Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DR Anam - 1
Uploaded by
MunawarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DR Anam - 1
Uploaded by
MunawarCopyright:
Available Formats
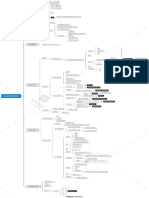
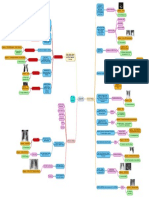
Myocardial Infarction
COMPLICATION (CAPS TRAP)
C→CHF T→Thromboembloism
A→Arrhythmias R→Rupture
P→Pericaditis A→Aneurysm
S→Shock P→Post MI Syndrome
Stable Angina
Atherosclerosis
Acute Rheumatic Fever
Cardiovascular
Ischemic Heart Disease
System
Endocarditis Congestive Heart Failure
Major Risk Factor Minor Risk Factors
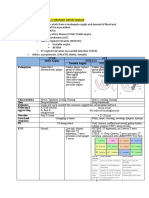
CLINICAL FEATURES
Diabetes Mellitus Obesity
Chest Pain on exertion Hyperlipidemia Sedentary life style
Relieved with nitroglycerin Cigarette smoking Stress
Onset- gradual Age (Men>45, Women Alcohol
Diaphoresis >55Y
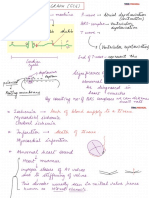
Unstable Angina
LEFT SIDED HEART FAILURE RIGHT SIDED HEART FAILURE
CAUSES: Ischemia, HTN, Dilated CAUSES: Most commonly due to left sided
Cardiomyopathy, Myocardial Infarction, HF and Cor pulmonale.
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
CLINICAL FEATURES: CLINICAL FEATURES:
• Awakening at night with shortness • Fluid retention causing swelling, or
of breath. pitting edema, in the ankles, legs
• Shortness of breath during exercise and/or feet.
or when lying flat. • Jugular venous distention
• Chronic coughing or wheezing. • Painful Hepatosplenomegaly with CLINICAL FEATURES
• Difficulty concentrating.
characteristics ‘nutmeg’ liver Chest Pain on Rest.
• Fatigue.
• Lack of appetite and nausea. TREATMENT:
LABS: 1. Positive Blood Culture TREATMENT: Based on etiology and symptoms. The distinction b/w unstable angina (USA) and NSTEMI is based on Cardiac enzyme.
2. Anemia of chronic disease (↓Hb, ↓MCV, ↓TIBC, ↑Ferritin ACE inhibitor, Digoxin, Nitrates Normal in USA.
3. Transesophageal echocardiogram
Page
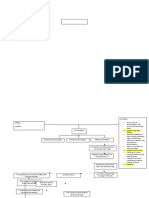
CARDIOMYOPATHY
2
DILATED HYPERTROPHIC RESTRICTIVE
CARDIOMYOPATHY CARDIOMYOPATHY CARDIOMYOPATHY
Dilation of all 4 chamber of heart Massive hypertrophy of left Decrease compliance of the
ventricle ventricular endomyocardium
RESULT ↓
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Restrict filling during diastole
makes the heart valve more tight
Systolic Dysfuction ↓
Can’t fill heart anymore
↓
Mitral & Tricuspid
Heart Walls lose compliance
Reggurgitation CAUSE
↓
Can’t fill heart, Diastolic
Arrthmias
❖ Amyloidosis
dysfunction
❖ Sarcoidosis
↓
❖ Endocardial fibroelastosis
Decrease Cardiac output
❖ Loeffler Syndrome
CAUSE CAUSE
CLINICAL FEATURE
❖ Genetic Mutation ❖ Genetic Mutation
❖ Myocarditis
❖ Present as CHF features
❖ Alcohol abuse
CLINICAL FEATURE ❖ Diminished QRS amplitude
❖Drugs → Doxorubicin
❖Pregnancy (Late or after child birth)
❖Hemochromatosis ❖ Decrease Cardiac output
❖ Sudden death due to
TREATMENT: Ventricular Arrhythmias
❖Syncope with exercise
Heart Transplant ❖Common in Young Athletes
You might also like
- OC-Ischemia Heart DiseaseDocument1 pageOC-Ischemia Heart DiseaseCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- SMLE MapDocument1 pageSMLE MapNazem Abd RaboNo ratings yet
- Coughdyspnea 2511 ArticleDocument1 pageCoughdyspnea 2511 ArticleGissele ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Medicine DamsDocument657 pagesMedicine DamsSubhashNo ratings yet
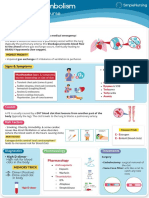
- Pulmonary Embolism: PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePulmonary Embolism: PathophysiologyTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- ARRYTHMIASDocument3 pagesARRYTHMIASitstheboyjayyNo ratings yet
- Materi - Gagal Jantung NeonatusDocument36 pagesMateri - Gagal Jantung NeonatusPutra AchmadNo ratings yet
- Gencardio LipidsDocument2 pagesGencardio LipidsRobertoNo ratings yet
- Ehab 607Document3 pagesEhab 607陈诗哲No ratings yet
- Anti ArrhythmiasDocument3 pagesAnti ArrhythmiasaqmalbaekNo ratings yet
- NCM 101-GenogramDocument1 pageNCM 101-GenogramCarolyn Moquerio-serniculaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocument1 pagePathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 pagesIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1Document48 pagesIM Part 1sasghfdgNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionTar digrateNo ratings yet
- RAAS InhibitorsDocument57 pagesRAAS InhibitorsMelissa DelgadoNo ratings yet
- ArrhysmiasDocument1 pageArrhysmiasBell GatesNo ratings yet
- Immunosero 3Document1 pageImmunosero 3Jillan MarieNo ratings yet
- 07 Heart Pathology (Part 1 and 2)Document13 pages07 Heart Pathology (Part 1 and 2)carlgangcaNo ratings yet
- PE - Pulmonary EmbolismDocument1 pagePE - Pulmonary EmbolismvishalmakadiaNo ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor C/PDocument1 pageKwashiorkor C/PSpider manNo ratings yet
- Compare & Contrast Map (Point-to-Point)Document1 pageCompare & Contrast Map (Point-to-Point)طفوف محمد.No ratings yet
- Low BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood FlowDocument2 pagesLow BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood Flowtantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- ACCA Cardiogenic and Septic ShockDocument1 pageACCA Cardiogenic and Septic Shockjose miguelNo ratings yet
- Vaskular DiseaseDocument2 pagesVaskular DiseaseRona Maulidia BakhitaNo ratings yet
- ACCA Cardiogenic and Septic ShockDocument1 pageACCA Cardiogenic and Septic ShockCatherine Morris100% (8)
- Acca Cs Syok SepsisDocument1 pageAcca Cs Syok SepsisSamuel KalonkNo ratings yet
- Pericardial Diseases - Dr. BartolomeDocument8 pagesPericardial Diseases - Dr. BartolomeMedisina101No ratings yet
- SF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - NotesDocument7 pagesSF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 pagesPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure PDFDocument18 pagesAcute Heart Failure PDFRiaak ImNo ratings yet
- RM 05 Form. Assessment IGDDocument5 pagesRM 05 Form. Assessment IGDsiti mutiaNo ratings yet
- ABI Worksheet: Patient Name: Patient ID: DateDocument2 pagesABI Worksheet: Patient Name: Patient ID: Datezaqqi ubaidillahNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument7 pagesUntitled DocumentDAVE BARIBENo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument12 pagesUntitled NotebookEvil QTNo ratings yet
- Iv Drip IsoxilanDocument1 pageIv Drip IsoxilannierbobierNo ratings yet
- CT3a 2.2 Heart Failure Hypertension Dyslipidemia Reyes WiniDocument14 pagesCT3a 2.2 Heart Failure Hypertension Dyslipidemia Reyes WiniAsylum AllegoryNo ratings yet
- Valvular Diseases 1Document6 pagesValvular Diseases 1Von LicudoNo ratings yet
- Med - CVSDocument31 pagesMed - CVSTHIRAVIYAM RAJNo ratings yet
- Vitals: Stridor (Upper Airway Obstruction), Use of Acc. Muscles, DroolingDocument1 pageVitals: Stridor (Upper Airway Obstruction), Use of Acc. Muscles, DroolingSean LamNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2deborah malnegro100% (5)
- Stroke 1Document1 pageStroke 1Trisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Stroke TIA ManagementDocument1 pageStroke TIA ManagementSara KalimNo ratings yet
- Stroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDocument3 pagesStroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDeclan O'KaneNo ratings yet
- Syncope Dr. Adrian RIzal PKB 2019Document39 pagesSyncope Dr. Adrian RIzal PKB 2019Fandy Hazzy AlfataNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFDocument8 pagesHemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFjenn1722No ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseNurul Aqilah MazlanNo ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument5 pagesSurgeryMary patrize GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PATHO CardiomyopathyDocument3 pagesPATHO CardiomyopathyNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan Kardio 1Document78 pagesKegawatdaruratan Kardio 1hnm mnhNo ratings yet
- PT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 4 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 4 Cheat SheetKat KatNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Angina AMI KuliahDocument47 pagesChest Pain Angina AMI KuliahRita AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document87 pagesNotes 2steveNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia & Residual RiskDocument26 pagesDyslipidemia & Residual RiskDan LeeNo ratings yet
- Cilacar CME Final 23-8-2010Document91 pagesCilacar CME Final 23-8-2010Kanchan Pathak100% (1)
- History of Palpitation: Editing LinkDocument6 pagesHistory of Palpitation: Editing LinkTouseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Rhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsDocument6 pagesRhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsRawabi rawabi1997No ratings yet
- CardiacDocument37 pagesCardiacRebecca TapiaNo ratings yet
- AGENCY Summer Ed.Document109 pagesAGENCY Summer Ed.AshAngeLNo ratings yet
- MDL ChallanDocument1 pageMDL ChallanPratik V PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Stop Motion RubricDocument3 pagesStop Motion Rubricapi-506782994No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management in The Hospitality Industry Is FullyDocument14 pagesHuman Resource Management in The Hospitality Industry Is FullykiahNo ratings yet
- HG G2 Q1 W57 Module 3 RTPDocument11 pagesHG G2 Q1 W57 Module 3 RTPJennilyn Amable Democrito100% (1)
- Theology NotesDocument3 pagesTheology NotesNia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Electrofusion Jointing ProceduresDocument12 pagesElectrofusion Jointing ProcedureslfpachecoNo ratings yet
- Polymer ConcreteDocument15 pagesPolymer ConcreteHew LockNo ratings yet
- Trading SecretsDocument99 pagesTrading SecretsGary100% (3)
- Percussion Catalog Eu Lep2001Document24 pagesPercussion Catalog Eu Lep2001isaac HernandezNo ratings yet
- Proiect La EnglezăDocument5 pagesProiect La EnglezăAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Company Law Registration and IncorporationDocument10 pagesCompany Law Registration and IncorporationAyush BansalNo ratings yet
- The Sacred Bee: Ancient Egypt: by Planet Bee FoundationDocument4 pagesThe Sacred Bee: Ancient Egypt: by Planet Bee Foundationsoha elmahdyNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting 14th Edition Warren Solutions Manual DownloadDocument28 pagesManagerial Accounting 14th Edition Warren Solutions Manual DownloadRose Speers100% (22)
- Nava V Artuz AC No. 7253Document7 pagesNava V Artuz AC No. 7253MACASERO JACQUILOUNo ratings yet
- 06 - Wreak Bodily HavokDocument40 pages06 - Wreak Bodily HavokJivoNo ratings yet
- SerpılDocument82 pagesSerpılNurhayat KaripNo ratings yet
- Dirt Bikes Financial and Sales DataDocument7 pagesDirt Bikes Financial and Sales Datakhang nguyenNo ratings yet
- Sol2e Printables Unit 5ADocument2 pagesSol2e Printables Unit 5AGeorgio SentialiNo ratings yet
- Revalida ResearchDocument3 pagesRevalida ResearchJakie UbinaNo ratings yet
- Question QP MCQ A BDocument60 pagesQuestion QP MCQ A BPrashant JhaNo ratings yet
- Tazkira Mujaddid AlfesaniDocument53 pagesTazkira Mujaddid AlfesanisayedNo ratings yet
- GRP 15 Property Law Final DDocument15 pagesGRP 15 Property Law Final DBruno OsananNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation (Company Update)Document17 pagesInvestor Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- CWWDocument2 pagesCWWmary joy martinNo ratings yet
- Archive Purge Programs in Oracle EBS R12Document7 pagesArchive Purge Programs in Oracle EBS R12Pritesh MoganeNo ratings yet
- Safety Management in Coromandel FertilizerDocument7 pagesSafety Management in Coromandel FertilizerS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Formulating Affective Learning Targets: Category Examples and KeywordsDocument2 pagesFormulating Affective Learning Targets: Category Examples and KeywordsJean LabradorNo ratings yet
- Decoding The Ancient Kemetic CalendarDocument9 pagesDecoding The Ancient Kemetic CalendarOrockjo75% (4)
- Eapp Las Q3 Week 1Document8 pagesEapp Las Q3 Week 1Maricel VallejosNo ratings yet