Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xi - Physics SP
Uploaded by
Pratyush sahooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xi - Physics SP
Uploaded by
Pratyush sahooCopyright:
Available Formats
Roll No.
Candidates must write the Set No. on
the title page of the answer book.
DAV PUBLIC SCHOOLS
SAMPLE PAPER 2023-2024
DAV PUBLIC SCHOOLS, ODISHA ZONE -A
PRE-ANNUAL EXAMINATION, 2023-24
SUBJECT: PHYSICS
Max Time:3 hr Max Marks:70
General Instructions:
(1) There are 33 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and
Section E.
(3) All the sections are compulsory.
(4) Section A contains sixteen questions, twelve MCQ and four Assertion Reasoning based
of 1 mark each, Section B contains five questions of two marks each, Section C
contains seven questions of three marks each, Section D contains two case study
based questions of four marks each and Section E contains three long answer
questions of five marks each.
(5) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one
question in Section B, one question in Section C, one question in each CBQ in Section
D and all three questions in Section E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in
such questions.
(6) Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION :A
1 If mass of an object is m= 4.2378 g and its volume is v= 2.51 cm3 then its density is 1
(a)1.688 gm/cm3 (b)1.6883 gm/cm3 (c)1.69 gm/cm3 (d)1.7 gm/cm3
2 An impulsive force of 100N acts on a body for a small time interval of∆t 1
seconds. The change ,in linear momentum of the body would be:
(a)100(∆t)N/s (b)100(∆t)Ns (c)100/(∆t)N/s (d)100/(∆t)Ns
3 A body moving along x- direction has at any instant its x-co-ordinate is given by 1
x= 2 - 8t+4t2,what is the position of the particle when velocity is zero.
(a) 0 (b) - 4 (c) 2 (d) - 2
4 Three masses are placed on the X - axis: 300 g at origin, 500 g at𝑥 = 40 cm and 1
400 g at𝑥 = 70 cm. The distance of the center of mass from the origin is
(a) 40 cm (b) 45 cm (c) 50 cm (d) 30 cm
5 𝑚𝑣 2 1
A force ( 𝑟 ) is acting on a body of mass 𝑚 moving with a velocity 𝑣 in a circle of
radius𝑟. What is the work done by the force in moving the body over half the
circumference of the circle
𝑚𝑣 2 𝑚𝑣 2 𝜋𝑟 2
(a) 𝑟 × 𝜋𝑟 (b) zero (c) 𝑟 2 (d) 𝑚𝑣2
6 The co-ordinates of a moving particle at any time t are given by x=αt3 and 1
y= βt3.The speed of the particle at time is given by:
1/2 2 1/2 2 1/2 1/2
(a)3t(α2+β2) (b) 3t (α2+β2) (c)t (α2+β2) (d)(α2+β2)
7 If the radius of earth were to increase by 1%, its mass remaining the same the 1
PRE ANNUAL/PHYSICS/XI /2023-24 Page 1 of 5
acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth will
(a)increase by 1% (b) decrease by 2% (c)decrease by 1% (d) increase by 2%
8 In a wire, when elongation is 2cm energy stored is E. If it is stretched by 10 cm , then 1
the energy stored will be
(a)E (b)2E (c) 4E (d)25E
9 A spherical liquid drop of radius R is divided into eight equal droplets. If surface 1
tension is T , then work done in the process will
(a)2𝜋R2T (b)3𝜋R2T (c)4𝜋R2T (d)2𝜋RT2
10 The SI unit of latent heat is 1
(a) Jkg-1K-2 (b) Jkg-1 (c) Jkg (d) Jkg-2K-1
11 Oxygen and hydrogen gases are at same temperature and pressure. The mass of 1
oxygen molecule is 16 times the mass of hydrogen molecule, then the ratio of r.m.s.
speed of Oxygen to Hydrogen is
(a)2 (b)1/4 (c)4 (d)16
12 A mass of 1 kg attached to the bottom of a spring has a certain frequency of vibration 1
Which of the following mass has to be added to it in order to reduce the frequency
by half?
(a)1kg (b)2kg (c)3 kg (d) 4kg
For Questions 13 to 16, two statements are given – one labelled Assertion (A) and other
labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the options
as given below.
a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is correct explanation of Assertion.
b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of
Assertion.
c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
13 Assertion: A particle strikes head on with another stationary particle such that 1
the first particle comes to rest after collision. The collision should
necessarily be elastic.
Reason: In elastic collision, there is a loss of momentum of the system of
particle.
14 Assertion : Uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion. 1
Reason : In uniform circular motion the velocity of the body is not
constant.
15 Assertion :The value of acceleration due to gravity decreases with both height 1
and depth.
Reason : At the centre of the Earth the value of acceleration due to
gravity is infinite.
16 Assertion: In adiabatic compression, the internal energy and temperature of the 1
system get decreased.
Reason: The adiabatic compression is a slow process
SECTION :B
17 A large fluid star oscillates in shape under the influence of its own 2
gravitational field. Using dimensional analysis find the expression for the
period of oscillation (T) in terms of radius of star(R), mean density of the
fluid (ρ)and universal gravitational constant (G).
18 The relation between𝑡 and displacement𝑥 is 𝑡 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥, where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are 2
constants. Express the instantaneous velocity in terms of instantaneous displacement.
OR
Show that for a given velocity of projection, a particle has the same horizontal range for
the complimentary angles.
19 What is isothermal process ? Find the expression for the amount of work done during 2
isothermal expansion from volume V1 to V2 .
PRE ANNUAL/PHYSICS/XI /2023-24 Page 2 of 5
20 If 20g of ice at 00C is converted in to steam at 1000 temperature. Find the amount of 2
heat required . Latent heat of ice is 334 J/g and steam is 2265J/g. Given the specific
heat of water is 4.2J/g.
21 How is the speed of sound waves in atmosphere affected by the humidity and 2
temperature.
SECTION : C
22 A body cover 32 m in 3rdsecond & 20 m in 5thsecond along a straight line. 3
Find the displacement covered by the particle at 10th second and in 10
seconds.
23 Derive the equation for rise of liquid in capillary tube. Hence show that the height of 3
liquid column supported is inversely proportion to the radius of capillary tube.
24 A boy stands at 39.2m from a building and throws a ball which just passes 3
through a window 19.6m above the ground. Calculate the velocity of
projection of the ball.
25 What is meant by potential energy of a spring? Obtain an expression for potential energy 3
of a spring and plot a graph of potential and kinetic energy versus distance for a spring.
26 State the law of equipartition of energy. Use it to obtain the value of γ 3
(𝐶𝑝/𝐶𝑣)for a monoatomic gas.
OR
Show that the average KE of gas molecule is directly proportional to the temperature of
gas. Hence give the kinetic interpretation of temperature
27 A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by 3
Y(x,t) = 3.0 Sin(6πt + 0.18x + 𝜋/4 )
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(i) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave?
(ii)What are its amplitude and frequency?
(iii)What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
(iv) what are the speed and direction of its propagation?
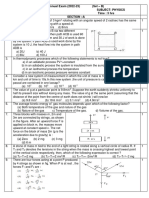
28 Two blocks of mass 2kg and 5 kg are connected by 3
an ideal string passing over a pulley. The block of
mass 2 kg is free to slide on a surface inclined at an
angle of 300 with the horizontal whereas block 5 kg
hangs freely. Find the acceleration of the system
and tension in the string. Given µ=0.30
SECTION:D
29 Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow. 4
The time rate of the total angular momentum of a system of particles about a point (taken
as the origin of our frame of reference) is equal to the sum of the external torques (i.e. the
torques due to external forces) acting on the system taken about the same point.
𝜏𝑒𝑥𝑡=𝑑𝐿/𝑑𝑡 If 𝜏𝑒𝑥𝑡=0 ,/𝑑𝑡 =0 or L = constant. 𝐼𝜔=𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
Thus, if the total external torque on a system of particles is zero, then the total angular
momentum of the system is conserved, i.e. remains constant.
(i)A dancer spinning on a rotating table that has no friction in its axle. When she
extends her arms,
(a)her moment of inertia increases and her angular speed decreases.
(b)her moment of inertia decreases and her angular speed increases.
(c)her moment of inertia increases and her angular speed increases.
(d)her moment of inertia increases and her angular speed remains the same.
(ii)Rotational analogue of mass in linear motion is
(a) Weight (b) Moment of inertia (c) Torque (d)Angular momentum
(iii)A Raw and A boiled egg are made to spin on a smooth table by applying the
same torque.
PRE ANNUAL/PHYSICS/XI /2023-24 Page 3 of 5
(a)Raw egg will be rotated faster (b) angular velocity will be same for both.
(c) boiled egg will be rotated faster. (d) Can’t say anything.
(iv)What will be a body's angular momentum if the time period is doubled and its
moment of inertia is kept constant?
