Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Herpes Simplex - Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Rainny CommsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Herpes Simplex - Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Rainny CommsCopyright:
Available Formats
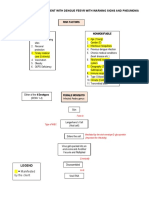
Predisposing Factors
Age
LEGEND: Precipitating Factors:
Immunodeficiency
Predisposing/Precipitating Factors Direct Contact
Atopy
Disease Process Oral-genital contact
Stress
Disease
Sun exposure
Symptoms and Lab/Diagnosis
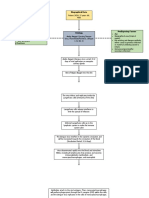
The virus attaches to specific
receptors on epithelial cells (skin,
mucous membranes).
The viral envelope merges with
the cell membrane, releasing the
viral capsid inside the cell.
Sign and Symptoms Viral DNA is released from the
Primary infection: capsid and enters the host cell
Fever, malaise, swollen lymph nucleus.
nodes.
Blisters or clusters of small, painful
vesicles at the site of infection (lips,
mouth, genitals, eyes).
Burning, itching, tingling sensation Viral genes are transcribed and
around the lesions. translated, producing new viral
Difficulty eating or drinking due to proteins and DNA.
mouth sores.
Recurrent infection:
Fewer and smaller blisters, usually
occurring in the same location as New viral particles are assembled
previous outbreaks. within the host cell.
Shorter duration of symptoms.
Diagnostic Tool:
Viral Culture New virus particles bud from the
Polymerase chain reaction infected cell membrane and
(PCR) Herpes Simplex
spread to infect other cells.
Serological Tests
Tzanck Smear
During primary infection, some
viral DNA becomes latent in
sensory ganglia near the site of
infection. These latent viruses
can reactivate years later under
certain conditions.
You might also like
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument6 pagesInfectious DiseasesAlexa QuizomNo ratings yet
- BIO CH21 Foundations PDFDocument15 pagesBIO CH21 Foundations PDFKristina CatomerisNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Classification of DiseaseDocument10 pagesCommunicable Disease Classification of DiseaseThe Von SevenNo ratings yet
- Henrickson 1972Document6 pagesHenrickson 1972Kmii TspNo ratings yet
- IX. Nursing Care Plan: November 10, 2020Document6 pagesIX. Nursing Care Plan: November 10, 2020LNo ratings yet
- Herpes SimpexDocument1 pageHerpes Simpexmkct111No ratings yet
- Genital HerpesDocument29 pagesGenital HerpesGliza Jane100% (1)
- 3.1 Communicable DiseasesDocument1 page3.1 Communicable Diseaseswill hayNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod5Document6 pagesNCM 112-Mod5Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Herpes ManuscriptDocument9 pagesHerpes ManuscriptALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of Patient With Dengue Feevr With Warning Signs and PneumoniaDocument4 pagesSchematic Diagram of Patient With Dengue Feevr With Warning Signs and PneumoniaJae TyNo ratings yet
- CD 1Document47 pagesCD 1RhobelieNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio DengueDocument1 pagePathophysio DengueDANICA BONBONNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CovidDocument7 pagesConcept Map CovidMaieca Demecillo100% (3)
- 2.3 PathogenesisDocument27 pages2.3 PathogenesisTobio KunnyNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Genetic Factors Environmental FactorsDocument5 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Genetic Factors Environmental Factorsjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Infectious Disease NotesDocument30 pagesModule 7 Infectious Disease NotesRebecca DaveyNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Reviewer Finals Finals FinalsDocument14 pagesFundamentals Reviewer Finals Finals Finalsleahrico1964No ratings yet
- Concept Map For DenvDocument4 pagesConcept Map For Denvnikki sabs67% (3)
- COVID 19 ManuscriptDocument17 pagesCOVID 19 ManuscriptFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Feb DTRDocument3 pagesFeb DTRFeb NamiaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Unit 3 - Infection and ResponseDocument5 pagesGCSE Biology Unit 3 - Infection and ResponsefeyrelysNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Document2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Venice Joy CelociaNo ratings yet
- Rach15 - Infection Control and Asepsis NuDocument1 pageRach15 - Infection Control and Asepsis NuFalqueza JanelleNo ratings yet
- Vesiculobullous Disease: Viral Disease: Herpes Simplex Infection Herpes Simplex Virus (HSVS) Infections AreDocument5 pagesVesiculobullous Disease: Viral Disease: Herpes Simplex Infection Herpes Simplex Virus (HSVS) Infections Aresullivan ilavaduNo ratings yet
- L10 Infectious DiseasesDocument2 pagesL10 Infectious DiseasesJamaema GasparNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Mycobacterium Leprae/ Mycobacterium LepromatosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Mycobacterium Leprae/ Mycobacterium LepromatosisAkeroNo ratings yet
- Gass DNA Viruses General Properties: NADocument10 pagesGass DNA Viruses General Properties: NAGianna SablanNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisPanJan BalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DenguePLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesSciencex.Dilys.x xNo ratings yet
- Micro OrganismsDocument5 pagesMicro Organismsnikitaria1603No ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Handouts)Document15 pagesCommunicable Diseases Handouts)snpjavierNo ratings yet
- Libutan, Jan Christian L. - Microbiology SDL 1Document1 pageLibutan, Jan Christian L. - Microbiology SDL 1JCLeornaNo ratings yet
