Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecindu1l Exp3 Roz
Uploaded by
Roz BrianCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecindu1l Exp3 Roz
Uploaded by
Roz BrianCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 3
Shunt Voltage Regulator
I. OBJECTIVES
At the end of this experiment, students should be able to:
• Describe the operation of a shunt voltage regulator
• Evaluate the line and load regulation of a shunt voltage regulator
II. COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES (CLOs)
• ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyse and interpret data.
III. BACKGROUND INFORMATION
Shunt voltage regulators use a regulating device, usually a transistor, in parallel with the output.
They are best suited for use in power supplies where line and load voltages are moderate.
Series regulators are well-suited to applications where there are wide variations in line voltage
or to applications that require variable output voltages.
Rs is a series dropping resistor, and the control voltage circuit provides base voltage for the
shunt regulating transistor, Q1.
Figure 1. Basic Shunt Regulating Circuit
Load current and transistor current both flow through series dropping resistor Rs. This resistor
must be selected to have ample power dissipation for normal regulator operation and also for
circuit protection in the event of an output short circuit.
The output voltage Vo of the voltage regulator circuit is determined by the Zener diode and Q1
as shown:
Vo = VZ + VBE
An increase in line voltage VA also causes the output voltage to increase. Increases Vo, applied
between the base and emitter of Q1, causes transistor conduction to increase in the same way as a
reduction in load current does. The shunt regulator circuit can compensate for changes in either
load resistance or changes in line voltage.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS - LAB
If the line voltage VA decreases substantially or if the load resistance drops significantly,
transistor conduction is reduced to zero at some point. Because the transistor no longer affects the
current flow through Rs, Vo can not be maintained at a nearly constant level. The circuit is not able
to regulate the output under these conditions.
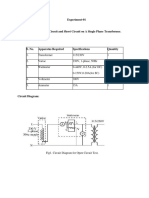
IV. EQUIPMENT/MATERIALS/DEVICES
QUANTITY EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATIONS
1 unit VARIAC
1 unit Ammeter Analog/Digital
1 unit Voltmeter Analog/Digital
1 unit Multimeter Analog/Digital
1 set Connecting wires
1 pc Breadboard
1 unit Bridge rectifier module
1 pc Zener Diode 1N4738A or 8.2-V equivalent
1 pc NPN Transistor 2N4401 or equivalent with Beta = 50
2 pcs Resistor one 120-ohm and one 100-ohm, ½ watt
1 pc Capacitor 470 µF, 25 V
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS - LAB
V. PROCEDURE
1. Prepare the materials needed.
2. Construct the circuit as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram of Shunt Voltage Regulator Circuit
3. Measure the values needed as indicated in Table 1.
4. Repeat the process in step 3 with input AC voltages set to 14 Vrms and 12 Vrms. Record the
values.
VI. DATA TABLE
Table 1
Parameter Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3
Vno-load 22 V 17.4 V 14.69 V
Vload 8.76 V 7.91 V 6.67 V
VBE 0.713 V 0.403 V 0.396 V
VZ 8V 7.51 V 6.28 V
VR1 13.3V 9.49 V 8V
% Load Regulation 151 % 120% 120.2%
ILOAD 151.7 A 114.75 A 93.87 A
ISUPPLY 151.7 A 114.75 A 93.87 A
IC 141.38 fA 80.57 fA 57.59 fA
% line regulation = (VoTrial1 – Vo Trial3) / Vo Trial3 * 100%
% line regulation = (8.76V – 6.67) / 6.67 * 100% = 31.33 %
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS - LAB
VII. QUESTIONS
1. With respect to the circuit of a shunt voltage regulator, what is the purpose of using a transistor?
In the circuit of a shunt voltage regulator, the purpose of using a transistor is to regulate and
stabilize the output voltage. A shunt voltage regulator is a type of linear voltage regulator that
uses a Zener diode to maintain a constant output voltage. However, the Zener diode alone
cannot handle high current loads efficiently. This is where the transistor comes into play.
2. If the regulating transistor of a shunt regulating circuit is cut off, the circuit can not properly
control the output voltage. Does the output level increase or decrease at cut off? Why?
In a shunt regulating circuit, the regulating transistor plays a crucial role in controlling the output
voltage. However, if this transistor is cut off, the circuit cannot properly control the output
voltage. In such a scenario, the output level decreases rather than increases.
3. How different is the operation of shunt voltage regulator as compared to series voltage
regulator?
The operation of a shunt voltage regulator differs significantly from that of a series voltage
regulator. In a shunt regulator, the regulating element is connected in parallel with the load. This
regulating element, typically a Zener diode, maintains a constant reference voltage across its
terminals. As the input voltage increases, the excess current flows through the regulating
element, bypassing the load and maintaining a constant output voltage.
On the other hand, a series regulator operates by placing the regulating element in series with
the load. The regulating element adjusts its resistance based on changes in input voltage to
maintain a constant output level. As input voltage rises, more current flows through the
regulating element to reduce output voltage and vice versa.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS - LAB
VIII. OBSERVATIONS
In my observations, the value of all voltages in each trial are decreasing while the value of
currents in each trial are also decreasing. I noticed that the value of load current and supply current is
same but the in each trial, the value decreases. I noticed that the load regulation exceeds to 100%.
Shunt voltage has rough value than series voltage regulators.
IX. CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, I understand and determined how shunt voltage regulator work and also to
solve the load and line regulation in shunt voltage regulator circuit. I conclude that a shunt voltage
regulator is a type of voltage regulator that maintains a constant output voltage by diverting excess
current away from the load. It operates by using a shunt resistor in parallel with the load, and a
reference voltage is compared to the output voltage to control the current flow through the shunt
resistor. This helps in regulating the voltage across the load.
X. PICTURE EVIDENCES
This is screenshot of my simulation in activity 3, We determine the value of currents in trial 3 from the
circuit.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS - LAB
This the second screenshot from my simulation in this activity. We determine the voltage values in trial
1 from the circuit.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS - LAB
You might also like
- Ecindu1l Exp2 RozDocument7 pagesEcindu1l Exp2 RozRoz BrianNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- HALIDDocument23 pagesHALIDBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Slup 075Document12 pagesSlup 075Gowtham SanampalliNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ManualDocument42 pagesPower Electronics ManualJavaria Chiragh50% (2)
- Lab 7 - StabilizatoareDocument21 pagesLab 7 - StabilizatoareIonelNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator ExperimentDocument4 pagesVoltage Regulator ExperimentPercival Cylas CabralesNo ratings yet
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pages1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualsDocument31 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualsMirza Umar Farooq BaigNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Hirasugar Institute of Technology, NidasoshiDocument67 pagesLaboratory Manual: Hirasugar Institute of Technology, NidasoshipriyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Zener Voltage Regulator Diode Clippers ClampersDocument7 pages4 Zener Voltage Regulator Diode Clippers ClampersmakreloadedNo ratings yet
- Zener Controlled Transistor Voltage RegulatorDocument9 pagesZener Controlled Transistor Voltage Regulatorkanye eastNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Changer ProjectDocument42 pagesThree Phase Changer ProjectDaniel Taiti Kimathi100% (1)
- Power Electronics and DC LecturesDocument159 pagesPower Electronics and DC LecturesOzzy the catNo ratings yet
- VOLTAGE REGULATOR CHARACTERISTICSDocument3 pagesVOLTAGE REGULATOR CHARACTERISTICSsivanesansirNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Series Voltage Regulator BBN 10205 (Done)Document10 pagesLab 10 Series Voltage Regulator BBN 10205 (Done)Zhamir ZhakwanNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Intro To AC Phase ControlDocument8 pagesExp 5 Intro To AC Phase Controlusmpowerlab67% (3)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ManualDocument67 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab ManualSudha Saravanan100% (3)
- Voltage Regulators - Electronic Tutorials - Mepits - MepitsDocument4 pagesVoltage Regulators - Electronic Tutorials - Mepits - MepitsJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- Efca 2 Lab 1vDocument8 pagesEfca 2 Lab 1vM Fa RizNo ratings yet
- ECE 1 Experiment 7 ZENER DIODESDocument6 pagesECE 1 Experiment 7 ZENER DIODESNicole Soriano CalisinNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Iit Delhi Summer Internship Report 2016Document31 pagesDokumen - Tips Iit Delhi Summer Internship Report 2016Shammas MohamedNo ratings yet
- Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocument11 pagesCourse - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜNo ratings yet
- ELG3316 - Transformer Lab - Fall 2016Document24 pagesELG3316 - Transformer Lab - Fall 2016Nicolas SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Circuit AnalysisDocument14 pagesDiode Rectifier Circuit Analysistungpham2014No ratings yet
- Voltage and Current TransformersDocument27 pagesVoltage and Current TransformersRebekah Powell100% (1)
- Static RelaysDocument11 pagesStatic RelaysBharathwaj SreedharNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Power Supply, DC Voltmeter, DC Ammeter SASTRA UniversityDocument25 pagesUnit 4 - Power Supply, DC Voltmeter, DC Ammeter SASTRA UniversitystarNo ratings yet
- Eeb 516 Lab 1Document5 pagesEeb 516 Lab 1mmoloki mosikareNo ratings yet
- N. Bacalso Avenue, Cebu City: Cebu Institute of Technology - UniversityDocument15 pagesN. Bacalso Avenue, Cebu City: Cebu Institute of Technology - UniversityTreyes RobertNo ratings yet
- 120EE1098 - Vennela Medaboina - Merged BEE Report-CompressedDocument83 pages120EE1098 - Vennela Medaboina - Merged BEE Report-CompressedSahasrabda Sai PradhanNo ratings yet
- Machine LabDocument7 pagesMachine LabNurjahan-Ara StudentNo ratings yet
- How Linear Regulators Work: Understanding the BasicsDocument5 pagesHow Linear Regulators Work: Understanding the BasicsAngelu VerasNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation OF Hydro Generator: Presented byDocument22 pagesVoltage Regulation OF Hydro Generator: Presented bySanjay Agrawal100% (1)
- 17eel37 Eml Lab ManualDocument64 pages17eel37 Eml Lab ManualpriyaNo ratings yet
- REPORT Ecd Lab 9Document3 pagesREPORT Ecd Lab 9ayazNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab Exp3.pdfDocument17 pagesElectronics Lab Exp3.pdfgacc4sitesNo ratings yet
- Beee Unit 3 RegulatorsDocument35 pagesBeee Unit 3 RegulatorsgnanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- 07-Series RegulatorDocument4 pages07-Series Regulatormuraliece muralieceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 16052020 045213pm 19062023 052331pmDocument49 pagesChapter 6 16052020 045213pm 19062023 052331pmAbdullah ZamirNo ratings yet
- Local Media5941271462837301265Document65 pagesLocal Media5941271462837301265jason mr.perfect11No ratings yet
- High Voltage Impulse GeneratorDocument10 pagesHigh Voltage Impulse GeneratorRoshan AkaravitaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Divider Circuit ExperimentDocument11 pagesVoltage Divider Circuit ExperimentLorshiel Anne TusingNo ratings yet
- Triggered Voltage Vs Sphere Gap DistanceDocument8 pagesTriggered Voltage Vs Sphere Gap Distanceprabodh119100% (1)
- Eca Lab ManualDocument78 pagesEca Lab ManualNageswariah.MNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationDocument24 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesFull Wave RectifierXavier0% (1)
- EN Rectifier CircuitsDocument4 pagesEN Rectifier Circuitsefecakir03No ratings yet
- Exp 5Document9 pagesExp 5Muhamad Fahim SadriNo ratings yet
