Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) Poster
Uploaded by
nnilam13080 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
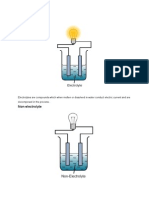
3 views1 pageElectrolysis of an aqueous copper sulfate solution produces oxygen gas and copper metal. The solution contains dissolved copper and sulfate ions, as well as free hydrogen and hydroxide ions from the water. During electrolysis, oxygen gas forms at the anode since there are no halide ions present. Copper metal forms at the cathode instead of hydrogen gas because copper is less reactive than hydrogen.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectrolysis of an aqueous copper sulfate solution produces oxygen gas and copper metal. The solution contains dissolved copper and sulfate ions, as well as free hydrogen and hydroxide ions from the water. During electrolysis, oxygen gas forms at the anode since there are no halide ions present. Copper metal forms at the cathode instead of hydrogen gas because copper is less reactive than hydrogen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageElectrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) Poster
Uploaded by
nnilam1308Electrolysis of an aqueous copper sulfate solution produces oxygen gas and copper metal. The solution contains dissolved copper and sulfate ions, as well as free hydrogen and hydroxide ions from the water. During electrolysis, oxygen gas forms at the anode since there are no halide ions present. Copper metal forms at the cathode instead of hydrogen gas because copper is less reactive than hydrogen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
(Copper Sulfate Solution)
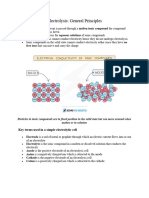
An aqueous solution consists of an ionic compound dissolved in water.
The ions in an aqueous solution are free to move and the solution can therefore conduct electricity.
Aqueous solutions are called electrolytes.
In aqueous solutions, water molecules break down to produce H+ ions and OH– ions.
H2O H+ + OH–
Aqueous solutions, therefore, contain a mixture of H+ and OH– ions as well as the ions of the ionic
compound.
The products of the electrolysis of an aqueous solution depend upon the relative reactivity of the
elements in the solution.
At the positive electrode (anode): At the negative electrode (cathode):
• negative ions lose electrons; • positive ions gain electrons;
• oxidation takes place; • reduction takes place;
• oxygen is produced unless the • hydrogen is produced unless the metal
solution contains halide ions, in which ion is less reactive than hydrogen, in
case the halogen is produced. which case the metal is produced.
Copper Sulfate Solution
Copper sulfate solution contains Cu2+, SO42–, H+ and OH– ions.
negative electrode (cathode)
power supply
positive electrode (anode)
copper sulfate solution
(electrolyte)
Since copper is less reactive
Since there are no halide ions than hydrogen, copper is
present, oxygen is formed at formed at the cathode.
the anode. Cu2+ + 2e– Cu
– –
4OH O2 + 2H2O + 4e This can be observed by
This can be observed by the the formation of a layer of
formation of bubbles at the orange-pink metal on the
anode. surface of the cathode.
You might also like
- Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions Sodium Chloride PosterDocument1 pageElectrolysis of Aqueous Solutions Sodium Chloride Posternnilam1308No ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes For SdaDocument13 pagesElectrolysis Notes For Sdatmoatshe96No ratings yet
- ElectroDocument48 pagesElectroMang friesNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSIS Notes Condensed 2Document3 pagesELECTROLYSIS Notes Condensed 2Diya ShahNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesCSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryCornflakes Toasted100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument24 pagesElectrolysisstudent purposesNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSI1Document10 pagesELECTROLYSI1jpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Electrolysis of AueqousDocument8 pagesElectrolysis of AueqousSelinawong Win Jing SelinawongNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Aqueous SolutionDocument40 pagesElectrolysis Aqueous SolutionVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisGowriram RamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahDocument3 pagesChemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahAdaugo UbahNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Silver SulphateDocument5 pagesElectrolysis of Silver SulphateJackson_de_Roz_6005100% (1)
- s.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Document9 pagess.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Ronald RomNo ratings yet
- SS2 Note ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSS2 Note ElectrolysisIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Electricity and ChemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Electricity and ChemistryAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Form 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsDocument9 pagesForm 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsGono TakaduuNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: ConductivityDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: Conductivityapi-181176018No ratings yet
- Electrolysis in SolutionsDocument13 pagesElectrolysis in SolutionsTeandraNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in MaterialsDocument16 pagesCorrosion in MaterialsARYAN PIRTANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Electricity and Chemical Change PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 8 - Electricity and Chemical Change PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ElectrochemistryAshraf Shaharudin100% (1)
- ELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Document33 pagesELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMDocument47 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMWalaa AdelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Notes Icse 10Document25 pagesChemistry - Notes Icse 10Suneet MohanNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument10 pagesElectrolysisFaithNo ratings yet
- New Electrolysis 1Document18 pagesNew Electrolysis 1Rethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument43 pagesElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Electrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode DischargeDocument28 pagesElectrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode Dischargeanwar9602020100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Olevel NotesDocument110 pagesOlevel Notestatendachimbandi1No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry #2Document8 pagesElectrochemistry #2swcaptain2008No ratings yet
- Summary - ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSummary - ElectrolysisKeertana SNNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesElectrochemistryShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis. Olevel ChemistryDocument53 pagesElectrolysis. Olevel ChemistrySaraYasinNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis LessonDocument21 pagesElectrolysis LessonShenaya HewaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesDocument13 pagesElectrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesNicaliaNo ratings yet
- Esis 2Document35 pagesEsis 2Amir Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSISDocument12 pagesELECTROLYSISKatlo KgosiyangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 11 Chapter VIIIDocument44 pagesChemistry Grade 11 Chapter VIIIJ.K HomerNo ratings yet
- CY-008 CorrossionDocument17 pagesCY-008 CorrossionakashNo ratings yet
- ''Chapter 4, SKKDocument21 pages''Chapter 4, SKKAung LayNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exp 2 Chm674Document4 pagesDiscussion Exp 2 Chm674Eva Lizwina MatinNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non-Metalsmonkey.luffy.kenNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisapi-381901280% (5)
- All About ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesAll About ElectrochemistryROY JAIVIN A/L SANTHANA DAS MoeNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- RQ - RP - RPT & FBNDocument35 pagesRQ - RP - RPT & FBNSlim.B100% (2)
- Holiday Gift Ideas 2013Document0 pagesHoliday Gift Ideas 2013Lillie NewspapersNo ratings yet
- Tobler - MWO Raum Und Zeit Final - English - FinalDocument6 pagesTobler - MWO Raum Und Zeit Final - English - Finalheinz_toblerNo ratings yet
- Wika Thermowell DS PDFDocument4 pagesWika Thermowell DS PDFaspdNo ratings yet
- IJAMSCR 14 221 Pawan MittalDocument5 pagesIJAMSCR 14 221 Pawan MittalMarcoAngeloLiwanNo ratings yet
- Documents AHNAY SERIES Bi 57 515 545 WEL E and PD 515 545 144 MPB HC 08 17 12 2021 6dfbf20656Document2 pagesDocuments AHNAY SERIES Bi 57 515 545 WEL E and PD 515 545 144 MPB HC 08 17 12 2021 6dfbf20656Vansh PandyaNo ratings yet
- Marriage BDocument7 pagesMarriage BNurul HabibahNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Health Grade 1Document12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Health Grade 1Grace Ma AyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Basic Principles of PlumbingDocument12 pagesLesson 1 - Basic Principles of PlumbingNicholas Bonn Sing100% (1)
- Dimmesdale Parris PaperDocument9 pagesDimmesdale Parris Paperjustinenguyen8No ratings yet
- NCP ScribdDocument3 pagesNCP ScribdAngela AyalaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Different Extraction Methods On Some PropertiesDocument13 pagesEffects of Different Extraction Methods On Some PropertiesDizon, Sean Andrei S.No ratings yet
- Tabel-Thermo Gas Hasil Pmbakaran Cengel (SI-18 HLM)Document18 pagesTabel-Thermo Gas Hasil Pmbakaran Cengel (SI-18 HLM)rasid redNo ratings yet
- The Paradox of Healing PainDocument12 pagesThe Paradox of Healing PainWaseem RsNo ratings yet
- Unistrut P2072A SubmittalDocument1 pageUnistrut P2072A SubmittalPaing Phyo AungNo ratings yet
- Subcontractor Passout For Kick Off MTG 1-23-2020Document1 pageSubcontractor Passout For Kick Off MTG 1-23-2020Patricia LeeNo ratings yet
- Print Version - 2010-2016 Audi A6 (C7) Fuse Box DiagramDocument6 pagesPrint Version - 2010-2016 Audi A6 (C7) Fuse Box DiagramAyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- DCL Report - Hygitech HSDocument2 pagesDCL Report - Hygitech HSFarhan RashidNo ratings yet
- Greta Thunberg Reading Comprehension TextDocument3 pagesGreta Thunberg Reading Comprehension TextGabriel OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Ati AtihanDocument13 pagesAti AtihanMary grace S. MuyonNo ratings yet
- Science Summative Test 1st and 2ndDocument11 pagesScience Summative Test 1st and 2ndGabrielMichaelMalubayCapuyan67% (3)
- Cadbury Operations ProjectDocument28 pagesCadbury Operations Projectparulhrm80% (5)
- Tube-to-Tubesheet Joints - BaherDocument51 pagesTube-to-Tubesheet Joints - BaherNAMO100% (3)
- Erythrocytes Alterations of Monosex Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus, Linnaeus, 1758) Produced Using MethyltestosteroneDocument8 pagesErythrocytes Alterations of Monosex Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus, Linnaeus, 1758) Produced Using MethyltestosteroneiqyuwidyaNo ratings yet
- Jewish Standard, February 26, 1016Document56 pagesJewish Standard, February 26, 1016New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- A005A120020-Basic Equipment (L0L) From April 2010Document1,105 pagesA005A120020-Basic Equipment (L0L) From April 2010Carlos Garcia GodoyNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Prevention During Acid Cleaning of Pulping EquipmentDocument22 pagesCorrosion Prevention During Acid Cleaning of Pulping EquipmentlyoufNo ratings yet
- Laporan Setelah BPK 22 April 2018Document869 pagesLaporan Setelah BPK 22 April 2018zulika siregarNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Birth in Denmark - April 2023Document4 pagesPregnancy and Birth in Denmark - April 2023valckefranNo ratings yet
- Nadi BookletDocument100 pagesNadi Bookletapi-528122992No ratings yet