Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry Reviewer 2024
Biochemistry Reviewer 2024
Uploaded by
velayochristine95Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochemistry Reviewer 2024
Biochemistry Reviewer 2024
Uploaded by
velayochristine95Copyright:
Available Formats
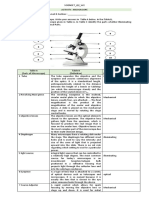
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEWER 2024 9.
Base:
Function: The base supports the
I. Microscope microscope and provides stability.
10. Illuminator (Light Source):
1. Eyepiece (Ocular Lens):
Function: The illuminator is the
Function: The eyepiece is where
light source that provides
you look through to observe the
illumination for the specimen. It
specimen. It typically magnifies the
can be built into the microscope or
image.
external.
2. Objective Lenses:
11. Rack Stop:
Function: These are the lenses
Function: The rack stop sets a limit
closest to the specimen and
on how far the stage or objective
provide different levels of
lenses can move, preventing
magnification. Users can rotate
damage to the specimen or lenses.
between objective lenses to
12. Mechanical Stage Controls:
achieve various magnification
Function: These controls include
levels.
3. Stage: knobs for moving the mechanical
stage horizontally and vertically,
Function: The stage is a platform
allowing precise positioning of the
where the specimen is placed for
specimen.
observation. It often includes clips
or a mechanical stage for securing II. pH Calculation
and moving the specimen. The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or
4. Condenser: alkalinity and is determined by the concentration
Function: The condenser focuses of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in the solution. The pH
light onto the specimen, scale ranges from 0 to 14, where:
optimizing illumination for clearer
visibility. pH less than 7 indicates acidity (0 being
5. Diaphragm: highly acidic).
Function: The diaphragm controls pH equal to 7 is neutral.
the amount of light reaching the pH greater than 7 indicates alkalinity (14
specimen. Adjusting the being highly alkaline).
diaphragm helps in optimizing
contrast and brightness. The pH is calculated using the formula:
6. Coarse Adjustment Knob:
Function: The coarse adjustment pH=−log[�+]pH=−log[H+]
knob is used for rough focusing,
quickly bringing the specimen into
where: [�+][H+] is the concentration of
view.
hydrogen ions in moles per liter.
7. Fine Adjustment Knob:
Function: The fine adjustment
If you know the hydrogen ion concentration, you
knob allows for precise focusing,
can use this formula to calculate the pH. For
refining the image for better
clarity. example, if the concentration of �+H+ is
8. Arm: 1×10−41×10−4 M:
Function: The arm provides
support and helps in carrying the pH=−log(1×10−4)pH=−log(1×10−4)
microscope.
pH=−(−4)pH=−(−4)
pH=4pH=4
You might also like
- Lightning PhotographyDocument25 pagesLightning PhotographyAndrei PitigoiNo ratings yet
- 01 Zoology MicrosDocument10 pages01 Zoology MicrosJohn AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Model Service Manual: Ophthalmic Yag Laser SystemDocument85 pagesModel Service Manual: Ophthalmic Yag Laser Systemمحمد خالدNo ratings yet
- Science 7: Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 2 Week 1Document11 pagesScience 7: Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 2 Week 1GINA OTARANo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument30 pagesMicroscopy ReviewMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- Manual of Optics & Refraction PDFDocument262 pagesManual of Optics & Refraction PDFJorge Flores100% (1)
- Activity 1 Microscope (1) PREIY JULIAN M. DE GUIADocument2 pagesActivity 1 Microscope (1) PREIY JULIAN M. DE GUIAPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Microscope PREIY JULIAN M. DE GUIADocument3 pagesActivity 1 Microscope PREIY JULIAN M. DE GUIAPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Microscope: Adelaide, Savero, & CharissaDocument12 pagesMicroscope: Adelaide, Savero, & CharissaPMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet
- 1 MicroscopeDocument3 pages1 MicroscopeMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Notes Specimen SlidesDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lab Notes Specimen SlidesAvi HylixNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 M1A v4 No Key AnswerDocument11 pagesScience7 Q2 M1A v4 No Key AnswerCastolo Bayucot Jvjc100% (1)
- Biology Lab Activity 1Document6 pagesBiology Lab Activity 1Adrian Anthony Villaluz GasatayaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Laboratory Activity #1A: Table 1.1 Parts of A Microscope and Its FunctionsDocument7 pagesLaboratory Report Laboratory Activity #1A: Table 1.1 Parts of A Microscope and Its FunctionsRGems PHNo ratings yet
- Microscope and Basic Plant Microtechnique Activity 2 WorksheetDocument9 pagesMicroscope and Basic Plant Microtechnique Activity 2 WorksheetEPHRAIM JOASH ABEJO GAGANTINGNo ratings yet
- Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound Light MicroscopeCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- Jeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFDocument3 pagesJeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1. MicroscopeDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1. MicroscopeMary Grace FeudoNo ratings yet
- 1 MicrosDocument7 pages1 MicrosJachelle KateNo ratings yet
- HES 032 BSN Lab Activity 1Document7 pagesHES 032 BSN Lab Activity 1delta bravoNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument4 pagesMICROSCOPEJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationDocument3 pagesInstruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationCyndel TindoyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1: Understanding CellsDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity 1: Understanding CellsmxrcuryyyNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Froggle Bunwich Lab Activity 2Document10 pagesGroup 1 Froggle Bunwich Lab Activity 2Belyn CancioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 EDITED #1Document8 pagesExperiment 1 EDITED #1Ronel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2885259728078242669Document8 pagesInbound 2885259728078242669niccolodenopol29No ratings yet
- Module 2 Explain Arial 11Document2 pagesModule 2 Explain Arial 11eryan binsentNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MicrosDocument8 pagesModule 1 MicrosmagwiNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ScriptDocument3 pagesScience 7 Scriptangeline vacalaresNo ratings yet
- Science 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEDocument6 pagesScience 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEEzzel Jan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- An Important Technique - Use of The Microscope: VCE BiologyDocument18 pagesAn Important Technique - Use of The Microscope: VCE BiologyC CdNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY SHEET ACT.1 LOQUIRE and GUIAPAR 1Document5 pagesLABORATORY SHEET ACT.1 LOQUIRE and GUIAPAR 1Mary Criscebel Kyla LoquireNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Proper Manipulation and Identificaton of The Different Parts of A MicroscopeDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1: Proper Manipulation and Identificaton of The Different Parts of A MicroscopemasorNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - MicrosDocument4 pagesExercise 1 - MicrosWin BalladaNo ratings yet
- Biochem No. 1Document7 pagesBiochem No. 1Allesa San JoseNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: The Microscope: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesActivity 2: The Microscope: ObjectivesKhim BalcitaNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument8 pagesMicrosValerie Frances AraoNo ratings yet
- Transes-Micropara Lab PrelimsDocument4 pagesTranses-Micropara Lab Prelimsmikhyla.cardenoNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A Microscopelarry machonNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportFatima Shiera BarraquiasNo ratings yet
- SLHT Science 7 Q2 Week 1 (Ok)Document9 pagesSLHT Science 7 Q2 Week 1 (Ok)Sarah Mae TulodNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual in HISTOLOGYDocument3 pagesLaboratory Manual in HISTOLOGYRIA ALEJANDRONo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument4 pagesMICROSCOPEChelsea SebastianNo ratings yet
- MOD1 Microscope&AnimalCellDocument2 pagesMOD1 Microscope&AnimalCellagg ;No ratings yet
- Act 2 Bot LabDocument3 pagesAct 2 Bot LabAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- At Least 0.4 NM Apart Numerical ApertureDocument5 pagesAt Least 0.4 NM Apart Numerical ApertureRaffy FlandesNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument69 pagesQ2 - Living Things and Their EnvironmentAURORA () CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Histo Lab Exercise #1Document3 pagesHisto Lab Exercise #1Gela ReyesNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPEFelisa Pauline VallarNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 MicrosDocument2 pagesPMLS 2 MicrosYlyza MarquezNo ratings yet