- How a linear voltage regulator maintains a steady output voltageDocument3 pagesHow a linear voltage regulator maintains a steady output voltageSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesEDC Lab ManualRocky AdityaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Voltage Regulator Project for Electrical NetworksDocument6 pagesZener Diode Voltage Regulator Project for Electrical Networksladchaitanya100% (1)
- Half Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF VinilDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF Vinilteamboys536No ratings yet
- Yog Patil - Expt. No. 3Document8 pagesYog Patil - Expt. No. 3Yog PatilNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibraryDocument9 pagesUnified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibraryAshutoshBhattNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply Introduction and TypesDocument39 pagesDC Power Supply Introduction and TypesHusamHaskoNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Automatic Voltage Regulator DesignDocument9 pagesSingle Phase Automatic Voltage Regulator DesignPeter JordanNo ratings yet
- NV6503Document45 pagesNV6503sandeep_226250% (2)
- Richardson Electronics Guide to World-Class Industrial Microwave ProductsDocument32 pagesRichardson Electronics Guide to World-Class Industrial Microwave Productsoscarnine0% (1)
- P124Document39 pagesP124Dipankar MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- AOC HP W17Q LCD Monitor Service ManualDocument58 pagesAOC HP W17Q LCD Monitor Service ManualHans Olief Numdert GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Anti Sleep Alarm For StudentsDocument9 pagesAnti Sleep Alarm For StudentsHimanshu Bisht100% (1)
- 759P Intronics Datasheet 13593Document4 pages759P Intronics Datasheet 13593Vinicius Belmuds VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- Low-Noise Electronic DesignDocument431 pagesLow-Noise Electronic Designminiteco100% (2)
- Lee Colortran ENR Series Pack Spec Sheet 1989Document6 pagesLee Colortran ENR Series Pack Spec Sheet 1989Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3Aylie PilobelloNo ratings yet
- CAN Bus Cables - Drawing (GSC-03-85752-22D) - Rev ADocument2 pagesCAN Bus Cables - Drawing (GSC-03-85752-22D) - Rev ACamilo Andrés Perdomo VelascoNo ratings yet
- Specification Sheet: High Performance Data TransmissionDocument4 pagesSpecification Sheet: High Performance Data TransmissionTribaktih SadennaNo ratings yet
- Asus A6R ManualDocument74 pagesAsus A6R ManualAleksandar KovačNo ratings yet
- Optix RTN 600 Radio Transmission System: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument7 pagesOptix RTN 600 Radio Transmission System: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDJervy SegarraNo ratings yet
- RMS and Average Value of ACDocument14 pagesRMS and Average Value of ACspidy warriorsNo ratings yet
- Eti 1979 10 79Document106 pagesEti 1979 10 79keidesh868No ratings yet
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument24 pagesCathode Ray OscilloscopeAntonovNo ratings yet
- Creating AXI-LITE 'Custom IP' in Vivado LabDocument33 pagesCreating AXI-LITE 'Custom IP' in Vivado Labwwahib2No ratings yet
- Moxa Eds 208a Series DatasheetDocument5 pagesMoxa Eds 208a Series DatasheetKourosh DavallouNo ratings yet
- ANALOG ELECTRONICS LAB MANUALDocument57 pagesANALOG ELECTRONICS LAB MANUALAnkur PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 4121L Report1Document3 pages4121L Report1even nunezNo ratings yet
- Pioneer 909Document34 pagesPioneer 909Alexandru PădeanuNo ratings yet
- Ekahau Wi-Fi Network Report TemplateDocument14 pagesEkahau Wi-Fi Network Report TemplateFrancisco CmxNo ratings yet
- Monolithic Dual JFETsDocument2 pagesMonolithic Dual JFETsba3jarNo ratings yet
- Interfacing 8255 Ports as Input and OutputDocument4 pagesInterfacing 8255 Ports as Input and OutputPon KrithikhaNo ratings yet
- Hardware Billing SystemDocument2 pagesHardware Billing SystemAnsilNo ratings yet
- Tascam SSCD R1 TechDocument3 pagesTascam SSCD R1 TechMatthew BakerNo ratings yet
- Manual 2Document300 pagesManual 2DanielAliNo ratings yet
- TL Equipment Manual - Mn00126e Ed.02Document300 pagesTL Equipment Manual - Mn00126e Ed.02darquezbeltranNo ratings yet
- Debug NasmDocument42 pagesDebug Nasmandromeda2020No ratings yet
- B - NTC Class B Exam Element 5Document4 pagesB - NTC Class B Exam Element 5rey amoloNo ratings yet