0% found this document useful (0 votes)
132 views5 pagesNormal Laboratory Values Overview
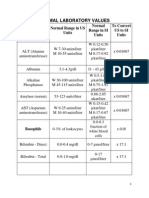
Normal laboratory values can vary between commercial laboratories and depend on factors like age, sex, pregnancy status, and time of day the sample was taken. Reference ranges are provided on lab reports in both U.S. and SI units, with conversion factors to change between the systems. Abnormal results should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Uploaded by
Yaser MCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
132 views5 pagesNormal Laboratory Values Overview
Normal laboratory values can vary between commercial laboratories and depend on factors like age, sex, pregnancy status, and time of day the sample was taken. Reference ranges are provided on lab reports in both U.S. and SI units, with conversion factors to change between the systems. Abnormal results should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Uploaded by
Yaser MCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd