Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tư thế đầu nhô phía trước
Tư thế đầu nhô phía trước
Uploaded by
cham.nguyen31030 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document discusses forward head posture, its symptoms, causes, and effects on health. Forward head posture is common, affecting 86.6% of people, and is caused by occupational posture, gravity, other faulty postures, and weak back muscles. Symptoms include headaches, neck discomfort, and pain in the arms. It increases stress on the cervical spine and can impact respiratory function, balance, and shoulder health. Evaluation involves clinical assessment and x-rays to measure angles such as the craniovertebral angle.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses forward head posture, its symptoms, causes, and effects on health. Forward head posture is common, affecting 86.6% of people, and is caused by occupational posture, gravity, other faulty postures, and weak back muscles. Symptoms include headaches, neck discomfort, and pain in the arms. It increases stress on the cervical spine and can impact respiratory function, balance, and shoulder health. Evaluation involves clinical assessment and x-rays to measure angles such as the craniovertebral angle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesTư thế đầu nhô phía trước
Tư thế đầu nhô phía trước
Uploaded by
cham.nguyen3103This document discusses forward head posture, its symptoms, causes, and effects on health. Forward head posture is common, affecting 86.6% of people, and is caused by occupational posture, gravity, other faulty postures, and weak back muscles. Symptoms include headaches, neck discomfort, and pain in the arms. It increases stress on the cervical spine and can impact respiratory function, balance, and shoulder health. Evaluation involves clinical assessment and x-rays to measure angles such as the craniovertebral angle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
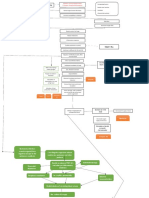
Tư thế đầu nhô phía trước
Triệu chứng:
Headaches
Neck discomfort
Muscle tension in the neck and shoulders
Discomfort in the mid back
Chest pain
Pain, pins & needles and numbness in the arms and hands
Ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe
FHP increases compressive loading on tissues in the cervical spine, particu-
larly the facet joints and ligaments.
Studies have reported that symptoms including neck pain, headache, temporo-
mandibular pain, and musculoskeletal disorders are related to FHP
FHP greatly influences respiratory function by weakening the respiratory mus-
cle.
FHP can have a negative impact on static balance.
Forward head and round-shoulder postures (FHRSP) can result in shoulder
pain and dysfunction because of altered scapular kinematics and muscle activ-
ity and consequently, placing increased stress on the shoulder.
In the posterior cervical muscles there is stretching and weakness
of Semispinalis cervicis and overaction with ultimate shortening
of Semispinalis capitis . The corresponding flexor muscles in front,
namely, Longus cervicis and Longus capitis shorten and lengthen respectively.
There is newly evidance that there is no relation between FHP and neck pain,
additionally individual with neck pain had lower ROM and slower neck move-
ment.
Dịch tễ/ nguyên nhân
Tỉ lệ mắc cao: 86,6%
Yếu tố nguy cơ: giới nữ, tuổi cao, từng hút thuốc, nhu cầu công việc cao, hỗ
trợ xã hội hoặc công việc thấp.
Nguyên nhân
Occupational posture: forward or backward leaning of head for long durations,
slouched or relaxed sitting, faulty sitting posture while using computer or
screen.
Effect of gravity: slouching, poor ergonomic alignment.
Other faulty postures like pelvic and lumber spine posture.
Sleeping with head elevated too high.
Poor posture maintained for long durations.
Lack of development of back muscle strength.
Biểu hiện lâm sàng
Muscle ischemia, pain and fatigue
Decreased range of motion of cervical spine
Early disc degeneration and osteophyte formation
Temporomandibular joint pain and inflammation
Tension Headache
Increase in dorsal kyphosis and decrease in height
Decrease in vital capacity and range of motion of shoulder and arm
Possible protrusion of nucleus pulposus and nerve compression
Mobility impairment in the muscles of the anterior thorax (intercostal mus-
cles), muscles of the upper extremity originating on the thorax (Pectoralis ma-
jor et minor, Latissimus dorsi , Serratus anterior ), muscles of the cervical spine
and head that attached to the scapula and upper thorax (Levator scapulae , Ster-
nocleidomastoid , Scalene, upper Trapezius ), and muscles of the suboccipital
region (Rectus capitis posterior major and minor, Obliquus capitis infe -
rior and superior).
