Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 6124916676002580174
5 6124916676002580174
Uploaded by
mohitsingh25400 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesThis document discusses key organic chemistry concepts including:
1) Aliphatic compounds which are straight or branched hydrocarbons like ethane and isobutane, and aromatic compounds which have delocalized pi electrons in ring structures like benzene.
2) Metamerism which is when compounds have different alkyl chain positions but the same molecular formula, like methoxypropane and ethoxyethane.
3) Stereoisomerism which is differences in atomic positions leading to geometric or optical isomers.
Original Description:
Original Title
5_6124916676002580174
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key organic chemistry concepts including:
1) Aliphatic compounds which are straight or branched hydrocarbons like ethane and isobutane, and aromatic compounds which have delocalized pi electrons in ring structures like benzene.
2) Metamerism which is when compounds have different alkyl chain positions but the same molecular formula, like methoxypropane and ethoxyethane.
3) Stereoisomerism which is differences in atomic positions leading to geometric or optical isomers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pages5 6124916676002580174
5 6124916676002580174
Uploaded by
mohitsingh2540This document discusses key organic chemistry concepts including:
1) Aliphatic compounds which are straight or branched hydrocarbons like ethane and isobutane, and aromatic compounds which have delocalized pi electrons in ring structures like benzene.
2) Metamerism which is when compounds have different alkyl chain positions but the same molecular formula, like methoxypropane and ethoxyethane.
3) Stereoisomerism which is differences in atomic positions leading to geometric or optical isomers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
AIM FREE EDUCATION TO ALL (APUL)
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles
and Techniques
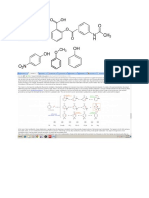
Straight or branched chain
compounds
Aliphatic
Compounds E.g. Ethane, Isobutane,
Acetaldehyde, Ethanol, etc.
Commonly called ‘arenes’. They
have a ring system with planar
structure and (4n + 2) π
electrons that are delocalised in
Aromatic the ring
Compounds
E.g. Benzene, Naphthalene,
Cyclopentadienyl anion,
Toluene, etc.
Different alkyl chains on
either side of the functional
group of the molecule, e.g.
Metamerism methoxypropane
(CH3OC3H7) and
ethoxyethane (C2H5OC2H5)
AIM FREE EDUCATION TO ALL (APUL)
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles
and Techniques
Difference in relative
positions of atoms or groups
in compounds with same
constitution and sequence of
Stereoisomerism covalent bonds
Geometrical and optical
isomerism
Nucleus seeking reagent that
donates an electron pair. They
are negatively charged ions or
neutral molecules with lone pair
Nucleophiles of electrons
E.g. hydroxide (HO– ), cyanide
(NC–) ions and carbanions
(R3C–), H2O, R3N, R2NH, etc.
Electron seeking reagent
that accepts an electron pair
Electrophiles E.g. carbocations, carbonyl
group (>C=O) or alkyl
halides, etc.
AIM FREE EDUCATION TO ALL (APUL)
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles
and Techniques
An ability of substituent(s) to
either withdraw or donate
electron density to the attached
carbon atom
Inductive Effect Electron withdrawing groups
- halogen, -NO2, -CN, -COOH,
-COOR, etc.
Electron donating groups -
alkyl groups
Transfer of electrons away from
an atom or substituent group
attached to the conjugated
Positive Resonance system
Effect (+R effect) E.g. – halogen, –OH, –OR, –
OCOR, –NH2, –NHR, –NR2, –
NHCOR
Transfer of electrons towards
the atom or substituent group
Negative Resonance attached to the conjugated
system
Effect (-R effect)
E.g. – COOH, –CHO, >C=O, –
CN, –NO2
AIM FREE EDUCATION TO ALL (APUL)
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles
and Techniques
Positive Electromeric Effect
(+E effect) - The π−electrons of
the multiple bond are
transferred to the atom that gets
attached to the reagent
Electromeric Effect
Negative Electromeric Effect
(E effect) (–E effect) - The π−electrons of
the multiple bond are
transferred to the atom that
does not get attached to the
reagent
You might also like
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Organic Chemistry - ODLDocument48 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Organic Chemistry - ODLNURUL BALQIS DZULKIFLINo ratings yet
- 02-729-Pt2 Iss2Document23 pages02-729-Pt2 Iss2br1ggsy100% (1)
- Organic Chemicstry: Inductive Effect: Polarisation of σ-bond caused by the polarisation of adjacentDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemicstry: Inductive Effect: Polarisation of σ-bond caused by the polarisation of adjacentnattusharanNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Version 2Document20 pagesThe Periodic Table Version 2yoonglespianoNo ratings yet
- 搜尋Document1 page搜尋SophiaNo ratings yet
- Chem 242 - Chapters 1&2 PDFDocument30 pagesChem 242 - Chapters 1&2 PDFKhaled AbeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Overview of Mechanisms 2022Document43 pagesChapter 3 - Overview of Mechanisms 2022Hoài Nguyễn Phan VũNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesFundamental of Organic ChemistryBernie Suarez50% (2)
- Mass Spectrometry: - IntroductionDocument28 pagesMass Spectrometry: - IntroductionNelson Enrique Bessone MadridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sesi 2 20212022Document50 pagesChapter 1 Sesi 2 20212022Noor farahin bainNo ratings yet
- 1 Aqa ChemistryDocument50 pages1 Aqa Chemistryoliviaojemen15No ratings yet
- Inductive Effect.... (Note)Document4 pagesInductive Effect.... (Note)NorUddin Sayeed100% (1)
- Orientation in Electrophilic Substitution Reactions on Benzene RingDocument4 pagesOrientation in Electrophilic Substitution Reactions on Benzene RingMohammadHussainKhanNo ratings yet
- Orangic Chemistry 1 Study GuideDocument5 pagesOrangic Chemistry 1 Study Guideanmol3No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Bonding and Isomerism Part 1Document49 pagesChapter 1 - Bonding and Isomerism Part 1Miguel MaralitNo ratings yet
- Substituent Effects - Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesSubstituent Effects - Organic ChemistrytracyymendozaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewPatrick Jay ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Geo-Chemistrty HandoutDocument22 pagesGeo-Chemistrty HandoutAbdi KhadirNo ratings yet
- 7 - XPS PDFDocument44 pages7 - XPS PDFtiraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Matter: in Water and Polar Solvents)Document3 pagesElectronic Structure of Matter: in Water and Polar Solvents)Chelsea DizonNo ratings yet
- CXBBCDocument18 pagesCXBBCboiroyNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Classification of ElementsDocument13 pagesCH 3 Classification of Elementsamittt0650No ratings yet
- ESCA Electron Spectroscopy For Chemical Analysis XPS: X-Ray Photoelectron SpectrosDocument72 pagesESCA Electron Spectroscopy For Chemical Analysis XPS: X-Ray Photoelectron SpectrosAnurag TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: A Simple Model For Chemical Bonds: Inorganic OrganicDocument21 pagesChapter 1: A Simple Model For Chemical Bonds: Inorganic OrganicLaura BeltranNo ratings yet
- 12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument9 pages12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and TechniquesmohammedNo ratings yet
- Inductive and Resonance EffectDocument20 pagesInductive and Resonance EffectNehalPatelNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument7 pagesChem NotesLorena ArguetaNo ratings yet
- Electronic EffectDocument46 pagesElectronic EffectJyöt Sîlvēr100% (3)
- 14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistrygoverotaropafadzwaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Basic Principles - 2Document3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basic Principles - 2sangeeta.pgcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1 (Modified - 210316)Document40 pagesChapter 2-1 (Modified - 210316)Santiago BritoNo ratings yet
- CHEM01 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY 1st Sem 2021 2022Document98 pagesCHEM01 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY 1st Sem 2021 2022EGAS JAYSON RABENo ratings yet
- 2014 - Agnieszka - Optical Properties of Unsymmetrical Azomethines With One Imine BondsDocument6 pages2014 - Agnieszka - Optical Properties of Unsymmetrical Azomethines With One Imine BondsTomas Delgado MontielNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4.2 Electrochemistry PDFDocument51 pagesMODULE 4.2 Electrochemistry PDFhey yutNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction Learning Objectives:: Module 1 - Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction Learning Objectives:: Module 1 - Organic ChemistryTwinkle ToesNo ratings yet
- Orbital Symmetry Lecture For StudentDocument101 pagesOrbital Symmetry Lecture For StudentEmil Ranjan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-10 PDFDocument151 pagesChapter 6-10 PDFdushimirimana eliasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Lesson: 1Document44 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry: Lesson: 1Nikol BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument71 pagesAtoms and Molecules: The Chemical Basis of LifeMekz Zon100% (1)
- Objectives:: Chapter Seven: Aromatic ChemistryDocument25 pagesObjectives:: Chapter Seven: Aromatic Chemistryalechamark57No ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry GuideDocument34 pagesA Level Chemistry GuideRexton Jarvis100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Electronic Structure of AtomsHong Hong WongNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations & Periodicity: Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument21 pagesElectron Configurations & Periodicity: Electronic Structure of AtomsFarukIslamNo ratings yet
- NIM Unit 1 NotesDocument32 pagesNIM Unit 1 Notesakjhasd kjhasdkjhNo ratings yet
- Organic With Drug MoleculeDocument73 pagesOrganic With Drug Moleculedipankargh48No ratings yet
- Note 6 - Chemical PeriodicityDocument2 pagesNote 6 - Chemical PeriodicityJhoanna Marie Manuel-AbelNo ratings yet
- Goc MTHDocument12 pagesGoc MTHmanthangoel11jeeNo ratings yet
- College of EngineeringDocument17 pagesCollege of EngineeringClarkNo ratings yet
- 7 GlossaryDocument8 pages7 GlossaryEhtıram SeyıdovNo ratings yet
- General and Inorganic Chemistry For Pharmacy PDFDocument91 pagesGeneral and Inorganic Chemistry For Pharmacy PDFthucinorNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Molecules and Solids: Nearly Classical ConceptsDocument15 pagesBonding in Molecules and Solids: Nearly Classical Conceptszenox07No ratings yet
- Geochemistry IntroductionDocument25 pagesGeochemistry Introductionkristiano97100% (1)
- Module 3Document24 pagesModule 3Jessalyn PaclebNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HandoutsDocument2 pagesChemistry Handoutsiyahh5.comNo ratings yet
- Heteroaromatic Systems: Intermediates, Orientation, Structure and Reactivity RelationshipsDocument13 pagesHeteroaromatic Systems: Intermediates, Orientation, Structure and Reactivity RelationshipsFATHIMA THANHA T NNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5the Periodic Table PDFDocument23 pagesLecture 5the Periodic Table PDFMohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document48 pagesChapter 2pxh4tncf9yNo ratings yet
- Organic PresentationDocument25 pagesOrganic PresentationsaheedvkNo ratings yet
- OippioDocument22 pagesOippioZia RathoreNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Tetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 3.21-30From EverandTetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 3.21-30Derek BartonNo ratings yet
- Summary (Chemical Engineering Calculations) Lecture Notes 1: Introduction To Chemical Engineering CalculationsDocument13 pagesSummary (Chemical Engineering Calculations) Lecture Notes 1: Introduction To Chemical Engineering CalculationsTaanzNo ratings yet
- FTA ReportDocument20 pagesFTA Reportzen AlkaffNo ratings yet
- 04.10.20 SR - CO-SC Jee Adv 2015 P2 CTA-4 QPDocument19 pages04.10.20 SR - CO-SC Jee Adv 2015 P2 CTA-4 QPManju ReddyNo ratings yet
- Application of Gaussian Plume Model - Arystanbekova2004Document8 pagesApplication of Gaussian Plume Model - Arystanbekova2004Muhammad Tozan Ajie RonowijoyoNo ratings yet
- Moseley's Law Is An Empirical Law Concerning The CharacteristicDocument3 pagesMoseley's Law Is An Empirical Law Concerning The Characteristicranjit sahaNo ratings yet
- Panpsychism - The Idea That Everything From Spoons To Stones Are Conscious Is Gaining Academic CredibilityDocument5 pagesPanpsychism - The Idea That Everything From Spoons To Stones Are Conscious Is Gaining Academic CredibilityWalkinLA100% (1)
- SM4000 00 - en UsDocument6 pagesSM4000 00 - en UsAngga SuryadarmaNo ratings yet
- SJI Steel-Deck-Webinar FINAL 03-19-2018 1 HandoutDocument71 pagesSJI Steel-Deck-Webinar FINAL 03-19-2018 1 HandoutlolitaNo ratings yet
- Astm D4318 PDFDocument16 pagesAstm D4318 PDFcatalina_tudosa100% (3)
- Anaconda Brand Type SHD-GC Power, Shielded Round Portable w/Ground-Check, EPR/CPEDocument1 pageAnaconda Brand Type SHD-GC Power, Shielded Round Portable w/Ground-Check, EPR/CPECarlos JavierNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Sinterability and in Vitro Bioactivity of Barium-Doped AkermaniteDocument7 pagesEnhanced Sinterability and in Vitro Bioactivity of Barium-Doped AkermaniteJean AndradeNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 Course OutlineDocument15 pagesChem 2 Course Outlineapi-607966786No ratings yet
- Trenter2004 - Approaches To The Design of Cantilever Retaining WallsDocument9 pagesTrenter2004 - Approaches To The Design of Cantilever Retaining WallsValerioNo ratings yet
- Camera Ready Iccs205Document5 pagesCamera Ready Iccs205syed1188No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledapi-171616606No ratings yet
- Form I MathsDocument13 pagesForm I Mathsashariluvonga8No ratings yet
- Calorific ValueDocument3 pagesCalorific ValueIrah Louise GARINGNo ratings yet
- Moles and EquationsDocument16 pagesMoles and EquationssksksksNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Material and MANUFACTURINGDocument68 pagesWeek 2 Material and MANUFACTURINGضياء بن احمد الكباريNo ratings yet
- AsdfvvDocument1 pageAsdfvvbradhakemanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document6 pagesLecture 10Muhammad Sameer NawazNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A 10 MW Recompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Cycle For Tropical Climatic Conditions Sathish Et AlDocument14 pagesAnalysis of A 10 MW Recompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Cycle For Tropical Climatic Conditions Sathish Et AlTanatswa MoyoNo ratings yet
- JVS Manual JRP 011Document12 pagesJVS Manual JRP 011Tamilventhan_sNo ratings yet
- Heliodon StudiesDocument2 pagesHeliodon StudiesIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 - I and II Order ProcessDocument4 pagesExp 2 - I and II Order ProcessErmias NigussieNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Open Loop Temp Control - SignedDocument10 pagesLab 1 - Open Loop Temp Control - SignedShashitharan PonnambalanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 4Document5 pagesPhysical Science 4Morelei FernandezNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering May 2021 Review: Engr. Karren May A. SimplinaDocument1 pageTransportation Engineering May 2021 Review: Engr. Karren May A. SimplinaNaigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- (L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Basic Kinematics - 5th AprDocument79 pages(L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Basic Kinematics - 5th AprDiganta Chattopadhyay 11-A,30.No ratings yet