Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy GI Tract
Uploaded by
Jerico Carag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesAnatomy GI Tract
Uploaded by
Jerico CaragCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
B.
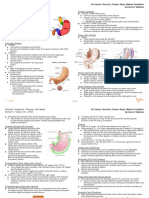
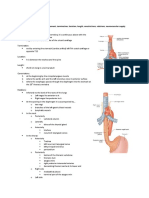
Gastrointestinal Tract The Stomach Exterior
− 5 meters in live subjects Stomach
− 9 meters in cadavers - At the upper left quadrant of the abdomen
− Divided into Upper and Lower GI Tract - Covered by the left lobe of the liver
o Demarcated by the Ligament of Trietz Cardia
at the terminal portion of the - Initial dilated portion of the stomach that
duodenum connects the stomach to the esophagus
Fundus
Upper GI Tract: - Adjacent to cardia, beneath the diaphragm
1. Esophagus Body
2. Stomach - Central dilated portion of the stomach
3. Duodenum - Bordered by the greater and lesser curvatures
Lower GI Tract: on the sides
1. Jejunum Greater curvature
2. Ileum - Convex side of the body
3. Cecum - Attachment of the greater omentum
4. Colon Lesser curvature
5. Sigmoid - J-shaped concave side of the body
6. Rectum - Incisura angulare – sharp angulation of the
curvature, attachment of the lesser omentum
Greater Omentum Pylorus
- Curtain-like structure hanging in front of the - Tapering region of the body before connecting
abdominal viscera to the duodenum
- Attached to the greater curvature of the - Divided into two:
stomach o Antrum – connects the body of the
- Double layered visceral peritoneum; folds stomach to the pylorus
back to attach to the transverse colon o Pyloric canal – connects pylorus to
Divisions of the Greater Omentum: the first part of duodenum
1. Gastrocolic ligament – greater curvature to
the transverse colon Blood Vessels of the Stomach
2. Gastrosplenic ligament – greater curvature to 1. Left Gastric Artery
the spleen o From Celiac Trunk
o Supplies the Upper half off the lesser
Lesser Omentum curvature
- Connects the lesser curvature of the stomach o Anastomoses with the right gastric
and the proximal part of the duodenum to the artery
inferior surface of the liver 2. Right Gastric Artery
- Hepatogastric ligament – lesser curvature to a. From Common Hepatic Artery
the inferior surface of liver b. Inferior half of the lesser curvature
- Hepatoduodenal ligament – proximal portion 3. Left Gastroepiploic Artery
of duodenum to inferior surface of liver a. From Splenic Artery (branch of celiac
trunk)
Esophagus b. Upper half of greater curvature
- Muscular tube extending from the pharynx to c. Anastomoses w/ right gastroepiploic
the stomach artery
- Posterior to trachea, pierces the diaphragm at 4. Right Gastroepiploic Artery
the level of T10 (Eat-10) a. From Gastroduodenal Artery
- Lower esophageal sphincter – constriction of b. Lower half of greater curvature
the esophagus prior to its connection to the 5. Short Gastric Arteries
stomach, protects and guards the segment a. From Splenic Artery
from the harmful acids of the stomach, b. Fundus
prevents reflux of food to the esophagus 6. Left and Right Gastric Veins
- Z line – inner wall of the esophagus, zigzag a. To the Portal Vein
line appearance at the wall of the distal b. Drains the lesser curvature
esophagus, transition of epithelial lining from 7. Left and Right Gastroepiploic Artery
stratified squamous nonkeratinized to simple a. Drains the greater curvature
columnar b. Left: to Splenic vein
c. Right: to Superior Mesenteric Vein Second part: Descending
- Ampulla of Vater
Celiac Trunk branches: - Duct of Santorini
- Left gastric artery Third part: Horizontal
- Common hepatic artery - Crossed by the Superior mesenteric artery and
o Hepatic artery proper – supplies the vein
liver via L+R hepatic arteries and the Fourth part: Ascending
gallbladder via the Cystic artery - Held by the Ligament of Treitz
o Gastroduodenal artery – supplies the o Attaches duodenum to diaphragm
duodenum (Ant Sup + Pos Sup *All other parts of duodenum are RETROPERITONEAL
pancreaticoduodenal arteries), SUPERIOR MESENTERIC ARTERY
greater curvature (R gastroepiploic - From the anterior surface of abdominal aorta
artery) Branches of SMA:
o *Superior pancreaticoduodenal 1. Inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
arteries anastomose w/ the inferior a. Anterior and posterior
pancreaticoduodenal arteries (from b. Supplies the Inferior half of pancreas
Superior Mesenteric Artery) and distal duodenum
o Right Gastric artery 2. Jejunal and ileal arteries
- Splenic artery a. Supplies the jejunum and ileum,
o Passes horizontally behind the respectively
stomach to reach the splenic hilum b. Anastomose to form the arcade
o Gives off the short gastric arteries arteries
c. Vasa Recta – from the arcade arteries,
STOMACH INTERIOR supplies the wall of small intestine
Gastric Rugae 3. Ileocolic artery
- Folds of the stomach wall a. Supplies the cecum, appendix, and
Pyloric sphincter proximal segment of the ascending
- Strong ring of smooth muscle guarding the colon
terminal portion of the pyloric canal 4. Right colic artery
- Regulates release of gastric content to the a. Terminal branch of SMA
duodenum b. Supplies the distal end of the
ascending colon and the hepatic
Duodenum flexure
Pancreatic head 5. Middle colic artery
- At the concave side of the duodenum a. Supplies the proximal 2/3 of the
Plicae circulares / Valves of Kerckring transverse colon
- Numerous folds of the lumen of duodenum SUPERIOR MESENTERIC VEIN
Major duodenal papilla Branches:
- Ampulla of Vater 1. Right gastroepiploic vein – distal half of lesser
- Small, rounded elevation on the medial side of curvature
the lumen of the duodenum 2. Inf pancreaticoduodenal vein – lower half of
- Opening for the bile duct and pancreatic duct duodenum and pancreas
on the medial wall of the descending part of 3. Jejunal and ileal veins – jejunum and ileum
duodenum 4. Ileocolic vein – cecum and appendix
Duct of Santorini 5. Right colic vein – ascending colon
- Accessory pancreatic duct 6. Middle colic vein – transverse colon
- Bypasses the ampulla of Vater
- Nonfunctional JEJUNUM AND ILEUM
Blood supply of the duodenum: Jejunum – middle portion of the small intestine,
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries – from begins after the ligament of Trietz
gastroduodenal artery Ileum – last segment of the small intestine
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries – from *no clinical landmark between jejunum and ileum
superior mesenteric artery
Cecum
First part: Superior - First segment of the large intestine
- Continuation of pylorus - At the right iliac fossa
- INTRAPERITONEAL - Blood vessels: ileocolic artery and vein
Appendix - Lies on the upper and lower quadrants of the
- Vermiform appendix abdomen
- At the McBurney’s point Sigmoid colon
o Line between ASIS and umbilicus, 1/3 - Last segment of the colon
distance from ASIS - Terminates at the rectosigmoid junction
Taenia Coli - Supplied by the sigmoid arteries, on of the
- Three band smooth muscle at the anterior terminal branches of the inferior mesenteric
surface of the cecum, ascending, transverse, artery
descending, and sigmoid colon VASCULATURE OF THE COLON
- Haustration of the large intestine SMA: supplies the cecum, appendix, ascending and
Mesoappendix proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
- Portion of mesentery connecting the ileum to - Ileocolic
the appendix - Right colic
- Encloses appendicular vessels and lymphatics - Middle colic – watershed area demarcates
Appendicular artery midgut and hindgut
- Terminal branch of the ileocolic artery Terminal branches of Inferior mesenteric artery(IMA) -
- Branch of SMA supplies the rest of the colon
Appendicular vein - Left colic
- Accompanies the appendicular artery - Sigmoid
- Tributary of the ileocolic vein, drains to the Marginal artery
