Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Difference Between Physical and Logical Topology 17.01.2024
Uploaded by
aloishp36Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Difference Between Physical and Logical Topology 17.01.2024
Uploaded by
aloishp36Copyright:
Available Formats
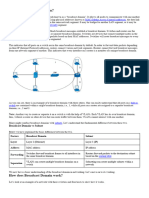
Difference between Physical and Logical Topology
1. Physical Topology :
Physical topology indicates arrangement of different elements of a network. It reflects physical
layout of devices and cables to a form a connected network. It is concerned with essentials of
network ignoring minute details like transfer of data and device type. The pattern of arrangement
of nodes (computers) and network cables depends on ease of installation and setup of the network.
It affects cost and bandwidth capacity based on solution of devices. It takes into account
placement of nodes and distance between them. Devices can be arranged to form a ring (Ring
Topology) or linearly connected in a line called Bus Topology.
2. Logical Topology :
Logical Topology reflects arrangement of devices and their communication. It is the transmission
of data over physical topology. It is independent of physical topology, irrespective of
arrangements of nodes. It is concerned with intricate details of network like type of devices
(switches, routers) chosen and their quality, which affect rate and speed of data packets delivery.
The logical topology ensures optimal flow control that can be regulated within network.
The data can either flow in a linear pattern called Logical bus or in form of a circle Logical ring.
Difference between Physical and Logical Topology :
Physical Topology Logical Topology
Depicts logistics of network concerned with
Depicts physical layout of network.
transmission of data.
There is no interference and manipulation
The layout can be modified based on needs.
involved here.
It can be arranged in star, ring, mesh and bus
It exists in bus and ring topologies.
topologies.
This has major impact on cost, scalability and This has major impact on speed and delivery of
bandwidth capacity of network based on data packets. It also handles flow control and
selection and availability of devices. ordered delivery of data packets.
It is actual route concerned with transmission. It is a high level representation of data flow.
Physical connection of the network. Data path followed of the network.
You might also like
- Resolume-Arena-Manual (EN) PDFDocument298 pagesResolume-Arena-Manual (EN) PDFijmusicesongsNo ratings yet
- Free Digital Planner Undated Monday StartsDocument22 pagesFree Digital Planner Undated Monday StartsSofía Fernández SeijasNo ratings yet
- What is Network TopologyDocument33 pagesWhat is Network TopologyUMARNo ratings yet
- Network TeologyDocument1 pageNetwork TeologyAMIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Skip To ContentDocument18 pagesSkip To ContentFikru TesefayeNo ratings yet
- WECONF48837 2020 9131160 Pdf#view FitHDocument5 pagesWECONF48837 2020 9131160 Pdf#view FitHKallur AkshathaNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 NETWORKINGDocument20 pagesPresentation1 NETWORKINGDan ChiongNo ratings yet
- Fisheye State Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDocument8 pagesFisheye State Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksswatiiiitmNo ratings yet
- Netwirk Topology SemiDocument4 pagesNetwirk Topology SemiHorlars LeeNo ratings yet
- Network Design by Using Opnet™ It GuruDocument7 pagesNetwork Design by Using Opnet™ It GuruVladimir OleynikovNo ratings yet
- Ch 5 Remaining NotesDocument8 pagesCh 5 Remaining NotesJyoti PatelNo ratings yet
- Khantsithu CNGA2Document24 pagesKhantsithu CNGA2Sithu KhantNo ratings yet
- CSE Fundamental - TopologyDocument14 pagesCSE Fundamental - TopologySYED FARHAN REZANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Core Network ComponentsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Core Network Componentskad feroNo ratings yet
- A Review On Ad Hoc Network Security: January 2011Document9 pagesA Review On Ad Hoc Network Security: January 2011KhadijaNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies..: Megha Bansal (2021451)Document16 pagesNetwork Topologies..: Megha Bansal (2021451)Megha BansalNo ratings yet
- Topologies NetsDocument8 pagesTopologies NetshfdhfdNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument13 pagesNetwork TopologySara AbidNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Routing Protocols For Ad H PDFDocument6 pagesComparison of Routing Protocols For Ad H PDFJet TruongNo ratings yet
- Genetic algorithm for shortest path routingDocument5 pagesGenetic algorithm for shortest path routingDR. DILLIP ROUTNo ratings yet
- What Is Network Topology - Best Guide To Types & Diagrams - DNSstuffDocument18 pagesWhat Is Network Topology - Best Guide To Types & Diagrams - DNSstuffcoxihiNo ratings yet
- Spectrum and Network Management Convergence For Wireless CommunicationsDocument7 pagesSpectrum and Network Management Convergence For Wireless Communicationsmps125No ratings yet
- Understanding Network Topologies and Internet ArchitectureDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Network Topologies and Internet ArchitectureSuman AhujaNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document9 pagesExp 2Chaimae ELHAMAMINo ratings yet
- An 77a 00 PDFDocument16 pagesAn 77a 00 PDFLjubomir StrezovNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networking TopologiesDocument26 pagesWireless Networking TopologiesTamilarasan DeenathayalanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks PDFDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks PDFnazm basmNo ratings yet
- An Adaptive Hybrid Routing Protocol For Efficient Data Transfer and Delay Control in Mobile Ad Hoc Network-IJETT-V71I5P226Document8 pagesAn Adaptive Hybrid Routing Protocol For Efficient Data Transfer and Delay Control in Mobile Ad Hoc Network-IJETT-V71I5P226Augustine OnuoraNo ratings yet
- Noc Basics: 2.1 Noc Structure and Design SpaceDocument15 pagesNoc Basics: 2.1 Noc Structure and Design SpacemohandossNo ratings yet
- Routing Protocols in Wireless Mesh Networks: Challenges and Design ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesRouting Protocols in Wireless Mesh Networks: Challenges and Design ConsiderationsSatish NaiduNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Application NotesDocument8 pagesNetwork Topologies: Application NotesBassantMohamadNo ratings yet
- InterTubes - A Study of The US Long-Haul Fiber-Optic Infrastructure - p565Document14 pagesInterTubes - A Study of The US Long-Haul Fiber-Optic Infrastructure - p565JohnNo ratings yet
- Networking Assignment 1Document9 pagesNetworking Assignment 1M.Bilal JattNo ratings yet
- Tree Topology 2Document11 pagesTree Topology 2Jamiah Abdullah50% (2)
- Presentation of NetworkingDocument27 pagesPresentation of Networkingkamal jamal0% (1)
- IIIT Network Design and TopologyDocument9 pagesIIIT Network Design and TopologyHarshit PahujaNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Algorithms in Broadband Wireless NetworksDocument12 pagesScheduling Algorithms in Broadband Wireless Networksaidden03No ratings yet
- BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit 2: Networking Infrastructure ASSIGNMENT 1 FRONT SHEETDocument39 pagesBTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit 2: Networking Infrastructure ASSIGNMENT 1 FRONT SHEETVu Quang Hai (FGW HN)No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DCCN Computer NetworkingDocument34 pagesChapter 1 DCCN Computer Networkingeskedar assefaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lecture NotesDocument50 pagesComputer Networks Lecture NotesRam Kumar0% (1)
- Amoussou OW06Document6 pagesAmoussou OW06lucraoNo ratings yet
- NW TopologyDocument6 pagesNW Topologygagan.kulal619No ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document7 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- C PPPPPP PPP PPDocument9 pagesC PPPPPP PPP PPahils100% (1)
- Jurnal 10Document12 pagesJurnal 10Ahmad fadilNo ratings yet
- Real Time Mesh Network For Industrial Automation 4009Document6 pagesReal Time Mesh Network For Industrial Automation 4009Esteban ChiclanaNo ratings yet
- Sys Ad AssignmentDocument5 pagesSys Ad AssignmentKiah AstrologoNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Approach To Support Qos and Bandwidth Efficiency inDocument9 pagesAn Efficient Approach To Support Qos and Bandwidth Efficiency inaoanh02No ratings yet
- Internet QoS Signaling SurveyDocument26 pagesInternet QoS Signaling SurveyLuka ŠpanićNo ratings yet
- What Is Network TopologyDocument2 pagesWhat Is Network TopologyFiaz Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Units 1 5Document105 pagesComputer Networks Units 1 5yuvanaNo ratings yet
- A Secure Hierarchical Protocol For Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument13 pagesA Secure Hierarchical Protocol For Wireless Sensor NetworksAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Data Transmission Capacity On Satellite Links With Non-Zero Bit Error RatesDocument8 pagesOptimizing Data Transmission Capacity On Satellite Links With Non-Zero Bit Error Ratespcitest123No ratings yet
- Routing in Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument8 pagesRouting in Wireless Sensor NetworksDivya LunawatNo ratings yet
- INSIGNIA: An IP-Based Quality of Service Framework For Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDocument33 pagesINSIGNIA: An IP-Based Quality of Service Framework For Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksdokimquyNo ratings yet
- Singh 2017Document16 pagesSingh 2017Nikhil VaishNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Enhanced DSDV Protocol For Efficient Routing in Wireless Ad Hoc NetworksDocument8 pagesPerformance Analysis of Enhanced DSDV Protocol For Efficient Routing in Wireless Ad Hoc NetworksMokshada YadavNo ratings yet
- Performance Comparison of Multihop Wireless Mobile Ah-Hoc Routing ProtocolsDocument8 pagesPerformance Comparison of Multihop Wireless Mobile Ah-Hoc Routing ProtocolsUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Itws ManualDocument7 pagesItws ManualKalavakunta Dharanidhar DharanidharNo ratings yet
- Topology PDFDocument11 pagesTopology PDFVIJAY KNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Definition of Network Units Packet, Fragments, Frame, Datagram, SegmentDocument6 pagesDefinition of Network Units Packet, Fragments, Frame, Datagram, Segmentaloishp36No ratings yet
- What Is A Broadcast Domain 10.02.2024Document3 pagesWhat Is A Broadcast Domain 10.02.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- What Is FTP 17.01.2024Document4 pagesWhat Is FTP 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- What Is OSI Model 17.01.2024Document7 pagesWhat Is OSI Model 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- Transmission Modes in Computer NetworksDocument5 pagesTransmission Modes in Computer NetworksLokong OtimNo ratings yet
- The Seven Layers of Networking 17.01.2024Document3 pagesThe Seven Layers of Networking 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- This Is Exactly Why We Still Use The OSI Model When We Have TCP 17.01.2024Document5 pagesThis Is Exactly Why We Still Use The OSI Model When We Have TCP 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- DTW300 SparePartsDocument3 pagesDTW300 SparePartsDaniel SchallerNo ratings yet
- Waterloo Iowa Death of Angela BuckDocument6 pagesWaterloo Iowa Death of Angela BuckImprintNo ratings yet
- EZ 220 Songbook Web PDFDocument152 pagesEZ 220 Songbook Web PDFOscar SpiritNo ratings yet
- Bả N Chính: Phòng Giáo Dục Và Đào TạoDocument3 pagesBả N Chính: Phòng Giáo Dục Và Đào TạobohucNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Breakers GuideDocument2 pagesHydraulic Breakers GuideLU YO0% (1)
- (Adorno) Bach Defended Against His DevoteesDocument7 pages(Adorno) Bach Defended Against His DevoteesYung Bin Kwak100% (1)
- Eggplant ParmesanDocument12 pagesEggplant ParmesanAnton CampbellNo ratings yet
- Borrowing a Match: The Frustrating Search for a Simple MatchDocument5 pagesBorrowing a Match: The Frustrating Search for a Simple MatchBlair BassNo ratings yet
- MB Manual Ga-Z170n (h170n) - Wifi eDocument44 pagesMB Manual Ga-Z170n (h170n) - Wifi eBrahNo ratings yet
- Ssu 05124474Document59 pagesSsu 05124474Sagar ShiwakotiNo ratings yet
- National Geographic Traveler USA October-November 2017Document103 pagesNational Geographic Traveler USA October-November 2017glezglez1100% (2)
- Acquisitions: Number Acquisition Date Company Business Country Value Used As or Integrated With RefDocument16 pagesAcquisitions: Number Acquisition Date Company Business Country Value Used As or Integrated With RefHemraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Euphoria 106 The Next Episode 2019Document67 pagesEuphoria 106 The Next Episode 2019Ahmed SamehNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 4 - Q3 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - Mapeh 4 - Q3 - W1Reynold Cueto PentinioNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan: Front ViewDocument5 pagesFloor Plan: Front Viewangelandlucifergabriel009No ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat EC15K EC18K Forklift Lift Trucks Service Repair Manual SNA3EC1-10200 and Up PDFDocument25 pagesCaterpillar Cat EC15K EC18K Forklift Lift Trucks Service Repair Manual SNA3EC1-10200 and Up PDFfjkskkdhsjmdnNo ratings yet
- Past Continous ExercisesDocument13 pagesPast Continous ExercisesGeorgiana DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Harga Satuan Bahan dan Material Konstruksi JalanDocument2 pagesHarga Satuan Bahan dan Material Konstruksi JalansubanNo ratings yet
- The Story of EltonjohnDocument134 pagesThe Story of EltonjohnSzilvia KovacsNo ratings yet
- Ceriatone Overtone Special 20W Mini Amplifier ManualDocument18 pagesCeriatone Overtone Special 20W Mini Amplifier ManualNeurocasterNo ratings yet
- 3 Agustus - SheeterDocument6 pages3 Agustus - Sheeternawang wahyuNo ratings yet
- Secondary UnitDocument10 pagesSecondary Unitapi-334477826No ratings yet
- Sophos Firewall Vs Checkpoint BCDocument8 pagesSophos Firewall Vs Checkpoint BC(unknown)No ratings yet
- Art & Culture Notes - 001 PDFDocument29 pagesArt & Culture Notes - 001 PDFDebajit Kar100% (1)
- Vonage RTP300Document98 pagesVonage RTP300Berks HomesNo ratings yet
- Clothes: Reading and WritingDocument2 pagesClothes: Reading and WritingDAYELIS DUPERLY MADURO RODRIGUEZ100% (1)
- Soal Dril Dan Latihan Chapter 2 Kelas 10 PDFDocument5 pagesSoal Dril Dan Latihan Chapter 2 Kelas 10 PDFNana MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Wedding Registry Checklist - The KnotDocument9 pagesWedding Registry Checklist - The KnotAndre Marin SolorzanoNo ratings yet