Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resistance
Resistance
Uploaded by
Muhammad Hammad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageElectrical resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a conductor. Resistance is caused by the collision of free electrons with fixed atoms in a metal. According to Ohm's law, resistance is equal to the ratio of voltage to current, with resistance increasing as length or temperature increase or cross-sectional area decreases for a given material.
Original Description:
Resistance of Resistors
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectrical resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a conductor. Resistance is caused by the collision of free electrons with fixed atoms in a metal. According to Ohm's law, resistance is equal to the ratio of voltage to current, with resistance increasing as length or temperature increase or cross-sectional area decreases for a given material.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageResistance
Resistance
Uploaded by
Muhammad HammadElectrical resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a conductor. Resistance is caused by the collision of free electrons with fixed atoms in a metal. According to Ohm's law, resistance is equal to the ratio of voltage to current, with resistance increasing as length or temperature increase or cross-sectional area decreases for a given material.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Electrical Resistance: Opposition offered to the flow of charges is called resistance
Explanation
In metallic conductor the current is due to flow of free electrons and resistance is due to collision of
these electrons with fixed atoms inside the conductor.
Mathematically:
According to ohm law it is ratio of applied voltage to the current flow in conductor
R = V/I
Unit : SI Unit of Resistance is ohm denoted by Greek symbol omega Ω
One Ohm: Resistance is one ohm when potential difference of one volt is applied across the conductor
and it cause the one ampere current to flow
Ω = 1V /1A
Circuit Symbol : The circuit symbol is
Factors Effect the Resistance:
Following factors effect the resistance
Length of Conductor: If length increases resistance also increases
R α L. ( Draw Figure 14.2 )
Cross sectional area: Resistance increases if area of conductor decreases
R α 1/A ( Draw figure 14.2
Temperature: Resistance increases as temperature increases
R α Τ. For some specific material ( Draw figure 14.2 )
Material: If length area and temperature is kept constant the resistance varies with nature of material l
Draw figure 14.2
You might also like
- LESSON 7.2 Physics Form 5Document10 pagesLESSON 7.2 Physics Form 5Intan Nur DaniaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Electric CurrentDocument10 pagesElectricity: Electric CurrentTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- D.C. CircuitDocument64 pagesD.C. CircuitKim MNo ratings yet
- Define Electrical Charge and Electrical Current.: Beeta1Document4 pagesDefine Electrical Charge and Electrical Current.: Beeta1ariunzul batbayrNo ratings yet
- NEE+311-intro+part+2Document18 pagesNEE+311-intro+part+2Arrianna AngelesNo ratings yet
- 4.2.4 Resistance: R Resistance of A Conductor V P.D Between Two Ends of A Conductor I Current Through A ConductorDocument23 pages4.2.4 Resistance: R Resistance of A Conductor V P.D Between Two Ends of A Conductor I Current Through A Conductorjeremiah341harry0No ratings yet
- Provided by Pn. Zuraidah BT Ali Mech. Eng. Dept. PUODocument53 pagesProvided by Pn. Zuraidah BT Ali Mech. Eng. Dept. PUOMuhd AkmalNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument66 pagesElectricitybhaveshjangaleNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 13 CURRENT ELECTRICITYDocument5 pagesPhysics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 13 CURRENT ELECTRICITYflyfalcon80% (5)
- Current Electricity NotesDocument14 pagesCurrent Electricity NotesAngelina DanyNo ratings yet
- P.D and Ohm's LawDocument6 pagesP.D and Ohm's LawSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectObito UchihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Electrics & Direct Current - 2016 - ReviewedDocument89 pagesChapter 3 - Electrics & Direct Current - 2016 - ReviewedSyaza Izzaty100% (1)
- Chapter 01 DC CircuitsDocument42 pagesChapter 01 DC CircuitsRAJANo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Current, Ampere) ECE 1101 Dr. Md. Shamim AhsanDocument3 pagesLecture 1 (Current, Ampere) ECE 1101 Dr. Md. Shamim AhsanSOURAV BORMONNo ratings yet
- WK 7 - Q3 - GP2 - GSJDocument59 pagesWK 7 - Q3 - GP2 - GSJildeanne GNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricitymohitverma303No ratings yet
- 5.1: Electrical DistributionDocument31 pages5.1: Electrical DistributionShuhada SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Class 12 Notes Chapter 3Document6 pagesCurrent Electricity Class 12 Notes Chapter 3Sri DharshanNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Unit 2 PhysicsDocument34 pagesA Level Physics Unit 2 Physicsprofitmaker_2No ratings yet
- Widya F. Rompas 19101105017Document14 pagesWidya F. Rompas 19101105017Widya RompasNo ratings yet
