Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GR 12 Organic Chemistry
GR 12 Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Iniya RajasekharOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GR 12 Organic Chemistry
GR 12 Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Iniya RajasekharCopyright:
Available Formats
Gr.
12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by NescafeAbusive32 (nescafeabusive32) via cheatography.com/53385/cs/14402/
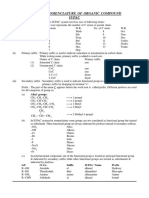
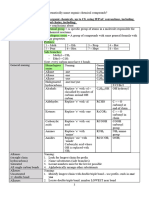
Introduction Root Name/Branch Prefixes (cont) Importance of Functional Groups (cont)
The term organic generally means "som‐ 9 non- nona- RCCR' - ane Always used as a
ething made from the earth" or "not 10 dec- deca- (alkane) suffix
chemically synthesized." R(X)R' Always See Haloalkyl‐
Special nomenclature prefixes: See
Organic chemistry refers to the study of used as a s/Other Functional
Importance of Functional Groups, Haloal‐
compounds that contain carbon atoms as prefix Groups
kyl/Other Functional Groups, and Special
the principal element. [1]
Alkyl Branches [branch] and [root] refer to the length of
The simplest organic compounds are the carbon group's prefix (meth-, eth-, prop-
hydrocarbons made from C and H atoms All prefixes are listed in alpha order when , etc.)
[2]
Despite the term organic generally meaning writing the name of an organic compound, If the carbon in the RCOOH group is not
"natural," organic compounds can in fact be except for cyclo- and iso- . the parent chain, the highest precedence
chemically synthesized (first synthesized suffix is -carboxylic acid
[3]
organic compound was urea - found in Importance of Functional Groups If the carbon in the RCO group is not the
mammal urine) parent chain, the highest precedence suffix
Functional Suffix if Prefix if
is - carbaldehyde, and the alternate prefix is
Carbon has a bonding capacity of 4 so each Group Highest Lower
formyl-
C atom must always make 4 bonds within a Precedence Precedence
[4]
If a compound is both an alkene and an
compound RC(=O)OH - oic acid 2
carboxy-
alkyne, both -ene and -yne are used
(carboxylic
General Nomenclature acid)
Haloalkyls/Other Functional Groups
Usual follows order prefix + root + suffix RC(=O)OR' [branch]1- yl alkoxycar‐
Functional Group Prefix
Prefix Indicates name/multiplying prefix‐ (ester) [root]1- oate bonyl-
1
R-O-R' (ether) [branch]-oxy-
es/position of branches RC(=O)ON(‐ - amide carbamoyl-
R')R" R-C-R (cycloalkyls) cyclo-
Root Indicates number of carbons in the
parent chain (amide) R-F fluoro-
Suffix Indicates the parent chain's RC≡N - nitrile cyano- R-Br bromo-
functional group (nitrile) R-Cl chloro-
RC=O - al 3 oxo- 3 R-I iodo-
Root Name/Branch Prefixes (aldehyde)
R-NO2 nitro-
Number of C atoms Root Multiplying RC(=O)R' - one oxo- 2
1,2-[branch(es)] ortho-[branch(es)]
/ branches prefix prefix (ketone)
2
1,3-[branch(es)] meta-[branch(es)]
1 meth- mono- R(OH)R' - ol hydroxy-
(alcohol) 1,4-[branch(es)] 2 para-[branch(es)]
2 eth- di -
[1]
R(N(R')R")‐ - amine amino- Ethers take precedence in prefixes over
3 prop- tri-
R'" (amine) all other prefixes, except the branches
4 but- tetra-
attached to the ether group
RC=CR' - ene 4 Always
5 pent- penta- [2]
Applies only to benzene ring branches
(alkene) used as a
6 hex- hexa-
suffix
7 hep- hepta- 4
RC≡CR' - yne Always
8 oct - octa- (alkyne) used as a
suffix
By NescafeAbusive32 Published 23rd January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(nescafeabusive32) Last updated 29th December, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish
Page 1 of 5. Yours!
https://apollopad.com
cheatography.com/nescafeabusive32/
Gr. 12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by NescafeAbusive32 (nescafeabusive32) via cheatography.com/53385/cs/14402/
Special Alkyl Branches Alkynes Alcohols
Propyl Butyl Contain at least one triple bond between C Any compound that contains a hydroxyl (R(-
n-propyl (normal) n-butyl (normal) atoms OH)-R') group
isopropyl (y-shape) isobutyl (y-shape) General CnH2n-2 (n = whole number) General CnH2n-1OH (n = whole
chemical chemical number)
sec-butyl (2nd C)
formula formula
tert-butyl (t-shape)
Odour Almost odourless Odour Slightly pungent
Alkanes Polarity Non-polar (only C-H bonds) Polarity Polar (between O-H bonds);
Solubility Slightly soluble longer C chains decrease in
Contain only single bonds between C atoms
in water polarity
General CnH2n+2 (n = whole number)
Boiling/m‐ Depends on length of parent C Solubility Very soluble; longer C chains
chemical
elting chain (more C = BP, less C in water decrease solubility
formula
point = BP) Boiling/m‐ Depends on length of parent C
Odour Odourless
elting chain (more C = BP, less C
Polarity Non-polar (only C-H bonds) Cycloalkyl point = BP)
Solubility Slightly soluble Alkane/alkene/alkyne where the C atoms
in water Aldehydes/Ketones
are joined in a ring shape
Boiling/m‐ Depends on length of parent C General C2H2n (cycloalkane) Any compound that contains a carbonyl (R-
elting chain (more C = BP, less C chemical C(=O)-R') group
C2H2n-2 (cycloalkene)
point = BP) formula Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the
C2H2n-4 (cycloalkyne)
(n = whole number) first and/or last C atom of the molecule
Alkenes
Odour Odourless/almost odourless Ketones have the carbonyl group in the
Contain at least one double bond between middle C atom(s) of the molecule
Polarity Non-polar (only C-H bonds)
C atoms
General CnH2nO (n = whole number)
Solubility Slightly soluble
General CnH2n (n = whole number) chemical
in water
chemical formula
formula Boiling/m‐ Depends on length of parent C
Odour Pungent (aldehyde)
elting chain (more C = BP, less C
Odour Almost odourless Sweet (ketone)
point = BP)
Polarity Non-polar (only C-H bonds) Polarity Polar (between C=O bonds);
Solubility Slightly soluble longer C chains decrease
in water polarity
Boiling/m‐ Depends on length of parent C Solubility Very soluble; longer C chains
elting chain (more C = BP, less C in water decrease solubility
point = BP)
By NescafeAbusive32 Published 23rd January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(nescafeabusive32) Last updated 29th December, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish
Page 2 of 5. Yours!
https://apollopad.com
cheatography.com/nescafeabusive32/
Gr. 12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by NescafeAbusive32 (nescafeabusive32) via cheatography.com/53385/cs/14402/
Aldehydes/Ketones (cont) Ethers (cont) Intermolecular Forces (IMFs)
Boilin‐ Very high, increases with length of Polarity Polar (between C-O bonds); Forces that occur between molecules
g/m‐ parent C chain (more C = BP, longer C chains decrease Influence the physical properties of a
elting less C = BP) polarity substance
point Solubility Very soluble; longer C chains Weaker than intramolecular forces (forces
in water decrease solubility within molecules)
Carboxylic Acids/Esters
Boilin‐ Depends on length of parent C 3 main types:
Any compound that contains a carboxyl (R- g/melting chain (more C = BP, less C
London Very weak forces that exist in
C(=O)-O-R') group point = BP)
Dispersion all atoms/molecules caused
Carboxylic acids have the carboxyl group at
Forces by temporary charges due to
the first and/or last C atom of the molecule Amines/Amides
(LDF) e¯ shifts; become stronger
Esters have the carboxyl group in the Any compound that contains a N atom in a with more e¯
middle C atom(s) of the molecule carboxyl or carbonyl group
Dipole- Attraction between opposite
General CnH2nCOOH (n = whole Amines have N atoms in a carbonyl Dipole charges of polar molecules;
chemical number) group(s) (R-C(-N(-R')-R")-R'") main reason for difference in
formula Amides have N atoms in a carboxyl melting/boiling points
Odour Unpleasant (carboxylic acid) group(s) (R-C(=O)-N(-R')-R") Hydrogen Strong dipole-dipole forces
Pleasant (ester) General CnH2n-1NO (n = whole bonding with H atoms covalently
Polarity Polar (between C=O bonds); chemical number) bonded with an N, O or F
longer C chains decrease formula atom
polarity Polarity Polar (between C=O, C-O and Strength of forces: (weakest) LDF
Solubility Very soluble; longer C chains C-N bonds); longer C chains Dipole-dipole H-bonding (strongest)
in water decrease solubility decrease polarity
Combustion Reactions
Boilin‐ Very high, increases with length Solubility Very soluble; longer C chains
g/melting of parent C chain (more C = in water decrease solubility All hydrocarbons burn with oxygen gas
point BP, less C = BP) State @ Depends on length of parent C (alkanes/alkenes/alkynes/alcohols)
SATP chain (more C = more solid, Combustion of CxHy + O2 CO2
Ethers less C = more gas) hydrocarbon + H2O
Any compound that contains an alkoxy (R- Combustion of CxHyOH + O2
O-R') group alcohol CO2 + H2O
General chemical CnH2n+2O (n = whole
formula number)
Odour Slightly pungent
By NescafeAbusive32 Published 23rd January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(nescafeabusive32) Last updated 29th December, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish
Page 3 of 5. Yours!
https://apollopad.com
cheatography.com/nescafeabusive32/
Gr. 12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by NescafeAbusive32 (nescafeabusive32) via cheatography.com/53385/cs/14402/
Elimination Reactions Addition Reactions (cont) Esterification/Hydrolysis of Esters
Take away 2 atoms to form double bond or The H atom of water/hydrogen gas/hy‐ Esterification
H2O drogen halide will always bond with the C Condensation reaction (forms H2O)
Also called condensation/dehydration atom that already had more H atoms
Catalyzed by concentrated H2SO4 and
reactions bonded to it in an addition reaction
high heat
Elimin‐ CxHyXz + [strong base] Esterific‐ CxHyCOOH + CxHyOH
Redox Reactions
ation of CxHy-1 + [halogen (X) salt] + ation [H2SO4] C2xH2yCO2 +
haloalkyl H2O Oxidation
H2O
C atoms will form more bonds to O atoms
Elimin‐ CxHyOH [conc acid] Hydrolysis of Esters
ation of CxHy-1 + H2O Occurs when an organic compound reacts
Reverse reaction to esterification
alcohol with an oxidizing agent (usually
KMnO4/K2Cr2O7) Hydro = water, lysis = break
Substitution Reactions Oxidation of CxHyOH [O] Hydrolysis C2xH2yCO2 + H2O
primary alcohol CxHy-1O (aldehyde ) of ester [H2SO4] CxHyCOOH +
Replace one atom with another
CxHyOH
Substitution CxHy + X2 [heat/pre‐ Oxidation of CxHyOH [O]
reaction ssure] CxHy-1X + HX secondary CxHy-1O (ketone) Remember: Ester is a party girl; she drank
alcohol some alcohol and did some acid
Benzene rings
Oxidation of CxHyOH [O] NO
Benzene does not have true double bonds,
tertiary alcohol Synthesis/Hydrolysis of Amides
RXN
so only substitution reactions can be
Oxidation of CxHyO + H2O [O] Synthesis of Amides
performed
aldehyde CxHy-1OH + H2 Condensation reaction (forms H2O)
Benzene C6H6 + X2 C6H5X +
substitution HX (carboxylic acid) Synthesis CxHyCOOH (carboxylic acid)
Reduction of amide + CxHyNH2 (amine)
Benzene C6H5X + X2 C6H4X2
halide substi‐ + HX C atoms will form fewer bonds to O atoms CxHyONH2 (amide) + H2O
tution Occurs when an organic compound reacts Hydrolysis of Amides
Halogen in benzene halide reactions forms with an reducing agent (usually H2/LiAlH4) Reverse reaction to synthesis
product meta position only (1,3-[X]benzene) Hydrogenation CxHyO + H2 [H] Hydrolysis CxHyONH2 (amide) + H2O
(reduction of CxHy+1OH (primary of amide CxHyCOOH (carboxylic
Addition Reactions aldehyde) alcohol) acid) + CxHyNH2 (amine)
Add atoms across double/triple bond Hydrogenation CxHyO + H2 [H]
Alkenes/alkynes are nucleophiles (they like (reduction of CxHy+1OH (secondary Synthesis of Amines
to give up e_ ) ketone) alcohol) Amines can be made from haloalkyls using
Hydrohalogen‐ CxHy + HX ammonia as a starting reactant
ation CxHy+1X Synthesis of CxHxX + NH3
Halogenation CxHy + X2 primary amines CxHyNH2 + HX
CxHyX2 Synthesis of CxHxX + CxHyNH2
Hydrogenation CxHy + H2 secondary C2xH2yNH + HX
CxHy+2 amines
Hydration CxHy + H2O Synthesis of CxHxX + C2xH2yNH
