Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SILUCDYLFWLVIR199046
Uploaded by
dashsuryabhanu5Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SILUCDYLFWLVIR199046
Uploaded by
dashsuryabhanu5Copyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology: Commonly Used Drugs
The board exam places a big emphasis on Pharmacology. The following PowerPage lists commonly used drugs in
veterinary medicine with their classification and important information related to the drugs. Most drugs in a certain
class will end in the same or similar suffix which can be helpful on boards if you see a drug with which you are not
familiar. (Controlled substances*)
Antibiotics:
• Gentamicin-aminoglycoside, can be renal-toxic
• Clindamycin- lincosamide
• Amoxicillin- aminopenicillin
• Enrofloxacin- fluoroquinolone (-oxacin suffix), may cause cartilage defects in young dogs, or blindness in
cats
• Cephalexin- 1st generation cephalosporin (oral)
• Cefpodoxime- 3rd generation cephalosporin (oral)
• Cefazolin- 1st generation cephalosporin (injectable)
• Cefovecin (Convenia)-3rd generation cephalosporin (injectable)
• Trimethoprim-Sulfa (TMS)- sulfonamide, may cause dry-eye
• Doxycycline- tetracycline antibiotic (Doxy doesn’t typically cause bone and teeth abnormalities or
discoloration in young animals but tetracyclines in general may cause this side effect). Should not be given as
a dry pill to cats, as esophageal strictures may occur.
• Metronidazole- used commonly to treat diarrhea or colitis, can rarely cause a neurotoxicity which
treatment for is diazepam. May be used to treat Giardia.
Corticosteroids:
• Prednisone
• Prednisolone
• Triamcinolone (Vetalog/Kenalog)- 4-10X more potent than hydrocortisone
• Methylprednisolone
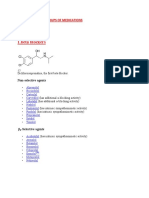
Analgesics:
Opioids: are mu agonists or partial mu agonists, reversed with naloxone
• Fentanyl*- injectable or comes in a patch
• Morphine*
• Hydromorphone*
• Buprenorphine*-injectable can also be used orally, absorbs through oral mucosa
• Butorphanol*- injectable or tablets (tablets used as antitussive)
• Tramadol* (Ultram)- tablets- synthetic mu-receptor opiate agonist
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatories: all NSAIDS cause increased risk of GI ulceration and may have effects on
the liver and kidneys, labwork should be monitored
• Carprofen (Rimadyl)-COX-2 inhibitor; rarely may cause liver failure, most commonly used post-operatively
for analgesia and for arthritis management or acute orthopedic injury
• Meloxicam (Metacam)- may enhance risk of nephrotoxicity, mostly COX-2 inhibitor
© 2018 VetTechPrep.com • All rights reserved. 1
Pharmacology: Commonly Used Drugs
• Ketoprofen (Ketofen)- used most frequently as a fever reducer
• Firocoxib (Previcox)- COX-2 inhibitor
• Deracoxib (Deramaxx)- COX-2 inhibitor (may have some COX-1 effects at higher doses)
• Flunixin Meglumine (Banamine)- used mostly in horses
• Phenylbutazone (“Bute”)- used mostly in horses
Anesthetics/Tranquilizers:
Injectables:
• Ketamine*- dissociative anesthetic, causes muscle rigidity (used with diazepam because of this)
• Tiletamine*- dissociative anesthetic, part of Telazol (along with zolazepam)
• Valium* -benzodiazepine (end in the suffix –pam), causes skeletal muscle relaxation and sedation by
enhancing GABA
• Propofol- short acting hypnotic agent/injectable anesthetic, given slowly, may cause apnea and
hypotension, white opaque in color
• Lidocane/Bupivicaine (local anesthetics, Lidocaine also given as anti-arrhythmic)
• Dexmedetomidine (Dexdomitor)- alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, reversed with atipamezole (Antesedan-an
alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist), should not be used in pets with cardiac disease or that are debilitated
• Xylazine- alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, reversed with yohimbine-an alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist)
