Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applications of Transistors
Applications of Transistors
Uploaded by
joe saidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Applications of Transistors
Applications of Transistors
Uploaded by
joe saidCopyright:
Available Formats
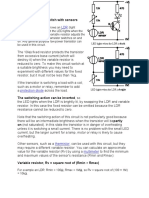
POTENTIAL DIVIDER
The transistor as an amplifier
When a person speaks into a microphone, sound waves are converted into
an alternating current.
The small changes in the base circuits cause the base current flows.
A small change in base current, will cause a big change in the collector
current.
Question The earphone thus receives a large alternating current from the collector
circuit and converts it into a loud sound.
The capacitor blocks a steady current (direct current) from flowing into the
transistor and microphone.
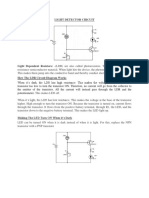
The transistor as a light controlled switch
Characteristic of LDR
LDR Dark : High resistance
Bright : Low resistance
RQ = 10 k
R
RP = 10 k
Determine VQ, VP, IQ and IP.
APPLICATIONS OF TRANSISTORS In bright light, the light-dependent resistor (LDR) has a very low resistance.
Therefore, the potential difference across LDR is low and hence the potential Characteristic of thermistor
difference across resistor R is high.
The base current flows and cause a large collector current flow. Cold : High resistance
The bulb lights up Hot : Low resistance
In darkness, the light-dependent resistor (LDR) has a very high resistance.
Therefore, the potential difference across LDR is high and hence the potential
difference across resistor R is low.
The base current does not flow and cause the collector current does not flow.
The bulb not lights up.
If the positions of the LDR and R are interchanged, the bulb is switched on in the When the thermistor is cold, it has a larger resistance than R.
dark and off in the bright light. Therefore, the potential difference across thermistor is high and hence the
potential difference across resistor R is low.
The base current does not flow and cause the collector current does not flow.
The bulb not lights up.
R When the temperature rises, the resistance of thermistor falls
The resistance of R is higher than the thermistor
The potential difference across R is higher
The base current flow and cause the collector current flow.
LDR The bulb lights up.
In bright light, the light-dependent resistor (LDR) has a very low resistance.
Therefore, the potential difference across LDR is low.
The base current does not flow and cause the collector current does not flow.
The bulb not lights up.
The base current flows and cause a large collector current flow.
The bulb lights up
In darkness, the light-dependent resistor (LDR) has a very high resistance.
Therefore, the potential difference across LDR is high
The base current flows and cause a large collector current flow.
The bulb lights up
The transistor as a temperature-controlled switch
You might also like
- DC Cable Sizing CalculatorDocument3 pagesDC Cable Sizing Calculatorphilipnart50% (2)
- InductorsDocument13 pagesInductorsManish AnandNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- 100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument22 pages100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDavid Atkinson100% (1)
- Year 10 Physics LDRs and Thermistors PDF v2Document12 pagesYear 10 Physics LDRs and Thermistors PDF v2sweet.miyuxNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi A800 ManualDocument714 pagesMitsubishi A800 ManualAlejandro Garcia50% (2)
- Electronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandElectronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionNo ratings yet
- Manual - Ar-Condicionado Do Tipo Split - Samsung - AR09HCSUBWQNAZDocument2 pagesManual - Ar-Condicionado Do Tipo Split - Samsung - AR09HCSUBWQNAZFelipe Santos100% (3)
- Positive & Zero Seq Impedence-R1Document88 pagesPositive & Zero Seq Impedence-R1goyalmanojNo ratings yet
- EATON Protection and Control RelaysDocument8 pagesEATON Protection and Control RelaysRazvan MaresNo ratings yet
- 6) 4H.1380.02.0.PR - Installation Service & Maintenance Manual For Ac Kirloskar Green Ac LS GeneratorDocument27 pages6) 4H.1380.02.0.PR - Installation Service & Maintenance Manual For Ac Kirloskar Green Ac LS GeneratorAlfiya AnamNo ratings yet
- Siemens India SICOP Datasheet 2016 PDFDocument64 pagesSiemens India SICOP Datasheet 2016 PDFAbrar HussainNo ratings yet
- TS1311 SpecDocument5 pagesTS1311 SpecAM7650% (2)