- Previews: Battling The Bite: Tradeoffs in Immunity To Insect-Borne PathogensDocument2 pagesPreviews: Battling The Bite: Tradeoffs in Immunity To Insect-Borne PathogensRobertus RonnyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- CDN - Ca2Document28 pagesCDN - Ca2ANGEL MICAH DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Insignis Pedia MMRV LopezDocument7 pagesInsignis Pedia MMRV LopezChrisfernan MondragonNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisChristian Remetio100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram: Predisposing PrecipitatingDocument5 pagesSchematic Diagram: Predisposing PrecipitatingKarl Wesley DillozonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DengueKevin50% (2)
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument7 pagesParasitology ReviewerSandra Mhay RodilloNo ratings yet
- Lucid Chart ManuscriptDocument11 pagesLucid Chart ManuscriptCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox 2Document1 pageChicken Pox 2Kristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Virus Zoster, Enterovirus,: Problem TreeDocument3 pagesVirus Zoster, Enterovirus,: Problem TreeIhtiramiNo ratings yet
- Final Patho Viral RhinitisDocument1 pageFinal Patho Viral RhinitisKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Activity IiDocument5 pagesActivity IiYVONNE PEARL BALIQUIDNo ratings yet
- Case Bacterial MeningitisDocument29 pagesCase Bacterial MeningitisMika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Immunity Grade 10Document36 pagesChapter 10 Immunity Grade 10gabiplayz47No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hansen's DiseaseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hansen's DiseaseGrace Lyn Borres ImpasNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 3Document20 pagesBiology Chapter 3Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- STI - HerpesDocument1 pageSTI - HerpesDanii LuvNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease XI312 RAMADocument1 pageInfectious Disease XI312 RAMAMuhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Édion: ImunityDocument11 pagesÉdion: ImunityMuhammad TahaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Yeast InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Yeast InfectionChelzie Laserna100% (2)
- Microbio Report (Dellava and Mamae)Document3 pagesMicrobio Report (Dellava and Mamae)JamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- Patient Based PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPatient Based PathophysiologyJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Table Virology 1Document28 pagesTable Virology 1Virgil CendanaNo ratings yet
- A) Immunization B) Vaccination C) Attenuation D) None of TheseDocument4 pagesA) Immunization B) Vaccination C) Attenuation D) None of TheseRevathi DadamNo ratings yet
- Virus Patogenik: Hishamuddin Bin AhmadDocument26 pagesVirus Patogenik: Hishamuddin Bin AhmadShareall RazhiftNo ratings yet
- Group I: DNA Viruses: PoxviridaeDocument3 pagesGroup I: DNA Viruses: PoxviridaeharoononlineNo ratings yet
- Paramyxoviruses Infecting Humans - The Old, The New and The Unknown Virtue 2009Document18 pagesParamyxoviruses Infecting Humans - The Old, The New and The Unknown Virtue 2009Laura CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1 Acellular and Prokaryotic MicrobesDocument6 pagesQuiz No. 1 Acellular and Prokaryotic Microbesmaglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- CH 13 Lecture PresentationDocument97 pagesCH 13 Lecture PresentationDalia M. MohsenNo ratings yet
- Section G: Vocabulary Cloze: Read The Passage Carefully, and Fill in The Blanks With The Words Provided in The BoxDocument1 pageSection G: Vocabulary Cloze: Read The Passage Carefully, and Fill in The Blanks With The Words Provided in The BoxNitya Nurul FadilahNo ratings yet
- Classification of VirusDocument9 pagesClassification of VirusHaris QurashiNo ratings yet
- I Key Concepts : Either in Their DNA Component (With 32P) or in Their Protein ComponentDocument2 pagesI Key Concepts : Either in Their DNA Component (With 32P) or in Their Protein ComponentValentina PecanacNo ratings yet
- What Are Viruses?Document5 pagesWhat Are Viruses?ZJC 2333No ratings yet
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Classification of Microbes Unit IIDocument66 pagesClassification of Microbes Unit IIjaskarn_jazz100% (1)
- Virus, Monera and ProtistaDocument42 pagesVirus, Monera and ProtistaGigih Putra100% (3)
- ViroDocument4 pagesVirolctorres7462antNo ratings yet
- General Properties of VirusDocument34 pagesGeneral Properties of VirusThoma D. BudhgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Hershey ChaseDocument1 pageHershey Chasemkohli64No ratings yet
- Oncogenic VirusesDocument5 pagesOncogenic VirusesManoj KhadseNo ratings yet
- Virology - Biology W3310/4310 Spring 2013 Prof. V. Racaniello Study Questions For Lecture 8 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument1 pageVirology - Biology W3310/4310 Spring 2013 Prof. V. Racaniello Study Questions For Lecture 8 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingJason de CairesNo ratings yet
- VvIBD in Peru AAAP Marco CisnerosDocument15 pagesVvIBD in Peru AAAP Marco CisnerosJoee SamiNo ratings yet
- Viruses For 300l Mls ClassDocument30 pagesViruses For 300l Mls ClassEvelyn OnosakponomeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 41 Flashcards QuizletDocument1 pageMicrobiology 41 Flashcards QuizletkumaranayakemadurangaNo ratings yet
- Aprendo en Casa Semana 2Document7 pagesAprendo en Casa Semana 2Yesi GNo ratings yet
- Pox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationDocument5 pagesPox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationIdraak BhatNo ratings yet
- Global Statistics Avian InfluenzaDocument2 pagesGlobal Statistics Avian InfluenzaSatria KinoNo ratings yet
- Bacteria QuizDocument10 pagesBacteria QuizMark Abion ValladolidNo ratings yet
- ParvovirusDocument8 pagesParvovirusAldila safitriNo ratings yet
- Multiplication of TMVDocument18 pagesMultiplication of TMVAlishaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Biosynthesis of Cucumber Mosaic VirusDocument6 pagesStructure and Biosynthesis of Cucumber Mosaic VirusRayhan Shikdar C512No ratings yet
- Monodnaviria: Virus ClassificationDocument7 pagesMonodnaviria: Virus ClassificationMiguel CarreraNo ratings yet