Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Uploaded by
Ali SafaaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Uploaded by
Ali SafaaCopyright:
Available Formats
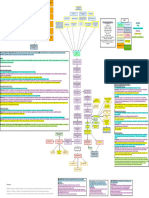
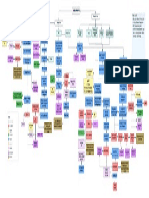
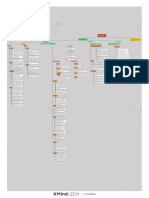
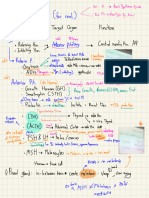
Aging
Etiology DHT and 5-alpha reductase
Men who had orchiectomy at young age will not
develop BPH
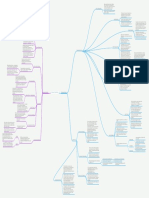
The self-administered questionnaire
Weak urinary stream
Abdominal straining
Postvoiding residual volume by U/S or by a Assessment of the severity
catheter
Terminal dribbling
Assess for Hydronephrosis Hesitancy
Obstructive voiding symptoms (early)
Incomplete emptying
Alpha-adrenergic agonists
Intermittency
Oral and topical cold remedies
Retention: the most serious one
Antihistamines Signs and symptoms
Nocturia
TCA (antidepressants)
Avoid medications that worsen symptoms like: Frequency
Testosterone replacement
Dysuria
Diuretics
Irritative voiding symptoms (late)
Urge incontinence
Antichlinergics
Whatchful waiting for patients with
Urgency
Antispasmodics mild symptoms
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Reduce alcohol intake
Smooth, firm and elastic enlargement of the prostate
On DRE
Reduce late day and evening water consumption
Behavior modifications
Physical examination Bladder distension
Limit caffeine intake
Abdominal examination There might be inguinal hernia that occurs due to
straining
1st generation are not used anymore due to their
systemic SEs
2nd generation like doxazosin GUE to exclude cystitis
Alpha- adrenergic antagonists
3rd generation are alpha1 selective antagonist, they have Treatment options Urea and creatinine to check the kidney function
less side effects, like tamsulosin and alfuzosin
PSA to exclude prostatic cancer
Like finasteride and dutasteride to reduce the size of the Investigations
prostate Sonography to calculate the size of the prostate ,
5-alpha reductase inhibitors
state of upper tract and the post voiding residual
volume of urine
If the prostate is more than 50g
Pressure flow studies and flow rate
To relief dynamic symptoms
To decrease the need for surgery Combination of the both
Long-term benefits of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
Pharmacological treatment
Like Saw palmetto
Phytotherapy 1. Urethral stricture.
2. Bladder neck contracture.
3. Neurogenic bladder: history of CVA, D.M. and
Failure of medical therapy spinal cord injury.
4. Cystitis. Simulate BPH and can be a
Reluctant urinary retention
Differential diagnosis
complication of this disease.
5. Bladder tumor. Esp. CIS which cause irritative
Recurrent UTI Voiding symptom
6. Vesicle stone.
Hydronephrosis Indications 7. Ca. prostate.
Recurrent hematuria
Bladder stone or Bladder diverticulum
Surgical intervention
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP)
Surgical options
Open prostatectomy
You might also like
- All Charts Final Exam 1 PDFDocument294 pagesAll Charts Final Exam 1 PDFYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ShockDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Shockkavindeep15122004No ratings yet
- Diarrhoea-Vomiting Pathway-Primary Care MAY 2015Document2 pagesDiarrhoea-Vomiting Pathway-Primary Care MAY 2015nimraNo ratings yet
- Pharma Complete PPDocument103 pagesPharma Complete PPHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Sym&Parasym DrugsDocument2 pagesMind Map Sym&Parasym Drugsjitpinun.sNo ratings yet
- Trematodes ScheduleDocument1 pageTrematodes ScheduleDr-positive EnergyNo ratings yet
- Laryngectomy Airway: Emergency Tracheostomy Airway ManagementDocument1 pageLaryngectomy Airway: Emergency Tracheostomy Airway ManagementDana IlieNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonist Anti-Cholinergic Agents Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (Nmba)Document1 pageCholinergic Agonist Anti-Cholinergic Agents Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (Nmba)Johnny BNo ratings yet
- Patient Data - 100Document1 pagePatient Data - 100pavankn0402No ratings yet
- Kassab R - Care Map 4 - PFDocument1 pageKassab R - Care Map 4 - PFranakassab7No ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Fluid Balance v14 PDFDocument1 pageICU One Pager Fluid Balance v14 PDFabobader2No ratings yet
- Master ChartDocument3 pagesMaster Chartsudhir74No ratings yet
- PHA 618: Human Physiology and Pathophysiology Cardiovascular ExercisesDocument2 pagesPHA 618: Human Physiology and Pathophysiology Cardiovascular Exerciseskaila lunaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FluidDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 FluidShaz NagaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyDocument1 pageRheumatic Fever PathophysiologyAlyssa Mae RadamNo ratings yet
- Pencatatan Hasil Kegiatan Kesehatan Lanjut Usia Puskesmas Bukoposo Bulan: AprilDocument1 pagePencatatan Hasil Kegiatan Kesehatan Lanjut Usia Puskesmas Bukoposo Bulan: AprilAlta ShoopNo ratings yet
- Posterior PituitaryDocument1 pagePosterior PituitaryfocussedlearnerNo ratings yet
- Suction Head CalcDocument5 pagesSuction Head CalcNghiaNo ratings yet
- Vitals: Stridor (Upper Airway Obstruction), Use of Acc. Muscles, DroolingDocument1 pageVitals: Stridor (Upper Airway Obstruction), Use of Acc. Muscles, DroolingSean LamNo ratings yet
- Or Rudimentary Minute Spine: Schistosoma Japonicum Oncomelania QuadrasiDocument1 pageOr Rudimentary Minute Spine: Schistosoma Japonicum Oncomelania QuadrasiMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- PDF Hoja de Registro Anestesico Gava CompressDocument2 pagesPDF Hoja de Registro Anestesico Gava CompressEDITH NATHALY CUMBAJIN PANELUISANo ratings yet
- Kidney AmatomyDocument1 pageKidney AmatomyCarlotta ranalliNo ratings yet
- Symposium Board 1Document1 pageSymposium Board 1api-482373029No ratings yet
- Endo Logbook FormsDocument3 pagesEndo Logbook FormsAmethystVonNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument1 pageCase PresentationGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- PFD of ETPDocument2 pagesPFD of ETPJahanzeb KhanNo ratings yet
- List MCUDocument1 pageList MCUdaryonoNo ratings yet
- Souq Waqif CHW Pump Head - Rev-01a As Per Approved DWGDocument1 pageSouq Waqif CHW Pump Head - Rev-01a As Per Approved DWGKarthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Automation Mind MapDocument1 pageAutomation Mind MapDanieleNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocument1 pageOsteoarthritis Concept MapJanselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Head / Hair Face Eyes Nose Oral / Throat Ears Neck: Physical Exam (Heent)Document1 pageHead / Hair Face Eyes Nose Oral / Throat Ears Neck: Physical Exam (Heent)Johnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Schematic Daigram-HNSS - 10.11.2020Document1 pageSchematic Daigram-HNSS - 10.11.2020snehaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Express Card HMCDocument2 pagesHeart Failure Express Card HMCalexNo ratings yet
- 2a-2b Uc Jandwala Oct 2023Document20 pages2a-2b Uc Jandwala Oct 2023lakhlanat345No ratings yet
- Column Cleaning and Storage: Together, We Can Do MoreDocument1 pageColumn Cleaning and Storage: Together, We Can Do MoreAdjieDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Pelatihan SSP Al FalahDocument26 pagesPengantar Pelatihan SSP Al Falaharie susantoNo ratings yet
- PressedDocument2 pagesPressedCathy ChuiNo ratings yet
- Modern Treatment Family Health Optima Insurance PlanDocument1 pageModern Treatment Family Health Optima Insurance PlanBhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiasDocument1 pageArrhythmiasAlessandro ZadraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonist MAPDocument1 pageAdrenergic Agonist MAPJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Modern Treatment Star Comprehensive Insurance PolicyDocument1 pageModern Treatment Star Comprehensive Insurance PolicyYashwanth KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Hormones สรุปDocument2 pagesHormones สรุปaomsinrinrada500No ratings yet
- Groin HerniasDocument1 pageGroin HerniasahmedNo ratings yet
- GGGGGGG: Bloodpotenc y Hitpoints Amaranth BloodDocument2 pagesGGGGGGG: Bloodpotenc y Hitpoints Amaranth BloodWannes IkkuhyuNo ratings yet
- SURGERY 10 TransplantationDocument1 pageSURGERY 10 TransplantationMikhail LamayoNo ratings yet
- Decaydecay Decay Decay Decay: Regurgitation ProblemsDocument1 pageDecaydecay Decay Decay Decay: Regurgitation Problemsnumber 2No ratings yet
- LA County Jail OptionsDocument5 pagesLA County Jail OptionsSouthern California Public RadioNo ratings yet
- Departments of Neurology, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NYDocument1 pageDepartments of Neurology, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NYyuliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminationDocument1 pageRespiratory ExaminationFANo ratings yet
- Online Edition - Digital AccessDocument1 pageOnline Edition - Digital Access18aw2708No ratings yet
- Unit 1, Pharmaceutical Analysis, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument14 pagesUnit 1, Pharmaceutical Analysis, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmapavanmistry19No ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ModelDocument1 pageRheumatoid ModelDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Managing Microbes Poster AIF 00612Document1 pageManaging Microbes Poster AIF 00612Devina Sari PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Attachment 4 L1 EHSS Competency Matrix and DefinitionsDocument10 pagesAttachment 4 L1 EHSS Competency Matrix and DefinitionsMohammad AshpakNo ratings yet
- Famplanenglishd 28533Document2 pagesFamplanenglishd 28533Sawera ChNo ratings yet
- Science - Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageScience - Circulatory SystemMUHAMMAD AZKA GHULAM IDRUS 2020bNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- Surgery: 4 StageDocument73 pagesSurgery: 4 StageAnsares SultanNo ratings yet
- Renal 2020 PDFDocument755 pagesRenal 2020 PDFlolaNo ratings yet
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia يوازمحلا يلع دمحا.د: Epidemiology of BPHDocument8 pagesBenign prostatic hyperplasia يوازمحلا يلع دمحا.د: Epidemiology of BPHAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Testicles & ScrotumDocument10 pagesDisorders of Testicles & ScrotumAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- PBL Git 2Document8 pagesPBL Git 2Ali SafaaNo ratings yet
- GIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument5 pagesGIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityEli Ezer SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Ocular Histoplasmosis SyndromeDocument17 pagesOcular Histoplasmosis SyndromeDiana PSNo ratings yet
- Adrenal PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesAdrenal PathophysiologyditabokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document27 pagesChapter 25Kriana RosalesNo ratings yet
- Marvel On 28Document16 pagesMarvel On 28Mizpah Jaireh Akot CarpinaNo ratings yet
- Detox - Louisa Williams HandoutDocument3 pagesDetox - Louisa Williams HandoutDaniel SolisNo ratings yet
- PONS: NeuroanatomyDocument20 pagesPONS: NeuroanatomyHassan IlyasNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Evaluation and Treatment in PediatricsDocument86 pagesPerioperative Evaluation and Treatment in Pediatricsmedpedshospitalist100% (2)
- Chapter 15 - Autoimmunity - Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 15 - Autoimmunity - Review QuestionsTreyton Sekani LopezNo ratings yet
- Newborn History TakingDocument9 pagesNewborn History TakingpriyankasekarNo ratings yet
- Ocular EmergencyDocument39 pagesOcular EmergencyAwadhesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Ebstein's Anomaly: Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Sarit Levinsky Group M1656Document36 pagesEbstein's Anomaly: Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Sarit Levinsky Group M1656Sarit LevinskyNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Nerve, Muscle and Neuromuscular JunctionDocument50 pagesDiseases of Nerve, Muscle and Neuromuscular JunctionMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Oet Writing Medicine PDFDocument30 pagesOet Writing Medicine PDFsushmita singh100% (2)
- Radiology Examination For Tractus Digestivus Chairunnisa, Dr. SP - RadDocument100 pagesRadiology Examination For Tractus Digestivus Chairunnisa, Dr. SP - RadDiana OCtavinaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Ischemic Stroke About A CaseDocument2 pagesPost Partum Ischemic Stroke About A CaseInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument26 pagesBrochureapi-466148385No ratings yet
- European Guidelines On Perioperative Venous.4Document6 pagesEuropean Guidelines On Perioperative Venous.4Mihai stancaNo ratings yet
- กรณีศึกษา (case study) อ.เพ็ญนภาDocument8 pagesกรณีศึกษา (case study) อ.เพ็ญนภาKanisthita ChutikittidechapatNo ratings yet
- Intestinal TuberculosisDocument15 pagesIntestinal Tuberculosisalfaz lakhaniNo ratings yet
- Up 'Til Dawn Position Paper AlsDocument6 pagesUp 'Til Dawn Position Paper AlsBrittany Morgan BooneNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Interpreting Ecgs A Practical Approach 3rd Edition Bruce ShadeDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Interpreting Ecgs A Practical Approach 3rd Edition Bruce Shadesuspendgruesome1iNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Abrupsio PlasentaDocument13 pagesJurnal Abrupsio Plasentaperussi pranadiptaNo ratings yet
- BLOCK II LMS Quiz AnatomyDocument27 pagesBLOCK II LMS Quiz AnatomyAshley BuchananNo ratings yet
- Reflection 7Document2 pagesReflection 7api-277407070No ratings yet
- Brain BeeDocument2 pagesBrain Beebubblegumlover96No ratings yet
- Glaucoma ImplantsDocument8 pagesGlaucoma Implantsarindamjha7041No ratings yet
- 002 Pediatric Obesity An IntroductionDocument24 pages002 Pediatric Obesity An IntroductionAnurag BhatejaNo ratings yet
- Koncpt Next/ Exit / Latest Neet PG Q Bank Sept 30 Onwards: DermatologyDocument8 pagesKoncpt Next/ Exit / Latest Neet PG Q Bank Sept 30 Onwards: DermatologyMarcelNo ratings yet
- FMGE July 2023 PrepLadder 1Document558 pagesFMGE July 2023 PrepLadder 1Sahil AhlawatNo ratings yet