Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CARDIOVASCULAR-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Janson SarmientoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CARDIOVASCULAR-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Janson SarmientoCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Nursing | 2nd Sem - Prelim tissues and function in the exchange of nutrients and
A.Y. 22-23 gases.
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
BLOOD PRESSURE
cardio = related to the heart, vascular = related to the
blood vessels DEFINITION: A specialized body fluid that flows through
the blood vessels. COMPOSITION: It is composed of the
COMPOSITION: fluid part known as plasma and blood cells.
Heart Plasma is mostly made up of water and also contains
proteins, salts and other substances.
Blood vessels
Blood cells: are of 3 types:
Blood - the cells and plasma Red blood cells (responsible for the transport of
respiratory gases) - due to hemoglobin pigment
MAIN FUNCTION: Maintains the circulation of life giving
White blood cells (responsible for immunity against
blood to all parts of our body which is necessary for
diseases)
delivery of nutrients, removal of wastes and exchange of
Platelets (responsible for blood clotting.)
oxygen and carbon dioxide.
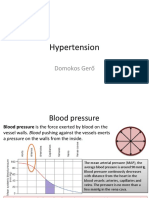
1. BLOOD PRESSURE
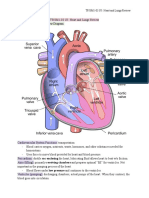
THE HEART
Blood pressure is the measurement of force applied to
artery walls
Composition: Muscular organ Refers to the measurement of force exerted by circulating
blood the walls of blood vessels, and constitutes one of
Parts: It has four chambers - ATRIA - 2 upper chambers the principal vital signs
known as atrial (receives blood) and
2. BLOOD PRESSURE
VENTRICLES - 2 lower ones known as ventricles (pumps
blood to the various parts of our body and the lungs). Refers to arterial pressure, i.e., the pressure in the larger
arteries, the blood vessels that take blood away from the
Location: Chest between the two lungs, slightly to the heart
left' protected by the rib cage.
Hypertension: Abnormally high blood pressure over 140
Function: It pumps blood to the various parts of our body mm Hg systolic and or about 90mm Hg diastolic for at
by repeated rhythmic contractions. It beats 72 times in a least two consecutive readings
minute.
ARTERIAL PRESSURE
Cardiac Cycle: Two parts:
The pressure of blood as a result of the contraction of the
SYSTOLE- contraction phase (ejection of blood from atria ventricles (100- 140mm Hg)
and then both ventricles) initiated by SA Node.
SYSTOLIC
DIASTOLE- resting, relaxation phase both atria and Above 140
ventricles The pressure when the ventricles are at rest (60-90mm
Hg)
BLOOD VESSELS --the tubes that carry the blood. DIASTOLIC
Above 90
They are of 3 types:
PULSE PRESSURE:
Arteries - carry blood from the heart to different parts of
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE SYSTOLIC & DIASTOLIC
our body
PRESSURE (Normal: 30-40mmHg)
Veins - carry blood from the different parts of our body
Hypotension: Abnormally low blood pressure, systolic
back to our heart
pressure below 100/60 mm Hg
Capillaries - small, thin walled vessels that form a
network between the arteries and veins in the
Orthostatic hypertension: A blood pressure that falls Phase 3 THUMP SOFTER THAN THE TAPPING IN PHASE 1
when the client sits or stands Phase 4 A SOFTER BLOWING MUFFLED
SOUND THAT FADES
Phase 5 SILENCE -The pressure level wherein the sound
disappear
Factors affecting Blood pressure
Age. Decreased elasticity of blood vessels METHODS OF TAKING BP
increases BP. A. DIRECT METHOD
Exercise. Increases cardiac output •Requires the use of sphygmomanometer and
stethoscope for auscultation and palpation as needed
Stress. SNS stimulation causes increase in BP.
•Most common site: client's arm over brachial artery
Obesity. BP is elevated among overweight and obese
people. Other sites: Leg site over popliteal artery (behind the
knee)
Sex. Males before age 65 have higher BP; females have
higher BP after 65 B. INDIRECT METHOD
Disease process. DM, Renal failures, Hyperthyroidism. An invasive procedure
NORMALBP: ADULT An intravenous catheter with an electronic sensor is
inserted into an artery and the artery-transmitted
pressure on an electronic display unit is read
PURPOSES
To have a baseline blood pressure measurement
To evaluate client's condition after treatment, therapies
and medications
To evaluate the cardio-vascular states of the client
EQUIPMENTS NEEDED:
Sphygmomanometer
Stethoscope
Cotton balls with alcohol
NORMAL VITAL SIGNS Watch or clock with second hand
EQUIPMENT
1. SPHYGMOMANOMETER
An instrument for measuring arterial pressure
3 Types of Blood Pressure Apparatus
(Sphygmomanometer)
MERCURY GRAVITY MANOMETER / MERCURIAL
- has a mercury filled cylinder or tube calibrated in
millimeter
Korotkoff sound-are sound heard during measurement
of blood pressure ANEROID MANOMETER/ ANEROIDAL
Phase 1 SHARP TAPPING SOUND
- has a cuff that is attached to a round calibrated dial with
Phase 2 SWISHING/SWOOSHING SOUND
a pointer that indicates pressure
ELECTRONIC BLOOD PRESSURE Gather, assemble, and appropriate size for the client
MEASUREMENT/sunzheng DIGITAL - electrically prepare equipment or to ensure accuracy Accurate
operated/battery operated articles needed. measurements depend on
functional equipment.
PARTS: Select a cuff appropriate for
the client. Measure with
a. Mercury Gauge / Aneroid/Digital (Pressure Gauge) a tape, the
circumference of the
bare upper arm at the
midpoint between the
b. Pressure cuff (velcro or hook) w/ rubber bladder. Note: shoulder (acromonion)
Inside the cuff in an elastic cloth covering - Airtight, and the elbow
flat and inflatable (olecranon). It should
cover 2/3rds of the
C. Pressure source Pressure control bulb Pump bulb upper arm.
Rubber bulb Hand bulb
Check the equipment and
supplies. Make sure
d. Handle
they work.
e. Rubber Tubing (2)
Procedure Establishes rapport and trust
f. Release valve (screw) 1. Introduce yourself and Encourages client's
verify client's identity. participation and reduces
2. STETHOSCOPE
client's anxiety
Explain to the client what
Used to auscultate the sound heard directly over the you are going to do, why it is Readings taken at different
artery as the pressure in the cuff is released necessary, and how the client times can be objectively
can cooperate. Have the compared when all are
Parts: client rest at least 5 minutes assessed with client at
(PHN 2007) before rest
A. Ear tips/Ear pieces measurement.
B. Metal tubing - Neck / Binaurals (Metal) 3. Perform hand hygiene, Reduces transmission of
and observe other microorganisms.
C. Rubber tube appropriate infection control
procedures.
D. Chest pieces / Stems - diaphragm; bell
4. Provide for client privacy. Minimizes or avoids
IMPLEMENTATION OF PROCEDURE ASSEMBLE THE embarrassment on the client.
EQUIPMENTS
A. Preparation To accurately assess BP and
significance of pressure Position the client comfortably and appropriately.
Assess the client. changes
5. Place the client in sitting Helps in the accurate
Signs and symptoms of Can cause false elevations in position, unless otherwise measurement of BP
hypertension, hypotension BP specified. Both feet should
Factors affecting blood be flat on the floor.
To avoid injuring the client;
pressure: exercise and smoking helps to determine type of
(wait for 15 minutes before BP apparatus to be used and
taking BP measurements) site of BP application 6. Moves client's clothing away Ensures proper cuff
Allergy to latex cuff from upper aspect of arm. application
Condition of client (injury)
Loosen and fold the client's
sleeve. Expose the upper arm.
Assemble equipment. Be sure that the cuff is an
7. Position client's arm at heart If the arm is above the level
level extending elbow with of the heart, the BP on skin. not on clothing over
palm turned upward. reading will be the site.
erroneously low; while
if the arm is below the a. Cleanse the earpieces with
level of heart, the BP
reading will be antiseptic wipe.
erroneously high.
b. Insert the ear attachments of
8. Wrap the deflated cuff the stethoscope in your ears so
around the upper arm. Locate that they tilt
the brachial artery.
c. Ensure that the stethoscope
9. Apply the center of the hangs
bladder directly over the
d. freely from the ears to the
artery.
diaphragm.
Adjust the cuff so that the Proper placement ensures
20. Hold the diaphragm with
lower border is approximately accuracy of result
the thumb and index fingers
2.5cm (1inch) above the
antecubital space. Proper BP 21. Auscultate the client's
apparatus would occupy blood pressure.
2/3rds of the upper arm.
Ensures accurate measurement
11. Locates the brachial artery of systolic pressure.
in the cubital space with the
fingertips. Too rapid or slow a decline in
mercury level can cause
If this is the client's initial assessment, perform a preliminary inaccurate readings.
palpatory determination of systolic pressure.
Pump up the cuff until the
12. Palpate the brachial (or Identifies approximate sphygmomanometer is
radial) artery with the systolic pressure and 30mmHg above the point
fingertips at one hand. determines maximum where the brachial pulse
inflation point for accurate disappeared.
reading. Prevents 23. Release the valve on the
auscultatory gap cuff carefully so that the
13. Close the valve on the bulb.
pressure decreases at a rate of
Prevents venous congestion 2-3mmHg per second.
and false high readings
14. Pump up the cuff until you 24. As the pressure falls,
no longer feel the brachial identify the manometer
pulse. reading at Korotkoff phases I,
IV and V.
Note the first clear sound
15. Note the pressure on the
heard. This indicates systolic
sphygmomanometer at which
pressure (KI). Note the point at
the pulse is no longer felt and
which the sound changes to a
add 30mmHg pressure above
muffled sound (K IV) the last
point which pulse disappears.
sound before silence (KV) is
diastolic pressure.
17. Position the stethoscope appropriately.
25. Deflate the cuff rapidly and
18. Place the bell of the Avoid transfer of
completely.
amplifier of the stethoscope microorganisms
over the brachial pulse Wait 1-2 minutes before
Proper placement ensures
making further determinations.
accuracy of result
(Manual: 20 to 30 minutes-to
19. Place stethoscope directly allow venous circulation in the
arm to stabilize.
26. Repeat the procedure on
client's other arm.
- Repeating steps once or twice
as necessary to confirm the
accuracy of reading.
27. Remove the cuff. Wipe the Prevents transmission of
cuff with an appropriate microorganism
disinfectant.
Assist client in returning to Restores comfort
comfortable position and cover
upper arm if previously clothed.
Inform client of reading Promotes participation in
care and understanding of
health status.
Wash hands Prevents transmission of
microorganisms.
Document and report pertinent Vital signs should be
assessment data according to recorded immediately to
agency policy. ensure accuracy.
You might also like
- IIAP Mock 1 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesIIAP Mock 1 Answer KeyTGiF Travel0% (1)
- High Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Broken Access ControlDocument3 pagesBroken Access ControlGlady GladsonNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument24 pagesExercise PhysiologyMohammed AlharbiNo ratings yet
- CVS L1Document4 pagesCVS L1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Pharma 6Document17 pagesPharma 6Cleo PizarrasNo ratings yet
- REGULATIONDocument19 pagesREGULATIONADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Autosaved)Document15 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Autosaved)Amy JessyNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument11 pagesBlood VesselsAndrea PeriguaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Anatomy and Functions of the Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Circulation, and Regulation of Blood Pressure</TITLEDocument85 pagesCardiovascular System: Anatomy and Functions of the Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Circulation, and Regulation of Blood Pressure</TITLEEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Topic 7: Transport in HumansDocument19 pagesTopic 7: Transport in HumansAmyrul Darwisy ZafranNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics Apparital RefillDocument7 pagesHemodynamics Apparital RefillAshley Jane S. CAMPANIELNo ratings yet
- MF-local Circulation 2016Document61 pagesMF-local Circulation 2016OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Blood PressureDocument128 pagesHeart Rate Blood PressureShubhra ShettyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Physiologykiruthikasettu46No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyHabib UllahNo ratings yet