SMV - Anastomoses of the arteries of the colon,
Ileocecal valve and sphincter gives rise to several vasa recta
- Bauhin’s valve Vasa Recta
- Controls the flow of contents from the ileum - Supplies directly to the walls of the colon
to the cecum Superior Rectal Artery
- Terminal continuation of the IMA
COLON - Supplies the superior region of the rectum
Haustra - Anastomoses with other arteries of the
- Sacculations of the large intestine, gives the rectum:
colon its segmental appearance caused by the o Midde rectal – from internal iliac
Taenia Coli artery
Epiploic appendages o Inferior rectal – from internal
- Small pouches of peritoneum forming fatty pudendal artery
tags attached on the surface of the colon Inferior Mesenteric Vein
- A.k.a. ornamental appendages - Left colic – drains distal third of transverse
Ascending colon colon, splenic flexure, and descending colon
- Retroperitoneal - Sigmoid – drains the sigmoid colon
- Supplied by the ileocolic and right colic artery - Superior rectal – drains the superior rectum
- Drained by corresponding veins
Hepatic flexure
- Right colic flexure
- Sharp bend from ascending to transverse
colon under the liver
Splenic flexure
- Left colic flexure
- Transverse to descending colon
- Below the spleen
Transverse colon
- Hangs off the stomach via the greater
omentum
- Attached to the posterior abdominal wall via
the transverse mesocolon
- Blood supply: middle colic (proximal), left colic
(distal)
Descending colon
- Supplied by the left colic artery and vein
You might also like
- Anatomy StomachDocument43 pagesAnatomy StomachBijo K BennyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorder PDFDocument324 pagesThyroid Disorder PDFsuci w100% (2)
- 1998 - Copper and Zinc in Inflammatory and Degenerative DiseasesDocument198 pages1998 - Copper and Zinc in Inflammatory and Degenerative DiseasesvmarinelliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of StomachDocument58 pagesAnatomy of StomachSkinny tuberNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingDocument57 pagesPacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingAhmad Khalil Ahmad Al-SadiNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Seeley's Chapter 8 Nervous SystemDocument100 pagesSeeley's Chapter 8 Nervous SystemChristine Tapawan88% (8)
- Somatic Embryogenesis Book PDFDocument503 pagesSomatic Embryogenesis Book PDFveeroo ahmad100% (1)
- Development of Gastrointestinal TractDocument28 pagesDevelopment of Gastrointestinal TractSaif100% (1)
- Science 8 Q4M1 Digestive System 2021 2022Document5 pagesScience 8 Q4M1 Digestive System 2021 2022carl helloNo ratings yet
- Final Compre Exam Key AnswersDocument14 pagesFinal Compre Exam Key Answersmj CanilangNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum and Peritoneal CavityDocument26 pagesPeritoneum and Peritoneal CavitytuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- General Arrangement of The Abdominal VisceraDocument30 pagesGeneral Arrangement of The Abdominal Visceraapi-249972919100% (2)
- Anatomi AbdomenDocument36 pagesAnatomi Abdomenari naNo ratings yet
- Transfer To Definitive Care EcaDocument40 pagesTransfer To Definitive Care EcaFahrurido Kusbari100% (1)
- Assignment Module 3Document14 pagesAssignment Module 3Asshi Sha50% (4)
- Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryDocument39 pagesHistochemistry and Enzyme Histochemistrykay100% (2)
- Screenshot 2022-10-07 at 3.25.27 AMDocument42 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-07 at 3.25.27 AMغدي بنت بن قاعدNo ratings yet
- Anatomy StomachDocument2 pagesAnatomy StomachtristineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SI and LIDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The SI and LIShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- StomachDocument13 pagesStomachSemNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Histology Gaster - DuodenumDocument149 pagesAnatomy and Histology Gaster - DuodenumRevila AuliaNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument162 pagesLearning ObjectivesNovita IskandarNo ratings yet
