Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
mar khOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
mar khCopyright:
Available Formats
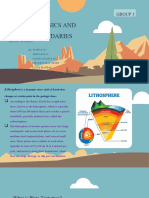
Tectonic Plate Margins: Earth’s Dynamic Puzzle Pieces
Tectonic plate margins, also known as plate boundaries, are the areas where the Earth’s lithospheric plates meet. These margins
are dynamic and constantly changing, playing a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface and influencing geological phenomena
such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain formation. Understanding tectonic plate margins is essential for
comprehending the processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
Types of Tectonic Plate Margins
There are three main types of tectonic plate margins: divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, and transform boundaries.
Divergent boundaries occur where two tectonic plates move away from each other. This movement creates a gap that is often filled
with molten rock from the mantle, leading to the formation of new crust. One of the most well-known examples of a divergent
boundary is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Convergent boundaries are characterized by tectonic plates moving towards each other. When an oceanic plate collides with a
continental plate, the denser oceanic plate is forced beneath the lighter continental plate in a process known as subduction. This
collision can lead to the formation of deep ocean trenches, volcanic arcs, and mountain ranges. The Pacific Ring of Fire is a region
known for its intense tectonic activity resulting from convergent boundaries.
Transform boundaries occur where two plates slide past each other horizontally. The friction between the plates can cause
earthquakes along fault lines such as the San Andreas Fault in California.
Impact on Geological Phenomena
The interactions at tectonic plate margins have significant effects on geological phenomena. For example, convergent boundaries
are associated with powerful earthquakes and volcanic eruptions due to the intense pressure and heat generated by subduction
processes. Divergent boundaries contribute to the formation of new oceanic crust and rift valleys, while transform boundaries result
in frequent seismic activity.
Human Implications
Understanding tectonic plate margins is crucial for assessing natural hazards and mitigating their impact on human populations.
Regions located near tectonic plate margins are more susceptible to earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. By studying
these margins, scientists can better predict potential geological hazards and implement measures to protect communities at risk.
In conclusion, tectonic plate margins are fundamental components of the Earth’s dynamic geology. Their interactions shape our
planet’s surface and influence natural phenomena that impact human societies. Continued research into tectonic plate margins is
essential for advancing our understanding of Earth’s geological processes and improving hazard preparedness.
Top 3 Authoritative Reference Publications or Domain Names Used in Answering this Question:
1. National Geographic - National Geographic provides comprehensive information on tectonic plate margins, including
articles, maps, and visual resources that offer valuable insights into Earth’s dynamic geology.
2. Geological Society of America - The Geological Society of America publishes peer-reviewed research articles and
educational materials related to tectonic plate margins, offering authoritative information for understanding these
geological features.
3. United States Geological Survey (USGS) - The USGS is a leading source of scientific data and research on tectonic
plate margins, providing reliable information on seismic activity, volcanism, and other geological phenomena
associated with plate boundaries.
You might also like
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentmar khNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Continental DriftDocument1 pagePlate Tectonics and Continental DriftrockNo ratings yet
- Earthquake ImportantDocument26 pagesEarthquake ImportantSanu Biswas 9102No ratings yet
- Science Student TeacherDocument2 pagesScience Student TeacherpurplieliaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1663507508465 6977256196788546956-3Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1663507508465 6977256196788546956-3Brenda Ongogan DollienteNo ratings yet
- CVS01Document8 pagesCVS01Janella CantaraNo ratings yet
- The Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetDocument32 pagesThe Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetsshoeburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Written Report in Science Group 4Document11 pagesWritten Report in Science Group 4Stephen Tracy TabamoNo ratings yet
- Subject:: ModèleDocument10 pagesSubject:: ModèleAnouar ChraibiNo ratings yet
- Earthquake NotesDocument22 pagesEarthquake NotesRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes - 2023 Session OnwardsDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes - 2023 Session Onwardsabdulhannanchaudary53No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument87 pagesPlate TectonicsAspiron Hangibayna KussitaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics EarthDocument21 pagesDynamics EarthMahesh HanmawaleNo ratings yet
- Frontier GeophysicsDocument21 pagesFrontier Geophysicsmuhammad RashidNo ratings yet
- Albaytar (Earthquake)Document4 pagesAlbaytar (Earthquake)Mark JosephNo ratings yet
- Eartquake EspedillonDocument2 pagesEartquake Espedillonchristopher layupanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of EarthquakeDocument7 pagesMechanism of EarthquakeArslan RaoNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift and PlateDocument10 pagesContinental Drift and Platejenazze cruzNo ratings yet
- Question No.1 Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesQuestion No.1 Plate TectonicsArslan RaoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1-Location of Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesLESSON 1-Location of Plate TectonicsAndreaNicoleBanzonNo ratings yet
- Science 4.3 Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesScience 4.3 Theory of Plate TectonicsRazel TercinoNo ratings yet
- The Earths CrustDocument2 pagesThe Earths Crustshaimaabdullah303No ratings yet
- Branches of Earth Science Geology: Hydrologists Study The Availability and Distribution of The Earth's FreshwaterDocument3 pagesBranches of Earth Science Geology: Hydrologists Study The Availability and Distribution of The Earth's FreshwaterJoya Sugue AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Movements: Can They Change An EcosystemDocument19 pagesTectonic Movements: Can They Change An Ecosystemmeljan degamonNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Module 9-10Document6 pagesEarth Science Module 9-10Lopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument6 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryAENA JangraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Elements of SeismologyDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Elements of SeismologyJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Tektonik IndonesiaDocument8 pagesTektonik IndonesiaArfaq Fauqi RomadlonNo ratings yet
- EAS 1600 Lab 08 Fall 2018 "Plate Tectonics" ObjectivesDocument20 pagesEAS 1600 Lab 08 Fall 2018 "Plate Tectonics" ObjectivessamNo ratings yet
- Geology Essay ScribdDocument2 pagesGeology Essay ScribdMichael BurtonNo ratings yet
- C1L4 - Elementary Knowledge On Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (By MG Biscocho)Document19 pagesC1L4 - Elementary Knowledge On Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (By MG Biscocho)Marnoel MalapitanNo ratings yet
- C1 GeoDocument46 pagesC1 GeoAfiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesLearning OutcomesAida EsonNo ratings yet
- What Is Plate TectonicsDocument27 pagesWhat Is Plate Tectonics15-0001No ratings yet
- EssayDocument3 pagesEssayglen.curitnNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Plate Tectonics (From The Late Latin: Tectonicus, From TheDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonics: Plate Tectonics (From The Late Latin: Tectonicus, From ThemcmusbixNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Engineering GeologyDocument64 pagesPlate Tectonics Engineering GeologyChiranjaya Hulangamuwa50% (2)
- Faults Earthquakes Ss2012Document2 pagesFaults Earthquakes Ss2012musaNo ratings yet
- Sci Reporting Lesson InfaurrDocument6 pagesSci Reporting Lesson InfaurrmelissakatevfloresNo ratings yet
- 8 Plate TectonicsDocument5 pages8 Plate Tectonics22100204No ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Plate BoundariesDocument44 pagesLesson 1. Plate BoundariesMa’am Diana V.No ratings yet
- Types of Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesTypes of Plate BoundariesIsabella persadNo ratings yet
- Geology For Engineers: 2 Credit Load - 2 Units Status - RequiredDocument46 pagesGeology For Engineers: 2 Credit Load - 2 Units Status - RequiredAbiodun RichardNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Group 3Document17 pagesEarth Science Group 3reignchan640No ratings yet
- 3a .Physiographic Features of EarthDocument5 pages3a .Physiographic Features of EarthAzaz Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Hand OutsDocument6 pagesHand OutsMJ DejosNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Building Blocks of RocksDocument6 pagesMinerals: Building Blocks of RocksHeather Simonette Rose IntongNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryRonald PurigayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Earthquake EngineeringDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Earthquake EngineeringZankhana DaveNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesPlate TectonicsIlyass ChahoudNo ratings yet
