Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions Sodium Chloride Poster
Uploaded by
nnilam13080 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageAn aqueous solution consists of an ionic compound dissolved in water allowing the ions to move freely and conduct electricity, making it an electrolyte. During electrolysis of an aqueous solution, the products depend on the reactivity of elements. For a sodium chloride solution, chlorine gas is produced at the anode since it contains halide ions, while hydrogen gas forms at the cathode since sodium is more reactive than hydrogen. Sodium and hydroxide ions also react to form a sodium hydroxide solution.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn aqueous solution consists of an ionic compound dissolved in water allowing the ions to move freely and conduct electricity, making it an electrolyte. During electrolysis of an aqueous solution, the products depend on the reactivity of elements. For a sodium chloride solution, chlorine gas is produced at the anode since it contains halide ions, while hydrogen gas forms at the cathode since sodium is more reactive than hydrogen. Sodium and hydroxide ions also react to form a sodium hydroxide solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageElectrolysis of Aqueous Solutions Sodium Chloride Poster
Uploaded by
nnilam1308An aqueous solution consists of an ionic compound dissolved in water allowing the ions to move freely and conduct electricity, making it an electrolyte. During electrolysis of an aqueous solution, the products depend on the reactivity of elements. For a sodium chloride solution, chlorine gas is produced at the anode since it contains halide ions, while hydrogen gas forms at the cathode since sodium is more reactive than hydrogen. Sodium and hydroxide ions also react to form a sodium hydroxide solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
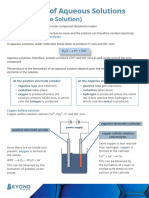
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
(Sodium Chloride Solution)
An aqueous solution consists of an ionic compound dissolved in water.
The ions in an aqueous solution are free to move and the solution can therefore conduct electricity.
Aqueous solutions are called electrolytes.
In aqueous solutions, water molecules break down to produce H+ ions and OH- ions.
H2O H+ + OH–
Aqueous solutions, therefore, contain a mixture of H+ and OH– ions as well as the ions of the ionic
compound.
The products of the electrolysis of an aqueous solution depend upon the relative reactivity of the
elements in the solution.
At the positive electrode (anode): At the negative electrode (cathode):
• negative ions lose electrons; • positive ions gain electrons;
• oxidation takes place; • reduction takes place;
• oxygen is produced unless the • hydrogen is produced unless the metal
solution contains halide ions, in which ion is less reactive than hydrogen, in
case the halogen is produced. which case the metal is produced.
Sodium Chloride Solution
Sodium chloride solution contains Na+, Cl–, H+ and OH– ions.
negative electrode (cathode)
power supply
positive electrode (anode)
sodium chloride solution
(electrolyte)
Since the solution contains
Since sodium is more reactive
halide ions (Cl–) the halogen
than hydrogen, hydrogen is
chlorine is formed at the
formed at the cathode.
anode.
2H+ + 2e– H2
2Cl– Cl2 + 2e–
This can be observed by the
This can be observed by the
formation of bubbles at the
formation of bubbles at the
cathode.
The remaining Na+ ions and OH- ions react to produce NaOH, sodium hydroxide solution.
You might also like
- Electrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) PosterDocument1 pageElectrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) Posternnilam1308No ratings yet
- Electrolysis LessonDocument21 pagesElectrolysis LessonShenaya HewaNo ratings yet
- ElectroDocument48 pagesElectroMang friesNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesDocument13 pagesElectrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesNicaliaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis in SolutionsDocument13 pagesElectrolysis in SolutionsTeandraNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exp 2 Chm674Document4 pagesDiscussion Exp 2 Chm674Eva Lizwina MatinNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSI1Document10 pagesELECTROLYSI1jpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes For SdaDocument13 pagesElectrolysis Notes For Sdatmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Electrolysis of AueqousDocument8 pagesElectrolysis of AueqousSelinawong Win Jing SelinawongNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument13 pagesElectricity and Chemistrysalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Electricity and ChemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Electricity and ChemistryAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetDocument83 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetbhargavintnaiduNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsLana Arsyad100% (2)
- Chapter 8 - Electricity and Chemical Change PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 8 - Electricity and Chemical Change PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisapi-381901280% (5)
- ELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Document33 pagesELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument6 pagesChemical ChangesmahmudswordofjusticeNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument24 pagesElectrolysisstudent purposesNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Chem IGCSE 1 - Module 5Document5 pagesChem IGCSE 1 - Module 5carrisanicole2No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument43 pagesElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesCSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryCornflakes Toasted100% (1)
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument5 pagesElectricity and Chemistrymohamed komiNo ratings yet
- SS2 Note ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSS2 Note ElectrolysisIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Notes Hydrogen 2023Document12 pagesNotes Hydrogen 2023Ayush GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- ''Chapter 4, SKKDocument21 pages''Chapter 4, SKKAung LayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: ConductivityDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: Conductivityapi-181176018No ratings yet
- Electrolysis Summary IGCSEDocument1 pageElectrolysis Summary IGCSEeriotacidNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisChemistryKlipz97% (34)
- ELECTROLYSIS Notes Condensed 2Document3 pagesELECTROLYSIS Notes Condensed 2Diya ShahNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMDocument47 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMWalaa AdelNo ratings yet
- Electrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode DischargeDocument28 pagesElectrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode Dischargeanwar9602020100% (1)
- Group 17 Elements - F, CL, BR, ..Document36 pagesGroup 17 Elements - F, CL, BR, ..Looi Chui YeanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry #2Document8 pagesElectrochemistry #2swcaptain2008No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument83 pagesElectrolysismoizbadri100% (3)
- C12 Electrochemistry IgcseDocument33 pagesC12 Electrochemistry IgcseAnna DixonNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 InstructorDocument26 pagesChap 4 InstructorOsama MohsinNo ratings yet
- Lab Exp 1Document9 pagesLab Exp 1mahmoudNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Formulae Equations and Amount Edexcel 15 17Document3 pages8.2 Formulae Equations and Amount Edexcel 15 17Stephan MinhNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemistry - Unit 4Document30 pagesElectricity and Chemistry - Unit 4Cloud WtafNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Ol Notes 2Document7 pagesElectrochemistry Ol Notes 2Ahmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemistry 23 (AutoRecovered)Document19 pagesElectricity and Chemistry 23 (AutoRecovered)taliassalimNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis O LevelDocument17 pagesElectrolysis O LevelInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Document22 pagesChemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Hayan LeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Electrolytic CellDocument8 pagesExperiment 2 - Electrolytic CellafifiNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisGowriram RamNo ratings yet
- F332 Notes (Elements From The Sea)Document11 pagesF332 Notes (Elements From The Sea)Becky Tenney100% (1)
- Chemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahDocument3 pagesChemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahAdaugo UbahNo ratings yet
- Olevel NotesDocument110 pagesOlevel Notestatendachimbandi1No ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Mechanisms and Catalysis: The Role of Reactive Intermediates in Organic ProcessesFrom EverandOrganometallic Mechanisms and Catalysis: The Role of Reactive Intermediates in Organic ProcessesNo ratings yet
- NCHRP W27-ADocument155 pagesNCHRP W27-AHuy ChungNo ratings yet
- Failure Report For Cathodic Protection SystemDocument6 pagesFailure Report For Cathodic Protection SystemHoang Thang0% (1)
- Grade 12 Physical Sciences Platinum Navigation PackDocument66 pagesGrade 12 Physical Sciences Platinum Navigation PackKhehla TshabalalaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification For Cathodic Protection SystemDocument43 pagesTechnical Specification For Cathodic Protection SystemCương Lê Văn100% (2)
- EEGUCDocument135 pagesEEGUCR SKNo ratings yet
- ASRJC H2 Chem 2021 P1 SolutionsDocument29 pagesASRJC H2 Chem 2021 P1 Solutionsantesipation ฅ'ω'ฅNo ratings yet
- Tubular Vent BinderDocument12 pagesTubular Vent BinderbayuNo ratings yet
- Biochemical MeasurementsDocument25 pagesBiochemical Measurementsulaga nathanNo ratings yet
- Exploring Competitive Features of Stationary Sodium BatteryDocument22 pagesExploring Competitive Features of Stationary Sodium BatteryCB Dong SuwonNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Op MondayDocument2 pagesCorrosion Op MondayjasmineammaNo ratings yet
- SunanodeDocument2 pagesSunanodeKaleeswari GNo ratings yet
- NORSOK Standard M-503Document16 pagesNORSOK Standard M-503cristianoclemNo ratings yet
- Manganese Corrosion PDFDocument20 pagesManganese Corrosion PDFdutuconstantinNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument70 pagesChemistryRasigaaNo ratings yet
- 2.9 Durability Theory: Why Reinforced Concrete Structures Don't Fall DownDocument53 pages2.9 Durability Theory: Why Reinforced Concrete Structures Don't Fall DownRahul patilNo ratings yet
- E Book of RME 2 PDFDocument215 pagesE Book of RME 2 PDFHimanshuDasNo ratings yet
- Fan Reverse Engineering ReportDocument7 pagesFan Reverse Engineering Reportapi-352647685100% (1)
- Introduction To Metal ExtractionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Metal ExtractionschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Battery Testert Arduino ProyectDocument65 pagesBattery Testert Arduino ProyectRolando VlNo ratings yet
- MHC EEE132 Autumn 2020 Lecture 2 09 12 2020Document103 pagesMHC EEE132 Autumn 2020 Lecture 2 09 12 2020Samina TohfaNo ratings yet
- API 571 For API 570 ExamDocument28 pagesAPI 571 For API 570 ExamAdilMunir100% (1)
- JPCL Watertank Ebook PDFDocument31 pagesJPCL Watertank Ebook PDFTamerGalhoum100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Questions AnswersDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Questions AnswersDivyansh Rana100% (1)
- DO Analyser ManualDocument24 pagesDO Analyser ManualambeshNo ratings yet
- Fibreglass Boat Inspection ReportDocument18 pagesFibreglass Boat Inspection ReportAllen Alex LalisNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersAbrar Abdallah SiamNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Basic'sDocument58 pagesCorrosion Basic'sMayang Centya FebriaryNo ratings yet
- Gadag R. V., Shetty A. V., Engineering Chemistry (3rd Edition)Document278 pagesGadag R. V., Shetty A. V., Engineering Chemistry (3rd Edition)Prateek sblNo ratings yet
- Lec06 04 LVDocument4 pagesLec06 04 LVgiyagirlsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and NanomaterialsDocument76 pagesElectrochemistry and NanomaterialsCharles Arthel ReyNo ratings yet