- Electricity Note DC Current PDFDocument8 pagesElectricity Note DC Current PDFSolomonNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Electriicy Notes HighlitedDocument9 pagesClass 10 Electriicy Notes HighlitedSTUDY MANTRANo ratings yet
- Current, Voltage and ResistanceDocument18 pagesCurrent, Voltage and ResistanceJustine FariscalNo ratings yet
- Ohmic Vs NonOhmic DevicesDocument2 pagesOhmic Vs NonOhmic DevicesBinodNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument40 pagesDocumentHaseeb AhemdaniNo ratings yet
- What Is Electrical ResistanceDocument2 pagesWhat Is Electrical ResistanceGillie May SalubreNo ratings yet
- What Is A ResistorDocument4 pagesWhat Is A ResistorHernández OscarNo ratings yet
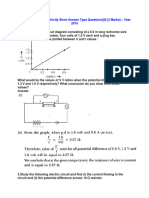
- Class 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument39 pagesClass 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsLawrence GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Electrical QuestionsDocument416 pagesElectrical QuestionsSoutrik Chowdhury100% (1)
- Current ElectricityDocument40 pagesCurrent ElectricityAnshu MakinNo ratings yet
- UG DocumentDocument6 pagesUG DocumentSliman 1No ratings yet
- Bab 2 ElectricityDocument65 pagesBab 2 ElectricityAnonymous oW9OeJvEvNo ratings yet
- Current and Resistance Current and Current DensityDocument20 pagesCurrent and Resistance Current and Current Densityminhajul.cse.diuNo ratings yet
- Electricity-Current and ResistanceDocument4 pagesElectricity-Current and ResistanceLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Current, Resistivity, and ResistanceDocument36 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Current, Resistivity, and ResistanceDharyl Ballarta100% (3)
- App Ied Physics Important NotesDocument33 pagesApp Ied Physics Important NotesAbdullah ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Engineering Chapter 1Document25 pagesBasic Electronics Engineering Chapter 1HabHabNo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity FinalsDocument33 pages12 Electricity FinalsKelly FajardoNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDFDocument52 pagesCurrent Electricity PDFMaahiNo ratings yet
- 36160chapter 2 Current and ResistanceDocument17 pages36160chapter 2 Current and Resistancemrb96mptqqNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class XDocument9 pagesElectricity Class XHemant YadavNo ratings yet
- GROUP3 Hand Outs Voltage Current and ResistanceDocument7 pagesGROUP3 Hand Outs Voltage Current and Resistancekristel castroNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument35 pagesElectricityPoorna MathivananNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesElectric Current and Ohm's LawSheldon MillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 NotesDocument15 pagesChapter 13 NotesphooolNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orDocument23 pagesScience Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orAayushiNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 12Document11 pagesElectricity Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 12vatnik100% (1)
- Ohm's LawDocument9 pagesOhm's Lawkare-kare CJNo ratings yet
- 10TH-CHP 12-Elecricity (Notes) - 2Document8 pages10TH-CHP 12-Elecricity (Notes) - 2NavaneetDDeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Physics (5054) For Grade 11: Chapter 19: "Current Electricity"Document45 pagesPhysics (5054) For Grade 11: Chapter 19: "Current Electricity"Hammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument44 pagesElectricityKirancivilNo ratings yet
- B GR 11 Chapter 10 NotesDocument13 pagesB GR 11 Chapter 10 NotesKo Win Myint SoeNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument3 pagesElectricityAlstroNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (CH-03)Document19 pagesCurrent Electricity (CH-03)kingbossff16No ratings yet
- FWS IGCSE Electrical QuantitiesDocument17 pagesFWS IGCSE Electrical QuantitiesHunterNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument42 pagesClass 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsShardul SumantNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Addition of Vector: Steps To Add Vectors by Head To Tail RuleDocument8 pagesAddition of Vector: Steps To Add Vectors by Head To Tail RuleMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Past Papers 2018 Abbottabad Board 10th Class Physics Both ObjectiveDocument1 pagePast Papers 2018 Abbottabad Board 10th Class Physics Both ObjectiveMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Progress Report For The Month of July 2016 Neighborhood Council: Chappargram Tehsil: BattagramDocument4 pagesProgress Report For The Month of July 2016 Neighborhood Council: Chappargram Tehsil: BattagramMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Progress Report For The Month of July 2016 Neighborhood Council: Chappargram Tehsil: BattagramDocument4 pagesProgress Report For The Month of July 2016 Neighborhood Council: Chappargram Tehsil: BattagramMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Waqar: Career ObjectivesDocument2 pagesMuhammad Waqar: Career ObjectivesMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Duplicate Gat Result Card S T NS T N: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesDuplicate Gat Result Card S T NS T N: Personal InformationMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet