0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views25 pagesUnderstanding Phylogenetic Trees and Methods
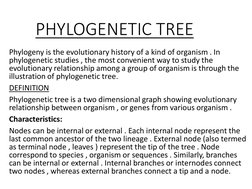
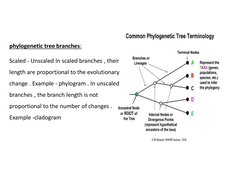
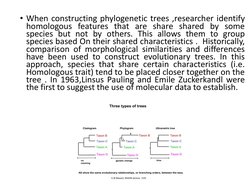
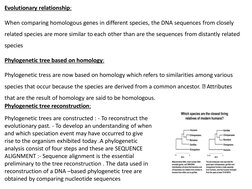
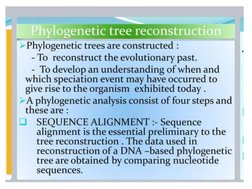
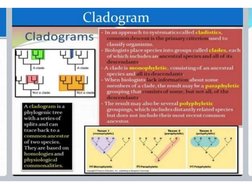
This document discusses phylogenetic trees, which illustrate the evolutionary relationships among organisms or genes. Phylogenetic trees are constructed using homologous features shared between species. There are two main types of phylogenetic tree branches: scaled branches, where length represents evolutionary change, and unscaled branches, where length is not proportional to changes. Common methods for reconstructing phylogenetic trees include maximum parsimony, which minimizes evolutionary steps, and distance-based methods like UPGMA and neighbor joining, which are based on distances between aligned sequences.
Uploaded by
freelancerhamzaabbasiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views25 pagesUnderstanding Phylogenetic Trees and Methods
This document discusses phylogenetic trees, which illustrate the evolutionary relationships among organisms or genes. Phylogenetic trees are constructed using homologous features shared between species. There are two main types of phylogenetic tree branches: scaled branches, where length represents evolutionary change, and unscaled branches, where length is not proportional to changes. Common methods for reconstructing phylogenetic trees include maximum parsimony, which minimizes evolutionary steps, and distance-based methods like UPGMA and neighbor joining, which are based on distances between aligned sequences.
Uploaded by
freelancerhamzaabbasiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd