0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views8 pagesUnderstanding Biomolecules in High School
1) The document discusses the four major types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
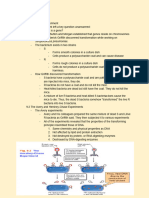
2) It describes the composition and structures of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, triglycerides, amino acids, and nucleotides that make up these biomolecules.
3) Students are asked to analyze structural formulas of the biomolecules and identify the elements in each, as well as whether the structures are the same.
Uploaded by
Karlyn Kaye SalungaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views8 pagesUnderstanding Biomolecules in High School
1) The document discusses the four major types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
2) It describes the composition and structures of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, triglycerides, amino acids, and nucleotides that make up these biomolecules.
3) Students are asked to analyze structural formulas of the biomolecules and identify the elements in each, as well as whether the structures are the same.
Uploaded by
Karlyn Kaye SalungaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd