Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 Functions
Uploaded by
icnemmyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Functions
Uploaded by
icnemmyCopyright:
Available Formats
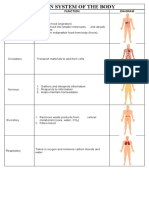
5 Functions of The Skeletal System
1. Body support.
2. Organ protection.
3. Body movement.
4. Mineral storage.
5. Blood cell production
3 Functions of the human skeleton:
1. Protection & support: It protects the internal organs, supports and gives shape to the body and allows for
movement.
2. Hematopoiesis: The production of all types of blood cells which occurs in the marrow of some bones.
3. Mineral homeostasis: Calcium / Phosphorus / Carbonate /Magnesium
5 Functions of the Bones
1. Support body and cradle soft organs
2. Protect vital organs
3. Movement: muscles move bones
4. Storage of minerals (calcium, phosphorus) & growth factors
5. Blood cell formation in bone marrow
6 Function of Muscles
1. Body movement
2. Maintenance of posture
3. Respiration
4. Production of body heat
5. Constriction of organs and vessels
6. Heart beat
6 Cartilages Function:
1. Acts as a shock absorber.
2. Plays a role in bone repair.
3. A template for the rapid growth and development of the musculoskeletal system.
4. Provide flexibility for joints to be able to bend.
5. Prevent collapse and damage of the airways, where cartilage rings around the trachea.
6. Allows the ribcage to swing upwards and outwards during inspiration.
4 Ligaments:
1. Connect bone to bone
2. Either limit or enhance movement
3. Provide joint stability
4. Enhance joint strength
Tendons
1. Enable bones to move when muscles contract
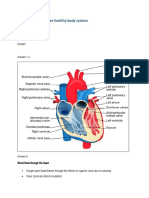
3 The functions of the blood:
1. Transportation of:
▪ Oxygen and nutrients to the tissues for use and storage.
▪ Metabolic wastes to the kidney, liver and skin.
▪ Hormones from the glands to the target tissues.
▪ Enzymes.
▪ Processed molecules: (e.g. Vitamin D & Lactate).
2. Regulation:
▪ Osmosis: (proper concentrations of ions).
▪ pH (Acid base balance).
▪ Body temperature.
3. Protection:
▪ Against excessive loss (Hemostasis).
▪ Against disease: WBCs, phagocytosis, antibodies,…etc.
Function of RBCs (Erythrocytes):
1. transport O2 from the lungs to the various tissues of the body and to help transport CO2 from the tissues to
the lungs.
2 Function of hemoglobin
1. Carries oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the body cells
2. The major breakdown product of hemoglobin is bilirubin.
3 Platelets (Thrombocytes):
1. Involved in the clotting process
2. Seal wounds and prevent blood loss
3. Help repair damaged vessels
2 White Blood Cells (Leucocytes)
1. Primary cells of the immune system
2. Fights disease and foreign invaders
2 Functional anatomy of respiratory system
1. Conducting zone (Gas passages): Anatomical dead space: space within the conductive airway, with NO gas exchange, consists of:
Nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi
Functions: Cleanse, warm, & humidify the incoming air.
2. Respiratory zone (Site of gas exchange): Bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli
5 Functions of Respiratory System
1. Gas exchange: Oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves.
2. Regulation of blood pH: Altered by changing blood carbon dioxide levels
3. Voice production: Movement of air past vocal folds makes sound and speech
4. Olfaction: Smell occurs when airborne molecules are drawn into the nasal cavity
5. Protection: Against microorganisms by preventing entry and removing them
7 Different Functions of the Kidneys:
1. Regulate water & electrolyte balance.
2. Regulate arterial pressure.
3. Regulate extracellular fluid pH (acid-base balance).
4. Regulate red blood cell synthesis (erythropoietin).
5. Excrete metabolic wastes and foreign substances such as drugs or toxins.
6. Converting vitamin D to its active form.
7. Gluconeogenesis: During prolonged fasting
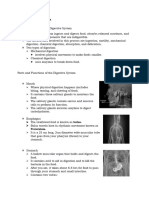
6 Functions of Digestive System
1. Ingestion and mastication: Ingestion is the consumption of solid or liquid food, usually through the mouth.
Mastication is chewing.
2. Propulsion and mixing: The movement of food from one end of the digestive tract to the other. Mixing is the
movement of food back and forth in the digestive tract
3. Digestion: Breakdown of large organic molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed. Digestion occurs
through mechanical and chemical means.
4. Secretion: The addition of liquids, enzymes, and mucus to the ingested food.
5. Absorption: The movement of molecules out of the digestive tract and into the blood or lymphatic system.
6. Elimination: Elimination is the removal of undigested material, such as fiber from food, plus other waste products
from the body as feces.
6 Functions of Each part of Digestive System
1. Mouth: Bite and chewing (teeth).
2. Pharynx and esophagus: Transport food from mouth to stomach.
3. Stomach: Chemical & mechanical digestion; absorption of water & alcohol
4. Small intestine: Chemical & mechanical digestion & absorption
5. Large intestine: Absorption of electrolytes & vitamins (B and K)
6. Rectum and anus: Eliminate undigested food (Defecation)
4 Functions of Saliva
1. Cleanses the mouth
2. Dissolves food chemicals so they can be tasted
3. Moistens food and helps compact it into a bolus
4. Contains “amylase” that begins the digestion of starchy foods
5 Functions of Stomach secretions
1. Hydrochloric acid (HCL):
a. Helps in protein digestion.
b. Kill bacteria in food into the stomach
c. Helping Fe2+、Ca2+ absorption.
2. Mucus:
a. Soluble mucus: Helps to lubricate chyme.
b. Insoluble mucus: Forms a protective barrier against the high acidity of the stomach content.
3. Intrinsic Factor:
a. Helps absorption of vitamin B12
4. Pepsin: Digests protein into smaller peptide chains
5. Gastric lipase: Starts to break down triacylglycerols.
4 Functions of The gall bladder
1. Storage of bile: ( the main function)
2. Concentration of bile: The maximum volume of the gall bladder is about 20-60 ml, but it can store up till 450
ml of bile
3. Acidification of bile: This maintain the properties of bile, Keep it in solution, Prevents stone formation
4. Prevention of marked increase in the biliary pressure: increase the biliary pressure to 320 ml of bile in 30
minutes due to stopping of bile secretion.
6 Functions of the liver
1. Produce bile
2. Store absorbed nutrients & vitamins
3. Produce Plasma proteins
4. Regulate blood levels of amino acids
5. Convert poisonous ammonia to urea
6. Detoxification: Clearing the blood of drugs and other poisonous substances
You might also like
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Biology For Form II-IV NotesDocument28 pagesBiology For Form II-IV NotesChrispin MsofeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory+Digestive System 2Document20 pagesCirculatory+Digestive System 2madeleine.gaudissartNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument5 pagesBrainWarda KhanNo ratings yet
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanNo ratings yet
- The Functions of Internal Organ: D I S U S U N Oleh: Name: Putri Anggraika NIM: 21115086 Prodi: PsikDocument8 pagesThe Functions of Internal Organ: D I S U S U N Oleh: Name: Putri Anggraika NIM: 21115086 Prodi: Psikputri anggraikaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument123 pagesPhysiology of Digestive Systemkidusabeje7No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Nutrition (Part 1)Document41 pagesChapter 6 - Nutrition (Part 1)Ema FatimahNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2aifs000001No ratings yet
- Class 10 Life ProcessDocument11 pagesClass 10 Life ProcessShubham Tiwari100% (2)
- 2013-G10 Bio Rev Note & Exe 2Document2 pages2013-G10 Bio Rev Note & Exe 2Bitania SolomonNo ratings yet
- First Lesson Questions and Their Answer: What Is Homeostasis?Document5 pagesFirst Lesson Questions and Their Answer: What Is Homeostasis?YonasNo ratings yet
- HSBDocument12 pagesHSBjemima MillsNo ratings yet
- Section A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationDocument12 pagesSection A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationJerry100% (1)
- 1ST Term S3 BiologyDocument36 pages1ST Term S3 BiologyFaith Opadele100% (2)
- 1st Term s3 BiologyDocument35 pages1st Term s3 BiologyAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document4 pagesUntitled 1Umang MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Z-03 Digest Part EVDocument50 pagesZ-03 Digest Part EVXaveer AzadNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument3 pagesDigestivePrishaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System LOVE YOU ENNDocument6 pagesDigestive System LOVE YOU ENNSharonNo ratings yet
- Nutrition NotesDocument8 pagesNutrition NotesDC MSME AttendanceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10Document12 pagesChapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10senthil2003kasNo ratings yet
- Name - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsDocument5 pagesName - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsRJ CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Interactions ChartDocument3 pagesBody Systems Interactions ChartAisha GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesDocument24 pages6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesWILSON KosheyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 1Document15 pagesNutrition 1Bada MubarakNo ratings yet
- Chapter6biological Processes in The Human BodyDocument23 pagesChapter6biological Processes in The Human Bodyanju sulishaNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition: The MouthDocument7 pagesAnimal Nutrition: The Moutheugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesLife ProcessesLal BhaiNo ratings yet
- MLM10 Life Processes2Document18 pagesMLM10 Life Processes2anshuman2683No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)Document16 pagesHuman Anatomy (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)Abdullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- SS3 Biology Lesson NoteDocument64 pagesSS3 Biology Lesson Notepalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSES NotesDocument6 pagesLIFE PROCESSES Notes9 D 140413 LOHITH KUNAPARAJUNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife ProcesseskrithicktcrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Food and DigestionDocument4 pagesChapter 4 - Food and DigestionAnonymous IqLK0OBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4hmNo ratings yet
- HLTAAP001 Recognize Healthy Body System 9Document17 pagesHLTAAP001 Recognize Healthy Body System 9yESHEy T100% (2)
- Digestion and Absorption Study GuideDocument6 pagesDigestion and Absorption Study GuideBritanny NelsonNo ratings yet
- Biological Systems Module 7.1Document9 pagesBiological Systems Module 7.1xara zinkNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemFeiNo ratings yet
- Past Paper by BSN Nazarn Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPast Paper by BSN Nazarn Anatomy and Physiologyhe4riphdxbNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemDocument32 pagesHuman Body SystemMehedi MahinNo ratings yet
- Sci NotesDocument4 pagesSci NotesMangoooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Nutrition (B)Document30 pagesChapter 6 Nutrition (B)Mei QiiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Note 3Document5 pagesNutrition Note 3Jewel WorrellNo ratings yet
- Garland Herridge HCA220 October 10,2010Document11 pagesGarland Herridge HCA220 October 10,2010Soliel MoonNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument53 pagesLife Processessagar100% (1)
- Assignment Bio Semester 3Document11 pagesAssignment Bio Semester 3api-317569592No ratings yet
- Zeotechnical Science Chap 2Document19 pagesZeotechnical Science Chap 2nkalamariejosee765No ratings yet
- DU - Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDU - Digestive SystemAlexandra MatysováNo ratings yet
- Biology Express Notes SPM 2010Document8 pagesBiology Express Notes SPM 2010nazrin_yusof_1No ratings yet
- Notes Ch-6 LIFE PROCESSESS-converted (1) (1) 2Document21 pagesNotes Ch-6 LIFE PROCESSESS-converted (1) (1) 2luv manotNo ratings yet
