Professional Documents
Culture Documents
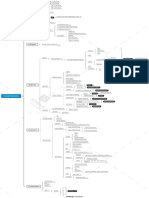
Patho Notes - Blood Dyscrasias
Uploaded by
s21514.laiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patho Notes - Blood Dyscrasias
Uploaded by
s21514.laiCopyright:
Available Formats
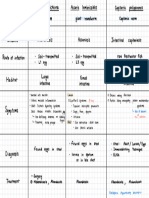
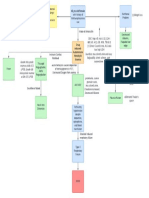
Fatigue
Dyspnea
Pallor
Headache
Tachycardia
Heartburn
Symptoms & Signs
Edema, especially of the ankles
Jaundice & enlargemnt of spleen (<-
hemolysis)
Numbness & tingling sensations
Syncope
Excessive blood loss
Menstruation
Pregnancy
Iron loss, demand for iron outstrips supply
Rapid growth during adolscence
Malabsorption syndrome/chronic diseases
of intestines/stomach
Negative iron balance -> iron storage in
Iron-deficiency (the leading cause) body depletes -> synthesis of hemoglobin
becomes impaired -> RBCs lose shape,
appear cigar-/pencil-shaped upon
microscopic analysis
Oral iron supplementation
Treatment Injectable iron supplements for individuals
with malabsorption/intolerable with oral
supplementation
Severe cases associated with rheumatoid
Secondary to chronic inflammatory/ arthritis/TB
infectious/autoimmune diseases
-> Defect in erythropoiesis
Moderate cases associated with cardiac
conditions
Of chronic disease
Treat underlying disease
Treatment
Therapy with erythropoietin(EPO)
Kidney fails to produce adequate amounts
Of renal disease of EPO Severe cases may result from renal failure
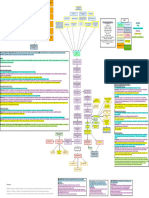
caused by impaired DNA synthesis
- megablobalstic RBCs are large, immature
RBCs that contain an increased ratio of RNA
to DNA - reduced hemoglobins volume
Principle dietary sources of VB12: animal
摄入不足 (vegetarians susceptible) food products
吸收障碍 - 内因子缺乏 (先天/后天 - removal
Magablobalstic Anemia 巨幼细胞贫血 Pernicious Anemia (Vitamin B12-deficiency) 缺乏原因
of stomach/bowel)
利用障碍
Etiology - 叶酸
叶酸, 维生素 (DNA合成过程中的
维生素B12( 合成过程中的 Principle dietary sources of folic acid:
重要参与部分)缺乏 摄入不足 fruits & veg
Alcohol Abuse
Inflammation of the bowel/Crohn’s disease
吸收障碍
Folic acid deficiency 缺乏原因
Adverse effects of certain medications eg.抗
癫痫药物
需求增加 eg. pregnancy
A reduction in the quantity of RBCs/
利用障碍
hemoglobin in a measured volum of blood
-> reduced blood’s ability to carry oxygen
to cells (tissue hypoxia) Types of anemia (classified by causative A reduction in circulating RBCs caused by
Anemias factor) accelerated destruction of RBCs
Heredity
Exposure to chemical toxins/certain
Etiology
bacterial toxins
Autoimmunity
Hemolytic Degradation降解 of heme in the destroyed
RBC -> accumulation of bilirubin ->
jaundiced appearance in tissues & urines &
feces
Splenectomy - decrease the risk of
gallstones, severe episodes of hemolysis,
For inherited cases pathological changes to bone marrow
For hemorrhage Blood transfusions
Treatment
For infectious causes Antibiotics & supportive therapies
For immune disorders Immune suppressive therapies
Results from an insult to the hematopoietic
cells in bone marrow - exposure to
Aplastic anemia再生障碍性贫血
再生障碍性贫血 myelotoxins
a chronic hereditary hemolytic form of
anemia, found predominately in black race
Heterozygous -> mild; Homozygous ->
severe
Sickle cell crises - painful episodes;
increased susceptibility to infections
RBCs assume a sickle shape, inflexible,
Presence of hemoglobin S along with rigid -> obstruct small arterioles &
Sickle cell anemia hemoglobin A in erythrocytes -> as RBC capillaries -> ischemia -> tissue hypoxia,
deoxygenated, hemoglobin S cross-links great pain, organ failure
with other hemoglobin S & develop long
Etiology crystals
RBCs fragile -> hymolysis -> hemolytic
anemia
Usually established in childhood, can’t be
cured
Hemoglobinopaties - affecting the Diagnosis & treatment Analgesics-> relieve pain
structure/function/production of Blood transfusions and fluid replacement->
hemoglobin expand blood volume & improve circulation
in blocked blood vessels
Inherited disorder, most common genetic
disorder
About 14% of African Americans are
carriers for alpha thalassemia
