Professional Documents
Culture Documents
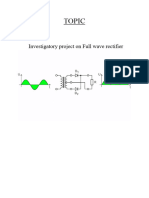
Class 12 Science Project 2024
Uploaded by
jjrs18690 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesOriginal Title
class 12 Science project 2024
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesClass 12 Science Project 2024
Uploaded by
jjrs1869Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Acknowledgement
In the accomplishment of this project
successfully, Many people have best owned upon
me their blessings and the heart pledge support,
this time I am utilizing to thank all the people
who have been concerned with this project.
Primarily I would like thank god for being able to
complete this project with success. Then I would
like to thank my principal Mr. V.K Yadav sir and
my physics teacher Mr. A. P. Singh. Sir whose
valuable guidance has been the ones that helped
me patch this project and make it full proof
success, his suggestions and instruction has
served as the major contribution towards the
completion of this project.
Then I would like to thank my parents who have
helped me with their valuable suggestions and
guidance has been very helpful in various phases
of the completion of the project.
Saurabh Kumar
Class 12 (Science)
AIM
To construct and study the working conditions of
a full wave
INTRODUCTION
1. RECTIFIER
A rectifier is an electrical device that (AC),
which periodically reverses direction, to (DC),
which flows in only one direction. The process is
known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take
a number of forms, including Rectifiers have
many uses, but are often found serving as
components of DC and power transmission
systems. It is a combination of Diodes and
Resistors either in series or in parallel It gives
appropriate output to be used in DC
combination
2. FULL WAVE RECTIFIER
While this method may be suitable for low power
applications it is unsuitable to applications which
need a “steady and smooth” DC supply voltage.
One method to improve on this is to use every half-
cycle of the input voltage instead of every other half-
cycle. The circuit which allows us to do this is called
a Full Wave Rectifier. Like the half wave circuit, a
full wave rectifier circuit produces an output voltage
or current which is purely DC or has some specified
DC component.
Full wave rectifiers have some fundamental
advantages over their half wave rectifier counterparts.
The average (DC) output voltage is higher than for
half wave, the output of the full wave rectifier has
much less ripple than that of the half wave rectifier
producing a smoother output waveform.
N Vs- Vmsinwt i.e., sinusoidal input voltage
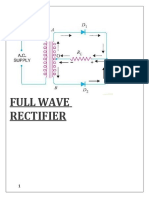
In a Full Wave Rectifier circuit two diodes are now
used, one for each half of the cycle. A is used whose
secondary winding is split equally into two halves
with a common canter tapped connection. This
configuration results in each diode conducting in turn
when its anode terminal is positive with respect to the
transformer canter point C producing output during
both half cycles, twice that for the half wave rectifier
as it is 100 percent efficient.
The full wave rectifier circuit consists of two power
diodes connected to a single load resistance (RL) with
each diode taking it in turn to supply current to the
load. When point A of the transformer is positive with
respect to point C, diode DI conducts in the forward
direction as indicated by the arrows
When point B is positive (in the negative half of the
cycle) with respect to point C diode D2 conducts in
the forward direction and the current flowing through
resistor R is in the same direction for both half-cycles.
As the output voltage across the resistor R is the
phasor sum of the two waveforms combined, this type
of full wave rectifier circuit is also known as a
“diphase” circuit
COMPARISION CHART
PARAMETERS HALF-WAVE FULL-WAVE
RECTIFIER RECTIFIER
Rectification 40.6% 81.2%
efficiency
Ripple factor 1.21 0.482
Transformer 0.286 0.692
utilization factor
Voltage regulation Good Better
Fundamental Equal to supply Double of supply
frequency of ripple frequency frequency, 2f
From factor 1.57 1.11
Peak factor 2 1.414
Number of diodes Only 1 Vary from 2 to 4,4
in case of bridge
rectifier
Peak inverse Vs 2vs
DC output voltage Imax/πRL 2πRL Imax
Application of full wave rectifier:
To provide full wave rectification, usually as a
first step to Convert AC power to DC.
Car alternator
Any cell phone charger
Laptop/tablet charger Power bank
Any other switching supply: alarm, charger,
Bluetooth Device charger, LAN/router supply
etc.
Audio power supply in pre amp and power
amplifier
Any video device
Lead battery charger LED driver, any LED
lamp over 10 Watts in general
Characteristics of Full Wave Rectifier:
Advantages of Full Wave Rectifier:
You can use four individual power diodes to make a full
wave bridge, readymade bridge rectifier components are
available off the-shelf
shelf in a range of different voltage and
current sizes that can be soldered directly into a PCB
circuit board or be connected by spade connectors.
The full-wave
wave bridge rectifier gives us a greater mean DC
value with less superimposed ripple while the output
waveform is twice that of the frequency of the input
supply. Therefore, increase its average DC output level
even higher by connecting a suitable smoothing capacitor
across the output of the bridge circuit.
The advantages of a full
full-wave bridge rectifier are that it has
a smaller AC ripple value for a given load and a smaller
reservoir or smoothing capacitor than an equivalent half-
half
wave rectifier circuit. The fundamental frequency of the
ripple voltage is twice that of the AC supply frequency
You might also like
- Physics Class 12 Full Wave Rectifier Project FileDocument16 pagesPhysics Class 12 Full Wave Rectifier Project FileNavneet Nigam0% (2)
- Lab 3 - Logisim Sequence CircuitDocument37 pagesLab 3 - Logisim Sequence CircuitMinh Nhật TrầnNo ratings yet
- Doosan Servo Alarm Action Manual 1axis - en - Rev - ADocument39 pagesDoosan Servo Alarm Action Manual 1axis - en - Rev - A323ci0% (1)
- Presentation PHYSICS 12Document19 pagesPresentation PHYSICS 12Vaishali ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit With WorkingDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Circuit With WorkingKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- Physics Final ReportDocument17 pagesPhysics Final Reportprasannad726No ratings yet
- Full Wave ContentDocument6 pagesFull Wave ContentAkshaya chandra sekarNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Xii-ADocument32 pagesPhysics Project: Xii-AneharNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument13 pagesFull Wave RectifierSundar RajanNo ratings yet
- PN Junction HW and FWDocument15 pagesPN Junction HW and FWSHIVANSH SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit With Working TheoryDocument7 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Circuit With Working Theorysuraj vishnoiNo ratings yet
- SIMULINKDocument5 pagesSIMULINKshresth.gupta.ug22No ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument15 pagesRECTIFIERAni AniNo ratings yet
- Physics Project FileDocument17 pagesPhysics Project FileDhana sekaranNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifierutkarsh devNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument17 pagesFull Wave RectifierDhana sekaranNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument17 pagesINTRODUCTIONPRASHANTNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier and Bridge Rectifier TheoryDocument7 pagesFull Wave Rectifier and Bridge Rectifier TheorySuresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 03Document8 pagesLab Report 03fkhan201160No ratings yet
- Full Wave TheoryDocument6 pagesFull Wave Theorypunjabe2004No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument36 pagesBasic Electronicswhatsapp status clipsNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument26 pagesRectifierAyush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Abraar PhysicsDocument28 pagesAbraar PhysicsRahulking 2007No ratings yet
- A Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentDocument9 pagesA Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- Zero CrossingDocument16 pagesZero CrossingAryan KapsNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge Rectifier Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesFull Wave Bridge Rectifier Explained in 40 CharactersSachit KumarNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument4 pagesRectifierAngellicaNo ratings yet
- What is a Rectifier ExplainedDocument10 pagesWhat is a Rectifier ExplainedRutvikNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesDocument7 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesArun PratapNo ratings yet
- Full wave rectifier circuit explainedDocument9 pagesFull wave rectifier circuit explaineds aravindNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier: Anshu PalDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectifier: Anshu PaledhyrgNo ratings yet
- Physics Project MohithaDocument20 pagesPhysics Project MohithaB.LOHITHA BALANo ratings yet
- EC: Rectifiers & Filters ExperimentDocument6 pagesEC: Rectifiers & Filters ExperimentMadamNo ratings yet
- AC to DC Conversion with RectifiersDocument16 pagesAC to DC Conversion with RectifiersJaiom JoshiNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifireDocument9 pagesFull Wave Rectifireالزهور لخدمات الانترنيت100% (1)
- Electronic Circuits Last 2Document30 pagesElectronic Circuits Last 2AimanNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave RectifierMurali Krishna GbNo ratings yet
- Project On Full Wave RectifierDocument16 pagesProject On Full Wave RectifierTiasa BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- The Full Wave Rectifier: Power DiodesDocument3 pagesThe Full Wave Rectifier: Power DiodesReeju_VargheseNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier ProjectDocument20 pagesFull Wave Rectifier ProjectKhushi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierAnonimen AnonimenNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesFull Wave RectifierAtul Namdeo0% (1)
- HarshDocument12 pagesHarshHitesh AnandNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterLemuel C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab - Full Wave Rectifier With and Without Filters - Notes - SboDocument6 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab - Full Wave Rectifier With and Without Filters - Notes - SboECEOCETNo ratings yet
- What Is Half Wave Rectifier DeepuDocument15 pagesWhat Is Half Wave Rectifier Deepuharshvardhan singhNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicspraveensivan22No ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierPurabi DasNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics Projectish varyaNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier: Power DiodesDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectifier: Power Diodespapasky100% (2)
- Battery Charging UnitDocument19 pagesBattery Charging UnitAbinMiranda100% (1)
- Full Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesFull Wave RectifierSanjana SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Power SupplyDocument81 pagesLecture On Power SupplyMATE0100% (2)
- Full Wave Rectifier and Bridge Rectifier TheoryDocument17 pagesFull Wave Rectifier and Bridge Rectifier TheoryMrmouzinhoNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier FormulaDocument11 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier FormulaVelu Samy86% (7)
- Final Act PtedDocument8 pagesFinal Act PtedCARLIN JOSH MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Rectifiers, Filters and RegulatoDocument12 pagesRectifiers, Filters and Regulatono.1slytherinprincessNo ratings yet
- Mendoza FinalActivityPTEDDocument8 pagesMendoza FinalActivityPTEDCARLIN JOSH MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- B.Tech R20 III Year ECE Model Papers FINAL ws-16-23Document8 pagesB.Tech R20 III Year ECE Model Papers FINAL ws-16-23Bandaru Jaswanth kumarNo ratings yet
- Cooper Power SeriesDocument47 pagesCooper Power Seriesrtupp2.plnup2dbantenNo ratings yet
- 08140h PDFDocument12 pages08140h PDFAmine EmineNo ratings yet
- Vpis 61958 enDocument2 pagesVpis 61958 enmlliumingyang666No ratings yet
- 160 Um004 - en P PDFDocument60 pages160 Um004 - en P PDFHector ChaileNo ratings yet
- Lecture Two Pulse ShapingDocument53 pagesLecture Two Pulse Shapingaldamati2010No ratings yet
- Sandisk Sdinbdg4 16G Za - C2830401Document45 pagesSandisk Sdinbdg4 16G Za - C2830401Muhammad RafiqueNo ratings yet
- KDL 32bx330 331Document40 pagesKDL 32bx330 331salomonNo ratings yet
- 1783-ETAP Module Components 1783-ETAP1F, 1783-ETAP2F Module ComponentsDocument3 pages1783-ETAP Module Components 1783-ETAP1F, 1783-ETAP2F Module ComponentsdurbanmejiasNo ratings yet
- HSI Configuration for GPONDocument16 pagesHSI Configuration for GPONShubham VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- EPABX User's Guide for Making Calls and Using FeaturesDocument4 pagesEPABX User's Guide for Making Calls and Using FeaturesPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Tech-System 239 Manual - 08 - enDocument38 pagesTech-System 239 Manual - 08 - enviniciustim9No ratings yet
- Capacity From 500 KG To 200000 KG: Compression / Tension Load Cells Compression / Tension Load CellsDocument2 pagesCapacity From 500 KG To 200000 KG: Compression / Tension Load Cells Compression / Tension Load CellsAyman AlhalfawyNo ratings yet
- RF, Digital Radio, and Metamaterials Final Project: Nonreciprocal AcousticsDocument3 pagesRF, Digital Radio, and Metamaterials Final Project: Nonreciprocal Acousticsrhill55_911701980No ratings yet
- Gujarat PGCET Question Bank ECDocument262 pagesGujarat PGCET Question Bank ECsuhradamNo ratings yet
- R&S TSMW ManualDocument12 pagesR&S TSMW ManualmiansufyanNo ratings yet
- CSN Call Processing FunctionsDocument36 pagesCSN Call Processing FunctionsNeel Kanak100% (1)
- EYR207Document8 pagesEYR207Gabor KomuvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 2 PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Part 2 PDFKhairil Azwan TugimanNo ratings yet
- Bcom & B.A - Notes - NmeDocument180 pagesBcom & B.A - Notes - NmeDarshini BNo ratings yet
- Integrated 1710-2690MHz Antenna with 2-10° Electrical DowntiltDocument2 pagesIntegrated 1710-2690MHz Antenna with 2-10° Electrical DowntiltkhoabomthaobomNo ratings yet
- Deco PDFDocument4 pagesDeco PDFTabish ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Revista Raspberry PiDocument100 pagesRevista Raspberry PiLucas Mota100% (1)
- Ixys dpg60c300hb Datasheets 9568Document5 pagesIxys dpg60c300hb Datasheets 9568matesimic50No ratings yet
- Lab 2 PDFDocument3 pagesLab 2 PDFTawsif ahmedNo ratings yet
- Ads 1220Document71 pagesAds 1220Mohamed BelkaidNo ratings yet
- Multi-band/Multi-Mode RF Front-End Receiver For Basestation ApplicationsDocument87 pagesMulti-band/Multi-Mode RF Front-End Receiver For Basestation Applicationswrite2arshad_mNo ratings yet
- Tda 2595Document13 pagesTda 2595beta2009No ratings yet