- Earth System 3rd Edition Kump Solutions ManualDocument13 pagesEarth System 3rd Edition Kump Solutions Manualkathleenjonesswzrqcmkex100% (24)
- Plate TectonicsDocument31 pagesPlate TectonicsRyan HoganNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For s1 Earth Science Final ExamDocument4 pagesStudy Guide For s1 Earth Science Final Examapi-474509282No ratings yet
- ALI AHMED AWAN EqSe1Document13 pagesALI AHMED AWAN EqSe1Zeeshan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Referat Seismica-World Seismic ZoneDocument6 pagesReferat Seismica-World Seismic ZoneMoldovan Adrian NeluNo ratings yet
- About EarDocument7 pagesAbout EarAbdul RazalNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesPlate Tectonics: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlexandra LicaNo ratings yet
- 1st Chapter Elements of SismologyDocument11 pages1st Chapter Elements of SismologyRohan ShreshthiNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument19 pagesPlate Tectonicsaditya2053No ratings yet
- Venn Diagram: The Inner Planets of The Solar System The Outer Planets of The Solar SystemDocument10 pagesVenn Diagram: The Inner Planets of The Solar System The Outer Planets of The Solar SystemJovie MedsNo ratings yet
- Agro-Ecological Zones of India: March 2013Document16 pagesAgro-Ecological Zones of India: March 2013abinash SethiNo ratings yet
- Talc in Polyester Putties - Mondo Minerals PDFDocument10 pagesTalc in Polyester Putties - Mondo Minerals PDFJuanan LopezNo ratings yet
- METAMORPHISM Earth and Life Science Week 4Document22 pagesMETAMORPHISM Earth and Life Science Week 4Jessicalyn LabitoriaNo ratings yet
- LAB - Relative and Absolute DatingDocument2 pagesLAB - Relative and Absolute DatingbrikylaNo ratings yet
- Cauvery Basin, South IndiaDocument16 pagesCauvery Basin, South IndiaSonal MevadaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science MelcsDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Science MelcsGeraldine V. LantanoNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Evolution of The Northern Afric PDFDocument27 pagesTectonic Evolution of The Northern Afric PDFEmira ZrelliNo ratings yet
- FinalPaperSubmission DFII2219 0820110318Document10 pagesFinalPaperSubmission DFII2219 0820110318nirbhay narayanNo ratings yet
- G10 Q1 Module 1Document31 pagesG10 Q1 Module 1Mikaela FabrosNo ratings yet
- Biogeography BookDocument72 pagesBiogeography BookDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- UW BrazosValleyFarmLLC ApplicationDocument11 pagesUW BrazosValleyFarmLLC ApplicationKBTXNo ratings yet
- Precis Passage PDFDocument2 pagesPrecis Passage PDFMuhammad Ali SajjadNo ratings yet
- Learning Strand 2Document6 pagesLearning Strand 2Krisjelyn GumaroNo ratings yet
- Tropical SoilsDocument88 pagesTropical SoilsBernard Kipng'eno100% (1)
- Lecture - 01 Unit 1 - : The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument27 pagesLecture - 01 Unit 1 - : The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University School of Geography and Environmental Studies Geography of Ethiopia and The Horn ModuleDocument19 pagesHaramaya University School of Geography and Environmental Studies Geography of Ethiopia and The Horn ModuleTofik Mohammed0% (2)
- Soil Mechanics and Soil Stabilisation Techniques: Reference CSPHLR01O00012 (Oud)Document2 pagesSoil Mechanics and Soil Stabilisation Techniques: Reference CSPHLR01O00012 (Oud)Robert SagaNo ratings yet
- 12072022211703ASP - Mineral - Sept 2022Document4 pages12072022211703ASP - Mineral - Sept 2022Mahendra KumarNo ratings yet
- CHROMITEDocument5 pagesCHROMITETayyab FiazNo ratings yet
- Data Tanah 4Document1 pageData Tanah 4m rizkiNo ratings yet
- Jiang Et Al. (2014) - The Genesis and Paleoenvironmental Records of Longji Agricultural in TerracesDocument10 pagesJiang Et Al. (2014) - The Genesis and Paleoenvironmental Records of Longji Agricultural in TerracesDemetrio Angelo Lama IsminioNo ratings yet
- Module 4 The Continental DriftDocument25 pagesModule 4 The Continental DriftOwene Miles AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To GeologyDocument5 pages1 Introduction To GeologyMay Alyssa BalladNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q 4 Week 1Document3 pagesScience 7 Q 4 Week 1Maricris Amor Compra100% (1)
- Culture and Landscape of India-R2Document47 pagesCulture and Landscape of India-R2RachanaNo ratings yet
- EclipseDocument134 pagesEclipseChukwunoso Nwonye100% (3)
- Relative & Radiometric DatingDocument2 pagesRelative & Radiometric DatingBread GuyNo ratings yet
- Shale QuantDocument11 pagesShale QuantjavacobNo ratings yet
- Jumlah Soal: 10 Butir Passage 1Document4 pagesJumlah Soal: 10 Butir Passage 1Alfiya HasnaNo ratings yet
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (595)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (35)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Microscopy of Numerology: Numerology SimplifiedFrom EverandMicroscopy of Numerology: Numerology SimplifiedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1003)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)