- All About Microscope PresentationDocument11 pagesAll About Microscope Presentationearlyn angelie gopioNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab NotesDocument24 pagesAnaphy Lab NotesBrylle MitchiNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercises For BiologyDocument13 pagesLab Exercises For BiologyMari SoleiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Compound Final For PDFDocument3 pagesActivity 2 Compound Final For PDFAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their FunctionsAlfina SafiraNo ratings yet
- The Microscope PDFDocument10 pagesThe Microscope PDFPrincess Angie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ManualDocument11 pagesMicroscopy ManualozlemNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 1Document3 pagesLab Manual 1elizabeth shaw gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - MicroscopeDocument4 pagesModule 1 - MicroscopeGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument8 pagesMICROSCOPEALTHE NICOLE ALVIOLANo ratings yet
- Q2 W2Document2 pagesQ2 W2B20Taroy, Miguel BernarteNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - BIO 201L Week 2 MICROSCOPY LAB ACTIVITY 2 - BS BIO 2103Document9 pagesGROUP 2 - BIO 201L Week 2 MICROSCOPY LAB ACTIVITY 2 - BS BIO 2103Deadpool FrancisNo ratings yet
- Line Scan Lens: Makro-Symmar 5.6/120-0.75xDocument3 pagesLine Scan Lens: Makro-Symmar 5.6/120-0.75xwilco23No ratings yet
- SON RM IP10 - UserguideDocument84 pagesSON RM IP10 - UserguideYacoub DOMANo ratings yet
- Zenit E EngDocument9 pagesZenit E EngMassimo PedrinaNo ratings yet
- Anker ROAV C1 Dash CamDocument14 pagesAnker ROAV C1 Dash CamVenu RajputNo ratings yet
- Diagrams of EyeballDocument7 pagesDiagrams of EyeballHelworNo ratings yet
- Silent Sentinel - 20200411-Deployment - Guide - Kit - TripodDocument11 pagesSilent Sentinel - 20200411-Deployment - Guide - Kit - TripodidosachsNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE12DF0T-LFS Datasheet 20231113Document5 pagesDS-2CE12DF0T-LFS Datasheet 20231113nkoyoyojohnpaul56No ratings yet
- MCQ Class 10Document34 pagesMCQ Class 10mondalkakoli83No ratings yet
- Avizia Horus Scope: Focus On Enhancing TelemedicineDocument4 pagesAvizia Horus Scope: Focus On Enhancing TelemedicineL2D TelemedicinaNo ratings yet
- DIY Remote Control For Canon EOS CamerasDocument1 pageDIY Remote Control For Canon EOS CamerasJamie RandolphNo ratings yet
- Romel B. Guray - DEBATEDocument3 pagesRomel B. Guray - DEBATERomel GurayNo ratings yet
- 88FDTimes ZEISS Supremes ReportDocument44 pages88FDTimes ZEISS Supremes ReportCarlos Perez JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Body Worn Cam SOPDocument6 pagesBody Worn Cam SOPmatthewpleasantNo ratings yet
- Math's Around Us VI Standard Higher Level Math - PracticeDocument69 pagesMath's Around Us VI Standard Higher Level Math - PracticeDinesh GKNo ratings yet
- Price List Update Februari 2021Document6 pagesPrice List Update Februari 2021dewapalgunaNo ratings yet
- DSC-P71/P51/P31 Sony Digital Still CameraDocument108 pagesDSC-P71/P51/P31 Sony Digital Still CameraguilleamodeoNo ratings yet
- NecksnappersDocument105 pagesNecksnappersAndreaNo ratings yet
- Wislawa Szymborska - The Courtesy of The BlindDocument1 pageWislawa Szymborska - The Courtesy of The BlindjunkydawnNo ratings yet
- Utsav Jha Camera AngleDocument9 pagesUtsav Jha Camera AngleOTT NEPALNo ratings yet
- sb700 PDFDocument191 pagessb700 PDFValentin MiroiuNo ratings yet
- IOLMaster 700-Quick-Guide-Calculation-Suites-ENDocument10 pagesIOLMaster 700-Quick-Guide-Calculation-Suites-ENAlejandra Silvia Arando VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Kdlinks x1 Dash Cam ReviewsDocument15 pagesKdlinks x1 Dash Cam Reviewseld mandatebizNo ratings yet
- Oscar 3.0 11 2021 DCDocument2 pagesOscar 3.0 11 2021 DCSebastian RentschNo ratings yet
- Capstone 1: International University - VNU-HCMC School of Electrical EngineeringDocument21 pagesCapstone 1: International University - VNU-HCMC School of Electrical EngineeringQuốc KhánhNo ratings yet
- LARRY CLARK Death Is More Perfect Than LifeDocument5 pagesLARRY CLARK Death Is More Perfect Than LifexmisstakexNo ratings yet
- Sony HDR-SR5/SR5C/SR5E/SR7//SR8 Service ManualDocument118 pagesSony HDR-SR5/SR5C/SR5E/SR7//SR8 Service ManualThanos AnastasiadisNo ratings yet
- Hikvision DVR Won't Display Channels (Solved) : DownloadDocument6 pagesHikvision DVR Won't Display Channels (Solved) : DownloadSaso SaskoNo ratings yet