• Acepromazine- phenothiazine tranquilizer, may lower seizure threshold (this is controversial but could be
asked on boards)
• Apomorphine- used to cause vomiting (emetic), injectable or comes in a tablet which can be placed in the
conjunctival sac in the eye, opioid
• Thiopental- short acting thiobarbiturate, not recommended for greyhounds or other sighthounds due to slow
metabolism of this drug
Inhalants: most common side effect of inhalants is hypotension
• Isoflurane
• Sevoflurane
• Halothane (not widely used due to side effects, especially cardiac)
Cardiac/Blood Pressure
• Furosemide (Lasix)- Loop diuretic most often used in congestive heart failure
• Enalapril/Benazapril- ace-inhibitors (end in suffix –pril), used in treating heart failure and hypertension,
sometimes used in chronic renal failure, causes vasodilation
• Pimobendan (Vetmedin)- inodilator, used in treating congestive heart failure
• Spironolactone (potassium sparing diuretic)
• Amlodipine (decreases blood pressure, choice anti-hypertensive for cats)
• Atropine- anticholinergic, used to increase heart rate; used in CPCR and also during anesthesia to treat
bradycardia
© 2018 VetTechPrep.com • All rights reserved. 2
POWERPAGE TITLE - BOLD (22 pt)
Pharmacology: Commonly Used Drugs
VERTICALLY CENTERED
Anti-Parasitics:
• Fenbendazole (Panacur)- general anthelmentic, also commonly used to treat Giardia
• Sulfadimethoxine (Albon)- treats coccidia
• Pyrantel- used primarily for ascarids
• Emodepside and Praziquantel (Profender)- topical dewormer for felines (Praziquantel is the treatment for
tapeworms)
• Praziquantel, Pyrantel, and Febantel (Drontal plus) dewormer for canine or feline
• Selamectin (Revolution)- topical parasite prevention (ear mite tx, flea control, hooks, rounds, heartworm
prevention), treatment for Sarcoptes
• Ivermectin (Heartgard or injectable)- heartworm prevention, hooks, rounds, demodex treatment with
injectable, contraindicated in Collie type breeds
• Milbemycin (Interceptor)- (dogs or cats) heartworm prevention, hooks, rounds, whips
Gastrointestinal:
• Famotidine (Pepcid AC)- H2 receptor blocker
• Carafate (Sucralfate)- gastroprotectant, also known as a “band-aid” for the GI tract, may impair absorption
of some oral medications
• Metoclopramide (Reglan)- upper GI pro-kinetic agent, may cause excitement or hyperactivity in cats, anti-
emetic- prevents nausea by blocking dopamine in the chemo-receptor trigger zone (CRTZ)
• Maropitant (Cerenia)- anti-nausea/anti-vomiting agent
• Cisapride- pro-motility agent for upper and lower GI, used in cats with megacolon (not commercially
available, must get compounded)
• Omeperazole (Prilosec)- proton pump inhibitor, used for treating and preventing GI ulcers
• Misoprostol- prostaglandin E1 analog, used to prevent gastric ulceration
Other Miscellaneous Drugs:
• Methocarbamol (Robaxin)- muscle relaxant
• Fluconazole/ketoconazole/itraconazole- anti-fungals, potentially hepatotoxic
• Trilostane (Vetoryl)- adrenal steroid synthesis inhibitor, used in treating hyperadrenocorticism
• Levothyroxine- thyroid hormone, treats hypothyroidism
• Methimazole (Tapazole)- inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormone, treatment for hyperthyroidism
• Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)- anti-histamine, used for allergies and allergic reactions
• Epinephrine- alpha and beta- adrenergic agonist, used mostly in anaphylaxis and cardiac resuscitation
• Guafenisen- muscle relaxant/ oral expectorant used primarily in large animal anesthesia for the muscle
relaxation
• Pentobarbital* (Beuthanasia, Fatal Plus, others)- barbiturate, mostly used for euthanasia in vet med
• Phenobarbital*- barbiturate, anti-seizure medication
• Mirtazapine- tetracyclic antidepressant/ 5-HT3 antagonist- used as appetite stimulant in dogs and cats
References
1) Plumb, Donald C. Plumb’s Veterinary Drug Handbook. 6th edition. Blackwell Publishing. 2008.
2) Bill, Robert L. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics for the Veterinary Technician. Mosby. 2006.
© 2018
2017 VetTechPrep.com • All rights reserved. z 1
3
You might also like
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NAVLE Anesthetic Pharmacology Review 2018 PDFDocument63 pagesNAVLE Anesthetic Pharmacology Review 2018 PDFmmatthew74No ratings yet
- PHARM ATI ReviewDocument76 pagesPHARM ATI Reviewth233100% (1)
- Veterinary Drug ListDocument23 pagesVeterinary Drug ListDineshNo ratings yet
- MedsDocument8 pagesMedscharitoaveNo ratings yet
- Emetics, Anti Emetics-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument15 pagesEmetics, Anti Emetics-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahNo ratings yet
- Pcare Week 13 - PharmacotherapyDocument31 pagesPcare Week 13 - Pharmacotherapy;'SiLeNt';No ratings yet
- Pain Management in AnimalsDocument46 pagesPain Management in AnimalsSunilNo ratings yet
- List of veterinary drugsDocument27 pagesList of veterinary drugsvet.cynophileNo ratings yet
- Tugas Farmasi: Pembimbing: Yudi Purnomo, S.Si, Apt, M.KesDocument225 pagesTugas Farmasi: Pembimbing: Yudi Purnomo, S.Si, Apt, M.KesAglalita Jamhur Risia TamaNo ratings yet
- Jiggar DrugsDocument3 pagesJiggar DrugsRockeven DesirNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument236 pagesPharmacologyyalahopa100% (2)
- Medicinal Agents for GI Disorders: Emetics & Anti-EmeticsDocument5 pagesMedicinal Agents for GI Disorders: Emetics & Anti-EmeticsAhmed BajahNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument13 pagesDrugsChristine UdhayNo ratings yet
- Neuro3: Study Online atDocument3 pagesNeuro3: Study Online atcharitoaveNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Emetics, Anti-EmeticsDocument16 pagesEmetics, Anti-EmeticsSachin ParamashettiNo ratings yet
- Adrenoceptor Antagonists Classification & Clinical UsesDocument23 pagesAdrenoceptor Antagonists Classification & Clinical UsesMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Management-of-Specific-Poisons-Respiratory-DrugsDocument41 pagesManagement-of-Specific-Poisons-Respiratory-Drugsjdrancap0746qcNo ratings yet
- Seminar ANS Drugs & NTDocument27 pagesSeminar ANS Drugs & NTKirtishAcharyaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Patient AssessmentDocument5 pagesPreoperative Patient Assessmenthonovezaann.a.campita.ctucvmNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal and Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal and Cardiovascular MedicationsIntanNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drugs: Mechanisms and ClassesDocument32 pagesAntiemetic Drugs: Mechanisms and ClassesAnisa Karamina WardaniNo ratings yet
- Injectable Anesthetics: Barbiturates, Propofol, Ketamine & MoreDocument28 pagesInjectable Anesthetics: Barbiturates, Propofol, Ketamine & MoreDhaif dhaifNo ratings yet
- Crash Course - General PharmacologyDocument62 pagesCrash Course - General PharmacologyDhanesh VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Stage 1 Seminar: Clinical Pharmacology of The Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesStage 1 Seminar: Clinical Pharmacology of The Nervous SystemCollin FreemanNo ratings yet
- 1.beta Blockers: List of Different Groups of MedicationsDocument18 pages1.beta Blockers: List of Different Groups of MedicationsJayshree ParmarNo ratings yet
- Toxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiDocument59 pagesToxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiTan Geok EngNo ratings yet
- 1.1-Antacids: Chapter One: Gastro-Intestinal SystemDocument129 pages1.1-Antacids: Chapter One: Gastro-Intestinal SystemHaiv1297No ratings yet
- Drugs Acting on the Gastrointestinal TractDocument27 pagesDrugs Acting on the Gastrointestinal TractJames PerianayagamNo ratings yet
- Types and Uses of Anti-Anxiety DrugsDocument39 pagesTypes and Uses of Anti-Anxiety DrugsArkene LevyNo ratings yet
- Veterinary FormularyDocument22 pagesVeterinary FormularyMohit Bansal100% (2)
- Pharmacology: Quick ReviewDocument39 pagesPharmacology: Quick ReviewDocRNNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Guide For Pharmacy Students-1Document132 pagesSummer Training Guide For Pharmacy Students-1Rania T. Sabri100% (2)
- Anticonvulsant DrugsDocument2 pagesAnticonvulsant Drugsshai padillaNo ratings yet
- Antinauseants and AntiemeticsDocument8 pagesAntinauseants and AntiemeticsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- التدريب الصيفي محلولهDocument129 pagesالتدريب الصيفي محلولهMohamed MosawiNo ratings yet
- Histamine, Serotonin & The Ergot AlkaloidsDocument31 pagesHistamine, Serotonin & The Ergot AlkaloidsnicewanNo ratings yet
- DR IsraDocument29 pagesDR IsraMuhammad MasroorNo ratings yet
- Analgesics - New Microsoft Office Power Point PresentationDocument21 pagesAnalgesics - New Microsoft Office Power Point Presentationrozha100% (4)
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument29 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsBenedict Brashi100% (1)
- AntiemeticsDocument30 pagesAntiemeticsDustyNo ratings yet
- Gastric and Doudenal Peptic Ulcer: DR - Rania Khalil MostafaDocument44 pagesGastric and Doudenal Peptic Ulcer: DR - Rania Khalil MostafaMai OssamaNo ratings yet
- Analgesics and Pain Control in DentistryDocument51 pagesAnalgesics and Pain Control in DentistryIyad Abou-Rabii0% (1)
- Top Drugs: 1. ACETAMINOPHEN (Tylenol)Document12 pagesTop Drugs: 1. ACETAMINOPHEN (Tylenol)epingNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument60 pagesPsychotropic DrugsLaTasha Lindemann RNNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument23 pagesAnti EpilepticsSalman HabeebNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Digestive System of AnimalsDocument32 pagesDrugs Acting On Digestive System of AnimalsSunil100% (3)
- Antiemetics and ProkineticsDocument29 pagesAntiemetics and ProkineticsGilbert Girising100% (1)
- Caring For The Client With Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Pharmacologic PrinciplesDocument57 pagesCaring For The Client With Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Pharmacologic PrinciplesgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesDocument20 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesPooja KumariNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesAnesthesiaعلي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Guide For Pharmacy StudentsDocument129 pagesSummer Training Guide For Pharmacy Studentstalal150% (2)
- Classification of Drugs PDFDocument15 pagesClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Management of Adverse Drug ReactionsDocument27 pagesTopic 8 - Management of Adverse Drug ReactionsPrincewill SmithNo ratings yet
- Drugs For GI DisordersDocument5 pagesDrugs For GI DisordersAalap ShahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Management of Parkinson'S DiseaseDocument19 pagesPharmacological Management of Parkinson'S DiseaseSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- VPHM55 Lessons 18 and 19Document129 pagesVPHM55 Lessons 18 and 19Camille Faith MaglaquiNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Local HormonesDocument38 pagesAutacoids Local HormonesbelindaNo ratings yet
- Nad C541iDocument37 pagesNad C541iapi-3837207No ratings yet
- CotomDocument8 pagesCotommuangawaNo ratings yet
- Risus License Information PDFDocument1 pageRisus License Information PDFSam CorbenNo ratings yet
- FND Global and FND Profile PDFDocument4 pagesFND Global and FND Profile PDFSaquib.MahmoodNo ratings yet
- BOM RMCC Parking-Shed Rev2Document15 pagesBOM RMCC Parking-Shed Rev2Ephrem Marx AparicioNo ratings yet
- SAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008Document6 pagesSAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008cjherrera2No ratings yet
- Beef & Dairy 2016Document36 pagesBeef & Dairy 2016The Standard NewspaperNo ratings yet
- Audiology DissertationDocument4 pagesAudiology DissertationPaperWritingHelpOnlineUK100% (1)
- Workbook. Unit 3. Exercises 5 To 9. RESPUESTASDocument3 pagesWorkbook. Unit 3. Exercises 5 To 9. RESPUESTASRosani GeraldoNo ratings yet
- APMP Certification Syllabus and Program V3.1 March 2019 PDFDocument20 pagesAPMP Certification Syllabus and Program V3.1 March 2019 PDFMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- BW Query GuidelinesDocument10 pagesBW Query GuidelinesyshriniNo ratings yet
- Computer 8 Q2 Set B ModuleDocument6 pagesComputer 8 Q2 Set B ModuleEmvie Loyd Pagunsan-ItableNo ratings yet
- Vertical Transportation SystemDocument15 pagesVertical Transportation SystemAnupama MorankarNo ratings yet
- Media KitDocument22 pagesMedia KitEmilyNo ratings yet
- Aruksha ResumeDocument2 pagesAruksha Resumeapi-304262732No ratings yet
- Diesel fuel system for Caterpillar 3208 engineDocument36 pagesDiesel fuel system for Caterpillar 3208 engineLynda CarrollNo ratings yet
- LEEA-030.2c2 Certificate of Thorough Examination (Multiple Items) (Overseas) (Dev)Document1 pageLEEA-030.2c2 Certificate of Thorough Examination (Multiple Items) (Overseas) (Dev)GaniyuNo ratings yet
- MT Series User Manual MT4YDocument28 pagesMT Series User Manual MT4YDhani Aristyawan SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Confidentiality Agreement With Undertaking and WaiverDocument1 pageConfidentiality Agreement With Undertaking and WaiverreddNo ratings yet
- Steady State Modeling and Simulation of The Oleflex Process For Isobutane Dehydrogenation Considering Reaction NetworkDocument9 pagesSteady State Modeling and Simulation of The Oleflex Process For Isobutane Dehydrogenation Considering Reaction NetworkZangNo ratings yet
- 4 Types and Methods of Speech DeliveryDocument2 pages4 Types and Methods of Speech DeliveryKylie EralinoNo ratings yet
- 7 Ways of Looking at Grammar China EditDocument20 pages7 Ways of Looking at Grammar China EditAshraf MousaNo ratings yet
- Consumer PerceptionDocument61 pagesConsumer PerceptionPrakhar DwivediNo ratings yet
- Dental Pulp TissueDocument77 pagesDental Pulp TissueJyoti RahejaNo ratings yet
- Update 2.9?new Best Sensitivity + Code & Basic Setting Pubg Mobile 2024?gyro On, 60fps, 5 Fingger. - YoutubeDocument1 pageUpdate 2.9?new Best Sensitivity + Code & Basic Setting Pubg Mobile 2024?gyro On, 60fps, 5 Fingger. - Youtubepiusanthony918No ratings yet
- Appendix A - Status Messages: Armed. Bad Snubber FuseDocument9 pagesAppendix A - Status Messages: Armed. Bad Snubber Fuse이민재No ratings yet
- A An Some Any Jamie Oliver Pancake With Answer KeyDocument8 pagesA An Some Any Jamie Oliver Pancake With Answer Keygcciprian66570% (3)
- Wind Hydro 2Document6 pagesWind Hydro 2Vani TiwariNo ratings yet
- The 10 Most Inspiring Quotes of Charles F HaanelDocument21 pagesThe 10 Most Inspiring Quotes of Charles F HaanelKallisti Publishing Inc - "The Books You Need to Succeed"100% (2)
- Business English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Document2 pagesBusiness English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Ben RhysNo ratings yet
![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)