(a) remain constant (b) become half (c) doubles (d) become 4 times
OR
If L is the angular momentum and I is the moment of inertia of a rotating body, then
L2/2I represents its
(a)rotational PE (b)total Energy (c)rotational KE (d)translational KE
30 Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow. 4
In our daily life, we come across various types of motions: such as periodic, non-periodic,
oscillatory and non-oscillatory. The study of oscillatory motion is of great importance as
its concepts are required for the understanding of many physical phenomena, for example
(𝑖) vibrating strings produces pleasant sounds in musical instruments like the sitar, guitar
or the violin (i) the oscillations of the atoms in solid about their mean positions to convey
the sensation of temperature. All oscillatory motions are periodic motions but all periodic
motion may not be oscillatory. An oscillatory motion is further classified as harmonic and
non-harmonic oscillation.
(i)Which of the following quantities remains constant in simple harmonic motion?
(a) Displacement (b) Velocity (c) Acceleration (d) Total Energy
(ii)Which of the following motions is not simple harmonic?
(a)Vertical oscillations of a spring (b)Motion of a simple pendulum
(c)Motion of planet around the Sun (d)Oscillation of liquid in a U-tube
(iii) The time period of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by:
𝐸𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 𝐼𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟
(a)2𝜋√ 𝐼𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 (b)2𝜋√ 𝐸𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟
(c)2𝜋√ 𝐼𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑎 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 (d)2𝜋√ 𝐸𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟
(iv)A place where g = 980 cm/sec2 the length of seconds pendulum is about
(a) 50 cm (b)100 cm (c)2 cm (d)2m
OR
The maximum velocity for a particle in S.H.M is 0.16 m/s and maximum
acceleration is 0.64 m/s2 .The amplitude is
(a)4 x 10-2 m (b)4 x 10 -1 m (c)4x10-3m (d) 4x102 m
SECTION: E
31 (a) Define Orbital velocity and derive an expression for orbital velocity. 5
(b) Calculate the height of geostationary satellite above the surface of earth.
(R= 6400 km)
OR
(a)Define the term Gravitation potential energy of a body? What is significance
of negative potential energy ?What is zero level of potential energy?
(b) Find the potential energy of a System of four particles each of mass m, placed at
the vertices of a square of side l.
32 (a)What is the need of banking of roads? 5
(b)Obtain an expression for the maximum safety speed of a vehicle moving on a
banked horizontal road.
OR
(a) State parallelogram law of vector addition and find the magnitude and direction of
resultant of two vectors 𝐴⃗ and 𝐵
⃗⃗ in terms of their magnitude and angle between them.
(b) Calculate the area of a parallelogram whose adjacent sides are given by the vectors.
PRE ANNUAL/PHYSICS/XI /2023-24 Page 4 of 5
𝐴⃗ = 𝑖 + 2𝑗 + 3𝑘; 𝐵 ⃗⃗ = 2𝑖 − 3𝑗 + 𝑘
33 (a)State Bernoulli’s theorem. 5
(b)Prove that the sum of ' pressure head', 'Velocity head' and the 'gravitation head'
remain constant during the stream line flow of ideal liquid.
OR
(a)State any two assumptions of kinetic theory of gas.
(b)On the basis of kinetic theory , derive an expression for the pressure exerted by an
ideal gas.
PRE ANNUAL/PHYSICS/XI /2023-24 Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- XI Sample Papers 2023Document33 pagesXI Sample Papers 2023Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- XI Sample Papers 2023Document33 pagesXI Sample Papers 2023Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- QP G11 Phy Ae 2023Document9 pagesQP G11 Phy Ae 2023snikitha.padalaNo ratings yet
- Cbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12Document8 pagesCbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12sciencepedia9No ratings yet
- Physics 2Document7 pagesPhysics 2iitiansrd2025No ratings yet
- 11 Physics Practice PaperDocument10 pages11 Physics Practice PaperIshan AhujaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24Document6 pagesSample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24jethvadevashyaNo ratings yet
- SQP Class 11th PhysicsDocument41 pagesSQP Class 11th Physicsprecisebusiness23No ratings yet
- 11th Final PhysicsDocument5 pages11th Final Physicsanand tiwariNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Document4 pages11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44No ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp06Document18 pages11 Physics23 24sp06Vettri PrintersNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 QuestionDocument24 pagesSample Paper 2 QuestionHarsha RNo ratings yet
- C022Document17 pagesC022FATHIMANo ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp02Document17 pages11 Physics23 24sp02Vettri PrintersNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationDocument12 pagesSample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationSuhaim SahebNo ratings yet
- +1 Physis Annual ExamDocument6 pages+1 Physis Annual ExamRejeena SNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPDocument8 pagesClass 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPSanjukta ChandaNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp05Document17 pages11 Physics23 24sp05Vettri PrintersNo ratings yet
- Samplepape03022024112234 0Document7 pagesSamplepape03022024112234 0bladex605No ratings yet
- 11 PHY Set 2Document5 pages11 PHY Set 2dikshachoud44No ratings yet
- Physics exam with 30 questionsDocument7 pagesPhysics exam with 30 questionsHarsh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Ioqp (Part 1) 2020Document5 pagesIoqp (Part 1) 2020kritikasingh181221No ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument13 pagesPhysics QPAniket DebnathNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics-1Document3 pagesClass 11 Physics-1Mask Man LifeNo ratings yet
- QPDocument5 pagesQPSamuelNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper Class 11thDocument10 pagesPhysics Paper Class 11thMahiNo ratings yet
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Document13 pagesSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessNo ratings yet
- PPPPPPPPDocument102 pagesPPPPPPPPTGX DevilNo ratings yet
- Xi - Physics - Trem Ii - 2020Document5 pagesXi - Physics - Trem Ii - 2020pranjaliNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Physics Sample PaperDocument7 pagesClass Xi Physics Sample PaperHarekrishna DasNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFSilva scary svNo ratings yet
- G11 Final Revision Worksheet AjnkhlygDocument10 pagesG11 Final Revision Worksheet Ajnkhlygrishi.amaravathi123No ratings yet
- Class 11 Annual Qp2023-24Document8 pagesClass 11 Annual Qp2023-24prajittokdarNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DEHRADUN REGION SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (2022-23) CLASS XI PHYSICSDocument13 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DEHRADUN REGION SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (2022-23) CLASS XI PHYSICSAmythNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Mid Term Set A QPDocument6 pagesGrade 11 Mid Term Set A QPgoodboyjatin1981No ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument6 pagesPhysics QPch22b039No ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument21 pagesPHYSICSdishugirdhar08100% (1)
- The Indian Community School, Kuwait: Code: M 042Document7 pagesThe Indian Community School, Kuwait: Code: M 042Lalitha GorantlaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Annual QP 2023-24Document6 pagesClass 11 Physics Annual QP 2023-24karthika.rvNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp04Document19 pages11 Physics23 24sp04Vettri PrintersNo ratings yet
- XI_PHY_MODEL PAPER PAPER _FFFDocument7 pagesXI_PHY_MODEL PAPER PAPER _FFFAkash ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Upsee-2011 Model Test Paper Paper 1 ( (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics)Document14 pagesUpsee-2011 Model Test Paper Paper 1 ( (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics)Kundan AnandNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Sp01Document20 pages11 Physics Sp01HyPeR ZeelNo ratings yet
- Btech Model QuestionsDocument22 pagesBtech Model QuestionsAkshayKannanNo ratings yet
- NEET 2019 Physics Sample Question Paper IIDocument10 pagesNEET 2019 Physics Sample Question Paper IImisostudyNo ratings yet
- Solution As To No MyDocument22 pagesSolution As To No MyAshutosh ShawNo ratings yet
- Annual Xi Sample Paper 23-24Document6 pagesAnnual Xi Sample Paper 23-2419adityakushwahaNo ratings yet
- Duration: 3Hrs: Hale Yearly Examination PhysicsDocument4 pagesDuration: 3Hrs: Hale Yearly Examination PhysicsVinodd.V 9eNo ratings yet
- Amu 2 (2017)Document23 pagesAmu 2 (2017)Deep JattNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument18 pagesPhysicsHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 1091普物會考考卷 (最終版) 1100111Document9 pages1091普物會考考卷 (最終版) 1100111lllllin920722No ratings yet
- XI SEE Physics QPDocument6 pagesXI SEE Physics QPParivesh JainNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 11Document9 pagesPhysics Class 11eagleankush5No ratings yet
- Mock Test 9-02-09-2021Document21 pagesMock Test 9-02-09-2021nagendra_gm100% (1)
- Xii Neet Physics Question (Xi TH Full Portion) (1) (1) 4651.47530Document8 pagesXii Neet Physics Question (Xi TH Full Portion) (1) (1) 4651.47530vijiramraj786No ratings yet
- Disha Publication - Leading Publisher Providing Books for Competitive ExamsDocument23 pagesDisha Publication - Leading Publisher Providing Books for Competitive ExamskeerthyNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)