Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Scientific Theories, Milkyway and The Sun, Formation of The Early Earth
Uploaded by
Faith Joy Alonzo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Research Scientific Theories, Milkyway and the Sun, Formation of the Early Earth
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesResearch Scientific Theories, Milkyway and The Sun, Formation of The Early Earth
Uploaded by
Faith Joy AlonzoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
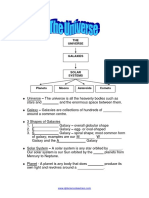
Scientific Theories & Models
Bigbang Theory
o This theory was born of the observation that other galaxies are moving
away from our own at great speed in all directions, as if they had all been
propelled by an ancient explosive force.
o In the first 10^-43 seconds of its existence, the universe was very
compact, less than a million billion billionth the size of a single atom. It's
thought that at such an incomprehensibly dense, energetic state, the four
fundamental forces—gravity, electromagnetism, and the strong and weak
nuclear forces—were forged into a single force
Milky way and the Sun
Milky way –
o Is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the
galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night
sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by
the naked eye.
o From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped
structure is viewed from within.
o It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number
of planets.
o The Milky Way is moving at a velocity of approximately 600 km per second
with respect to extragalactic frames of reference. The oldest stars in the
Milky Way are nearly as old as the Universe itself and thus probably formed
shortly after the Dark Ages of the Big Bang.
Sun –
o the heart of our solar system – is a yellow dwarf star, a hot
ball of glowing gases. Its gravity holds the solar system
together, keeping everything from the biggest planets to the
smallest particles of debris in its orbit.
o Electric currents in the Sun generate a magnetic field that is
carried out through the solar system by the solar wind – a
stream of electrically charged gas blowing outward from the
Sun in all directions.
o Earth orbits the Sun from about 93 million miles. The
connection and interactions between the Sun and Earth
drive our planet's seasons, ocean currents, weather,
climate, radiation belts, and aurorae.
Formation of the Early Earth
Earth formed around 4.54 billion years ago, approximately one-third the age of the universe,
by accretion from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the
primordial atmosphere and then the ocean, but the early atmosphere contained almost no oxygen.
Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme
volcanism. While the Earth was in its earliest stage (Early Earth), a giant impact collision with a
planet-sized body named Theia is thought to have formed the Moon. Over time, the Earth cooled,
causing the formation of a solid crust, and allowing liquid water on the surface.
You might also like
- The Photon Belt and Soul AscensionDocument7 pagesThe Photon Belt and Soul AscensionCherakkal Chakkara AshwinNo ratings yet
- The Truth of Nibiru and The Anu PeopleDocument12 pagesThe Truth of Nibiru and The Anu PeopleNetjer Neb KD Hartley-el100% (2)
- The Cosmic Perspective Ch.1Document23 pagesThe Cosmic Perspective Ch.1Anthony Truong-Nguyen100% (1)
- The Influence of The Sun On Human AffairsDocument8 pagesThe Influence of The Sun On Human AffairsLagdufNo ratings yet
- 9 Planets.Document3 pages9 Planets.Yam MuhiNo ratings yet
- 130 Stars NaksatrasDocument8 pages130 Stars NaksatrasComputershastriNoproblem100% (1)
- MysteriesOfTheSun BookDocument20 pagesMysteriesOfTheSun BookRavindran VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Scale of The UniverseDocument20 pagesScale of The UniverseAman Chokshi100% (2)
- Word DocumentDocument12 pagesWord Documentayushi tiwariNo ratings yet
- The Influence of The Sun On Human Affairs (1979)Document8 pagesThe Influence of The Sun On Human Affairs (1979)Valerio777100% (1)
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument19 pagesEarth and Life ScienceLj Santos Deuna100% (2)
- Sun DiagramDocument2 pagesSun DiagramAngel SolivanNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument28 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemArenvy JazzieNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument58 pagesSolar SystemJohn Aldric SibumaNo ratings yet
- 207 Jyotish K PDocument170 pages207 Jyotish K PPritee MathurNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension TestDocument4 pagesReading Comprehension Testapi-3278251570% (1)
- Theories of The Origin of The UniverseDocument2 pagesTheories of The Origin of The UniverseVia Amor NadalNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Planets in The Solar SystemDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Planets in The Solar SystemVeanca EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science HandoutsDocument7 pagesEarth Science HandoutsAnnie VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 The Solar SystemDocument31 pagesUnit-3 The Solar SystemArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sun (Sol) : NamesakeDocument7 pagesSun (Sol) : NamesakeJermaine QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Midterm ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth Science Midterm ReviewerPatrick RamirezNo ratings yet
- IAO 2011 ProblemsDocument22 pagesIAO 2011 ProblemsScience Olympiad Blog50% (2)
- Astronomical Terminology: Appendix ADocument77 pagesAstronomical Terminology: Appendix AShuvrodeb BiswasNo ratings yet
- Geo GS Part-1provedDocument139 pagesGeo GS Part-1provedAbhishek TiwariNo ratings yet
- Astronomy: Reported By: Cheniel Nica Robles Bsba Ii Submitted To: Mrs. Catalina PunzalanDocument25 pagesAstronomy: Reported By: Cheniel Nica Robles Bsba Ii Submitted To: Mrs. Catalina PunzalanChenielNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanMarose Pantalunan86% (7)
- The Solar System: Magda Stavinschi, Beatriz García, Andrea SosaDocument77 pagesThe Solar System: Magda Stavinschi, Beatriz García, Andrea SosaMarinko MićunovićNo ratings yet
- Els Lesson 1 Reviewer - 082730Document4 pagesEls Lesson 1 Reviewer - 082730pinieraaurapaulaNo ratings yet
- Universe by Sanchit KabraDocument30 pagesUniverse by Sanchit KabrasanchitNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document11 pagesLesson 2francojessavelNo ratings yet
- John Vincent CarismaDocument3 pagesJohn Vincent CarismaVincent CarismaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Earth Science PDFDocument58 pagesLecture 1 Earth Science PDFThea Narciso QuinquitoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Formation of The Universe & The Solar System 2Document2 pagesLesson 1 The Formation of The Universe & The Solar System 2solivasravennicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1 Introduction To Earth ScienceDocument58 pagesLesson-1 Introduction To Earth ScienceChat GazaNo ratings yet
- Formation and Evolution of The Solar System: HistoryDocument5 pagesFormation and Evolution of The Solar System: HistoryAljohn GarciaNo ratings yet
- SCI1 - Earth and Life Science LESSON 1: The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument24 pagesSCI1 - Earth and Life Science LESSON 1: The Universe and The Solar SystemMs. ArceñoNo ratings yet
- 2024 FIRST 2.the Origin of Solar SystemDocument52 pages2024 FIRST 2.the Origin of Solar SystemAmiro IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Unti 1 Indiv Activity Piczon, Christian Victor P.Document25 pagesUnti 1 Indiv Activity Piczon, Christian Victor P.CHRISTIAN VICTOR PICZONNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Universe and The Solar System (Protoplanet Hypothesis-Current Hypothesis)Document9 pagesLesson 2 Universe and The Solar System (Protoplanet Hypothesis-Current Hypothesis)huehuehueNo ratings yet
- SUN Ni PintsDocument27 pagesSUN Ni PintsErikaAlidioNo ratings yet
- General Astronomy Project: Astro 102Document29 pagesGeneral Astronomy Project: Astro 102Nida AbabtainNo ratings yet
- Selectedreference - Unit 2 Solar SystemDocument116 pagesSelectedreference - Unit 2 Solar SystemJiyoor JinedoNo ratings yet
- 1 Earths Origin and MineralsDocument37 pages1 Earths Origin and MineralsshiimiineeNo ratings yet
- Page 288-301Document17 pagesPage 288-30105 陳宗榮 RYAN GERALD CHUANo ratings yet
- A Neutron StarDocument2 pagesA Neutron StarDannamei EmbanecidoNo ratings yet
- Животот на СонцетоDocument9 pagesЖивотот на СонцетоNever2everNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesLesson 2: The Universe and The Solar SystemMichelle Al OrejasNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Reviewer1Document6 pagesSci 10 Reviewer1SeviNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles Galactic Superclusters Big Bang TheoryDocument4 pagesSubatomic Particles Galactic Superclusters Big Bang TheorynermamehiNo ratings yet
- Els 1St Quarter Prelims Reviewer: Solar SystemDocument27 pagesEls 1St Quarter Prelims Reviewer: Solar Systemaki hayakawaNo ratings yet
- Space PhysicsDocument10 pagesSpace PhysicsDark VariantNo ratings yet
- Earth Scienceppt. GRADE 11Document47 pagesEarth Scienceppt. GRADE 11Mary Grace Manaeg HerederoNo ratings yet
- The SunDocument5 pagesThe SunCarl Christian GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Solar Nebula Notes1Document3 pagesSolar Nebula Notes1Demigod ValencourtNo ratings yet
- Space Concept Part IIDocument84 pagesSpace Concept Part IIggihklghNo ratings yet
- Formation and Evolution of The Solar SystemDocument29 pagesFormation and Evolution of The Solar Systemrcu8cdvgfdtujcNo ratings yet
- 02 - Universe and The Solar System (Part 2) PDFDocument41 pages02 - Universe and The Solar System (Part 2) PDFZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cloze UniverseDocument2 pagesCloze UniverseMasood AfraidiNo ratings yet
- Features of The UniverseDocument16 pagesFeatures of The UniverseSamara DiasNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science PowerPointDocument53 pagesEarth and Life Science PowerPointAlthea Mae DuqueNo ratings yet
- Geography: Chapter - IDocument59 pagesGeography: Chapter - IPrateek KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Answer SheetDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheetapi-240302279No ratings yet
- Space GlossaryDocument6 pagesSpace GlossaryHenry SadlerNo ratings yet
- Module 3, Earth Science 11Document19 pagesModule 3, Earth Science 11Gregorio Rizaldy100% (1)
- Solar SystemDocument9 pagesSolar SystemCheryl-lyn EsbertoNo ratings yet
- Pointers: Earth and Life Science The Sun ProfileDocument5 pagesPointers: Earth and Life Science The Sun ProfileRuel DaitolNo ratings yet
- Kyla Cammile S. Lim Grade 5 - St. CeciliaDocument16 pagesKyla Cammile S. Lim Grade 5 - St. CeciliaAngela LimNo ratings yet
- Copernican, Ptolemaic, TychonicDocument5 pagesCopernican, Ptolemaic, TychonicEsther Macugay100% (1)
- HIG 72, Bharatnagar Colony, Hyderabad-500018. Mobile: 9440152397 E-Mail: Siva - Gantha@gmail - CoDocument2 pagesHIG 72, Bharatnagar Colony, Hyderabad-500018. Mobile: 9440152397 E-Mail: Siva - Gantha@gmail - CoRavindraNo ratings yet
- Planetary NebulaDocument19 pagesPlanetary NebulaAbraxazNo ratings yet
- ARVAL Catalog of Bright Globular Clusters (Cúmulos Globulares)Document7 pagesARVAL Catalog of Bright Globular Clusters (Cúmulos Globulares)Pedro RicardoNo ratings yet
- May 2021 Sky ChartDocument1 pageMay 2021 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet
- Theories of The Solar SystemDocument30 pagesTheories of The Solar SystemHannah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Sample Galaxy WorksheetsDocument9 pagesSample Galaxy WorksheetsJuggyNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Solar SystemDocument29 pagesFormation of The Solar SystemDarwin ValdezNo ratings yet
- Assign 1Document3 pagesAssign 1Philip PeñaNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Writing - Language Arts - 8th Grade by SlidesgoDocument56 pagesPersuasive Writing - Language Arts - 8th Grade by SlidesgoGhizola KaidNo ratings yet
- William Herschel's Double Star CatalogDocument15 pagesWilliam Herschel's Double Star CatalogGiannis TheodorouNo ratings yet
- World Biofuel DayDocument63 pagesWorld Biofuel Daytolendarhan8No ratings yet
- Components of A Lyrical EssayDocument8 pagesComponents of A Lyrical EssayElizabeth K GordonNo ratings yet
- DHF A.K.A DBD: Demam Berdarah DengueDocument55 pagesDHF A.K.A DBD: Demam Berdarah DengueFITRIA ULFAHNo ratings yet
- What I Know What I Want To Know What I LearnedDocument2 pagesWhat I Know What I Want To Know What I LearnedJan Rhey MoogNo ratings yet
- 6.8.23 - Nguyen Mai Khanh ChiDocument5 pages6.8.23 - Nguyen Mai Khanh ChiVeronica NguyenNo ratings yet
- Robtics The Nightsky Observer's Guide Volume 2 - Lente & Zomer NLDocument3 pagesRobtics The Nightsky Observer's Guide Volume 2 - Lente & Zomer NLadinicoNo ratings yet