- L-S17 11KV Dry-Type Distribution Transformer JKR 2012 New SpecDocument43 pagesL-S17 11KV Dry-Type Distribution Transformer JKR 2012 New Specmardhiah100% (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Catalog SemiconductorsDocument69 pagesCatalog SemiconductorsRobert RoabyNo ratings yet
- HVCableJointing PDFDocument27 pagesHVCableJointing PDFFatima Buhlal100% (1)
- Electrcal Mcqs Indiabix Compiled by ASK PDFDocument245 pagesElectrcal Mcqs Indiabix Compiled by ASK PDFAsad AliNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Behaviour of ComponentsDocument20 pagesHigh Frequency Behaviour of ComponentsjascnjNo ratings yet
- Light Detector CircuitDocument1 pageLight Detector Circuitnavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- Laser Security Alarm SystemDocument7 pagesLaser Security Alarm Systemanuj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Electronic Part 2Document5 pagesChap 5 Electronic Part 2Siew MeiNo ratings yet
- Symbols CollaborativeDocument3 pagesSymbols CollaborativeSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent ResistorDocument6 pagesLight Dependent ResistorSagar GulatiNo ratings yet
- Circuit ComponentsDocument14 pagesCircuit ComponentstingzixuanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Light Depending Resistor: Fig.2.2 LDRDocument1 page2.2 Light Depending Resistor: Fig.2.2 LDRSiji VargheseNo ratings yet
- Electronics ComponentsDocument9 pagesElectronics ComponentsViviana BarinasNo ratings yet
- 4 3transistor 100805015532 Phpapp02Document12 pages4 3transistor 100805015532 Phpapp02Hafeeza YusofNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Capacitor and Inductor Is Given Below in The Tabulated Form. Basis Capacitor InductorDocument2 pagesThe Difference Between Capacitor and Inductor Is Given Below in The Tabulated Form. Basis Capacitor InductorAhad KhanNo ratings yet
- LDR Properties: The LDR Resistance Decreases With Increasing Light IntensityDocument11 pagesLDR Properties: The LDR Resistance Decreases With Increasing Light IntensityJr AndysNo ratings yet
- Circuit Components in Details: Metal ConductorsDocument4 pagesCircuit Components in Details: Metal ConductorsQuazi Rafquat HossainNo ratings yet
- Lect 5Document6 pagesLect 5Gotam DasNo ratings yet
- Smoke Detector CircuitDocument1 pageSmoke Detector CircuitBhushan NikumbhNo ratings yet
- Physics: Investigatory ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics: Investigatory ProjectabiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics ProjectPiyush ShahNo ratings yet
- Circuit ExplanationDocument1 pageCircuit ExplanationPayas SinghNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document6 pagesPresentation 2Anik Saha Toni 1912619643No ratings yet
- LDRPPTDocument14 pagesLDRPPTPraneshNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp Using LDRDocument3 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp Using LDRBihaz EtaraNo ratings yet
- LDR Project PresentationDocument16 pagesLDR Project PresentationIndra Devi100% (1)
- Automatic Street Light ControllerDocument50 pagesAutomatic Street Light ControllerGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Light Sensor Including Photocell and LDR SensorDocument11 pagesLight Sensor Including Photocell and LDR SensorKhairiBudayawanNo ratings yet
- Q: Draw A Full Wave Bridge Rectifier and Explain Its Working PrincipleDocument13 pagesQ: Draw A Full Wave Bridge Rectifier and Explain Its Working PrincipleAmir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Q: Draw A Full Wave Bridge Rectifier and Explain Its Working PrincipleDocument12 pagesQ: Draw A Full Wave Bridge Rectifier and Explain Its Working PrincipleAmir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Aa (0000)Document9 pagesAa (0000)Prajwol TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 31 Aug 2022Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 31 Aug 2022Kannan VandanaasreeNo ratings yet
- Using A Transistor Switch With SensorsDocument2 pagesUsing A Transistor Switch With SensorsShail DoshiNo ratings yet
- HFSI New Age High WayDocument4 pagesHFSI New Age High WayNirvan teckchandaniNo ratings yet
- Automatic - Street - Light PDFDocument2 pagesAutomatic - Street - Light PDFTiberlin LaminNo ratings yet
- LR Circuit With DC SourceDocument1 pageLR Circuit With DC SourcemuhammadusamachaduharyNo ratings yet
- Transducers: Light Dependent ResistorDocument3 pagesTransducers: Light Dependent ResistorIssa GrantNo ratings yet
- 9 3 TransistorDocument9 pages9 3 Transistorsuemozac100% (1)
- Physics - Topic 10Document6 pagesPhysics - Topic 1088wbh6hs8sNo ratings yet