Beta thalassemia occurs among 10%~15%
of people from Mediterranean countries and
Occurence Southeast Asia
Thalassemia 地中海贫血 - 珠蛋白生成障碍
About 1000 severe cases occur annually in
the US
Life-threatening anemia, bone marrow
hyperactivity, enlargement of spleen, growth
Symptoms of most severe form retardation, bone deformities
Blood studies, may show reduced RBC
numbers/reduced hemoglobin levels/
hematocrit
Diagnosis changes in the morphology of the corpuscles
Bone marrow studies
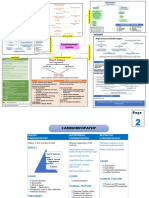
Dizziness
Headaches
Visual disturbances
Neurologic symptoms
Syncope
Mental sluggishness
Irritability
Dyspnea
Symptoms & Signs - related to increased Hypertension
RBC mass (increased blood viscosity)
Itching & pain in fingers and toes
Splenomegaly
Night sweats
Weight loss
In severe cases - circulatory stagnation,
thromboembolism with death may occur
When plasma volume is reduced, no
decrease in RBCs
Dehydration
Relative polycythemia
Plasma loss
Possible causes
Fluid & electrolyte imbalance
An abnormal increase in the amount of of Etiology Burns
hemoglobin/the RBC count/hematocrit红细
红细
Polycythemia (Vera) 真性红细胞增 胞比容 -> an absolute increase in RBC mass
A rise in RBC accompanied by an increase
多 in WBCs & platelets
Most common in men 40-50 yrs old
Absolute polycythemia (Polycytheia Vera)
干细胞非控制的肿瘤性增生
病因尚不明确, 可能的发病机制 干细胞对红细胞生成素敏感度增强
造血干细胞基因突变 超过95%患者可见JAK2 V617F基因突变
An abnormal increase in RBC numbers &
hemoglbin levels & Hematocrit
Elevated leukocyte & thrombocyte counts
Diagnosis
Enlarged spleen
Clinical picture & total RBC mass evaluation
Periodic phlebotomy to reduce blood volume
Chemotherapeutic agents to help suppress
the production of blood cells by bone
Treatment Decreasing the thickness of blood
marrow
Pain medication
Managing symptoms
Antihistamine
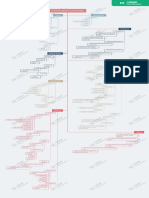
Results from impaired production/increased
destruction of platelets
A common cause - cancer chemotherapy/
radiation treatment -> suppress platelet
formation by destroying bone marrow
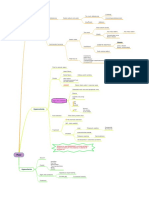
Blood Dyscrasias Etiology
The most common bleeding problem among
hospitalized patients
Body vulnerable to prolonged bleeding
Spontaneous hemorrhages often visible on
skin as small, flat, red spots - petechiae 瘀
点; large purplish patches - ecchymoses 瘀
斑
Blood microscopic examination & bone
Diagnosis marrow examination
Thrombocytopenia 血小板减少症
Treat underlying causes
Preventive measures - avoid accidental
Treatment trauma
Platelet transfusions reserved for severe
condition/severe bleeding
An autoimmune disorder resulting in excess
destruction of platelets
Most commonly occurs as an acute problem
in children less than 5yrs following a viral
infection; in adults - chronic/rarely follows
viral infection
Characterized by the sudden appearance of
*A subtype - Idiopathic thrombocytopenia petechiae
purpura (ITP) 特发性血小板减少性紫癜
Based on appearance of severe
thrombocytopenia
Diagnosis Suspected immune disorder -> analysis of
blood for presence of antibodies/phagocytic
cells
Hemorrhages usually controlled by
corticosteroids
Treatment Removal of spleen reserved for patients
who do not respond to medications/with
severe condition
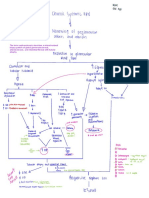
Disorders of hemostasis 大多数凝血因子再肝脏合成
大多数凝血因子再肝脏合成, 少数在内皮细胞等
位置合成
维生素
维生素K依赖性凝血因子:
依赖性凝血因子:II因子(凝血酶原)
因子(凝血酶原)VII
因子 IX因子
因子 X因子
因子
一些physio
Interrupted synthesis of vitamin K/Impaired
absorption of vitamin K -> vitamin K
deficiency
Vitamin K - a fat soluble vitamin thats
synthesized by intestinal bacteria Vitamin K deficiency can occur in newborns - some have not yet
developed the intestinal bacteria that
synthesize the vitamin
An X-linked recessive disorder, primarily
affects males
Etiology - genetic, deficiency in clotting
factor VIII
Bleeding often occurs in the GI tract/in the Without proper treatment, chronic bleeding
joints of hip/knee/elbow/ankle -> inflammation -> joint fibrosis -> major
inflammation with acute pain & swelling disability
Hemophilia A 血友病
血友病A
Intracranial hemorrhage - a cause of death
in severe hemophilia
Regular replacement of factor VIII with
additional doses administered during
phases of acute bleeding
Coagulation Defects (deficiency/impairment Inherited bleeding disorders Mild cases - sometimes treated with
Treatment
of one or more of the clotting factors) desmopression (a synthetic hormone that
stimulates the release of the carrier for
factor VIII)
Caused by a deficiency in the von
Willebrand clotting factors (vWF)
Von Willebrand’s Disease (vWD) 血管性假血
友病 Defect in the adhesion of platelets
Reduced level of factor VIII
A potentially life-threatening condition that
involves destruction of the platelets &
consumption of clotting factors
Sepsis/blood infection
Endothelial damage
Shock
Etiology
Obstetrical complications associated with
delivery of a child
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (
DIC) 弥散性血管内凝血 Some types of cancer
Usually diagnosed on the basis of
underlying disease
Diagnosis Low platelet counts on a. Peripheral blood
test, increases in bleeding times, presence
of degradation products in blood plasma
Treating underlying disorder
Platelet transfusions
Treatment
Administration of concentrates of
Supportive treatment coagulation inhibitors
Administration of an intravenous
anticoagulant
Reduction of circulating neutrophils ->
increased risk for bacterial & fungal
infections
Classic signs eg swelling & pus formation
may be diminished/absent in a severely
neutropenic individual
Infectious complications depend on severity
of the condition -> symptoms eg fever, skin
inflammation
cancer chemotherapy or medical immune
suppression (suppress cellular proliferation
within bone marrow)
Agranulocytosis (Neutropenia) 粒细胞缺乏症 Frequently secondary to
Rheumatoid arthritis
Etiology
Primary condition with unknown causes
Complete blood count + bone marrow
Diagnosis examination
May resolve without treatment
For severe cases - hospitalization with
isolation & IV antibiotic therapy
Treatment For neutropenia secondary to cancer
treatment - Growth factors (colony-
stimulating factors) stimulates production of
WBCs
Autoimmune case - corticosteroids may help
*hypereosinophilia can occur in response to
Disorders of White Blood Cells a parasitic infection as a normal immune
response
IHS occurs mainly in males 20-50yrs
CHF
Myocarditis
Heart problems
Conduction defects
Persistent increases in blood eosinophils &
associated involvement of the heart and
Valve dysfunction
nervous system
Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
Altered behavior & cognitive function
Neurologic problems Spasticity痉挛状态
Ataxia(impaired coordination)
Eosinophill Abnormalities If without treatment - poor prognosis with
median survival of 1 yr; chemotherapy
recently reported to produce 70% survival at
10yrs
Related to the ingestion of L-tryptophan
Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome 嗜酸性粒细胞
增多-肌痛综合症 Characterized by muscle pain, fatigue, skin
changes, nervous system abnormalities,
pulmonary hypertension
You might also like
- Name of Homeo Mother Tincher SymptomsDocument17 pagesName of Homeo Mother Tincher SymptomsKarisma SenapatiNo ratings yet
- Coughdyspnea 2511 ArticleDocument1 pageCoughdyspnea 2511 ArticleGissele ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive RetinopathyDocument4 pagesHypertensive RetinopathyNikithaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionTar digrateNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Findings: Small Cell CarcinomaDocument4 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Findings: Small Cell CarcinomaTheresa Sombilla FacunlaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ShockDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Shockkavindeep15122004No ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument1 pageBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For My Baby DDocument7 pagesDrug Study For My Baby DJAMES PATRICK MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- Pathway Krisis TriroidDocument1 pagePathway Krisis TriroidRaisya Aulia PutriNo ratings yet
- Mind Map - FatigueDocument1 pageMind Map - FatigueLaylee ClareNo ratings yet
- Practical - 2Document38 pagesPractical - 2PeeyushNo ratings yet
- MCV: 80-100 FL MCV 100 FL: Normocytic Anemia Microcytic Anemia Macrocytic AnemiaDocument1 pageMCV: 80-100 FL MCV 100 FL: Normocytic Anemia Microcytic Anemia Macrocytic AnemiaMohiedine AbouljoudNo ratings yet
- Vitals: Stridor (Upper Airway Obstruction), Use of Acc. Muscles, DroolingDocument1 pageVitals: Stridor (Upper Airway Obstruction), Use of Acc. Muscles, DroolingSean LamNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument1 pageAnemiaCJMALNo ratings yet
- HW 1637Document1 pageHW 1637Genie NatdapornNo ratings yet
- Incident and Injuries DashboardDocument1 pageIncident and Injuries DashboardmurasolimaranNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Bacilli - RespiratoryDocument4 pagesGram Negative Bacilli - RespiratoryrefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Mind Map - 202221 - 181948Document1 pageMind Map - 202221 - 181948georgina daguioanNo ratings yet
- PDF Anemia Concept Map0000Document1 pagePDF Anemia Concept Map0000alvianmerzaradiputraNo ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor C/PDocument1 pageKwashiorkor C/PSpider manNo ratings yet
- CICUTA VIROSA (Cic)Document1 pageCICUTA VIROSA (Cic)mohd18160No ratings yet
- ESRD PathoDocument1 pageESRD PathoPrecious VernalNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDocument1 pageTuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDeni Marie GomonidNo ratings yet
- Biology 3Document1 pageBiology 3KacperCoghenNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: KidneysDocument1 pagePredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: KidneysChe CacatianNo ratings yet
- Histopathological Features in Anemia DisordersDocument1 pageHistopathological Features in Anemia Disorderskoki74No ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument12 pagesUntitled NotebookEvil QTNo ratings yet
- Pathway AnemiaDocument1 pagePathway AnemiaMuhammad AuliaNo ratings yet
- Primarily Neurologic, Reflecting The Development of Cerebral EdemaDocument1 pagePrimarily Neurologic, Reflecting The Development of Cerebral EdemaCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument4 pagesPath o PhysiologyDorinna Rizada BagaNo ratings yet
- PHA 618: Human Physiology and Pathophysiology Cardiovascular ExercisesDocument2 pagesPHA 618: Human Physiology and Pathophysiology Cardiovascular Exerciseskaila lunaNo ratings yet
- 3, Annex-3, Tables-13 A and B, 2018-19Document6 pages3, Annex-3, Tables-13 A and B, 2018-19Sumit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia HPWDocument1 pageHypercalcemia HPWfredericktingsyNo ratings yet
- All - RenalDocument3 pagesAll - RenalkumarNo ratings yet
- Trematodes ScheduleDocument1 pageTrematodes ScheduleDr-positive EnergyNo ratings yet
- EpitheliumDocument1 pageEpitheliumhawdeng xalitNo ratings yet
- Allergy Log TemplateDocument1 pageAllergy Log TemplateAydaNo ratings yet
- Ujian Patoflow Yola MTDocument1 pageUjian Patoflow Yola MTAdam SipahutarNo ratings yet
- Master ChartDocument3 pagesMaster Chartsudhir74No ratings yet
- Classification: Varicose Veins (Varicosities)Document2 pagesClassification: Varicose Veins (Varicosities)Queenet BelingonNo ratings yet
- Hepatology at A GlanceDocument1 pageHepatology at A GlanceAmelia Pebrianti KurniaNo ratings yet
- CPC CaseDocument1 pageCPC CaseJill ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolytes, Acid-Base BalanceDocument5 pagesFluid, Electrolytes, Acid-Base BalanceAmanda MariaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismDocument1 pageAntihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismAhmed YT100% (1)
- Kassab R - Care Map 4 - PFDocument1 pageKassab R - Care Map 4 - PFranakassab7No ratings yet
- DR Anam - 1Document2 pagesDR Anam - 1MunawarNo ratings yet
- Decrease Cardiac Output Patho NewDocument2 pagesDecrease Cardiac Output Patho NewGenette Sy SolisNo ratings yet
- ABCDE Table Crib SheetDocument1 pageABCDE Table Crib SheetdaeyangmgrNo ratings yet
- Kiltzs-Keto-Cure 2020 Spring EditionDocument50 pagesKiltzs-Keto-Cure 2020 Spring Editionafbengochea100% (5)
- Coronavirus - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology - APRIL UPDATE - Key AtfDocument1 pageCoronavirus - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology - APRIL UPDATE - Key AtfJuan Manuel Tapia AlzateNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMuhammad Jefri LukmanNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument1 pageSodium and Potassiumjoan1alejo1espirituNo ratings yet
- Three Steps For Reducing Total Cost of Ownership in Pumping SystemsDocument13 pagesThree Steps For Reducing Total Cost of Ownership in Pumping SystemsJuan AriguelNo ratings yet
- Phy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFDocument99 pagesPhy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFRaj Shekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Inter 10 - Third ClassDocument96 pagesInter 10 - Third ClassRicardo Jackichan Barzola LopezNo ratings yet
- Value For Money Analysis.5.10.12Document60 pagesValue For Money Analysis.5.10.12Jason SanchezNo ratings yet
- Name and Logo Design Contest For Public Wi-Fi Network Services Terms & ConditionsDocument2 pagesName and Logo Design Contest For Public Wi-Fi Network Services Terms & ConditionsAc RaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Edita O PanuncioNo ratings yet
- Swash Plate Leveling Tool Instructions: Trex 600 Electric & NitroDocument3 pagesSwash Plate Leveling Tool Instructions: Trex 600 Electric & NitroEdinal BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Case Study-Cereal PartnersDocument5 pagesCase Study-Cereal PartnersTariq MehmoodNo ratings yet
- The Brand AuditDocument9 pagesThe Brand AuditRohit RoyNo ratings yet
- How My Brother Leon Brought Home A WifeDocument16 pagesHow My Brother Leon Brought Home A Wifefusha23No ratings yet
- Leadership's Ramdom MCQsDocument48 pagesLeadership's Ramdom MCQsAhmed NoumanNo ratings yet
- GSKDocument22 pagesGSKChaudhary Hassan ArainNo ratings yet
- Gears DifferentialDocument13 pagesGears Differentialpulkitymcaust_112907100% (1)
- Passive Voice PDFDocument5 pagesPassive Voice PDFJohan FloresNo ratings yet
- Ten Questions Concerning Hybrid Computational Physical Mod - 2016 - Building andDocument10 pagesTen Questions Concerning Hybrid Computational Physical Mod - 2016 - Building andQU DAUPNo ratings yet
- EtamolDocument5 pagesEtamolthonyyanmuNo ratings yet
- XDocument2 pagesXSophiaFrancescaEspinosaNo ratings yet
- Kompilasi Soal Paket BDocument10 pagesKompilasi Soal Paket Babdul wahidNo ratings yet
- Okuma CL302L Parts List & ManualDocument3 pagesOkuma CL302L Parts List & Manualcoolestkiwi100% (1)
- Management Information SystemDocument65 pagesManagement Information SystemMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- 2 - ARM Cotex-M3 - IntroductionDocument124 pages2 - ARM Cotex-M3 - IntroductionNghĩa VũNo ratings yet
- Oops MCQ (Unit-1)Document7 pagesOops MCQ (Unit-1)Jee Va Ps86% (14)
- Procreate GuideDocument283 pagesProcreate GuideDiego D'Andrea100% (2)
- Most Popular Bootstrap Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesMost Popular Bootstrap Interview Questions and Answershassan TariqNo ratings yet
- GSPANN Returns To Adobe Summit 2021 As A Showcase SponsorDocument2 pagesGSPANN Returns To Adobe Summit 2021 As A Showcase SponsorPR.comNo ratings yet
- What Is System and Subsystem? What Is Its Relationship?Document6 pagesWhat Is System and Subsystem? What Is Its Relationship?Mulugeta kinde100% (1)
- The Blender InterfaceDocument22 pagesThe Blender InterfaceacocancerNo ratings yet
- Level 5 Part 1: Listening Comprehension (V.9) : Nro. de Control: ......Document16 pagesLevel 5 Part 1: Listening Comprehension (V.9) : Nro. de Control: ......Maco cacoseNo ratings yet
- Stats 2B03 Test #1 (Version 4) October 26th, 2009Document7 pagesStats 2B03 Test #1 (Version 4) October 26th, 2009examkillerNo ratings yet
- Inkubator TransportDocument8 pagesInkubator TransportYassarNo ratings yet