- Anatomi & Histologi GasterDocument24 pagesAnatomi & Histologi Gastersalvaryn neNo ratings yet
- Abdomen - Esophagus To ColonDocument42 pagesAbdomen - Esophagus To ColonBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Stomach PDFDocument7 pagesThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Stomach PDFredderdatNo ratings yet
- Esophagus & Stomach, Its Blood Supply& Development:: OesophagusDocument8 pagesEsophagus & Stomach, Its Blood Supply& Development:: OesophagusBoody KhalilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Abdominal VisceralsDocument189 pagesAnatomy of Abdominal VisceralsademabdellaaleNo ratings yet
- Blok GastrointestinalDocument103 pagesBlok GastrointestinalArLyne MakinNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument40 pagesPancreasMuthannah MarawanNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 3 Blok GI AndreasDocument124 pagesPemicu 3 Blok GI AndreasEko SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Git AnatomyDocument62 pagesGit AnatomyBimo HarmajiNo ratings yet
- PeritoneumDocument8 pagesPeritoneumDavid BadaruNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 2 GIDocument123 pagesPemicu 2 GIDessy DsyNo ratings yet
- Stomach 2Document14 pagesStomach 2Saad100% (1)
- 4 Peritoneum PDFDocument64 pages4 Peritoneum PDFN ANo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument142 pagesAbdomenleul TizazuNo ratings yet
- M1207 GIT E2 ForegutDocument29 pagesM1207 GIT E2 Foregutkavinduherath2000No ratings yet
- Stomach, Duodenum, Pancreas, and Spleen (Valera)Document4 pagesStomach, Duodenum, Pancreas, and Spleen (Valera)Joshua MandaweNo ratings yet
- GIT Anatomy Book WORD 2022Document35 pagesGIT Anatomy Book WORD 2022Kero amgedNo ratings yet
- STOMACHDocument20 pagesSTOMACHChoudhary FahadNo ratings yet
- Definition - It Is Muscular Bag Forming Widest &Document10 pagesDefinition - It Is Muscular Bag Forming Widest &Dr santosh100% (1)
- 1166 Stomach Dr.-RaviDocument38 pages1166 Stomach Dr.-RaviKubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- Curvature: Short and Slightly Concave Anterior Surface of Stomach From The Cardia ToDocument3 pagesCurvature: Short and Slightly Concave Anterior Surface of Stomach From The Cardia ToJohn Christian LopezNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AnatomyDocument17 pagesAbdominal AnatomyAbdu NaviNo ratings yet
- Amboss - GITDocument16 pagesAmboss - GITAllysahNo ratings yet
- Topographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery of The StomachDocument57 pagesTopographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery of The StomachEl Raai El Saleh HospitalNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 2 Git StephenDocument169 pagesPemicu 2 Git StephenRana RickNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document4 pagesLecture 12A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document14 pagesLecture 4X RamboNo ratings yet
- Yyyyycrash Course Anatomy - AbdomenDocument31 pagesYyyyycrash Course Anatomy - Abdomen黃芳昌No ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of Abdominal CavityDocument88 pagesClinical Anatomy of Abdominal CavityFahim NadvyNo ratings yet
- L6 - OmentumDocument12 pagesL6 - OmentumGoodone OneNo ratings yet
- Stomach: Presented By: Dushyanth MDocument17 pagesStomach: Presented By: Dushyanth MSanjay NaikNo ratings yet
- Ana SGD 15Document67 pagesAna SGD 15Bea ManzanoNo ratings yet
- DIgestive System EmbDocument85 pagesDIgestive System EmbDanish GujjarNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum 2022Document86 pagesPeritoneum 2022Tayyib KhanNo ratings yet
- Esphagus Stomach Duodenum Gross AnatomyDocument9 pagesEsphagus Stomach Duodenum Gross AnatomyWinchester LoapedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes (2nd Sem) 1Document133 pagesAnatomy Notes (2nd Sem) 1Abegail DanasenNo ratings yet
- Upper GITDocument33 pagesUpper GITWahida Amalin Ab RazakNo ratings yet
- LAB1MGDC1206.101 t179 15122008Document114 pagesLAB1MGDC1206.101 t179 15122008getsweetNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Abdomen: Dr. Ahmad Kamil Shahwan Ph.D. General SurgeryDocument87 pagesAnatomy of The Abdomen: Dr. Ahmad Kamil Shahwan Ph.D. General SurgeryDaniel SitungkirNo ratings yet
- 02 General SurgeryDocument34 pages02 General SurgerySarathi IrisNo ratings yet
- Celiac Trunk Definition - The Celiac Trunk Arises From TheDocument3 pagesCeliac Trunk Definition - The Celiac Trunk Arises From TheDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Abdomen (6) : - Abdominal Esophagus - Stomach - Small Intestine - Large IntestineDocument34 pagesAnatomy of The Abdomen (6) : - Abdominal Esophagus - Stomach - Small Intestine - Large IntestineBilal YimamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Small Intestine: Lecture-4Document23 pagesAnatomy of Small Intestine: Lecture-4Ahmed OudahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Esophagus & StomachDocument5 pagesAnatomy-Esophagus & StomachAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Gaster Dan DuodenumDocument179 pagesAnatomi Gaster Dan DuodenumHaraka NabdaNo ratings yet
- GasterDocument179 pagesGasterAraka Patriota100% (1)
- GIT EmbryologyDocument39 pagesGIT Embryologyqnz78swpjmNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia Pactical 1Document5 pagesKingdom Animalia Pactical 1Alexson UndiNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 7Document6 pagesScience Chapter 7Deb Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCell Membrane Structure and FunctionkyleeebooggNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Penyusunan Gigi Artifisial Kelompok 7Document53 pagesPrinsip Penyusunan Gigi Artifisial Kelompok 7gilangNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Anabolism and CatabolismDocument4 pagesMetabolism: Anabolism and CatabolismMedi OmicNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Reflex Threshold (ART) Patterns: An Interpretation Guide For Students and Supervisors: Course Material and Exam Questions Course MaterialDocument17 pagesAcoustic Reflex Threshold (ART) Patterns: An Interpretation Guide For Students and Supervisors: Course Material and Exam Questions Course Materialn_almagroNo ratings yet
- Acute Miocard InfarkDocument32 pagesAcute Miocard InfarkhansNo ratings yet
- A Farmer Wants To Buy A 10kg Bag of FertilizerDocument2 pagesA Farmer Wants To Buy A 10kg Bag of FertilizerJalfred SUDNo ratings yet
- Week 5: Module 9:central Nervous System and Special Senses Time Table (2nd Year Medicine, Semester 3: 2011-2012)Document17 pagesWeek 5: Module 9:central Nervous System and Special Senses Time Table (2nd Year Medicine, Semester 3: 2011-2012)Hairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 3Document11 pagesCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Management BurnDocument13 pagesFluid Management BurnWeronika StarrNo ratings yet
- Haemoptysis Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument57 pagesHaemoptysis Diagnosis and TreatmentMuhammad Cholid AlfahroziNo ratings yet
- Kreisberg-Zakarin Et Al IPNS Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999Document8 pagesKreisberg-Zakarin Et Al IPNS Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999ElNo ratings yet
- Cambios Fisiologicos UlcDocument16 pagesCambios Fisiologicos UlcLuisa Fernanda Laverde ChunzaNo ratings yet
- Irregular PluralsDocument19 pagesIrregular PluralsDj-mauro Mulchen ChileNo ratings yet
- Steps HemodialysisDocument3 pagesSteps HemodialysisCes LoNo ratings yet
- InterneuronsDocument6 pagesInterneuronsRafu DestajoNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors & UncouplersDocument7 pagesInhibitors & UncouplersValentino Dhiyu AsmoroNo ratings yet