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet