Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Symposium Board 1
Uploaded by
api-4823730290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageThis document summarizes a student project that aims to develop a targeted cancer drug delivery system using poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) hydrogels. The students synthesized pHEMA hydrogels using atom transfer radical polymerization and incorporated an antigen comonomer. They then analyzed the hydrogels' ability to release dye over multiple trials and evaluated the results statistically, finding the unpaired t-test but not the Mann-Whitney test to be significant. The document provides background on current cancer treatments, hydrogels for drug delivery, and the synthesis methods used in the project.
Original Description:
Original Title
symposium board 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes a student project that aims to develop a targeted cancer drug delivery system using poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) hydrogels. The students synthesized pHEMA hydrogels using atom transfer radical polymerization and incorporated an antigen comonomer. They then analyzed the hydrogels' ability to release dye over multiple trials and evaluated the results statistically, finding the unpaired t-test but not the Mann-Whitney test to be significant. The document provides background on current cancer treatments, hydrogels for drug delivery, and the synthesis methods used in the project.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageSymposium Board 1
Uploaded by
api-482373029This document summarizes a student project that aims to develop a targeted cancer drug delivery system using poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) hydrogels. The students synthesized pHEMA hydrogels using atom transfer radical polymerization and incorporated an antigen comonomer. They then analyzed the hydrogels' ability to release dye over multiple trials and evaluated the results statistically, finding the unpaired t-test but not the Mann-Whitney test to be significant. The document provides background on current cancer treatments, hydrogels for drug delivery, and the synthesis methods used in the project.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
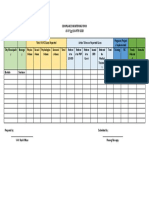
Shalika Neelaveni & Abhinav Adhikari
Loudoun Academy of Science
Background Method Statistical
Statistical Analysis
Analysis
Current Cancer Treatment v Mann-Whitney (trials 1-7)
v Cancer drugs have negative side effects due to the inaccurate nature of current ATRP Synthesis of pHEMA Hydrogels o Purpose: Compare initial dye solution concentration with concentration of
dye solutions after hydrogels were placed
treatment.
v Much of the healthy, non-cancerous tissue can be harmed. HEMA monomer and To this degassed Ethyl-α- o Summary:
Hydrogels • P-values for all tests are not considered significant
EGDMA crosslinker solution, the bpy bromoisobutyrate • Results were inconclusive because of an insufficient amount of data
v Hydrogels are a major development as a targeted drug delivery system to cancer were dissolved in a ligand and Cu(I)Br initiator was added to
cells. v Unpaired t test (trials 1-7)
v Hydrogels consist of monomers as the framework of the gel, and cross linkers as
methanol/water catalyst were added complete o Purpose: Compare initial dye solution concentration with concentration of
the bonding for the network. mixture. to the stirred solution. polymerization. dye solutions after hydrogels were placed
v Hydrogels for controlled drug delivery can be created with more than one o Summary:
polymer network partially interlaced (without covalent bonding) caused by radical • P-values for all tests are considered significant
polymerization; this can allow for easy separation, which can result in the release Synthesis of Antigen Comonomer • This indicates that if data with similar distribution and difference was
of a loaded therapeutic. observed, extremely statistically significant data would likely yield as a
v Poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate), otherwise known as pHEMA, hydrogels are N-succinimidyl acrylate was result Table 5: Statistical Analysis (α = 0.05)
added to a phosphate The resulting vinyl-Rabbit The vinyl-Rabbit IgG was
biocompatible and non-toxic making them successful in many drug delivery Statistical Test P-value
buffer solution containing IgG was purified by split into five units.
systems. Mann Whitney (trials 1-3) 0.1000
Rabbit IgG. The reaction removing the phosphate Methanol and water was
Antigens & Antibodies Antigens was carried out at 36°C for buffer solution through added to each unit to Unpaired t test (trials 1-3) 0.0002
v An antigen is a toxin or foreign substance which an hour to introduce vinyl centrifuge tube filtration reduce the concentration. Mann Whitney (trials 4-7) 0.1000
induces an immune response in the body, such groups into the Rabbit IgG. Unpaired t test (trials 4-7) 0.0002
as the creation of antibodies.
v Antibodies are a blood protein produced by the Cell
immune system in response to and Discussion
Discussion
counteracting a specific antigen. Antibodies ATRP Synthesis of pHEMA-EGDMA-Antigen-Antibody Hydrogels
ATRP The results of this research indicate that both the pHEMA hydrogels and vinyl-Rabbit
v Atom transfer radical
HEMA monomer, EGDMA To this degassed solution, IgG were synthesized correctly. FTIR graph 1, which compares the IR spectra of
polymerization (ATRP) is a
crosslinker, vinyl-Rabbit the bpy ligand and Ethyl-α- pHEMA hydrogels synthesized within this study with an IR spectra from a sample
polymerization method that bromoisobutyrate library displays a 76.26 match rating. Both spectra include peaks at 1725
requires a monomer, initiator, IgG, and GAR Anti-Rabbit Cu(I)Br catalyst were
IgG were dissolved in a added to the stirred initiator was added to wavenumbers and at 1150 wavenumbers suggesting carbon-oxygen stretch bonds.
catalyst, ligand, and solvent. complete polymerization. FTIR graph 2, which compares the IR spectra of the vinyl-Rabbit IgG, Rabbit IgG
Current Research https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ma0359032 methanol/water mixture. solution.
antigen, and N-succinimidyl acrylate, displays that the graphs of NSA and the vinyl-
v In 1999, scientists from Kansai University in Rabbit IgG contain peaks at 1100 wavenumbers, which suggests a carbon-oxygen
Japan developed a hydrogel with an antibody- stretch, and 1650 wavenumbers, which suggests a vinylidene bond. Both of these
antigen complex which swelled in response to a
specific free floating antigen.
Dye Loading support the idea that a vinyl group was attached to the antigen. These peaks can
also be found on IR spectra graphs of methylmethacrylate and succinimide, both of
v The hydrogel was prepared by grafting the rabbit The absorbance of the dye
Hydrogels were submerged Once the hydrogels were solution was then which have similar chemical structures to N-succinimidyl acrylate. Furthermore, FTIR
immunoglobulin G (rabbit IgG) antigen and goat for 24 hours in phosphate removed, the absorbance graph 3, which compares the pHEMA-EGDMA-antigen-antibody hydrogels with other
anti-rabbit IgG (GAR IgG) antibody, while subtracted from the initial
buffer solution containing of the solution was components of the hydrogels, displays a peak formed at 1650 wavenumbers which
acrylamide was used as the monomer.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10391240 absorbance to find the
dye, and later centrifuged recorded using a expresses modification of original pHEMA hydrogel structure to now incorporate the
v The results from the studies indicated that the hydrogel can swell and become difference. A standard curve
to separate the hydrogel spectrophotometer, using a vinyl-antigen and antibody. Lastly, the dye absorbance data for pHEMA hydrogels
porous in the presence of a free floating antigen because the bonds between was used to determine the
from dye solution. wavelength of 630nm. change in concentration. was statistically significant, and suggested that the concentration of dye after the
the antibody and antigen within the polymer dissociate due to the antibody’s
hydrogels were placed in was significantly lower than the initial concentration of the
much higher binding affinity for the free floating antigens.
dye.
Purpose Table 1: Change in absorbance based on hydrogel dye absorption
Conclusion
Conclusion & Application
Data & Results Trial
Number
Initial Absorbance
Absorbance after
Hydrogel
Dye Absorbance
by Hydrogel
Cancer drugs and therapeutics often have adverse side effects due to their 1 0.690 0.607 0.083 Through this research it was concluded that the pHEMA hydrogel had
interaction with healthy tissues that are not the intended target, thus it is necessary 2 0.690 0.617 0.073
to develop a treatment which is able to specifically target cancerous tissue. The
been modified by the vinyl-Rabbit IgG and the Goat-anti-rabbit IgG.
3 0.690 0.618 0.072
purpose of this research is to synthesize a targeted, anti-cancer drug delivery system Figure #1: FTIR comparison between synthesized pHEMA hydrogels and sample Current problems in the targeted therapy field include the inability of
library Average 0.690 0.614 0.076 Table 5: Absorbance of dye solution as a function of amount of antibody in
using antigen responsive hydrogels, with HEMA as a biocompatible monomer. Table 2: Change in concentration based on hydrogel dye absorption pHEMA-EGDMA-Antigen-Antibody hydrogel applying the research to real life medical uses. For instance, some
Trial Initial Concentration after Dye Absorbance Amount of
Initial Absorbance
Absorbance after Dye Absorbance monomers, such as acrylamide, are toxic and carcinogenic and thus
Number Concentration (%) Hydrogel (%) by Hydrogel (%) antibody (mg) hydrogel by Hydrogel
0 0.372 0.387 -0.015
cannot be applied to the human body. This research provides an
1 0.693 0.601 0.092
2 0.693 0.618 0.075 0.054 0.372 0.386 -0.014
alternative to current treatments by creating non-toxic and
3 0.693 0.619 0.074 0.074 0.372 0.35 0.022 biocompatible hydrogels that display potential for drug delivery to
Average 0.693 0.613 0.080 0.094 0.372 0.338 0.034 cancerous sites. By using materials found within the body as
Table 3: Change in absorbance based on hydrogel dye absorption Average 0.372 0.316 0.056 biomarkers, the cancerous regions can be effectively targeted and
Figure #2 FTIR comparison between synthesized pHEMA-EGDMA-Antigen-Antibody hydrogels, Trial Number Initial Absorbance
Absorbance after Dye Absorbance Table 6: Concentration of dye solution as a function of amount of antibody treated with this novel hydrogel.
hydrogel by Hydrogel in pHEMA-EGDMA-Antigen-Antibody hydrogel
vinyl-rabbit IgG, and GAR IgG antibody
4 0.382 0.398 -0.016 Amount of Initial Concentration after Dye Absorbance
antibody (mg) Concentration (%) hydrogel (%) by Hydrogel (%)
5 0.382 0.456 -0.074
0 0.376 0.391 0.015
6
7
0.382
0.382
0.343
0.349
0.039
0.033
0.054 0.376 0.390 0.014 Future
Future Direction
Work
0.074 0.376 0.355 -0.021
Average 0.382 0.387 -0.005
Hypothesis
Hypotesis Table 4: Change in concentration based on hydrogel dye absorption
0.094 0.376 0.343 -0.033 In the future, this research will focus on optimizing model drug absorption and
Initial Concentration Concentration after Dye Absorbance Average 0.376 0.321 -0.055 testing release of model drug in a free floating antigen solution. Additionally, this
Trial Number
(%) hydrogel (%) by Hydrogel (%) research looks toward using human cancer antigens and antibodies instead of
It is hypothesized that if an antibody-antigen complex is used as a secondary monomer
4 0.378 0.394 -0.016 models to replicate the environment of the human body and cancerous tissue. More
in a pHEMA hydrogel, the hydrogel will be able to respond to antigens in a free floating
5 0.378 0.453 -0.075 thorough analysis will be conducted on modification of pHEMA hydrogels through
solution and release a model drug. It is also hypothesized that if the amount of the
6 0.378 0.337 0.041 the incorporation of antigens and antibodies to understand the change in chemical
antibody in the hydrogel increases, the amount of model drug absorbed by the hydrogel
7 0.378 0.345 0.033 structure.
will increase as the polymer network will become more secure.
Average 0.378 0.382 -0.004
Template ID: deliberatingwatermelon Size: tri-fold
You might also like
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- The Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypesDocument12 pagesThe Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypestigriochelitoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Chemical ReactionsDocument5 pagesUnit 8 Chemical ReactionsNixon GrahamNo ratings yet
- Hse Traning Need Analisys 2018: Course CodeDocument7 pagesHse Traning Need Analisys 2018: Course Coderifki bahtiarNo ratings yet
- TrakCare Overview 09012015Document5 pagesTrakCare Overview 09012015keziajessNo ratings yet
- Dow OpacifiersDocument27 pagesDow OpacifiersAlfonso Dominguez Gonzalez100% (1)
- PMBOK Six Edition Data Flow Diagram by English: Project Life Cycle Description. Development ApproachDocument1 pagePMBOK Six Edition Data Flow Diagram by English: Project Life Cycle Description. Development ApproachErick Reyna ChirinosNo ratings yet
- O5 Vo4No4Document6 pagesO5 Vo4No4Muthanna Lo'ayNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine - C20H25ClN2O5 - PubChem PDFDocument72 pagesAmlodipine - C20H25ClN2O5 - PubChem PDFDavid HCNo ratings yet
- Experiment 25 - Determining The PH of Liquids Objectives:: Lab Write Up (Exercise)Document2 pagesExperiment 25 - Determining The PH of Liquids Objectives:: Lab Write Up (Exercise)নীল জোছনাNo ratings yet
- Nhs Bronchiolitis Pathway Acute Setting South East Coast SCNDocument2 pagesNhs Bronchiolitis Pathway Acute Setting South East Coast SCNdrgrizahNo ratings yet
- The Ambulatory Glucose Profile Opportunities For EnhancementDocument27 pagesThe Ambulatory Glucose Profile Opportunities For EnhancementyuriescaidaNo ratings yet
- 2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Document63 pages2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Taif SalimNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Analysis in Plasma-Serum and Urine Brochure en 4Document6 pagesAmino Acid Analysis in Plasma-Serum and Urine Brochure en 4yousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- نشرة الأرقام القياسية لأسعار المنتجين ابريل - مايو 2021Document58 pagesنشرة الأرقام القياسية لأسعار المنتجين ابريل - مايو 2021Hussain ElarabiNo ratings yet
- نشرة الأرقام القياسية للمنتجين عن شهرى ديسمبر2020 - يناير2021Document58 pagesنشرة الأرقام القياسية للمنتجين عن شهرى ديسمبر2020 - يناير2021Hussain ElarabiNo ratings yet
- Origins and Fate of PPCPs in TheDocument1 pageOrigins and Fate of PPCPs in TheRalph Charles Whitley, Sr.No ratings yet
- Top Down Proteomics Using Online Polymer Reversed Phase (PLRP) Nanocapillary-LC Coupled Fourier Transform Mass SpectrometryDocument1 pageTop Down Proteomics Using Online Polymer Reversed Phase (PLRP) Nanocapillary-LC Coupled Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometryapi-26001949No ratings yet
- Orchestrating A Winning Strategy: End-To-End Supply Chain SynchronizationDocument52 pagesOrchestrating A Winning Strategy: End-To-End Supply Chain SynchronizationANGELICANo ratings yet
- Strategic Directions 7TM504-2018-2019Document10 pagesStrategic Directions 7TM504-2018-2019Panos AnonioumNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Federal Child Welfare Grant Program Matrix TableDocument2 pagesFederal Child Welfare Grant Program Matrix TableBeverly TranNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Sym&Parasym DrugsDocument2 pagesMind Map Sym&Parasym Drugsjitpinun.sNo ratings yet
- Household Service Workers Policy Reform Package PDFDocument52 pagesHousehold Service Workers Policy Reform Package PDFMan HernandoNo ratings yet
- Temperature Solar Selective Coating Development For Power Tower ReceiversDocument1 pageTemperature Solar Selective Coating Development For Power Tower ReceiversВиктор ИсакNo ratings yet
- Vawc Compliance Monitoring FormDocument1 pageVawc Compliance Monitoring FormOmar Dizon100% (4)
- Va Medica: Treatment Efficacy of Language and Calculation Disorders and Speech Apraxia: A Review of The LiteratureDocument21 pagesVa Medica: Treatment Efficacy of Language and Calculation Disorders and Speech Apraxia: A Review of The LiteraturemohamerrNo ratings yet
- QMC A Floor 0219 WebDocument1 pageQMC A Floor 0219 Webgoogle manNo ratings yet
- HPLC Technical Tips PosterDocument1 pageHPLC Technical Tips PostermokhtarsimonNo ratings yet
- 1.1 PrevMed PrelimTopicsDocument24 pages1.1 PrevMed PrelimTopicsLaish Christle CapiendoNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Biotinylated Cyclooligosaccharides For Paclitaxel SolubilizationDocument11 pagesMolecules: Biotinylated Cyclooligosaccharides For Paclitaxel SolubilizationChris CordierNo ratings yet
- Reports-Sector Studies-Somaliland - Sector Functional Assessment - FINAL TECHNICAL MASTER - Geopolicity - April 19 2012 - Reduced SizeDocument189 pagesReports-Sector Studies-Somaliland - Sector Functional Assessment - FINAL TECHNICAL MASTER - Geopolicity - April 19 2012 - Reduced SizeMubarak Maal100% (1)
- 1) Electric Circuits - Basic ConceptsDocument9 pages1) Electric Circuits - Basic ConceptsJOSE AUGUSTO MODESTO HUAYLINOS GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Quadshot AbstractDocument3 pagesQuadshot AbstractHirak BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Digital BiogasTech2020Document25 pagesDigital BiogasTech2020kakangmasNo ratings yet
- Nrad Full ReportDocument115 pagesNrad Full ReportSophia RoseNo ratings yet
- 23 - Preoperative Patient Assessment and ManagementDocument1 page23 - Preoperative Patient Assessment and ManagementHenrique MachadoNo ratings yet
- Empagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Document2 pagesEmpagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Lord Carlo CabangalNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Project Guideline: Relevance of Topic: Suitable For: Own ContributionDocument2 pagesSix Sigma Project Guideline: Relevance of Topic: Suitable For: Own ContributionArun KangeyanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic MapDocument2 pagesMetabolic Mappablo.s4672No ratings yet
- 3-Hormonal Control of Metabolism and Regulation of Blood Glucose - 1Document10 pages3-Hormonal Control of Metabolism and Regulation of Blood Glucose - 1محمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- RACI TemplateDocument8 pagesRACI TemplateVanitha raoNo ratings yet
- Samples of AssignmentsDocument1 pageSamples of AssignmentsRochel OliverosNo ratings yet
- Neu.2017.5599 - NICE PaperDocument61 pagesNeu.2017.5599 - NICE PaperGregory MillánNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ModelDocument1 pageRheumatoid ModelDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Decaydecay Decay Decay Decay: Regurgitation ProblemsDocument1 pageDecaydecay Decay Decay Decay: Regurgitation Problemsnumber 2No ratings yet
- Angeline D. Alabastro, M.D.: CNS Pharmacology I: AntiepilepticsDocument10 pagesAngeline D. Alabastro, M.D.: CNS Pharmacology I: AntiepilepticsMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. New Criteria For AKI Diagnosis Are Displayed. in Order To Diagnose AKIDocument8 pagesFigure 1. New Criteria For AKI Diagnosis Are Displayed. in Order To Diagnose AKIMayra Alejandra Prada SerranoNo ratings yet
- Audit Iadp Bundle ChecklistDocument5 pagesAudit Iadp Bundle ChecklistAyu Ngurah SuarminiNo ratings yet
- Flow Based Market Coupling, SharmaDocument191 pagesFlow Based Market Coupling, SharmaFikret VelagicNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Nicotine in Tobacco Free Nicotine Commercial Products: Nicotine Enantiomers in Tobacco Free NicotineDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Nicotine in Tobacco Free Nicotine Commercial Products: Nicotine Enantiomers in Tobacco Free NicotineJoeHahnNo ratings yet
- Ccoch-Sgs-Min-Iperc-Linea BaseDocument7 pagesCcoch-Sgs-Min-Iperc-Linea BaseJuan Carlos Quille TaipeNo ratings yet
- Usaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Document1 pageUsaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Samson DesieNo ratings yet
- BarredojuliannenutritionquestionevidenceassignmentDocument5 pagesBarredojuliannenutritionquestionevidenceassignmentapi-639582054No ratings yet
- Lab Manual AC-407 Analytical Techniques I-CorrectedDocument26 pagesLab Manual AC-407 Analytical Techniques I-CorrectedYawar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Swage Optional Fase Wahlweise Optional Wahlweise: 04MAY2016 22SEP2016 21OCT2017 24SEP2018 3 4 5Document2 pagesSwage Optional Fase Wahlweise Optional Wahlweise: 04MAY2016 22SEP2016 21OCT2017 24SEP2018 3 4 5Usama TwabNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Six Edition Data Flow Diagram by English Planning ProcessDocument3 pagesPMBOK Six Edition Data Flow Diagram by English Planning ProcesssegoooNo ratings yet
- 2011 Publication of Guardian University Guide: Grid of Provisional Subject AppearancesDocument7 pages2011 Publication of Guardian University Guide: Grid of Provisional Subject AppearancesThe GuardianNo ratings yet
- Mathajadyala MachutunakaluDocument140 pagesMathajadyala MachutunakaluChanandler BongNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - Core Practical 2Document4 pagesCHEMISTRY - Core Practical 2Claudia ManchadoNo ratings yet
- Fri 394 Ilc2022Document1 pageFri 394 Ilc2022rtthrtfhNo ratings yet
- Vawt ReportDocument9 pagesVawt Reportapi-482373029No ratings yet
- Design of Tricuspid Polymeric Mechanical Heart Valve Replacements To Optimize Flow Pattern and Reduce Risk of ThrombosisDocument6 pagesDesign of Tricuspid Polymeric Mechanical Heart Valve Replacements To Optimize Flow Pattern and Reduce Risk of Thrombosisapi-482373029No ratings yet
- A Novel Laser Based Approach To Material Identification Corrosion Detection and Corrosion Removal For Space Debris RecyclingDocument10 pagesA Novel Laser Based Approach To Material Identification Corrosion Detection and Corrosion Removal For Space Debris Recyclingapi-482373029No ratings yet
- Nih AbstractDocument1 pageNih Abstractapi-482373029No ratings yet
- Final Research ReportDocument20 pagesFinal Research Reportapi-482373029No ratings yet
- SS 345-2015 - Preview PDFDocument9 pagesSS 345-2015 - Preview PDFAnirudhNo ratings yet
- Royal College of Science Narowal: CyanobacteriaDocument11 pagesRoyal College of Science Narowal: Cyanobacteriakiran maqsoodNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons & Halogen Derivatives PDFDocument326 pagesHydrocarbons & Halogen Derivatives PDFSuraj panditNo ratings yet
- Protección Contra La Corrosión Del Cobre Mediante La Deposición de Capas Atómicas de Al 2 O 3, TiO 2, ZnO, HfO 2 y ZrO 2Document10 pagesProtección Contra La Corrosión Del Cobre Mediante La Deposición de Capas Atómicas de Al 2 O 3, TiO 2, ZnO, HfO 2 y ZrO 2Daniel Elmer Parado SosaNo ratings yet
- EC26 - Flat Corrosion CellDocument2 pagesEC26 - Flat Corrosion CellGopinath PerumalNo ratings yet
- Architectural Concept Cabeihm Bsu NasugbuDocument4 pagesArchitectural Concept Cabeihm Bsu NasugbuArrnold DominguezNo ratings yet
- The Properties of MatterDocument22 pagesThe Properties of MatterLENON ANSANONo ratings yet
- Using Pop-Culture To Engage Students in The ClassroomDocument11 pagesUsing Pop-Culture To Engage Students in The ClassroomJean VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- SS4155 Technical Data SheetDocument6 pagesSS4155 Technical Data Sheethuynh thi y viNo ratings yet
- 014 SDS ForeE-7Bio. ForeE-8BioDocument10 pages014 SDS ForeE-7Bio. ForeE-8BioNinaNo ratings yet
- What Is Lithium CarbonateDocument8 pagesWhat Is Lithium CarbonateNurAneesaNo ratings yet
- Management of Perforation A ReviewDocument5 pagesManagement of Perforation A ReviewsmritiNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law of ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesFaraday's Law of ElectrolysispradeepvcpNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 - Task 4Document19 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 - Task 4peterNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On PolymerizationDocument6 pagesShort Notes On PolymerizationMohammed AshroffNo ratings yet
- CL EEE22 Ch1103 19 DecemberDocument46 pagesCL EEE22 Ch1103 19 DecemberSanjid HasanNo ratings yet
- Journal Publication Details of VIT For January 2024Document88 pagesJournal Publication Details of VIT For January 2024sugumaran.vNo ratings yet
- Wiedmann Diagnostics Solutions Analytical TestingDocument4 pagesWiedmann Diagnostics Solutions Analytical TestingOsvaldo ValienteNo ratings yet
- Monicaa Chemistry Project EditedDocument15 pagesMonicaa Chemistry Project Editedvix lunaNo ratings yet
- Cat Elc PDFDocument4 pagesCat Elc PDFVegamotor VnNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Organic Compound Containing Halogens Important QuestionsDocument15 pagesJEE Main Organic Compound Containing Halogens Important QuestionsRuchitha VNo ratings yet
- Costanzo Physiology 7Th Edition Costanzo PHD Full ChapterDocument67 pagesCostanzo Physiology 7Th Edition Costanzo PHD Full Chapterkristine.dixon271100% (6)
- Moving Cellular Material (Biology)Document1 pageMoving Cellular Material (Biology)Sebastian AguirreNo ratings yet
- SalineDocument15 pagesSalines.belarmino.kayeNo ratings yet
- UNIFAC Parameters For Four New GroupsDocument11 pagesUNIFAC Parameters For Four New GroupsmL 2023No ratings yet
- 2019 Water Quality ReportDocument10 pages2019 Water Quality Reportjdm81No ratings yet
- Applications of 33 Grade Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)Document2 pagesApplications of 33 Grade Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)Swamy ManiNo ratings yet