Impaired muscle performance due to stretched and weak lower cervical and
upper thoracic erector spinae and scapular retractor muscles (Rhomboids, mid-
dle Trapezius), anterior throat muscles (suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles),
and capital flexors (Rectus capitis anterior and lateralis, superior oblique
Longus colli , Longus capitis ).
With temporomandibular joint symptoms, the muscles of mastication may have
increased tension (Pterygoid, Masseter, temporalis muscles). [11][12]
Đánh giá
Đánh giá lâm sàng
Chụp Xquang
The craniovertebral angle is one of the most reliable methods and common an-
gles for evaluating the FHP. It examines head status relative to the seventh cer -
vical vertebrae (C7).
You might also like
- Postural Restoration Institute2023Document4 pagesPostural Restoration Institute2023Aryan KarkiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Rubins Pathology Sixth None Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesEssentials of Rubins Pathology Sixth None Edition Ebook PDFronald.allison470100% (54)
- Care of Shoulder Pain in The Overhead AthleteDocument8 pagesCare of Shoulder Pain in The Overhead Athlete110313No ratings yet
- InserviceDocument27 pagesInserviceapi-216088427No ratings yet
- Pilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFDocument17 pagesPilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFbrunoduartefr100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Case Study 2bDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Case Study 2bDylle Lorenzo ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Forward Head Posture - PhysiopediaDocument1 pageForward Head Posture - Physiopediajohn kantidesNo ratings yet
- Synopsis 77Document16 pagesSynopsis 77RiazaNo ratings yet
- Postural AssessmentDocument64 pagesPostural AssessmentNikks BoradeNo ratings yet
- Bad Posture - A Reason For Change in SpinalDocument58 pagesBad Posture - A Reason For Change in SpinalPooja jainNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Posture: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPDocument17 pagesAssessment of Posture: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPFloriza de Leon100% (1)
- Posture EvaluationDocument12 pagesPosture EvaluationpaconscribdNo ratings yet
- ProQuestDocuments 2022 03 01Document11 pagesProQuestDocuments 2022 03 01Éoghan McCulloughNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Panggul Dan UkurannyaDocument40 pagesAnatomi Panggul Dan UkurannyaGiritama IrwantoroNo ratings yet
- Postural Analysis of Cervical SpineDocument33 pagesPostural Analysis of Cervical SpineSNEHA DASNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Mobility The Link in Neck, Shoulder, and Low Back PainDocument3 pagesThoracic Mobility The Link in Neck, Shoulder, and Low Back PainJobbiomedicoNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spondylosis: Muhammad Yafidy Pembimbing: Dr. S. Dohar AL Tobing, SP - OT (K)Document31 pagesCervical Spondylosis: Muhammad Yafidy Pembimbing: Dr. S. Dohar AL Tobing, SP - OT (K)yafidyNo ratings yet
- Lumbo-Pelvic Stability and Back Pain: What's The Link?Document8 pagesLumbo-Pelvic Stability and Back Pain: What's The Link?atul-heroNo ratings yet
- Scapular Dyskinesis Disabled Throwing ShoulderDocument52 pagesScapular Dyskinesis Disabled Throwing Shouldersfxn2qrw7rNo ratings yet
- 1 Askep Low Back PainDocument16 pages1 Askep Low Back PainBr Komarudin100% (1)
- Low Back PainDocument100 pagesLow Back Painchandrusai100% (1)
- Biokare Posture PresentationDocument30 pagesBiokare Posture PresentationMarius Andre VisserNo ratings yet
- Mwchanical BackpainDocument46 pagesMwchanical BackpainKavi Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of SpineDocument41 pagesBiomechanics of SpineMuhammad MustaqeemNo ratings yet