- Function of Internal OrganDocument3 pagesFunction of Internal Organerika damayantiNo ratings yet
- 6 Human PhysiologyDocument29 pages6 Human PhysiologyRaynaahNo ratings yet
- Absorption and AssimilationDocument19 pagesAbsorption and AssimilationChe SalNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument10 pagesDigestive System NotesArchanna VyassNo ratings yet
- Understanding Fatty Liver and Metabolic Syndrome: A Simplified GuideFrom EverandUnderstanding Fatty Liver and Metabolic Syndrome: A Simplified GuideNo ratings yet
- A Study of Normal Hair Growth in The DogDocument9 pagesA Study of Normal Hair Growth in The DogRebeka MenezesNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Forearm JointDocument15 pages4 - The Forearm JointProfesseur Christian Dumontier100% (1)
- Tewodros Tafere ProposaDocument29 pagesTewodros Tafere ProposaTewodros TafereNo ratings yet
- DNA Methylation-6Document21 pagesDNA Methylation-6Mugo JamesNo ratings yet
- 2009-08-25 Nowak Thyroid PDFDocument47 pages2009-08-25 Nowak Thyroid PDFEndalew Alemu NathanNo ratings yet
- 2022 25 E1351 E1366Document16 pages2022 25 E1351 E1366Ricardo PietrobonNo ratings yet
- Pharmalogical Charateristics of PhenitolDocument4 pagesPharmalogical Charateristics of PhenitolM. C. Gallion Jr.No ratings yet
- AppendixDocument98 pagesAppendixGwen Marielle CursoNo ratings yet
- Shiatsu MassageDocument13 pagesShiatsu MassageLawrence Cada Nofies100% (1)
- Rudin 1975Document450 pagesRudin 1975Alexander WilkielNo ratings yet
- Concept of Poultry Insurance Schemes in India - Poultry ShortsDocument12 pagesConcept of Poultry Insurance Schemes in India - Poultry ShortsAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- OMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusDocument51 pagesOMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusMaryam XANo ratings yet
- Patient NCPDocument8 pagesPatient NCPlouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- TSH & D3 Test ReportsDocument2 pagesTSH & D3 Test ReportsJyoti PrakashNo ratings yet
- Typology of Nursing Problems FNCPDocument9 pagesTypology of Nursing Problems FNCPPrsnigarbha Dasi D PotianNo ratings yet
- NCQA PrimerDocument53 pagesNCQA Primerd_anto781063No ratings yet
- 4 Way Analysis of Body Talk Technique On Body and Energy FieldsDocument86 pages4 Way Analysis of Body Talk Technique On Body and Energy Fields11111100% (1)
- PsychequestionsDocument23 pagesPsychequestionsGeorgette Noquera CubayNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Pathology, An Atlas andDocument1,604 pagesPulmonary Pathology, An Atlas andDANIEL IZE RONCHINo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination EyeDocument2 pagesClinical Examination EyeKirti JamwalNo ratings yet
- Enteral and Parenteral NutritionDocument46 pagesEnteral and Parenteral NutritionbashiruaminuNo ratings yet
- Management of Migraine Headache: An Overview of Current PracticeDocument7 pagesManagement of Migraine Headache: An Overview of Current Practicelili yatiNo ratings yet
- Biofeedback For Vertigo 2ndry To Cervical LesionDocument7 pagesBiofeedback For Vertigo 2ndry To Cervical LesionBassam EsmailNo ratings yet
- Aesculap® NeuroendosDocument100 pagesAesculap® NeuroendosJuan Esteban Restrepo VNo ratings yet
- Open Cloze More PracticeDocument3 pagesOpen Cloze More PracticezvegaNo ratings yet
- Roles of Oncology Pharmacists in Korea 20140928Document17 pagesRoles of Oncology Pharmacists in Korea 20140928adeputra25No ratings yet
- Manual of Infection Control Procedu PDFDocument365 pagesManual of Infection Control Procedu PDFanon_789115535100% (1)
- Are You Programming Yourself To Fail?Document2 pagesAre You Programming Yourself To Fail?Bernard Ah Thau TanNo ratings yet
- An Intelligent Black Widow Optimization On Image Enhancement With Deep Learning Based Ovarian Tumor Diagnosis ModelDocument16 pagesAn Intelligent Black Widow Optimization On Image Enhancement With Deep Learning Based Ovarian Tumor Diagnosis ModelAgnesNo ratings yet
- Circular ExcisionDocument2 pagesCircular ExcisionIde Bagoes InsaniNo ratings yet