Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Particulate Nature of Matter
Uploaded by
animahadarkwahfrimpong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter
Uploaded by
animahadarkwahfrimpongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Particulate Nature of Matter
Basic Compositions of Matter
Basic compositions of matter
• Atoms, molecules and ions
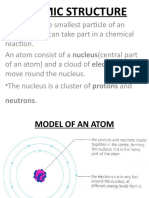
• An atom is the smallest particle of an elements that can take part in a
chemical reaction.
• An atom is an electrically neutral particle.
• In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of
protons.
Molecules
• A molecule is a group of two or more atoms chemically combined.
• Molecules can be homonuclear e.g. O2, O3, H2 etc or heteronuclear
eg. HCl, NH3,
Basic compositions of matter
• The number of atoms combined in one molecule of a substance is its
atomicity.
• Monatomic molecules contains only one atom. e.g. Ne, Ar, Kr etc.
• Diatomic molecules contain only two atoms e.g. O2, H2 Cl2, N2, HCl, CO
• Triatomic molecules contain three atoms e.g. O3 (ozone)
• Tetratomic molecule contains four atoms e.g. P4 (Phosphorus)
• Octatomic molecule contains eight (8) atoms e.g. S8 (Sulphur)
• The number of atoms in a molecule is placed as a right subscript of
the symbols of the element. For example, O2, P4, F2 etc.
Basic compositions of matter
• An ion is an electrically charged particle (atom or group of atoms).
Atoms of many elements can gain or lose electrons.
• Cation is formed when an atom loses an electron. e.g. Na+ , Cu2+, Ca2+
, Al3+ etc.
• Anion is formed an atom gains / accepts one or more electrons and
become negatively charged e.g. Cl− ,O2− , N 3− etc.
Evidence of the particulate nature of matter
• Brownian motion
• Crystallization
• Melting
• Evaporation
• Diffusion
Question
Classify the following substances, Na, H2O, SO42- , H2, and Ca2+ as
(i) atoms
(ii) ions
(iii) molecules
Classification of matter
ELEMENTS
• An element is a pure substance containing only one kind of atom
which cannot be broken down into simpler substance.
• For example, aluminium is an element which is made up of only
aluminium atoms. Iron, silver, gold, sulphur, oxygen, and copper are
other familiar examples of elements.
• There are 118 chemical elements. They are listed on the periodic table
in specific order.
ELEMENTS
• All elements can be classified into metals, non – metals and semi -
metals according to their various properties.
• Metals are found on the left and in the middle of the periodic table,
whereas non-metals are on the right.
ELEMENTS
• Chemists use symbols of one or two letters to represent the elements.
• The symbols of some elements are derived from their Latin names, for
example,
Au from aurum (gold),
Fe from ferrum (iron),
Na from natrium (sodium)
• However, most of the elements derive their names from English words
e. g. Oxygen (O), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N) etc.
ELEMENTS
• Some elements exist as individual atoms e. g. Helium, Neon, Argon
and the metals
• Some exist as molecules e.g. Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulphur, Hydrogen
etc.
COMPOUNDS
• A compound is a pure substance formed from two or more different
elements chemically combined in a fixed proportions.
• Water is a simple compound formed from the elements hydrogen and
oxygen
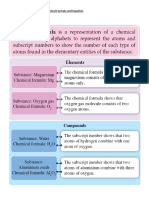
• Each compound can be represented by a chemical formula.
• The chemical formula is made up of the symbol of the elements that is
combined with the numbers to show the ratio in which the different
atoms are present
COMPOUNDS
• EXAMPLES OF COMPOUNDS WITH THEIR CHEMICAL FORMULAE
SEPARATION OF COMPOUNDS
• Compounds can be separated into their constituent elements by
chemical reactions, for example,
electricity
• Electrolysis of water H2O H2 + O2
and thermal decomposition CaCO3 CO2 + CaO
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN COMPOUNDS AND
ELEMENTS
You might also like
- 4 From Atoms To CompoundDocument14 pages4 From Atoms To CompoundJerik Christoffer Ordinario GasparNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Elements, Compounds, Chem Equations and CalculationsDocument93 pagesChapter 2 - Elements, Compounds, Chem Equations and CalculationsDn Zack100% (2)
- CH3 Atoms and Molecules Part 2Document3 pagesCH3 Atoms and Molecules Part 2raghavakansha084No ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and Ions: Formulas and Naming of Chemical CompoundsDocument60 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and Ions: Formulas and Naming of Chemical CompoundsMike MarquisNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: - Year 9, Week 3Document37 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures: - Year 9, Week 3Agim OnyekaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical BondingDanushanDayaparanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 StudentDocument8 pages3.3 StudentturkeyzqwanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Matter and Its SystemsDocument34 pagesThe Structure of Matter and Its SystemsgenusxyzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - FundamentalsDocument47 pagesChemistry - FundamentalsNicolas DagherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDocument34 pagesLecture 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ionsapi-19824406100% (1)
- Global Indian International School Uppal, Hyderabad Subject: Chemistry Chapter 3 .Atoms and MoleculesDocument13 pagesGlobal Indian International School Uppal, Hyderabad Subject: Chemistry Chapter 3 .Atoms and MoleculesKhatrasNo ratings yet
- Chap2-Elements, Compounds, Chem Equations and CalculationsDocument62 pagesChap2-Elements, Compounds, Chem Equations and Calculationssarah575No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document17 pagesChapter 6Fera Cherilyn JulianNo ratings yet
- Science Project Atom and Molecules Best PresenytDocument17 pagesScience Project Atom and Molecules Best PresenytYug khuntNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Compounds, Mixtures, Molecules and ElementsDocument91 pagesAtoms, Compounds, Mixtures, Molecules and ElementsYara RedaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument29 pagesAtomic StructureAnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 3 PDFadasdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3Ayro CrochetNo ratings yet
- CH3 Molecules and CompoundsDocument25 pagesCH3 Molecules and Compoundscyl2013003No ratings yet
- Naming Molecules and Molecular CompoundsDocument32 pagesNaming Molecules and Molecular CompoundsAlexandra Venice Ann M. PerezNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Ap Chemistry: Mahua ChakrabortyDocument33 pagesWelcome To Ap Chemistry: Mahua ChakrabortyKahfiantoroNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument53 pagesElementskmalionsNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL FORMULAS NOMENCLATURE ofCOMPOUNDS AND CHEMICAL EQUATIONSDocument26 pagesCHEMICAL FORMULAS NOMENCLATURE ofCOMPOUNDS AND CHEMICAL EQUATIONSFajarNo ratings yet
- Non Metalic Substances and Covalent BondingDocument47 pagesNon Metalic Substances and Covalent Bonding42h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - CHEM 151 - Lecture SlidesDocument91 pagesChapter 3 - CHEM 151 - Lecture SlidesjohnNo ratings yet
- 2 Brown Et Al - Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2Document44 pages2 Brown Et Al - Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2AfwaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 - Naming Ionic Molecular CompoundsDocument31 pages2 2 - Naming Ionic Molecular Compoundsapi-263048875100% (1)
- BondingDocument45 pagesBondingRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Divine Word University ST Benedict's Year 1 Semester 1: GN 102:anatomy and Physiology Topic:Basic ChemistryDocument18 pagesDivine Word University ST Benedict's Year 1 Semester 1: GN 102:anatomy and Physiology Topic:Basic ChemistryArkfeld HeangreNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, Chemical Equations and CalculationsDocument104 pagesElements, Compounds, Chemical Equations and CalculationsNurain HuzaineNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Oil and ChemicalDocument101 pagesPhysical Properties of Oil and ChemicalD kuiNo ratings yet
- Atom Element and Atomic StructrureDocument48 pagesAtom Element and Atomic StructrureMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atoms and ElementsDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and Elementschitminthu560345No ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument37 pagesAtoms and Molecules: Larry Brown Tom HolmemattNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Ionic BondsDocument27 pagesCH 7 Ionic Bondsapi-239855791No ratings yet
- CHEM111 Week 4.1 - Chemical Bonds and Compounds Part 1 - Ionic Bond ModelDocument26 pagesCHEM111 Week 4.1 - Chemical Bonds and Compounds Part 1 - Ionic Bond ModelKharl Roei SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules & IonsDocument29 pagesAtoms, Molecules & IonsThanh LanNo ratings yet
- Principles of BiochemistryDocument68 pagesPrinciples of Biochemistryblackss copsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chem IDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- GC1-Lesson-3-Atoms-Molecules-and-Ions-3-The-Periodic-Table (1)Document31 pagesGC1-Lesson-3-Atoms-Molecules-and-Ions-3-The-Periodic-Table (1)Yeri KimNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Ionic BondingDocument144 pagesAtomic Structure and Ionic BondingKasman Kasonde MumbaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Matterial 04.38.48 04.38.48Document36 pagesMatter and Matterial 04.38.48 04.38.48Trevor KobeNo ratings yet
- Lectures 1 2Document61 pagesLectures 1 2Lily ChanNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, & MixturesDocument72 pagesElements, Compounds, & MixturesWendz ArominNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument47 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Ionszekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, Ions and Chemical EquationsDocument106 pagesAtoms, Molecules, Ions and Chemical EquationsLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document48 pagesChapter 2lelouchali1234No ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, and IonsDocument45 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, and IonsCitra BuhatikaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDocument44 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and Ionsholley_kennethNo ratings yet
- Atoms Mol IonDocument20 pagesAtoms Mol IoncmizalpccfuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BDocument47 pagesChapter 5 Bafaflotfi_155696459No ratings yet
- Elements Grade 9Document4 pagesElements Grade 9Mario ButlerNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY Year 1 B 1Document195 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY Year 1 B 1hamiltonNo ratings yet
- 9th Atoms and Molecules Revision Notes-1Document10 pages9th Atoms and Molecules Revision Notes-1ADITYA RAI100% (1)
- Chemistry Quiz NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Quiz NotesDanielleNo ratings yet
- DJJ30113 CHAPTER 2 Material Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument30 pagesDJJ30113 CHAPTER 2 Material Structure and Interatomic BondingPraveen NaiduNo ratings yet
- Eat 131/4 Environmental ChemistryDocument41 pagesEat 131/4 Environmental ChemistryRufus TsaiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure of Elements and CompoundsDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure of Elements and CompoundsSanhitha RameshNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- NuclearDocument10 pagesNuclearUsman MunirNo ratings yet
- Quimica Problemas ImpresionDocument8 pagesQuimica Problemas Impresionshaalii9cuellar9boniNo ratings yet
- G4Si1 - Lot 19042054 (20200204)Document1 pageG4Si1 - Lot 19042054 (20200204)Peter TvardzíkNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements ExplainedDocument5 pagesThe Periodic Table of Elements Explained301 Dhia JaharahNo ratings yet
- Formulae of Ionic CompoundsDocument1 pageFormulae of Ionic CompoundsWalter PerryNo ratings yet
- Aims of ExperimentDocument6 pagesAims of ExperimentKojo EghanNo ratings yet
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesDocument14 pagesClass X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- Types of Chemical Reactions LabDocument15 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions LabChitlet FrancheNo ratings yet
- 0216 CodebookDocument91 pages0216 CodebookDanh Thắng100% (1)
- Group VIII Noble Gases and Trends Across A PeriodDocument8 pagesGroup VIII Noble Gases and Trends Across A PeriodknjNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Manya PunjabiNo ratings yet
- SS Two Revised Second Term Note (Repaired)Document149 pagesSS Two Revised Second Term Note (Repaired)TahmidNo ratings yet
- En P 01 PrinciplesOfBrazingTechnologyDocument14 pagesEn P 01 PrinciplesOfBrazingTechnologySyed Noman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Elements Pics 11x8.5Document1 pageElements Pics 11x8.5Ana Sophya Camelo RochaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases YMS X ALJDocument9 pagesAcids and Bases YMS X ALJFaqihah Syahindah Mohammed FiroozNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements & Compounds 7 QPDocument8 pagesAtoms, Elements & Compounds 7 QPkarishmaNo ratings yet
- Handbook On The Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths, Volume 18Document643 pagesHandbook On The Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths, Volume 18Eliezer Alves MartinsNo ratings yet
- Displacement Worksheet ExtraDocument2 pagesDisplacement Worksheet ExtraMalooka AlyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/52Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/52hasanmahamudchistyNo ratings yet
- Nitrite and NitrateDocument28 pagesNitrite and NitrateBe NiNo ratings yet
- Salt Cake John N. HyrnDocument14 pagesSalt Cake John N. HyrndavidNo ratings yet
- Clasification of Elements in The Periodic TableDocument81 pagesClasification of Elements in The Periodic TableAZIAH ABUNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Diagram - Siemens VelaroDocument1 pageLife Cycle Diagram - Siemens VelaroJobin PuthuparampilNo ratings yet
- Acs ReagentDocument3 pagesAcs ReagentjycortesNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Trace Mineral: AnalysisDocument1 pageQuantitative Trace Mineral: AnalysisloisNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Analysis of Ferric Complex SaltsDocument3 pagesPreparation and Analysis of Ferric Complex SaltsJan Rommel Duterte100% (1)
- 4.6 Science Form 4Document14 pages4.6 Science Form 4Kenix ChanNo ratings yet
- Tin (IV) IodideDocument2 pagesTin (IV) IodideHeikki100% (1)
- 0654 w18 QP 21Document16 pages0654 w18 QP 21lddangNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry June 2016 P2Document20 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2016 P2kevie Frederick100% (1)