- LDRDocument2 pagesLDRBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) - Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesLight Dependent Resistor (LDR) - Physics Investigatory ProjectVarun Ji56% (18)
- HTT TankDocument37 pagesHTT TankAprilia KrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Electronics FinalsDocument8 pagesElectronics FinalsAngelica FerrerNo ratings yet
- Resistencias VariablesDocument7 pagesResistencias VariablesJose CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Green & White Watercolor Simple Hello December Document (A4) - 20240104 - 074426 - 0000Document15 pagesGreen & White Watercolor Simple Hello December Document (A4) - 20240104 - 074426 - 0000Ayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 8Document8 pagesElectrical Circuits 8Gpg BioNo ratings yet
- Power Devices Part 1Document37 pagesPower Devices Part 1Anonymous rIBUACyoNo ratings yet
- MSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-LdrDocument16 pagesMSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-Ldrjigyasa BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Using A Transistor Switch With SensorsDocument2 pagesUsing A Transistor Switch With SensorsKalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- Transistor VoltageRegulators BJT SimpleDocument1 pageTransistor VoltageRegulators BJT SimpleAnonymous dGFqrw5vONo ratings yet
- 1.1 Active Components:: ExampleDocument18 pages1.1 Active Components:: ExampleNeelakanth BenakalNo ratings yet
- Electronic SymbolsDocument15 pagesElectronic SymbolsJuliannie LinggayoNo ratings yet
- Ece113 Lec05 Components at RFDocument42 pagesEce113 Lec05 Components at RF許耕立No ratings yet
- What Is Light Dependent ResistorDocument1 pageWhat Is Light Dependent ResistormirazNo ratings yet
- 320W Single Output With PFC Function: SeriesDocument4 pages320W Single Output With PFC Function: SeriesJesus HolmesNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse: Coupling Capacitor Potential DevicesDocument8 pagesWestinghouse: Coupling Capacitor Potential DevicesRick JordanNo ratings yet
- Parameter Identification of Electromagnetic Unit in Capacitive Voltage TransformerDocument4 pagesParameter Identification of Electromagnetic Unit in Capacitive Voltage Transformerreza hariansyahNo ratings yet
- 2.5 SQ - MM Push in Feed Through Compact Terminal Blocks: Images Cat. No. Description Std. PackDocument2 pages2.5 SQ - MM Push in Feed Through Compact Terminal Blocks: Images Cat. No. Description Std. PackNitinNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: High Performance Compact InverterDocument41 pagesInstruction Manual: High Performance Compact InverterMadison MadisonNo ratings yet
- Fuse Speed ExplainedDocument3 pagesFuse Speed ExplainedASPIRER63No ratings yet
- IGBT Module Series For Advanced-NPC Circuits: Kosuke Komatsu Takahito Harada Yoshiyuki KusunokiDocument6 pagesIGBT Module Series For Advanced-NPC Circuits: Kosuke Komatsu Takahito Harada Yoshiyuki KusunokivinaykumaarNo ratings yet
- 4 - Miroslav DIjakovic - Opportunities and Challenges For Commercial Rooftop Solar PV PDFDocument8 pages4 - Miroslav DIjakovic - Opportunities and Challenges For Commercial Rooftop Solar PV PDFvishansNo ratings yet
- Manual UPS New N 6 10kVA en UsDocument56 pagesManual UPS New N 6 10kVA en UsKhách Sạn Hoàng PhốNo ratings yet
- Power Inlet Assy: 13NO 14NODocument1 pagePower Inlet Assy: 13NO 14NOananth bhuvanaNo ratings yet
- User Manual 738 114: 1 DescriptionDocument1 pageUser Manual 738 114: 1 DescriptionBillel TalbiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Non-Salient Pole Synchronous Generator Using Phasor DiagramsDocument19 pagesAnalysis of Non-Salient Pole Synchronous Generator Using Phasor DiagramsNavitha RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 3-1/2 Digit LCD Multimeter With Tachometer Kit: Instructions and PrecautionsDocument16 pages3-1/2 Digit LCD Multimeter With Tachometer Kit: Instructions and Precautionsevil vavuNo ratings yet
- ECE312 Lec03 PDFDocument46 pagesECE312 Lec03 PDFLakshminathSinganapudiNo ratings yet
- Cable Review Paper PDFDocument13 pagesCable Review Paper PDFoadipphone7031No ratings yet
- VD4 - Vacuum Circuit-Breaker - BrosuraDocument2 pagesVD4 - Vacuum Circuit-Breaker - Brosuradorin serbanNo ratings yet
- Habilis Review Center 6Document8 pagesHabilis Review Center 6Marhmello PadriqueNo ratings yet
- Owner'S Instruction Manual: Tractor Driven AlternatorDocument16 pagesOwner'S Instruction Manual: Tractor Driven Alternatormarvin17No ratings yet
- Curve PV QVDocument7 pagesCurve PV QVAdel DjariNo ratings yet