CxHy+1OH tertiary amines C3xH3yN + HX
Markovnikov's Rule: "the rich get richer"
By NescafeAbusive32 Published 23rd January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(nescafeabusive32) Last updated 29th December, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish
Page 4 of 5. Yours!
https://apollopad.com
cheatography.com/nescafeabusive32/
Gr. 12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by NescafeAbusive32 (nescafeabusive32) via cheatography.com/53385/cs/14402/
Polymers
Large molecules that are composed of
many repeated subunits called monomers
Created through polymerization
Examples include plastics , DNA, and
proteins
Unique physical properties - checmically
unreactive , flexible/mouldable /stretchable
Polymeriz‐ CxHy + CxHy+ CxHy+ ...
ation (addition [CxHy]n
- chain
reaction of
alkene)
Polymeriz‐ HOCxHyOH +
ation (conde‐ HOOCCxHyCOOH + ...
nsation with [O2CCxHyO2CxHyO2]n
alcohol -
polyester)
Polymeriz‐ H2NCxHyNH2 +
ation (conde‐ HOOCCxHyCOOH + ...
nsation with [NOCCxHyO2CxHyON]n
alcohol -
polyamide)
Polymerization (condensation) need the
reacting functional group(s) to be on both
sides of the monomer(s) to be able to
complete the chain reaction (-dioic acid , -
diol, -diamine)
By NescafeAbusive32 Published 23rd January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(nescafeabusive32) Last updated 29th December, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish
Page 5 of 5. Yours!
https://apollopad.com
cheatography.com/nescafeabusive32/
You might also like
- Gr. 12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument5 pagesGr. 12 Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaDenis Đurđević100% (1)
- Basic IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesBasic IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsApril Joyce Raymundo100% (1)
- Case 2 - Tank Heat LossDocument86 pagesCase 2 - Tank Heat Lossahmad santosoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesClassification of Organic Compoundskvp0107No ratings yet
- WKM Pow R Seal Gate Valves BrochureDocument28 pagesWKM Pow R Seal Gate Valves BrochureKhai Huynh100% (1)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Cleaning and SanitizingDocument30 pagesCleaning and SanitizingAngie Filler100% (3)
- Reconditioning of ValvesDocument6 pagesReconditioning of ValvesPaul PhiliphsNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Enthalpy DiagramDocument13 pagesPressure and Enthalpy DiagramAravindNo ratings yet
- Chap 01 Some Basic Principles of Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesChap 01 Some Basic Principles of Organic ChemistryParth JainNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument36 pagesNomenclature of Organic CompoundsRx Nadeem ChhipaNo ratings yet
- Altitude Correction FactorsDocument6 pagesAltitude Correction FactorsMayank YadavNo ratings yet
- Organicchemistry CheatsheetDocument5 pagesOrganicchemistry CheatsheetShradha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronics by Sir JoelDocument47 pagesElectronics by Sir JoelDann SarteNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument179 pagesChromatographyMUTHUKRISHNAN100% (1)
- Pipesim User GuideDocument196 pagesPipesim User Guidemikegibbons2750% (2)
- Organic Compounds, Classification and Properties: For General Chemistry 1/ Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 6Document14 pagesOrganic Compounds, Classification and Properties: For General Chemistry 1/ Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 6ariinnggg onichaNo ratings yet
- N28 GWDocument3 pagesN28 GWmakineci_67No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Organic CompoundDocument103 pagesLesson 1 - Organic CompoundFreshieeNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic MoleculesFrom EverandThe Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic MoleculesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Module 1 - Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Organic ChemistrySelena MoonNo ratings yet
- Pharm Organic Chem SummaryDocument5 pagesPharm Organic Chem SummaryJoanna MalizaNo ratings yet
- CHEM1090 Final - Module 2Document10 pagesCHEM1090 Final - Module 2Dani R.No ratings yet
- LG 1.3 Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument11 pagesLG 1.3 Nomenclature of Organic CompoundswangmorisNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups Name, Structure, ReactionDocument48 pagesFunctional Groups Name, Structure, ReactionmichaelmarshallNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic CompoundsDocument19 pagesNomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic CompoundsH to O ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesOrganic ChemistryVatsal KaseraNo ratings yet
- More On Nomenclature. Compounds Other Than Hydrocarbons%: IupacDocument21 pagesMore On Nomenclature. Compounds Other Than Hydrocarbons%: Iupacmail2quraishi3084No ratings yet
- 12chem Nomenclature Worksheet AnswersDocument9 pages12chem Nomenclature Worksheet AnswersAya AbdelsanadNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NoteDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notemensahdelali73No ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesFundamental Principles of Organic ChemistryNewton SirNo ratings yet
- Star Coaching Centre Aligarh: (Organic Chemistry and Polymers)Document20 pagesStar Coaching Centre Aligarh: (Organic Chemistry and Polymers)hacker GodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesChemistry Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic Compound (11th) NotesDocument4 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compound (11th) NotesRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LG 1.2 Properties of Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsDocument10 pagesLG 1.2 Properties of Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupswangmorisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesChemistry Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- T SC 1631004159 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds A Study Guide - Ver - 1Document8 pagesT SC 1631004159 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds A Study Guide - Ver - 1Joel OkohNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupDocument20 pagesFunctional GroupCatherine R. FelipeNo ratings yet
- M3 OrganicchemDocument18 pagesM3 OrganicchemJelaica EspinuevaNo ratings yet
- Geokimia OrganikDocument29 pagesGeokimia OrganikAkbar Nurul FirdausNo ratings yet
- OrganicChemistry NoteDocument16 pagesOrganicChemistry NotetacocatNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupDocument45 pagesFunctional Groupmonasteriomatthew7No ratings yet
- Review BifunctionalDocument18 pagesReview BifunctionalMelva Hilderia SibaraniNo ratings yet
- 01 - Biochemistry & Biomolecules PDFDocument25 pages01 - Biochemistry & Biomolecules PDFNURDAYANA NADHIRAH HAFIZANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistryauni ramizahNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 page5.1 Carboxylic AcidsCaesyNo ratings yet
- 1.6. Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument16 pages1.6. Introduction To Organic ChemistryRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Chem113lec Week 3.1Document3 pagesChem113lec Week 3.1Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesOrganic ChemistryMichael lIuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Bonding in Organic CompoundsDocument20 pages3.1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Bonding in Organic CompoundsFadhla Fadhilatul Mariyatis SolihahNo ratings yet
- Safari - Jul 26, 2021 at 3:35 PMDocument1 pageSafari - Jul 26, 2021 at 3:35 PMBimbola AmusaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument36 pagesIUPAC NomenclatureRx Nadeem ChhipaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Introduction To Organic Chemistry: 2.1 Functional Group and Homologous SeriesDocument8 pagesChapter 2. Introduction To Organic Chemistry: 2.1 Functional Group and Homologous SeriesDavid PhilipNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (PB)Document10 pagesActivity 1 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (PB)Sittie Neharah S. MapandiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ADocument113 pagesOrganic Chemistry AChelsea Kyrell TupasNo ratings yet