- Purple Illustrative The Human Body PresentationDocument24 pagesPurple Illustrative The Human Body PresentationNETHRA ESWARE A/P KAMALANATHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Vascular Distensibility and Functions of The Arterial and 1Document83 pagesVascular Distensibility and Functions of The Arterial and 1gabby chaanNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument19 pagesCardiorespiratory SystemEmanuel JheadNo ratings yet
- CVS PharmacologyDocument19 pagesCVS Pharmacologymug ashNo ratings yet
- Circulation NotesDocument2 pagesCirculation NotesBhkti MittalNo ratings yet
- Health Care Provider Lab C: Vital Signs: Blood PressureDocument3 pagesHealth Care Provider Lab C: Vital Signs: Blood Pressureapi-522650514No ratings yet
- Vascular System-1 101857Document41 pagesVascular System-1 101857earth shineNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument27 pagesCirculatory SystemDylan WangNo ratings yet
- TPJ3M1-03 U5: Heart and Lungs ReviewDocument6 pagesTPJ3M1-03 U5: Heart and Lungs ReviewLynn TrinhNo ratings yet
- مخلص فسيولجيDocument10 pagesمخلص فسيولجيraseel571No ratings yet
- HCP MODULE 12 Circulatory Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesHCP MODULE 12 Circulatory Cardiovascular SystemLHYRA KATHLEEN LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Patho - 21 HeartAdv - 211005 - 230536Document91 pagesPatho - 21 HeartAdv - 211005 - 230536Puranjay ChandelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021Document43 pagesLecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021badarbhai222No ratings yet
- Body Fluids & CirculationDocument29 pagesBody Fluids & CirculationAyaan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dini's guide to the cardiovascular systemDocument52 pagesDr. Dini's guide to the cardiovascular systemReni TeeWeeNo ratings yet
- OpenStax Rice University 6100 Main Street MS-375 Houston, Texas 77005Document31 pagesOpenStax Rice University 6100 Main Street MS-375 Houston, Texas 77005D VNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovasular SystemAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- Goal of The Cardiovascular System: Deliver Blood To All Parts of The BodyDocument20 pagesGoal of The Cardiovascular System: Deliver Blood To All Parts of The BodyNestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Edit OngoingDocument7 pagesCirculatory System Edit OngoingclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes NCM 102: Union Christian College College of NursingDocument77 pagesLecture Notes NCM 102: Union Christian College College of Nursingnarswiponshistoryan100% (1)
- Vital Signs: Blood Pressure: Video 2.1: Introduction To The Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesVital Signs: Blood Pressure: Video 2.1: Introduction To The Blood VesselsNelu CastravetNo ratings yet
- Physiology of ExerciseDocument25 pagesPhysiology of ExerciseTedy Friyadi100% (1)
- HCP MODULE 12 - Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHCP MODULE 12 - Circulatory SystemAvea RiveraNo ratings yet
- A7 Cardiovascular DrugsDocument89 pagesA7 Cardiovascular DrugsSHIELOU LOMODNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System Blood VesselsDocument50 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Blood Vesselsyamlehtemagallanes888No ratings yet
- The Mammalian Circulatory SystemDocument58 pagesThe Mammalian Circulatory Systemirisgoldcaster100% (1)
- The Cardiovascular System Parts of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Parts of The Cardiovascular SystemBrent AnosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Review: Anatomy, Physiology & FunctionsDocument41 pagesCirculatory System Review: Anatomy, Physiology & FunctionsShayesra-Radina Laja SahibadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemMayim LouiseNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure MeasurementDocument70 pagesBlood Pressure MeasurementHOD BMENo ratings yet
- II. Blood Vessels Physiology By: Dr. Abdulrahman Aqra MD MSCDocument12 pagesII. Blood Vessels Physiology By: Dr. Abdulrahman Aqra MD MSCapi-290338101No ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood VesselDocument65 pagesPhysiology of Blood Vesselapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesBlood VesselsCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument27 pagesThe Cardiovascular System ExplainedMary100% (1)
- How Bloodis Propelled Throughthe Hum An Ci Rcula To Ry Sy StemDocument5 pagesHow Bloodis Propelled Throughthe Hum An Ci Rcula To Ry Sy Stemridwan100% (1)
- English PDFDocument46 pagesEnglish PDFGayatri BeheraNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure 2022Document29 pagesHeart Failure 2022agarrido2No ratings yet
- Hypertension-DG ENGDocument20 pagesHypertension-DG ENGDiana E KimNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument26 pagesBlood PressureEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument23 pagesBlood PressuresureshNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Explained in 40 CharactersDocument22 pagesCirculatory System Explained in 40 CharactersJheyrick Casipe BaliguatNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Circulatory SystemVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- Print Z 2014Document11 pagesPrint Z 2014Nathan BlancoNo ratings yet
- PE Blood Transport SystemDocument13 pagesPE Blood Transport Systemkunal ramcharunNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument15 pagesBlood Circulation and Transportqas1727No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GER Bangladesh EngDocument12 pagesGER Bangladesh Engfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet
- ARTIKEL 44 Famuntamah 391-399Document9 pagesARTIKEL 44 Famuntamah 391-399Dandi Aksan MasjudNo ratings yet
- Innogy Invitation For Seminar PCODocument6 pagesInnogy Invitation For Seminar PCOTivorshio MacabodbodNo ratings yet
- Oil Record Book InstructionsDocument6 pagesOil Record Book InstructionsNamal Fernando100% (1)
- Constance Carroll Cosmetics) Final.1Document4 pagesConstance Carroll Cosmetics) Final.1api-26027438100% (1)
- Examination of Power Electronics (Pel) : AnswerDocument10 pagesExamination of Power Electronics (Pel) : Answerves vegasNo ratings yet
- Laporan FaalDocument25 pagesLaporan FaalAgnes NathaniaNo ratings yet
- Online Pharmacy: Customer ProfilingDocument6 pagesOnline Pharmacy: Customer ProfilingGeorge SebastianNo ratings yet
- With Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western MountainsDocument3 pagesWith Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western Mountainshajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Ventilation, Step by StepDocument99 pagesNeonatal Ventilation, Step by StepMarely Ovando Castillo93% (14)
- Chapter III Pharmacokinetics: Durge Raj GhalanDocument64 pagesChapter III Pharmacokinetics: Durge Raj GhalanDurge Raj Ghalan100% (3)
- Labrel 104-195Document1,014 pagesLabrel 104-195Maria Seleena HipolitoNo ratings yet
- 4140DE Data SheetDocument1 page4140DE Data SheetNabeel AmeerNo ratings yet
- Different Mesh Sizes and Mesh To Micron ConversionDocument10 pagesDifferent Mesh Sizes and Mesh To Micron ConversionDevanandDongreNo ratings yet
- How To Check A Capacitor With Digital Multimeter and Analog AVO Meter. by Four (5) Methods With Pictorial ViewDocument7 pagesHow To Check A Capacitor With Digital Multimeter and Analog AVO Meter. by Four (5) Methods With Pictorial ViewDivagar PNo ratings yet
- Sorogon Medical Mission Group Hospital Operation RecordDocument3 pagesSorogon Medical Mission Group Hospital Operation RecordRoden BerdinNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Experiment 5)Document2 pagesLab Report (Experiment 5)Adrian FlorinNo ratings yet
- 0972 June 2021 QP 41 Cie Igcse Physics - Pdfquestion7Document2 pages0972 June 2021 QP 41 Cie Igcse Physics - Pdfquestion7Kareem YouakimNo ratings yet
- Causes of Poverty - Presentation On Poverty - Poverty in PakistanDocument20 pagesCauses of Poverty - Presentation On Poverty - Poverty in PakistanTop_Sledger92% (12)
- Discover the training secrets of legendary bodybuildersDocument129 pagesDiscover the training secrets of legendary bodybuildersfatmir100% (7)
- 14 People V Manalo (Verba Legis)Document15 pages14 People V Manalo (Verba Legis)zeynNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Reviewer: Surgical Handwashing QuizDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam Reviewer: Surgical Handwashing QuizOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- Traits and BehaviorDocument8 pagesTraits and BehaviorNorwafa Cariga EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Basic Science JSS 1 2NDDocument29 pagesBasic Science JSS 1 2NDAdeoye Olufunke100% (2)
- Product Brochure-Electronically Controlled Air Dryer-ECA PDFDocument4 pagesProduct Brochure-Electronically Controlled Air Dryer-ECA PDFAnonymous O0T8aZZNo ratings yet
- The Life and Works of Dr. Jose P. Rizal: Rizal As A DoctorDocument14 pagesThe Life and Works of Dr. Jose P. Rizal: Rizal As A DoctorPamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- FORM HSE MATRIX TRAINING (Contoh)Document1 pageFORM HSE MATRIX TRAINING (Contoh)Hifni GhazaliNo ratings yet
- 1619928348861forensic Science UNIT - VII 1 PDFDocument159 pages1619928348861forensic Science UNIT - VII 1 PDFVyshnav RNo ratings yet