- Naskah PublikasiDocument15 pagesNaskah PublikasiSuci AisyahNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PTDocument44 pagesTherapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PTMustafa ,GhulamNo ratings yet
- TCM and Cervical Sponylosis 22Document21 pagesTCM and Cervical Sponylosis 22wr48f26rjmNo ratings yet
- Adolescence and The Musculoskeletal System (2) (Autosaved)Document45 pagesAdolescence and The Musculoskeletal System (2) (Autosaved)memoona kaleemNo ratings yet
- Postural AssessmentDocument63 pagesPostural Assessmentdariand100% (1)
- Neck Pain: D - P. P. M, A P, D - PDocument9 pagesNeck Pain: D - P. P. M, A P, D - PRichaNo ratings yet
- Exercise & Flexibility in The Upper QuarterDocument11 pagesExercise & Flexibility in The Upper QuarterJocelyn924No ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Prof. Dr. Hidayet Sarı Cerrahpaşa Medical School Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation DepartmentDocument87 pagesLow Back Pain: Prof. Dr. Hidayet Sarı Cerrahpaşa Medical School Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation DepartmentAnonymous 1kXBTPvGeuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Injuries To The SpineDocument93 pagesAnatomy and Injuries To The Spineamoon12No ratings yet
- Cervical SharmanDocument17 pagesCervical SharmanDevsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument31 pagesAnkylosing SpondylitisArathy100% (1)
- Acute Low Back PainDocument39 pagesAcute Low Back PainSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- WMSD Dentist 2566Document77 pagesWMSD Dentist 2566pachara.p65No ratings yet
- CervicothoracicSpine AssessmentDocument16 pagesCervicothoracicSpine AssessmentKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- 1-5-22 OMM Repro Considerations MasterDocument67 pages1-5-22 OMM Repro Considerations MasterTanner HancockNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument23 pagesPosturebasavamruthag141No ratings yet
- Peat 1.2 PDFDocument16 pagesPeat 1.2 PDFArchita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument56 pagesUntitledDr. Disha Rupareliya BhateNo ratings yet
- 16BPT058 - e ASSIGNMENT-women's HealthDocument7 pages16BPT058 - e ASSIGNMENT-women's HealthShreny 2912No ratings yet
- Back Injuries: Conducted by Ms Farzana AshfaqDocument78 pagesBack Injuries: Conducted by Ms Farzana AshfaqAsaad JawedNo ratings yet
- Core Muscle Strengthening in The AthleteDocument48 pagesCore Muscle Strengthening in The AthleteNicu Tanase-RaduNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)Document4 pagesHerniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)Kevin CamilozaNo ratings yet
- Chap 14-1Document29 pagesChap 14-1abdul hannanNo ratings yet
- The Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation - American Family PhysicianDocument9 pagesThe Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation - American Family PhysicianAngelaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Rehab: Renovating The "House" From The Inside OutDocument3 pagesShoulder Rehab: Renovating The "House" From The Inside OutxaviermayNo ratings yet
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction and Piriformis Syndrome PDFDocument37 pagesSacroiliac Joint Dysfunction and Piriformis Syndrome PDFDevi SiswaniNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The NeckDocument2 pagesMuscles of The NeckAncuta VijanNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Spine Worksheet Filled inDocument6 pagesThoracic Spine Worksheet Filled in7ty42yr2v4No ratings yet
- Back and Nexk PainDocument7 pagesBack and Nexk PainDenise MathreNo ratings yet
- Posture Dr. Dr. MY, SP KFR-KDocument67 pagesPosture Dr. Dr. MY, SP KFR-KCikupaNo ratings yet
- 1.forward Head PostureDocument2 pages1.forward Head PostureJacklynlim Lkc100% (1)
- Rotator Cuff TendinitisDocument23 pagesRotator Cuff TendinitisVrushali NikamNo ratings yet
- Neck & Back Care: Michelle KwongDocument62 pagesNeck & Back Care: Michelle Kwonginragm100% (1)
- Core Stability Exercise PrinciplesDocument6 pagesCore Stability Exercise Principlesphysioali0% (2)
- Can Local Muscles Augment Stability in The Hip A Narrative Literature Review PDFDocument12 pagesCan Local Muscles Augment Stability in The Hip A Narrative Literature Review PDFBel SantosNo ratings yet
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesFrom EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesNo ratings yet
- Healthy Shoulder Handbook: 100 Exercises for Treating and Preventing Frozen Shoulder, Rotator Cuff and other Common InjuriesFrom EverandHealthy Shoulder Handbook: 100 Exercises for Treating and Preventing Frozen Shoulder, Rotator Cuff and other Common InjuriesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Blood TubesDocument4 pagesBlood Tubesgail_eunice12No ratings yet
- The Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesThe Nervous System NotesDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Body Systems 6-11Document2 pagesBody Systems 6-11Yelizaveta BondarenkoNo ratings yet
- Lafarge Construction Ergonomics in The WorkplaceDocument48 pagesLafarge Construction Ergonomics in The WorkplacehksNo ratings yet
- The Real Eve (Mitochondrial Mother of Humanity)Document4 pagesThe Real Eve (Mitochondrial Mother of Humanity)Godwin Ofori DeyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System MatchDocument2 pagesCirculatory System MatchInternational Tutoring Association50% (2)
- Hepatobiliary System. Anatomy, Histology, and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHepatobiliary System. Anatomy, Histology, and Physiologyjedi_idej67% (3)
- Control and CoordinationDocument17 pagesControl and Coordinationanjupal100% (1)
- Animal Kingdom PPT 3 - Class 9Document32 pagesAnimal Kingdom PPT 3 - Class 9vidushi rathi100% (1)
- PSG 252 Lecture 3 The StomachDocument5 pagesPSG 252 Lecture 3 The StomachMichael TobilobaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SummaryDocument3 pagesCirculatory System SummaryNiel S. DefensorNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Body Cavity and Diaphargm Brig (R) Liaqat Ali MinhasDocument38 pagesMuscular System Body Cavity and Diaphargm Brig (R) Liaqat Ali Minhasvickyjee1No ratings yet
- Slides 22 OrbitalMusclesInnervation HeadNeckAnatomyDocument25 pagesSlides 22 OrbitalMusclesInnervation HeadNeckAnatomyAli AdelNo ratings yet
- EntDocument11 pagesEntkhuzaima9No ratings yet
- Canine and Feline Cytopathology 4Th Edition Rose E Raskin Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesCanine and Feline Cytopathology 4Th Edition Rose E Raskin Full Chapter PDFvieshaoyu100% (5)
- Lec - 1H - Special Senses System ReviewerDocument18 pagesLec - 1H - Special Senses System ReviewerProfessor GhoulNo ratings yet
- Classification of Anemia OkDocument60 pagesClassification of Anemia OkAnonymous 7CnBF0cjNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral CavityDocument9 pagesLecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral Cavitykasonde bowaNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfucionDocument2 pagesBlood TransfucionShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Culture and Sensitivity: InhalationDocument3 pagesCulture and Sensitivity: Inhalationjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Pathfit MidtermDocument6 pagesPathfit MidtermEloiza Allado NemenioNo ratings yet
- Presentation Auto 2Document33 pagesPresentation Auto 2mlllNo ratings yet
- 2022 Anatmoy and Physiology Cheat Sheet!Document3 pages2022 Anatmoy and Physiology Cheat Sheet!Estella BrockwellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- 04Swt PathoDocument89 pages04Swt PathoFlowerNo ratings yet
- Hormonal and Nervous SystemsDocument2 pagesHormonal and Nervous SystemsTaha KamilNo ratings yet
- ChickStagingSeries PDFDocument9 pagesChickStagingSeries PDFPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral CirculationDocument16 pagesCerebral Circulationvarrakesh100% (1)