- Families of Organic CompoundsDocument13 pagesFamilies of Organic CompoundsFabe Maria Feb VeranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter16 UclassDocument88 pagesChapter16 Uclass배석우No ratings yet
- 02 Isomerism (Theory-01)Document22 pages02 Isomerism (Theory-01)Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Topic Overview: Delhi Public School Class X-Chemistry Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesTopic Overview: Delhi Public School Class X-Chemistry Carbon and Its CompoundsSanika TalathiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document262 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2Israk Mustakim IslamNo ratings yet
- MOD 7 Organic ChemistryDocument19 pagesMOD 7 Organic Chemistrycj.toll16No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Study of Hydrocarbons NotesDocument17 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Study of Hydrocarbons Noteszarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- s5 Organic Chemistry 30-03-20Document208 pagess5 Organic Chemistry 30-03-20ONAP PATRICK JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument26 pagesAldehydes and KetonesVoteone Enhypen100% (1)
- Organic 23 24Document18 pagesOrganic 23 24VigneshNo ratings yet
- W1L2 Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesW1L2 Organic ChemistryMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument33 pagesOrganic ChemistryTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- 2 Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesDocument6 pages2 Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesJohn Philip NapalNo ratings yet
- LkanesDocument94 pagesLkanesNizarNo ratings yet
- O.C. - Some Basic Concept of Organic ChemistryDocument137 pagesO.C. - Some Basic Concept of Organic Chemistryameena-11173No ratings yet
- D-Block Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDocument12 pagesD-Block Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesAhliaIkhwanNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 45 Community and Ecosystem Ecology QuizletDocument3 pagesTest Chapter 45 Community and Ecosystem Ecology Quizletapi-328608341No ratings yet
- Shell Brake Clutch Fluid DOT 4 ESL TDS PDFDocument2 pagesShell Brake Clutch Fluid DOT 4 ESL TDS PDFwicka3No ratings yet
- Sedex, VMS, MVTDocument89 pagesSedex, VMS, MVTRoland Rawlins Igabor100% (1)
- Cape Unit 1 Past Papers ChemDocument15 pagesCape Unit 1 Past Papers ChemShadésia GreeneNo ratings yet
- Adu & VduDocument25 pagesAdu & VduPrashanth ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- QC Instruments & Equipments Calibration LogDocument1 pageQC Instruments & Equipments Calibration Logkousick sundararajanNo ratings yet
- Polymer SyllabusDocument6 pagesPolymer SyllabusJOSEPH HERBERT MABELNo ratings yet
- WPM2006 User Guide GSHP EnglishDocument18 pagesWPM2006 User Guide GSHP Englishadrian arrowNo ratings yet
- Exam Report EASE 2 Physics 11 A-Level PDFDocument2 pagesExam Report EASE 2 Physics 11 A-Level PDFyusuf irfanNo ratings yet
- Plate and Frame Filter Press: Instruction ManualDocument8 pagesPlate and Frame Filter Press: Instruction ManualYatharth SahuNo ratings yet
- Enalapril Maleate EP 11.0Document3 pagesEnalapril Maleate EP 11.0noschNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 DmeDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 DmeSubash DgłNo ratings yet
- Engineering Standards: Autodeposition Coating For SteelDocument3 pagesEngineering Standards: Autodeposition Coating For SteelMuthu GaneshNo ratings yet
- 04 Lecture PPT NewDocument37 pages04 Lecture PPT Newapi-201447595No ratings yet
- The Binding Mode of The Ambidentate Ligand DicyanaDocument7 pagesThe Binding Mode of The Ambidentate Ligand Dicyanapyare08041996No ratings yet
- Asae S572-2004Document4 pagesAsae S572-2004hadiranji4No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Cracking of Soap: Innøleag e White PaperDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Cracking of Soap: Innøleag e White PaperarthurNo ratings yet
- Commercial Kitchen VentilationDocument59 pagesCommercial Kitchen VentilationSMBEAUTYNo ratings yet
- Promix 2Ks: Repair-PartsDocument60 pagesPromix 2Ks: Repair-PartsJose Padilla gaytanNo ratings yet